Difference between revisions of "Matrix - Joystick"
(→Features) |
(→Update Log) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
* We extend all three outputs: X, Y and Z and users can use them easily. | * We extend all three outputs: X, Y and Z and users can use them easily. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Applications== | ||
| + | The Matrix-Joystick module outputs analog signals which can be converted to digital signals with an ADC converter e.g. the Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter.<br> | ||
| + | For more details about the Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter module refer to wiki: [[Matrix_-_Analog_to_Digital_Converter]].<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi M1=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix_Joystick_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix_Joystick_nanopi_m1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Joystick || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || NanoPi M1 Pin9 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || NanoPi M1 Pin2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |X || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Y || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi 2=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-Joystick_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Joystick_nanopi_2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Joystick || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || NanoPi 2 Pin9 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || NanoPi 2 Pin2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |X || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Y || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix_Joystick_nanopi_m2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix_Joystick_nanopi_m2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Joystick || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || NanoPi M2 Pin9 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || NanoPi M2 Pin2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |X || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Y || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPC-T2=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix_Joystick_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix_Joystick_NanoPC-T2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Joystick || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || NanoPC-T2 USB Host GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || NanoPC-T2 USB Host 5V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |X || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Y || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Compile & Run Test Program== | ||
| + | Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git | ||
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compile and install Matrix: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd matrix | ||
| + | $ make && make install | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Run test program: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ matrix-joystick | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Note: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.<br> | ||
| + | Here is what you should observe:<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | x=1280 y=1280 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | When you move the stick you will see X and Y's value changes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Code Sample== | ||
| + | This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-joystick". Here is its source code: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
| + | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i = 0; | ||
| + | int x, y, board; | ||
| + | |||
| + | x = y = 0; | ||
| + | if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to init board\n"); | ||
| + | return -1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | system("modprobe "DRIVER_MODULE); | ||
| + | signal(SIGINT, intHandler); | ||
| + | for (i=0; i<PS2_READ_TIMES; i++) { | ||
| + | if (pcf8591Read(1, &x) != -1 && pcf8591Read(2, &y) != -1) { | ||
| + | printf("x=%4d y=%4d\n", x, y); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to [[Matrix API reference manual]] <br> | ||
| + | <!--- | ||
==Download Matrix Source Code== | ==Download Matrix Source Code== | ||
| − | All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - | + | All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br> |
Each branch in this hub contains the matrix modules' code samples for a board that the matrix modules can work with.<br> | Each branch in this hub contains the matrix modules' code samples for a board that the matrix modules can work with.<br> | ||
* The nanopi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi | * The nanopi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi | ||
| + | * The nanopi 2 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi 2 | ||
* The tiny4412 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the Tiny4412 | * The tiny4412 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the Tiny4412 | ||
* The raspberrypi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the RaspberryPi | * The raspberrypi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the RaspberryPi | ||
| Line 47: | Line 177: | ||
Clone the matrix code from GitHub | Clone the matrix code from GitHub | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | $ git clone | + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples. | If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Connect to NanoPi 2== | ||
| + | ===Hardware Connection=== | ||
| + | Please refer to the following connection diagram to connect the Matrix-Joystick to the NanoPi 2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-Joystick_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Joystick_nanopi_2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Joystick || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || NanoPi 2 Pin14 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || NanoPi 2 Pin2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |X || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Y || Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Compile Test Program=== | ||
| + | Please login the matrix hub and enter the nanopi2 branch | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd matrix | ||
| + | $ git checkout nanopi2 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compile the matrix code | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean | ||
| + | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- | ||
| + | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the NanoPi 2.<br> | ||
| + | Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. The test program is under the "install/usr/bin" directory.<br> | ||
| + | The modules are under the "modules" directory. The driver's source code is in github: https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Run Test Program=== | ||
| + | Please insert a TF card which is flashed with Debian to a Linux host and mount its boot and rootfs sections.<br> | ||
| + | We assume the rootfs is mounted to /media/rootfs then please run the following commands to copy the module, library and test program to the card.<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r | ||
| + | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d | ||
| + | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/ | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Insert this TF card to your NanoPi 2, power on and run the following commands to load the driver.<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd /modules | ||
| + | $ insmod pcf8591.ko | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Start the matrix-joystick program.<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ matrix-joystick | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Here is what you expect to observe:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:matrix-joystick_result.png|frameless||matrix-joystick_result]] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Code Sample=== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
| + | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i = 0; | ||
| + | int x, y; | ||
| + | |||
| + | x = y = 0; | ||
| + | for (i=0; i<PS2_READ_TIMES; i++) { | ||
| + | if (pcf8591Read(1, &x) != -1 && pcf8591Read(2, &y) != -1) { | ||
| + | printf("x=%4d y=%4d\n", x, y); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
==Connect to NanoPi== | ==Connect to NanoPi== | ||
| Line 240: | Line 446: | ||
==Connect to Arduino== | ==Connect to Arduino== | ||
| + | ---> | ||
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
| − | + | ==Update Log== | |
| + | ===Feb-23-2016=== | ||
| + | * Added the description for "NanoPi 2 branch" in Section 4 | ||
| + | * Added Section 5: Connect to NanoPi 2 | ||
| + | ===June-21-2016=== | ||
| + | * Re-organized and simplified wiki | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:03, 21 June 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
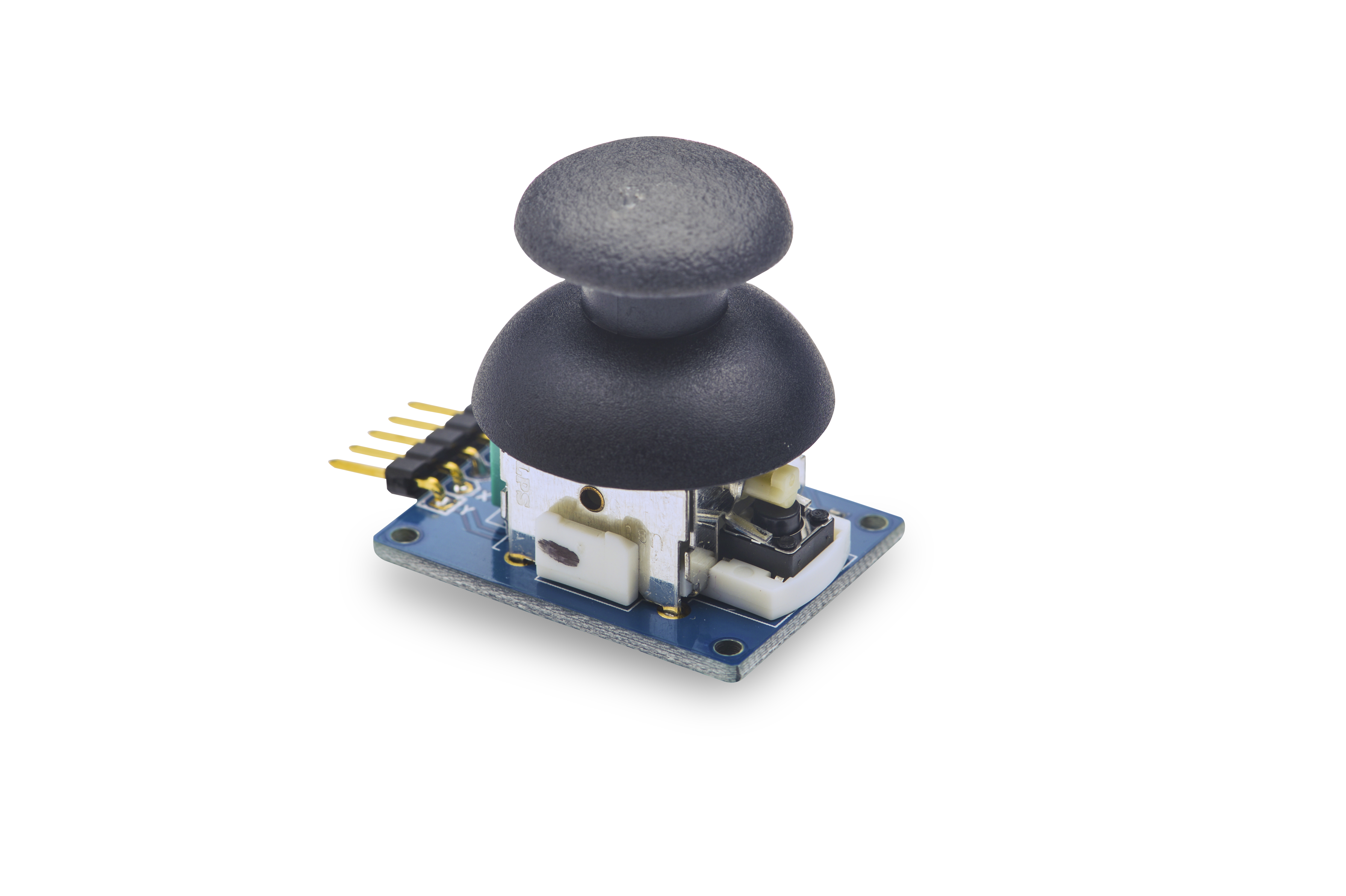
- The matrix-joystick module is a two-axis stick module. It consists of two Sliding rheostats and one button. It has two analog outputs and one digital output. Its positional states can be measured as X and Y axis values as the calibrated resistance of the two potentiometers.
- When you move the joystick the sliding rheostats' resistance will change and the corresponding x/y values will change too. When you push the joystick the SW level will turn low.
2 Features
- X and Y axis, and one button
- 2.54mm spacing pin
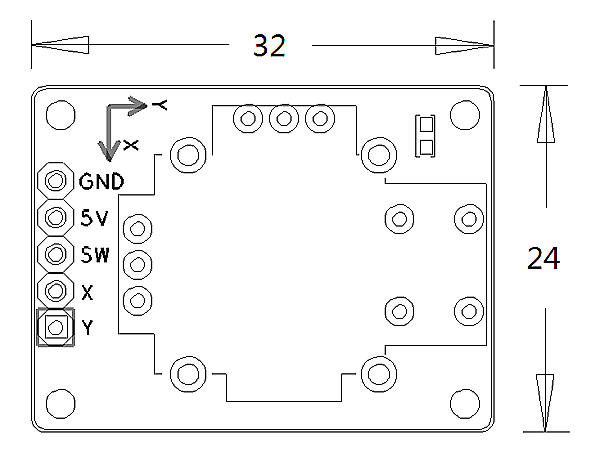
- PCB dimension(mm): 24 X 32
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| GND | Ground |
| 5V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| SW | Button |
| X | X Axis |
| Y | Y Axis |
3 Basic Device Operation
- It has two analog outputs and one digital output. The two analog outputs are measured as X and Y values as the calibrated resistance of the two potentiometers. The digital output is measured as Z value indicating whether or not the button is pressed.
- We extend all three outputs: X, Y and Z and users can use them easily.
4 Applications
The Matrix-Joystick module outputs analog signals which can be converted to digital signals with an ADC converter e.g. the Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter.
For more details about the Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter module refer to wiki: Matrix_-_Analog_to_Digital_Converter.
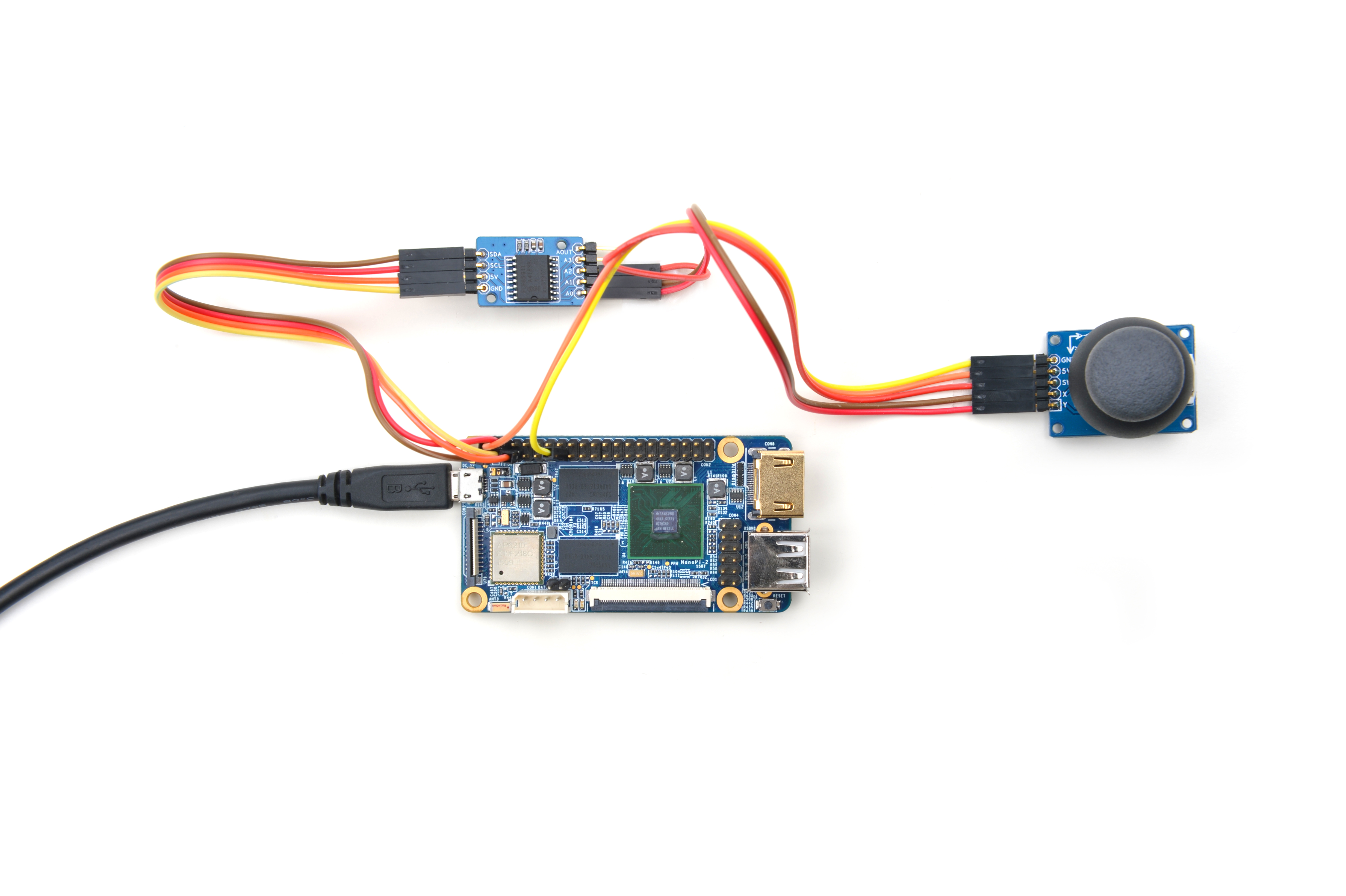
4.1 Connect to NanoPi M1
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Joystick | |
| GND | NanoPi M1 Pin9 |
| 5V | NanoPi M1 Pin2 |
| X | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 |
| Y | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 |
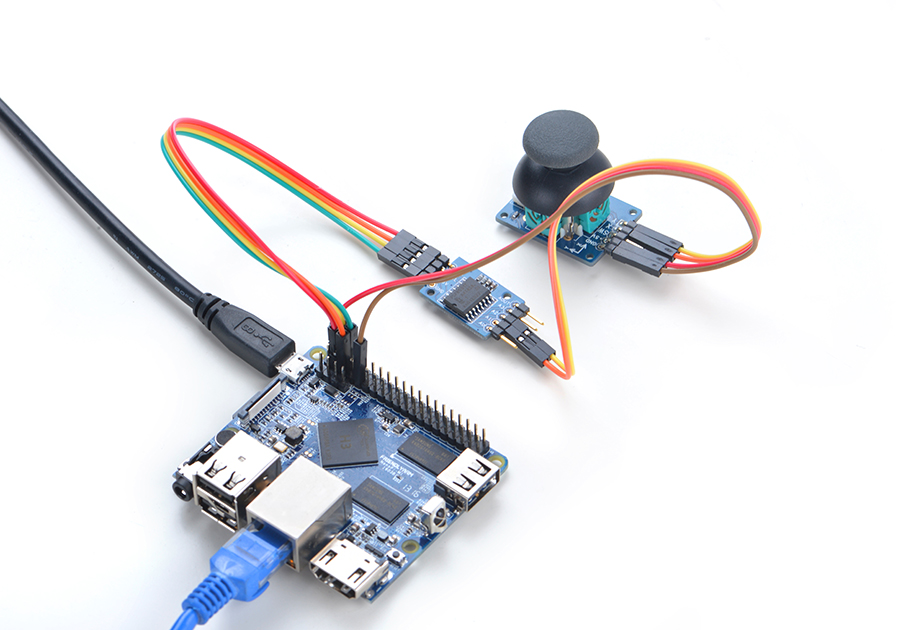
4.2 Connect to NanoPi 2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Joystick | |
| GND | NanoPi 2 Pin9 |
| 5V | NanoPi 2 Pin2 |
| X | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 |
| Y | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 |
4.3 Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire:
Matrix_Joystick_nanopi_m2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Joystick | |
| GND | NanoPi M2 Pin9 |
| 5V | NanoPi M2 Pin2 |
| X | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 |
| Y | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 |
4.4 Connect to NanoPC-T2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:
Matrix_Joystick_NanoPC-T2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Joystick | |
| GND | NanoPC-T2 USB Host GND |
| 5V | NanoPC-T2 USB Host 5V |
| X | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 |
| Y | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 |
5 Compile & Run Test Program
Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code:
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated.
Compile and install Matrix:
$ cd matrix $ make && make install
Run test program:
$ matrix-joystickNote: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.
Here is what you should observe:
x=1280 y=1280
When you move the stick you will see X and Y's value changes.
6 Code Sample
This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-joystick". Here is its source code:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int i = 0; int x, y, board; x = y = 0; if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { printf("Fail to init board\n"); return -1; } system("modprobe "DRIVER_MODULE); signal(SIGINT, intHandler); for (i=0; i<PS2_READ_TIMES; i++) { if (pcf8591Read(1, &x) != -1 && pcf8591Read(2, &y) != -1) { printf("x=%4d y=%4d\n", x, y); } } system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); return 0; }
For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to Matrix API reference manual
7 Resources
8 Update Log
8.1 Feb-23-2016
- Added the description for "NanoPi 2 branch" in Section 4
- Added Section 5: Connect to NanoPi 2
8.2 June-21-2016
- Re-organized and simplified wiki