Difference between revisions of "NanoPi NEO2"
(updated by API) |
|||
| (97 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[NanoPi NEO2| | + | [[NanoPi NEO2/zh|查看中文]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ==Introduction== |
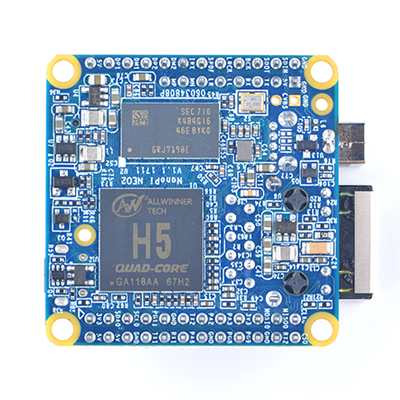
| + | [[File:NanoPi NEO2-1.jpg|thumb|frameless|300px|Overview]] | ||
| + | [[File:NanoPi NEO2-2.jpg|thumb|frameless|300px|Front]] | ||
| + | [[File:NanoPi NEO2-3.jpg|thumb|frameless|300px|Back]] | ||
| + | * The NanoPi NEO2 is a newly released super tiny ARM board by FriendlyElec. It uses Allwinner’s 64-bit H5 quad-core SoC (ARM Cortex-A53). It has internal hexa-core Mail450 GPU, 512M DDR3 RAM. A UbuntuCore and Armbian image files are ready for it. | ||
| + | * The NanoPi NEO2 inherits NEO's form factor and has compatible interfaces and ports with NEO. In addition in such a small dimension it has Gbps Ethernet and one USB host port. These features make it especially suitable for applications that require high data throughput , speedy data transmission and high performance. Hobbyists and makers will just love it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Hardware Spec== | ||
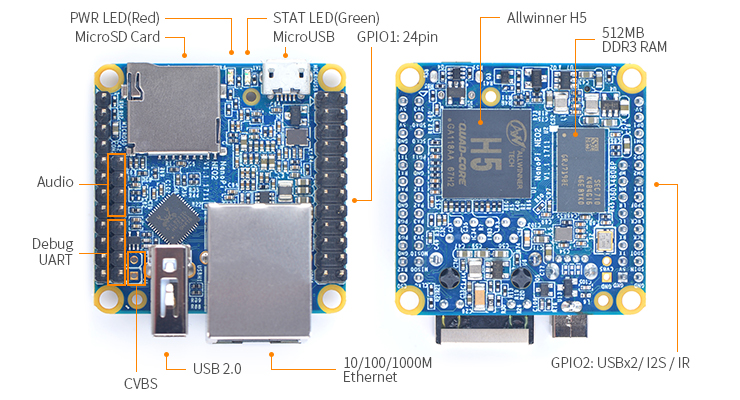
* CPU: Allwinner H5, Quad-core 64-bit high-performance Cortex A53 | * CPU: Allwinner H5, Quad-core 64-bit high-performance Cortex A53 | ||
* DDR3 RAM: 512MB | * DDR3 RAM: 512MB | ||
| − | * | + | * Connectivity: 10/100/1000M Ethernet, RTL8211E-VB-CG chip |
| − | * USB Host: | + | * USB Host: USB Type A x 1 and USB pin header x 2 |
| − | * MicroSD Slot: | + | * MicroSD Slot: MicroSD x 1 for system boot and storage |
| − | * | + | * LED: Power LED x 1, System LED x 1 |
| − | * GPIO1: | + | * GPIO1: 2.54mm pitch 24 pin-header, compatible with Raspberry Pi's GPIO pin1 - pin 24. It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc |
| − | * GPIO2: | + | * GPIO2: 2.54mm pitch 12 pin-header. It includes USB, IR receiver, I2S, IO etc |
| − | * | + | * Serial Debug Port: 2.54mm pitch 4pin-header |
| − | * | + | * Audio In/Out: 2.54mm pitch 4 pin-header |
| − | + | * MicroUSB: Power input(5V/2A) and OTG | |
| − | * MicroUSB: | + | * PCB Dimension: 40 x 40mm |
| − | * | + | * Working Temperature: -20℃ to 70℃ |
* Weight: 13g(WITHOUT Pin-headers) | * Weight: 13g(WITHOUT Pin-headers) | ||
| + | * OS/Software: u-boot,Ubuntu Core | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | ==Software Features== | ||
| + | ===uboot=== | ||
| + | * mainline uboot released on May 2017 | ||
| + | <!--- | ||
| + | * supports fastboot to update uboot | ||
| + | ---> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===UbuntuCore 16.04=== | ||
| + | * 64-bit system | ||
| + | * mainline kernel: Linux-4.14 | ||
| + | * rpi-monitor: check system status and information | ||
| + | * npi-config: system configuration utility for setting passwords, language, timezone, hostname, SSH and auto-login,and enabling/disabling i2c, spi, serial and PWM. When enabling PWM it will prompt that Serial debug port will be disabled. | ||
| + | * software utility: wiringNP to access GPIO pins | ||
| + | * software utility: RPi.GPIO_NP to access GPIO pins | ||
| + | * networkmanager: manage network | ||
| + | * system log output from serial port | ||
| + | <!--- | ||
| + | * nano editor | ||
| + | * auto-login with user account "pi" with access to npi-config | ||
| + | * sudoers include "fa" | ||
| + | * on first system boot file system will be automatically extended. | ||
| + | * supports file system auto check and repair on system boot. | ||
| + | * supports FriendlyElec's [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/NanoHat_PCM5102A NanoHat-PCM5102A] | ||
| + | ---> | ||
| + | * supports USB WiFi module: refer to [[#Connect USB WiFi to NEO]] | ||
| + | * supports audio recording and playing with 3.5mm audio jack | ||
| + | * supports I2C 0/1 | ||
| + | <!--- | ||
| + | * supports dynamic frequency scaling and voltage regulation | ||
| + | * relieves overheat compared to kernel Linux-3.4 | ||
| + | ---> | ||
| + | * fixed MAC address | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ubuntu OLED=== | ||
| + | * mainline kernel: Linux-4.14 | ||
| + | * supports FriendlyElec's OLED module | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Debian=== | ||
| + | * welcome window with basic system information and status | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Debian for NAS Dock=== | ||
| + | * mainline kernel: Linux-4.14 | ||
| + | * supports FriendlyElec's NAS Dock | ||
| + | * optimized OpenMediaVault configuration options | ||
| + | * allocated swap section | ||
| + | --> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Diagram, Layout and Dimension== |
| − | === | + | ===Layout=== |
| − | [[File:NanoPi-NEO2-layout.jpg |thumb|600px|NanoPi | + | [[File:NanoPi-NEO2-layout.jpg |thumb|600px|NanoPi NEO2 Layout]] |
[[File:NEO2 pinout-02.jpg|thumb|frameless|600px|pinout]] | [[File:NEO2 pinout-02.jpg|thumb|frameless|600px|pinout]] | ||
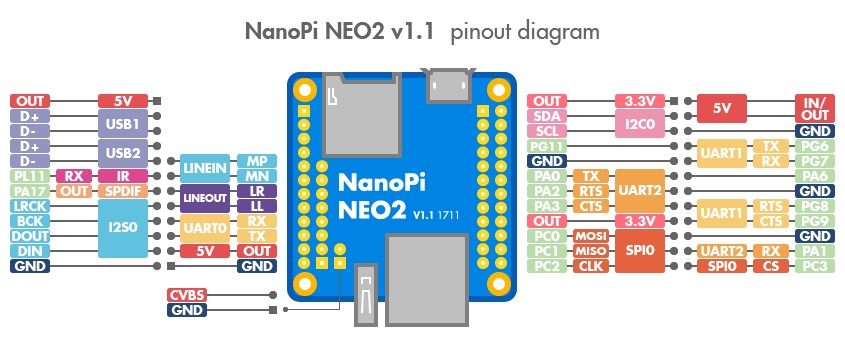
| − | * ''' | + | * '''GPIO Pin Description''' |
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 35: | Line 85: | ||
|1 || SYS_3.3V || ||2 || VDD_5V || | |1 || SYS_3.3V || ||2 || VDD_5V || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |3 || I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 || 12 | + | |3 || I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 || 12 ||4 || VDD_5V || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |5 || I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 || 11 | + | |5 || I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 || 11 ||6 || GND || |
|- | |- | ||
|7 || GPIOG11 || 203 ||8 || UART1_TX/GPIOG6 || 198 | |7 || GPIOG11 || 203 ||8 || UART1_TX/GPIOG6 || 198 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 108: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | * '''USB/Audio/IR | + | * '''USB/Audio/IR Pin Descripton''' |
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 95: | Line 145: | ||
|Pin# || Name || Description | |Pin# || Name || Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |1 || | + | |1 || MP || Microphone Positive Input |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |2 || | + | |2 || MN || Microphone Negative Input |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |3 || | + | |3 || LR || LINE-OUT Right Channel Output |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4 || | + | |4 || LL || LINE-OUT Left Channel Output |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
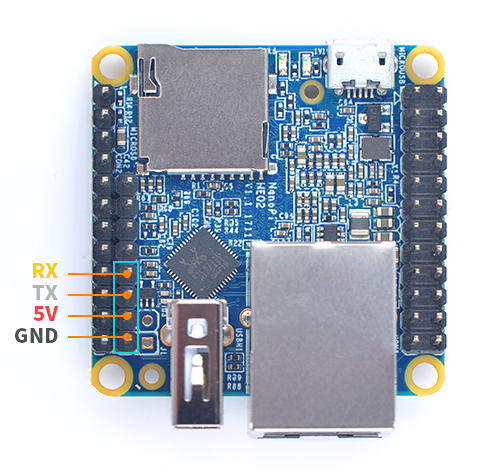
| Line 116: | Line 164: | ||
|2 || VDD_5V | |2 || VDD_5V | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |3 || UART_TXD0 | + | |3 || UART_TXD0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4 || UART_RXD0 | + | |4 || UART_RXD0 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | :''' | + | :'''Note''' |
| − | ::#SYS_3.3V: 3. | + | ::#SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output |
| − | ::#VDD_5V: | + | ::#VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.5V. It can take power input from the MicroUSB. |
| − | ::# | + | ::#All pins are 3.3V and output current is 5mA |
| − | ::# | + | ::#For more details refer to the document: [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/d/db/Schematic_NanoPi_NEO2-V1.1-1711.pdf NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1_1711-Schematic.pdf] |
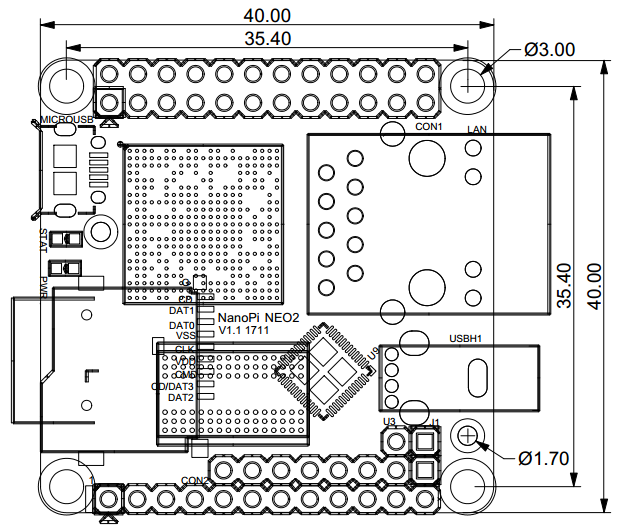
| − | === | + | ===Dimensional Diagram=== |
[[File:NanoPi-NEO2-1701-dimensions.png|frameless|400px|]] | [[File:NanoPi-NEO2-1701-dimensions.png|frameless|400px|]] | ||
| − | :: | + | ::For more details refer to [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/File:NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1-1711_PCB-Dimensional.rar pcb file in dxf format] |
| + | |||
| + | ==Software Features== | ||
| + | {{H5SoftwareFeature-FriendlyCore|NanoPi-NEO2}} | ||
| + | {{H5SoftwareFeature-FriendlyWrt|NanoPi-NEO2}} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Get Started== |
| − | === | + | ===Essentials You Need=== |
| − | + | Before starting to use your NanoPi NEO2 get the following items ready | |
| − | * NanoPi | + | * NanoPi NEO2 |
| − | * | + | * microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC |
| − | * | + | * microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must |
| − | * | + | * A host computer running Ubuntu 18.04 64 bit system |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{TFCardsWeTested}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Install OS=== | ||
| + | ====Get Image File==== | ||
| + | Get the following files from [http://download.friendlyelec.com/nanopineo2 download link] to download image files (under the officail-ROMs directory) and the flashing utility(under the tools directory):<br /> | ||
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan=2| | + | |colspan=2|Image Files: |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |nanopi- | + | |nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlycore-xenial_3.10_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img.zip || Base on UbuntuCore, kernel:Linux-3.10 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlycore-xenial_4.14_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img.zip || Base on UbuntuCore, kernel:Linux-4.14 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlywrt_4.14_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img.zip || Base on OpenWrt, kernel:Linux-4.14 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |colspan=2|Flash Utility: |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |win32diskimager.rar || Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd" |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{BurnOS-Allwinner|NanoPi-NEO2}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{FriendlyCoreGeneral|NanoPi-NEO2}} | |
| − | + | {{FriendlyCoreAllwinnerH5|NanoPi-NEO2}} | |
| − | === | + | ===Play & Record Audio=== |
| − | + | The NanoPi NEO2 has an audio interface (2.0mm pitch 5-pin header) whose pin description is as follows: | |
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 303: | Line 230: | ||
|3 || LINEOUTR || LINE-OUT Right Channel Output | |3 || LINEOUTR || LINE-OUT Right Channel Output | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4 || GND || | + | |4 || GND || Ground |
|- | |- | ||
|5 || LINEOUTL || LINE-OUT Left Channel Output | |5 || LINEOUTL || LINE-OUT Left Channel Output | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Here is a hardware setup on how to connect an audio device to a NEO2:<br> | |
| − | [[File:耳麦标注.jpg|frameless|400px| | + | [[File:耳麦标注.jpg|frameless|400px| Earphone]]<br> |
| − | + | Before begin to play or record a audio make sure your NEO2 is connected to an audio device.<br> | |
| − | + | Check a recognized audio device: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ aplay -l | $ aplay -l | ||
**** List of PLAYBACK Hardware Devices **** | **** List of PLAYBACK Hardware Devices **** | ||
| − | card 0: | + | card 0: Codec [H3 Audio Codec], device 0: CDC PCM Codec-0 [] |
Subdevices: 1/1 | Subdevices: 1/1 | ||
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0 | Subdevice #0: subdevice #0 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Both Allwinner's H5 and H3 have an internal codec which is named as [H3 Audio Codec] in mainline kernels.<br> | ||
| − | + | Play an audio file: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav -D plughw:0 | $ aplay /root/Music/test.wav -D plughw:0 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Record an audio file: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ arecord -f cd -d 5 test.wav | $ arecord -f cd -d 5 test.wav | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | {{OpenWrt1|NanoPi-NEO2}} | |
| − | === | + | {{MoreOS}} |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Make Your Own FriendlyCore== | |
| − | + | ===Mainline U-boot & Linux(64 bit)=== | |
| − | + | Now the NanoPi NEO2 can run a 64-bit Linux kernel with 64-bit Ubuntu Core 16.04. Here is a detailed reference on how to run mainline U-boot and Linux on H5: [[Mainline U-boot & Linux/zh|Mainline U-boot & Linux]] <br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ===Use Allwinner's BSP=== |
| − | === | + | ====Preparations==== |
| − | + | Visit this link [http://download.friendlyelec.com/nanopineo2 download link] and enter the "sources/nanopi-H5-bsp" directory and download all the source code.Use the 7-zip utility to extract it and a lichee directory and an Android directory will be generated.You can check that by running the following command: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | ls ./ | + | $ ls ./ |
| − | lichee | + | $ lichee |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Or you can get it from our github: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/h5_lichee.git lichee | + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/h5_lichee.git lichee --depth 1 |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Note: "lichee" is the project name named by Allwinner for its CPU's source code which contains the source code of U-boot, Linux kernel and various scripts. | |
| − | === | + | ====Install Cross Compiler==== |
| − | + | Visit this site [http://download.friendlyelec.com/nanopineo2 download link], enter the "toolchain" directory, download the cross compiler "gcc-linaro-arm-4.6.3.tar.xz" and "gcc-linaro-aarch64.tar.xz" and copy them to the "lichee/brandy/toochain/" directory.<br> | |
| − | + | "gcc-linaro-arm-4.6.3.tar.xz"is for compiling u-boot and "gcc-linaro-aarch64.tar.xz" is for compiling Linux kernel. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | ====Compile lichee Source Code==== |
| − | + | Compilation of the H5's BSP source code must be done under a PC running a 64-bit Linux.The following cases were tested on Ubuntu-14.04 LTS-64bit: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | sudo apt-get install gawk git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ | + | $ sudo apt-get install gawk git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ |
zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ | zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ | ||
libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ | libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ | ||
| Line 370: | Line 292: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Enter the lichee directory and run the following command to compile the whole package: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | cd lichee/fa_tools | + | $ cd lichee/fa_tools |
| − | ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t all | + | $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t all |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | After this compilation succeeds a u-boot, Linux kernel and kernel modules will be generated.<br> | |
| − | + | Note: the lichee directory contains cross-compilers we have setup. When the build.sh script runs it will automatically call these cross-compilers. | |
| − | + | The following commands can be used to update the u-boot on an installation TF card: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | cd lichee/fa_tools/ | + | $ cd lichee/fa_tools/ |
| − | ./fuse.sh -d /dev/sdx -p linux -t u-boot | + | $ ./fuse.sh -d /dev/sdx -p linux -t u-boot |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | /dev/ | + | Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system.<br> |
| − | + | The boot.img and kernel modules are under the "linux-3.10/output" directory. You can copy the new boot.img file to your TF card's boot partition. | |
| − | === | + | ====Compile U-boot==== |
| − | + | Note:you need to compile the whole lichee directory before you can compile U-boot individually.<br> | |
| + | You can run the following commands to compile u-boot individually: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | cd lichee/fa_tools/ | + | $ cd lichee/fa_tools/ |
| − | ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t u-boot | + | $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t u-boot |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | === | + | ====Compile Linux Kernel==== |
| − | + | Note:you need to compile the whole lichee directory before you can compile Linux kernel individually.<br> | |
| + | You can run the following commands to compile Linux kernel individually: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | cd lichee/fa_tools/ | + | $ cd lichee/fa_tools/ |
| − | ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t kernel | + | $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t kernel |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | The boot.img and kernel modules are under the "linux-3.10/output" directory. You can copy the new boot.img file to your TF card's boot partition. | |
| − | === | + | ====Clean Source Code==== |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | cd lichee/fa_tools/ | + | $ cd lichee/fa_tools/ |
| − | ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t clean | + | $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t clean |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | {{H5-KernelHeaderFile}} | ||
| + | ==Connect External Modules to NEO2== | ||
| + | ===DIY NAS Server with 1-bay NAS Dock & NEO2=== | ||
| + | The 1-bay NAS Dock is an expansion board which can be used to connect an external hard disk to a NanoPi NEO2.It uses JSM568 USB3.0 to SATA IC and communicates with a NanoPi NEO2 via USB interface. It works with a 2.5" SATA hard disk.It uses TI's DC-DC chipset to convert a 12V input to 5V. It has a power switch for users to turn on/off the device.It supports an onboard RTC battery. FriendlyElec migrated mainline Linux-4.14 kernel and Debian-Jessie with OpenMediaVault. Together with FriendlyElec's customized aluminum case you can quickly assemble a storage server. Here is a hardware setup :[[1-bay NAS Dock v1.2 for NanoPi NEO/NEO2]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[File:step4.png | frameless|300px| Step 4]] | ||
| − | == | + | ===Connect Python Programmable NanoHat OLED to NEO2=== |
| − | + | The NanoHat OLED module is a small and cute monochrome OLED module with low power consumption. It has three user buttons. We provide its driver's source code and a user friendly shell interface on which you can check system information and status.A customized aluminum case is made for it. You cannot miss this lovely utility! Here is a hardware setup:[[NanoHat OLED]]<br /> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[File:NanoHat OLED_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|NanoHat OLED_nanopi_NEO]] | [[File:NanoHat OLED_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|NanoHat OLED_nanopi_NEO]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Connect Python Programmable NanoHat Motor to NEO2=== |
| − | + | The NanoHat Motor module can drive four 5V PWM steering motors and four 12V DC motors or four 5V PWM steering motors and two 12V four-wire step motors.Here is a hardware setup: [[NanoHat Motor]]<br /> | |
[[File:NanoHat Motor_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|NanoHat Motor_nanopi_NEO]] | [[File:NanoHat Motor_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|NanoHat Motor_nanopi_NEO]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Connect NanoHat PCM5102A to NEO2=== |
| − | NanoHat | + | The NanoHat PCM5102A module uses TI's DAC audio chip PCM5102A, a convenient and easy-to-use audio module for hobbyists. Here is a hardware setup:[[NanoHat PCM5102A]]<br /> |
[[File:Matrix - NanoHat PCM5102A_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Matrix - NanoHat PCM5102A_nanopi_NEO]] | [[File:Matrix - NanoHat PCM5102A_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Matrix - NanoHat PCM5102A_nanopi_NEO]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Connect Arduino Compatible UNO Dock to NEO2=== |
| − | UNO | + | The UNO Dock module is an Arduino board compatible with Arduino UNO and works with Arduino programs.You can use Arduino IDE to run all Arduino programs on the Dock.It also exposes the NanoPi NEO2's pins.It converts 12V power input to 5V/2A output.You can search for various code samples from Ubuntu's ecosystem and run on the Dock. These features make it a powerful platform for IOT projects and cloud related applications. Here is a hardware setup:[[UNO Dock for NanoPi NEO v1.0]]<br /> |
[[File:Matrix-UNO_Dock_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Matrix-UNO_Dock_NEO]] | [[File:Matrix-UNO_Dock_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Matrix-UNO_Dock_NEO]] | ||
| − | ===Power Dock | + | ===Connect Power Dock to NEO2=== |
| − | Power Dock for NanoPi | + | The Power Dock for NanoPi NEO2 is a high efficiency power conversion module. It provides stable and reliable power source. Here is a hardware setup:[[Power Dock for NanoPi NEO]]<br /> |
[[File:Power Dock for NanoPi NEO_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Power Dock for NanoPi NEO_nanopi_NEO]] | [[File:Power Dock for NanoPi NEO_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Power Dock for NanoPi NEO_nanopi_NEO]] | ||
| − | ===NanoHat Proto | + | ===Connect NanoHat Proto to NEO2=== |
| − | NanoHat | + | The NanoHat Proto is an expansion board which exposes NEO2's various pins.It has an onboard EEPROM for data storage.Here is a hardware setup:[[NanoHat Proto]]<br /> |
[[File:Matrix - NanoHat Proto_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Matrix - NanoHat Proto_nanopi_NEO]] | [[File:Matrix - NanoHat Proto_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|300px|Matrix - NanoHat Proto_nanopi_NEO]] | ||
| − | ==3D | + | ===Connect Matrix - 2'8 SPI Key TFT to NanoPi NEO2=== |
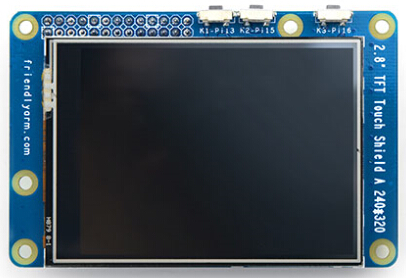
| − | [[File:NanoPi NEO2-3D.jpg|thumb| | + | The Matrix-2'8_SPI_Key_TFT module is a 2.8" TFT LCD with resistive touch. It uses the ST7789S IC and XPT2046 resistive touch IC. It has SPI interface and three configurable user keys.Here is its wiki page [[Matrix - 2'8 SPI Key TFT]]<br /> |
| − | [http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2180624 | + | [[File:Matrix-2'8_SPI_Key_TFT-1706.jpg|frameless|300px|File:Matrix-2'8_SPI_Key_TFT-1706]] |
| + | |||
| + | ==3D Printing Files== | ||
| + | [[File:NanoPi NEO2-3D.jpg|thumb|NanoPi_NEO2_V1.0-1701 3D Printed Housing|300px]] | ||
| + | *[http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2180624 NanoPi_NEO2_V1.0-1701 3D Printing Files] | ||
| + | *[xxx NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1-1711 3D Printing Files] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Resources== | ||
| + | ===Datasheet & Schematics=== | ||
| + | * Schematics | ||
| + | ** [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/a/a1/Schematic_NanoPi_NEO2-v1.0_1701.pdf NanoPi-NEO2-1701-Schematic.pdf] | ||
| + | ** [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/d/db/Schematic_NanoPi_NEO2-V1.1-1711.pdf NanoPi-NEO2-V1.1-1711-Schematic.pdf] | ||
| + | * Dimensional Diagram | ||
| + | ** [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/File:NanoPi_NEO_2_Dimesions(dxf).rar NanoPi-NEO2-1701 pcb in dxf format] | ||
| + | ** [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/File:NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1-1711_PCB-Dimensional.rar NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1-1711 pcb file in dxf format] | ||
| + | ** [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/3/35/NEO_Heat_sink_dimension.pdf NanoPi-NEO2 Heat sink file in pdf format] | ||
| + | * H5 Datesheet | ||
| + | ** [http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/d/de/Allwinner_H5_Datasheet_V1.0.pdf Allwinner_H5_Datasheet_V1.0.pdf] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Internet resources=== | ||
| + | * unofficial ROM | ||
| + | ** [http://www.dietpi.com/ DietPi] | ||
| + | ** [https://www.armbian.com/download/?tx_maker=friendlyelec armbian] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * article | ||
| + | ** [https://linux-sunxi.org/FriendlyARM_NanoPi_NEO2] | ||
| + | ** [https://www.cnx-software.com/2017/03/14/nanopi-neo2-development-bord-powered-by-allwinner-h5-64-bit-arm-processor-sells-for-15/] | ||
| + | ** [https://www.cnx-software.com/2017/03/26/nanopi-neo-2-board-nanohats-and-bakebit-starter-kit-review-part-1-hardware-overview-assembly/] | ||
| + | ** [https://www.cnx-software.com/2017/04/02/nanopi-neo-2-board-benchmarks-with-ubuntu-16-04-2-using-linux-3-10-and-linux-4-10/] | ||
| + | ** [https://tech.scargill.net/nanopi-neo-2/] | ||
| + | ** [https://tech.scargill.net/diy-nas/] | ||
| + | {{H5ChangeLog}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Hardware Change List== | ||
| + | * '''NanoPi NEO2 Version Compare & List(Hardware)''' | ||
| + | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |version || NanoPi NEO2 V1.0 || NanoPi NEO2 V1.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Photo || [[File:NanoPi-NEO2-V1.0-1701-update.jpg |thumb|]] || [[File:NanoPi-NEO2-V1.1-1711.jpg |thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |TF Card Slot || ① Non-Popup TF Card Slot<br> || ①Popup TF Card Slot | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Audio Connector ||②NanoPi NEO V1.0 1701's Audio connector is a 2.0mm 5Pin-header<br/> [[File:NanoPi-NEO-V1.1A.jpg |thumb|]] ||②NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711's Audio connector is a 2.54mm 4Pin-header<br/>[[File:NanoPi-NEO2-V1.1.jpg |thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |RJ45 Gbps Ethernet ||③ NanoPi NEO V1.0 1701's Ethernet port is an SMT connector ||③ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711's Ethernet port is a pin connector. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CVBS Output || ||④ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711 has a CVBS output which V1.0 doesn't have | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Mounting Hole || ||⑤ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711 has two more mounting holes of 1.7 mm in diameter | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO voltage regulation || ||⑥ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711 has 1.1V/1.3V GPIO voltage regulation | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{H5ChangeLog}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Update Log== | ||
| + | ===March-14-2017=== | ||
| + | * Released English Version | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===April-5-2017=== | ||
| + | * Added sections 5.2 and 5.8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===May-7-2017=== | ||
| + | * Added sections 7: mainline support for H5 | ||
| + | * Added sections 8: support for external modules | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===May-17-2017=== | ||
| + | * Added sections 5.9: WiringNP support for H5 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===May-24-2017=== | ||
| + | * Added section 3: Software Features | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===June-4-2017=== | ||
| + | * Updated section 5.3.1 | ||
| + | * Updated section 3: added more OS features | ||
| − | == | + | ===June-8-2017=== |
| − | + | * Updated section 3.2: added support for RPi.GPIO_NP | |
| − | * | + | * Added section 6.10: added support for RPi.GPIO_NP |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ===July-5-2017=== |
| − | + | * Updated sections 5.3.2, 6.5 and 6.8 | |
| − | * | + | * Added section 8.8: connect 2.8"TFT to NEO2 |
| − | === | + | ===July-9-2017=== |
| − | + | * Updated section 7.2 | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | ===March-20-2018=== |
| − | * | + | * Updated sections 4, 9 and 10 |
| − | * | + | * Added section 11 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 09:57, 21 March 2022
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Hardware Spec
- 3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
- 4 Software Features
- 5 Get Started
- 6 Work with FriendlyCore
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 System Login
- 6.3 Configure System with npi-config
- 6.4 Develop Qt Application
- 6.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
- 6.6 Extend TF Card's Section
- 6.7 WiFi
- 6.8 Ethernet Connection
- 6.9 WiringPi and Python Wrapper
- 6.10 Custom welcome message
- 6.11 Modify timezone
- 6.12 Set Audio Device
- 6.13 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
- 6.14 Check CPU's Working Temperature
- 6.15 Test Watchdog
- 6.16 Test Infrared Receiver
- 6.17 Read CHIP ID
- 6.18 Access GPIO Pins/Wirings with WiringNP
- 6.19 Run Qt Demo
- 6.20 How to install and use docker (for arm64 system)
- 6.21 Play & Record Audio
- 7 Work with OpenWrt
- 8 More OS Support
- 9 Make Your Own FriendlyCore
- 10 Build Kernel Headers Package
- 11 Connect External Modules to NEO2
- 11.1 DIY NAS Server with 1-bay NAS Dock & NEO2
- 11.2 Connect Python Programmable NanoHat OLED to NEO2
- 11.3 Connect Python Programmable NanoHat Motor to NEO2
- 11.4 Connect NanoHat PCM5102A to NEO2
- 11.5 Connect Arduino Compatible UNO Dock to NEO2
- 11.6 Connect Power Dock to NEO2
- 11.7 Connect NanoHat Proto to NEO2
- 11.8 Connect Matrix - 2'8 SPI Key TFT to NanoPi NEO2
- 12 3D Printing Files
- 13 Resources
- 14 Hardware Change List
- 15 Update Log
1 Introduction
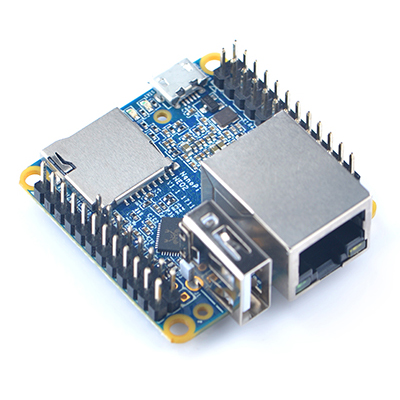
- The NanoPi NEO2 is a newly released super tiny ARM board by FriendlyElec. It uses Allwinner’s 64-bit H5 quad-core SoC (ARM Cortex-A53). It has internal hexa-core Mail450 GPU, 512M DDR3 RAM. A UbuntuCore and Armbian image files are ready for it.
- The NanoPi NEO2 inherits NEO's form factor and has compatible interfaces and ports with NEO. In addition in such a small dimension it has Gbps Ethernet and one USB host port. These features make it especially suitable for applications that require high data throughput , speedy data transmission and high performance. Hobbyists and makers will just love it.
2 Hardware Spec
- CPU: Allwinner H5, Quad-core 64-bit high-performance Cortex A53
- DDR3 RAM: 512MB
- Connectivity: 10/100/1000M Ethernet, RTL8211E-VB-CG chip
- USB Host: USB Type A x 1 and USB pin header x 2
- MicroSD Slot: MicroSD x 1 for system boot and storage
- LED: Power LED x 1, System LED x 1
- GPIO1: 2.54mm pitch 24 pin-header, compatible with Raspberry Pi's GPIO pin1 - pin 24. It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc
- GPIO2: 2.54mm pitch 12 pin-header. It includes USB, IR receiver, I2S, IO etc
- Serial Debug Port: 2.54mm pitch 4pin-header
- Audio In/Out: 2.54mm pitch 4 pin-header
- MicroUSB: Power input(5V/2A) and OTG
- PCB Dimension: 40 x 40mm
- Working Temperature: -20℃ to 70℃
- Weight: 13g(WITHOUT Pin-headers)
- OS/Software: u-boot,Ubuntu Core
2.1 UbuntuCore 16.04
- 64-bit system
- mainline kernel: Linux-4.14
- rpi-monitor: check system status and information
- npi-config: system configuration utility for setting passwords, language, timezone, hostname, SSH and auto-login,and enabling/disabling i2c, spi, serial and PWM. When enabling PWM it will prompt that Serial debug port will be disabled.
- software utility: wiringNP to access GPIO pins
- software utility: RPi.GPIO_NP to access GPIO pins
- networkmanager: manage network
- system log output from serial port
- supports USB WiFi module: refer to #Connect USB WiFi to NEO
- supports audio recording and playing with 3.5mm audio jack
- supports I2C 0/1
- fixed MAC address
2.2 Ubuntu OLED
- mainline kernel: Linux-4.14
- supports FriendlyElec's OLED module
2.3 Debian
- welcome window with basic system information and status
2.4 Debian for NAS Dock
- mainline kernel: Linux-4.14
- supports FriendlyElec's NAS Dock
- optimized OpenMediaVault configuration options
- allocated swap section
-->
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
- GPIO Pin Description
Pin# Name Linux gpio Pin# Name Linux gpio 1 SYS_3.3V 2 VDD_5V 3 I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 12 4 VDD_5V 5 I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 11 6 GND 7 GPIOG11 203 8 UART1_TX/GPIOG6 198 9 GND 10 UART1_RX/GPIOG7 199 11 UART2_TX/GPIOA0 0 12 GPIOA6 6 13 UART2_RTS/GPIOA2 2 14 GND 15 UART2_CTS/GPIOA3 3 16 UART1_RTS/GPIOG8 200 17 SYS_3.3V 18 UART1_CTS/GPIOG9 201 19 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC0 64 20 GND 21 SPI0_MISO/GPIOC1 65 22 UART2_RX/GPIOA1 1 23 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC2 66 24 SPI0_CS/GPIOC3 67
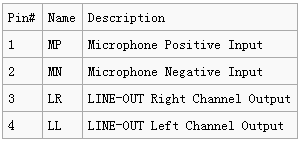
- USB/Audio/IR Pin Descripton
NanoPi-NEO2 Pin# Name Description 1 VDD_5V 5V Power Out 2 USB-DP1 USB1 DP Signal 3 USB-DM1 USB1 DM Signal 4 USB-DP2 USB2 DP Signal 5 USB-DM2 USB2 DM Signal 6 GPIOL11/IR-RX GPIOL11 or IR Receive 7 SPDIF-OUT/GPIOA17 GPIOA17 or SPDIF-OUT 8 PCM0_SYNC/I2S0_LRC I2S/PCM Sample Rate Clock/Sync 9 PCM0_CLK/I2S0_BCK I2S/PCM Sample Rate Clock 10 PCM0_DOUT/I2S0_SDOUT I2S/PCM Serial Data Output 11 PCM0_DIN/I2S0_SDIN I2S/PCM Serial Data Input 12 GND 0V
- Audio
Pin# Name Description 1 MP Microphone Positive Input 2 MN Microphone Negative Input 3 LR LINE-OUT Right Channel Output 4 LL LINE-OUT Left Channel Output
- Debug Port(UART0)
Pin# Name 1 GND 2 VDD_5V 3 UART_TXD0 4 UART_RXD0
- Note
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.5V. It can take power input from the MicroUSB.
- All pins are 3.3V and output current is 5mA
- For more details refer to the document: NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1_1711-Schematic.pdf
3.2 Dimensional Diagram
- For more details refer to pcb file in dxf format
4 Software Features
FriendlyCore System Cross-Compiler - gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.02-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu
- it applies to 64-bit Armv8 Cortex-A, little-endian architechture. FriendlyElec uses it for its H5 based boards.
U-boot-2017.11 - It can recognize a FriendlyElec's H5 based board and load its dtb file accordingly.
- It optimizes memory settings.
- It supports voltage regulation IC sy8106a and applies only to NanoPi K1 Plus/NanoPi NEO Core2.
- It supports MAC generation from H5's CPU ID.
- It supports system booting from either SD card or eMMC and can automatically load the kernel from the booting device.
Linux-4.14 - It supports LED. You can access it via "/sys/class/leds".
- It supports GPIO. You can access it via "/sys/class/gpio/".
- It supports UART0/1/2/3. You can access it via "/dev/ttySX".
- It supports I2C0. You can access it via "/dev/i2c-X".
- It supports SPI0. You can access it via "/dev/spidevX.X".
- It supports PWM0. You can access it via "/sys/class/pwm/". The UART0 pin is multiplexed.
- It supports I2S0. It works together with PCM5102A codec. The I2C1 pin is multiplexed.
- It supports Watchdog. You can access it via "/dev/watchX".
- It can read a CPU ID. You can access it via "/sys/bus/nvmem/devices/sunxi-sid0/nvmem".
- It supports IR Receiver. You need to connect an IR receiver to the board.
- It supports dynamic CPU voltage regulation.
- It supports Micro USB OTG.
- It supports USB Host1/2/3.
- It supports TF Card.
- It supports 1000M Ethernet.
- It supports H5's internal Codec and supports voice playing and recording.
- It supports USB Camera(CAM202).
- It supports popular USB WiFi Adapters.
- It supports popular USB Ethernet Adapters.
- It supports popular USB Serial Converters.
- It supports popular USB Sound Cards.
- It supports FriendlyElec's NanoHat PCM5102A.
File System - Based on UbuntuCore-16.04, it has original UbuntuCore features.
- It has popular utilties:VIM/Nano/SSHserver and etc.
- It has Qt-Embedded-4.8 and suitable for rapid product prototyping which needs a GUI.
- It has a network management utility "NetworkManager" which can automatically detect and connect to a network. For more details refer to: NetworkManager。
- It has a commandline utility "npi-config" which can be used to set a user password, language, timezone, Hostname, SSH enable/disable, auto-login, hardware interface and etc. For more details refer to Npi-config。
- It uses overlayfs.
- It expands the file system on the first system boot.
- It supports file system auto-repair on system boot.
- It supports 512MB's swap.
- It supports WiringNP which functions like Arduino's API and can be used to access NanoPi boards' gpio/i2c/spi and etc. For more details refer to: WiringNP。
- It supports FriendlyElec's BakeBit which is a set of sensor modules including hardware components(such as NanoHat Hub extension board) and software (such as BakeBit). For more details refer to BakeBit .
- It supports RPi.GPIO which can be used to access NanoPi boards' gpio with Python. For more details refer to RPi.GPIO.
- gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.02-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu
FriendlyWrt OS Cross Compiler - gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.02-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu
- Applicable for 64-bit Armv8 Cortex-A, little-endian. It has been tested and verified with FriendlyElec's Allwinner H5 boards.
U-boot-2017.11 - Same as FriendlyCore
Linux-4.14 - Same as FriendlyCore
File System - Based on OpenWrt-18.06 and keeps OpenWrt's original features;
- Based on a U-boot-2017.11 + Linux-4.14 system which is maintained by FriendlyElec
- Optimizes system initialization on a first time system boot
- Supports Huawei wifi 2 mini(E8372h)
- Supports 5G USB WiFi rtl8821cu, plug and play
- Supports Matrix-LCD2USB, by default it shows an IP address
- Utilizes overlayfs, for more details refer to How to use overlayfs on Linux
- Supports auto-extension of file system on a first time system boot
- Supports one-touch script to compile U-boot/Linux/FriendlyWrt rootfs and generate an image file, for more details refer to How to Build FriendlyWrt
- Supports flashing an image to eMMC with eflasher, for more details refer to EFlasher。
5 Get Started
5.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi NEO2 get the following items ready
- NanoPi NEO2
- microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must
- A host computer running Ubuntu 18.04 64 bit system
5.2 TF Cards We Tested
To make your device boot and run fast we highly recommend you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- Sandisk MicroSDHC V30 32GB Extreme Pro (Developer choice)
- SanDisk 32GB High Endurance Video MicroSDHC Card with Adapter for Dash Cam and Home Monitoring Systems (High reliability)
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD High Speed TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
5.3 Install OS
5.3.1 Get Image File
Get the following files from download link to download image files (under the officail-ROMs directory) and the flashing utility(under the tools directory):
Image Files: nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlycore-xenial_3.10_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Base on UbuntuCore, kernel:Linux-3.10 nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlycore-xenial_4.14_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Base on UbuntuCore, kernel:Linux-4.14 nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlywrt_4.14_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Base on OpenWrt, kernel:Linux-4.14 Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
5.3.2 Linux
5.3.2.1 Flash to TF
- FriendlyCore / Debian / Ubuntu / OpenWrt / DietPi are all based on a same Linux distribution and their installation methods are the same.
- Extract the Linux image and win32diskimager.rar files. Insert a TF card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your TF card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the TF card.
Take "nanopi-neo2_sd_friendlycore-xenial_4.14_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img" as an example here is the installation window. Other image files are installed on the similar window:
After it is installed you will see the following window:
- Insert this card into your board's BOOT slot and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and the STAT LED is blinking this indicates your board has successfully booted.
6 Work with FriendlyCore
6.1 Introduction
FriendlyCore is a light Linux system without X-windows, based on ubuntu core, It uses the Qt-Embedded's GUI and is popular in industrial and enterprise applications.
Besides the regular Ubuntu Core's features FriendlyCore has the following additional features:
- it integrates Qt4.8;
- it integrates NetworkManager;
- it has bluez and Bluetooth related packages;
- it has alsa packages;
- it has npi-config;
- it has RPiGPIO, a Python GPIO module;
- it has some Python/C demo in /root/ directory;
- it enables 512M-swap partition;
6.2 System Login
- If your board is connected to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and keyboard.
- If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will
allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB:
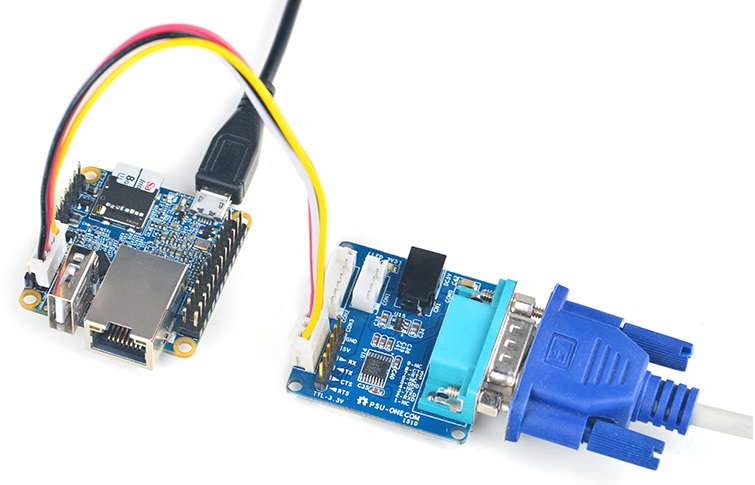
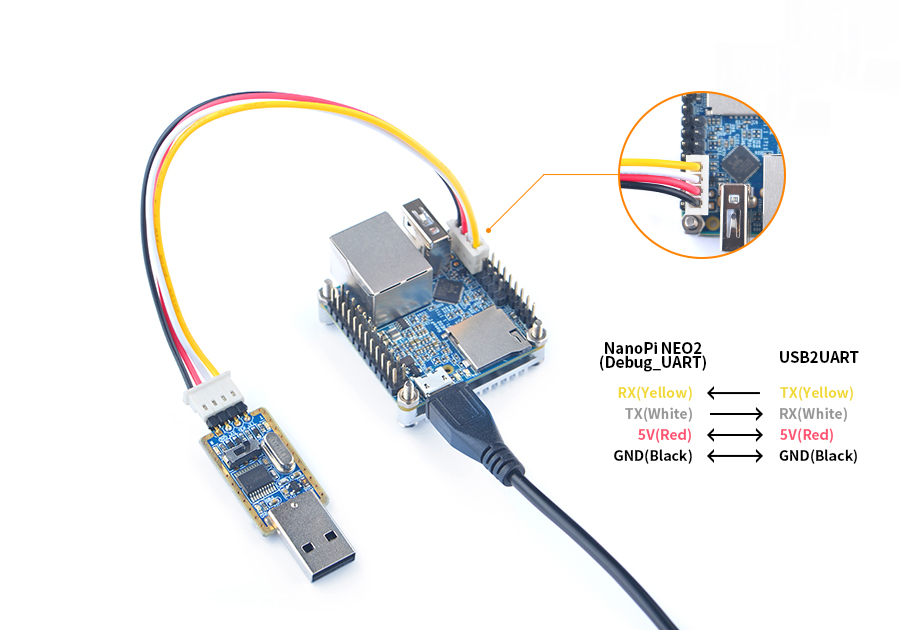
You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too.
Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:
- FriendlyCore User Accounts:
Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
The system is automatically logged in as "pi". You can do "sudo npi-config" to disable auto login.
- Update packages
$ sudo apt-get update
6.3 Configure System with npi-config
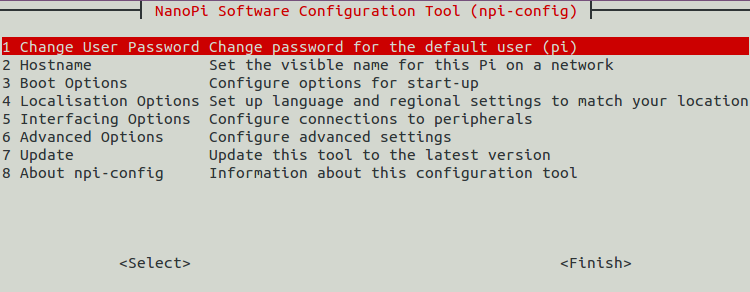
The npi-config is a commandline utility which can be used to initialize system configurations such as user password, system language, time zone, Hostname, SSH switch , Auto login and etc. Type the following command to run this utility.
$ sudo npi-config
Here is how npi-config's GUI looks like:
6.4 Develop Qt Application
Please refer to: How to Build and Install Qt Application for FriendlyELEC Boards
6.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
You can setup a program to autorun on system boot with npi-config:
sudo npi-configGo to Boot Options -> Autologin -> Qt/Embedded, select Enable and reboot.
6.6 Extend TF Card's Section
When FriendlyCore is loaded the TF card's section will be automatically extended.You can check the section's size by running the following command:
$ df -h
6.7 WiFi
For either an SD WiFi or a USB WiFi you can connect it to your board in the same way. The APXX series WiFi chips are SD WiFi chips. By default FriendlyElec's system supports most popular USB WiFi modules. Here is a list of the USB WiFi modules we tested:
Index Model 1 RTL8188CUS/8188EU 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 mi WiFi mt7601 6 5G USB WiFi RTL8821CU 7 5G USB WiFi RTL8812AU
You can use the NetworkManager utility to manage network. You can run "nmcli" in the commandline utility to start it. Here are the commands to start a WiFi connection:
- Change to root
$ su root
- Check device list
$ nmcli devNote: if the status of a device is "unmanaged" it means that device cannot be accessed by NetworkManager. To make it accessed you need to clear the settings under "/etc/network/interfaces" and reboot your system.
- Start WiFi
$ nmcli r wifi on- Scan Surrounding WiFi Sources
$ nmcli dev wifi- Connect to a WiFi Source
$ nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD" ifname wlan0
The "SSID" and "PASSWORD" need to be replaced with your actual SSID and password.If you have multiple WiFi devices you need to specify the one you want to connect to a WiFi source with iface
If a connection succeeds it will be automatically setup on next system reboot.
For more details about NetworkManager refer to this link: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
If your USB WiFi module doesn't work most likely your system doesn't have its driver. For a Debian system you can get a driver from Debian-WiFi and install it on your system. For a Ubuntu system you can install a driver by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install linux-firmware
In general all WiFi drivers are located at the "/lib/firmware" directory.
6.8 Ethernet Connection
If a board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP with DHCP activated after it is powered up. If you want to set up a static IP refer to: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings。
6.9 WiringPi and Python Wrapper
- WiringNP: NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with C
- RPi.GPIO : NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with Python
6.10 Custom welcome message
The welcome message is printed from the script in this directory:
/etc/update-motd.d/
For example, to change the FriendlyELEC LOGO, you can change the file /etc/update-motd.d/10-header. For example, to change the LOGO to HELLO, you can change the following line:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal $BOARD_VENDOR
To:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal HELLO
6.11 Modify timezone
For exampe, change to Shanghai timezone:
sudo rm /etc/localtime sudo ln -ls /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
6.12 Set Audio Device
If your system has multiple audio devices such as HDMI-Audio, 3.5mm audio jack and I2S-Codec you can set system's default audio device by running the following commands.
- After your board is booted run the following commands to install alsa packages:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libasound2 $ apt-get install alsa-base $ apt-get install alsa-utils
- After installation is done you can list all the audio devices by running the following command. Here is a similar list you may see after you run the command:
$ aplay -l card 0: HDMI card 1: 3.5mm codec card 2: I2S codec
"card 0" is HDMI-Audio, "card 1" is 3.5mm audio jack and "card 2" is I2S-Codec. You can set default audio device to HDMI-Audio by changing the "/etc/asound.conf" file as follows:
pcm.!default { type hw card 0 device 0 } ctl.!default { type hw card 0 }
If you change "card 0" to "card 1" the 3.5mm audio jack will be set to the default device.
Copy a .wav file to your board and test it by running the following command:
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav
You will hear sounds from system's default audio device.
If you are using H3/H5/H2+ series board with mainline kernel, the easier way is using npi-config。
6.13 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
The FA-CAM202 is a 200M USB camera. You can refer to <Connect DVP Camera (CAM500B) to Board> on how to connect a USB camera to a board.
You need to change the start.sh script and make sure it uses a correct /dev/videoX node. You can check your FA-CAM202's node by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install v4l-utils $ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video1 -D Driver Info (not using libv4l2): Driver name : uvcvideo Card type : HC 3358+2100: HC 3358+2100 Bus info : usb-1c1b000.usb-1 ...
Information above indicates that /dev/video1 is the device node of the FA-CAM 202.
6.14 Check CPU's Working Temperature
You can get CPU's working temperature by running the following command:
$ cpu_freq CPU0 online=1 temp=26581 governor=ondemand cur_freq=480000 CPU1 online=1 temp=26581 governor=ondemand cur_freq=480000 CPU2 online=1 temp=26581 governor=ondemand cur_freq=480000 CPU3 online=1 temp=26581 governor=ondemand cur_freq=480000
This message means there are currently four CPUs working. All of their working temperature is 26.5 degree in Celsius and each one's clock is 480MHz.
6.15 Test Watchdog
You can test watchdog by running the following commands:
$ cd /root/demo/watchdog/ $ gcc watchdog_demo.c -o watchdog_demo $ ./watchdog_demo /dev/watchdog0 10 Set timeout: 10 seconds Get timeout: 10 seconds System will reboot in 10 second
System will reboot in 10 seconds.
6.16 Test Infrared Receiver
Note: Please Check your board if IR receiver exist.
By default the infrared function is disabled you can enable it by using the npi-config utility:
$ npi-config
6 Advanced Options Configure advanced settings
A8 IR Enable/Disable IR
ir Enable/Disable ir[enabled]Reboot your system and test its infrared function by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install ir-keytable $ echo "+rc-5 +nec +rc-6 +jvc +sony +rc-5-sz +sanyo +sharp +mce_kbd +xmp" > /sys/class/rc/rc0/protocols # Enable infrared $ ir-keytable -t Testing events. Please, press CTRL-C to abort.
"ir-keytable -t" is used to check whether the receiver receives infrared signals. You can use a remote control to send infrared signals to the receiver. If it works you will see similar messages as follows:
1522404275.767215: event type EV_MSC(0x04): scancode = 0xe0e43 1522404275.767215: event type EV_SYN(0x00). 1522404278.911267: event type EV_MSC(0x04): scancode = 0xe0e42 1522404278.911267: event type EV_SYN(0x00).
6.17 Read CHIP ID
As for Allwinner H2+/H3/H5/ SoCs each of these CPUs has an internal 16-btye CHIP ID which can be read by running the following commands in the Linux-4.14 kernel:
$ apt-get install bsdmainutils $ hexdump /sys/bus/nvmem/devices/sunxi-sid0/nvmem 0000000 8082 0447 0064 04c3 3650 ce0a 1e28 2202 0000010 0002 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000020 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000030 0000 0008 0508 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000040 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
"8082 0447 0064 04c3 3650 ce0a 1e28 2202" is the 16-byte CHIP ID.
6.18 Access GPIO Pins/Wirings with WiringNP
The wiringPi library was initially developed by Gordon Henderson in C. It contains libraries to access GPIO, I2C, SPI, UART, PWM and etc. The wiringPi library contains various libraries, header files and a commandline utility:gpio. The gpio utility can be used to read and write GPIO pins.
FriendlyElec integrated this utility in FriendlyCore system allowing users to easily access GPIO pins. For more details refer to WiringNP WiringNP
6.19 Run Qt Demo
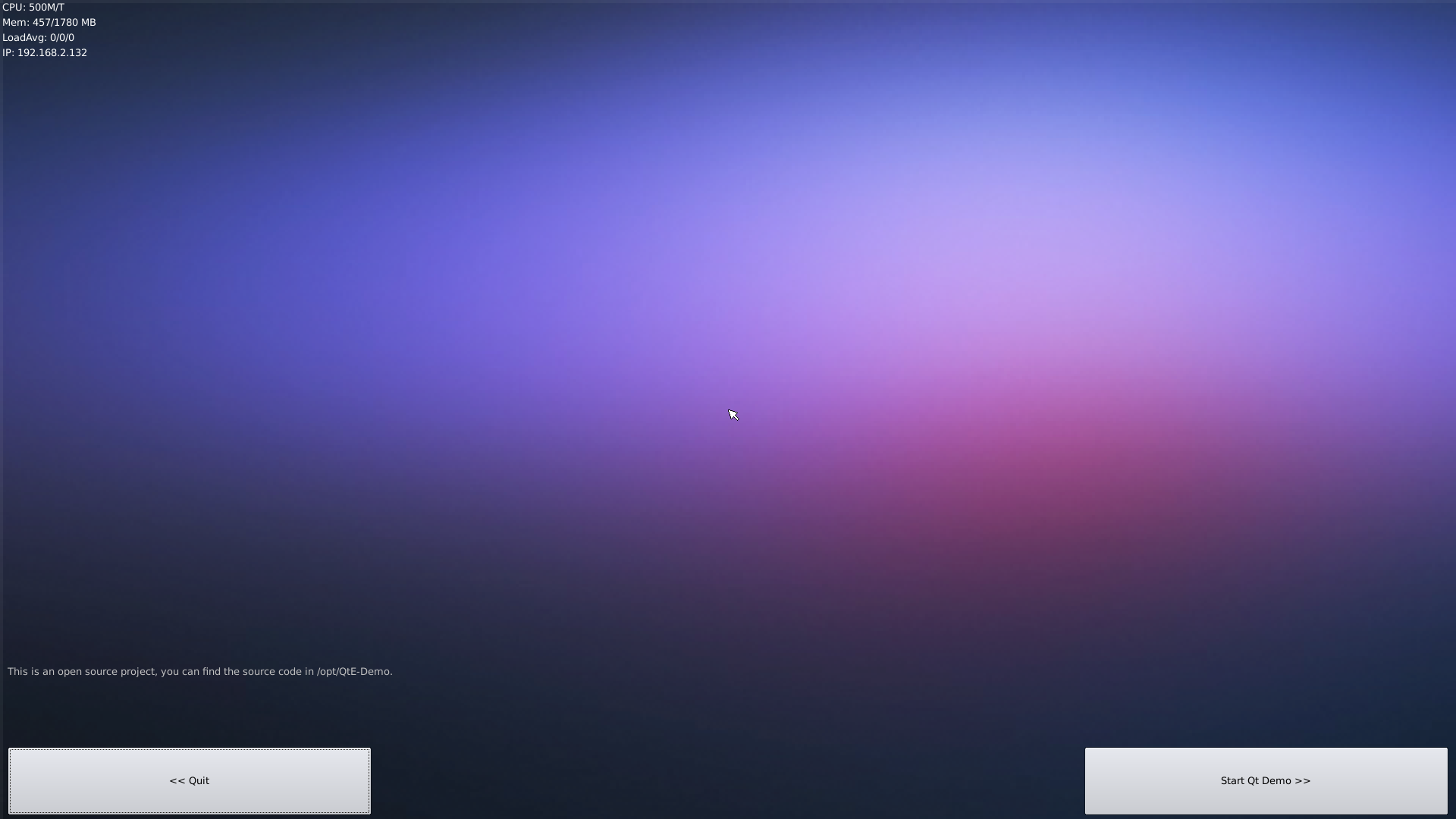
Run the following command
$ sudo /opt/QtE-Demo/run.sh
Here is what you expect to observe. This is an open source Qt Demo:
6.20 How to install and use docker (for arm64 system)
6.20.1 How to Install Docker
Run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker.io
6.20.2 Test Docker installation
Test that your installation works by running the simple docker image:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/debian-jessie-arm-docker cd debian-jessie-arm-docker ./rebuild-image.sh ./run.sh
6.21 Play & Record Audio
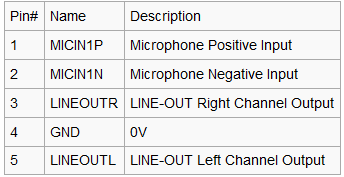
The NanoPi NEO2 has an audio interface (2.0mm pitch 5-pin header) whose pin description is as follows:
Pin# Name Description 1 MICIN1P Microphone Positive Input 2 MICIN1N Microphone Negative Input 3 LINEOUTR LINE-OUT Right Channel Output 4 GND Ground 5 LINEOUTL LINE-OUT Left Channel Output
Here is a hardware setup on how to connect an audio device to a NEO2:
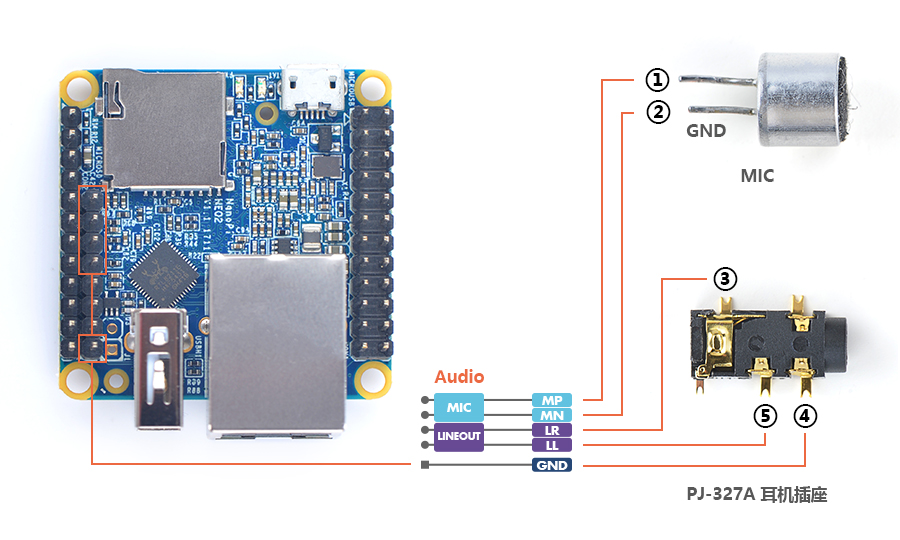
Before begin to play or record a audio make sure your NEO2 is connected to an audio device.
Check a recognized audio device:
$ aplay -l **** List of PLAYBACK Hardware Devices **** card 0: Codec [H3 Audio Codec], device 0: CDC PCM Codec-0 [] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
Both Allwinner's H5 and H3 have an internal codec which is named as [H3 Audio Codec] in mainline kernels.
Play an audio file:
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav -D plughw:0
Record an audio file:
$ arecord -f cd -d 5 test.wav
7 Work with OpenWrt
7.1 Introduction
OpenWrt is a highly extensible GNU/Linux distribution for embedded devices.Unlike many other distributions for routers, OpenWrt is built from the ground up to be a full-featured, easily modifiable operating system for embedded devices. In practice, this means that you can have all the features you need with none of the bloat, powered by a modern Linux kernel. For more details you can refer to:OpenWrt Website.
7.2 System Login
- Login via Serial Port
When you do kernel development you'd better get a serial communication board. After you connect your board to a serial communication board you will be able to do development work from a commandline utility.
Here is a hardware setup:
After you connect your board to a serial communication board (e.g. FriendlyElec's serial communication board) you can power the whole system from either the DC port on the serial communication board or the MicroUSB port(if there is one) on your board:

or you can use a USB to serial board and power on the whole system at the MicroUSB port with a 5V/2A power:

By default you will login as root without a password. You can use "passwd" to set a password for root.
On first boot the system will automatically extend the file system on the TF card to the max capacity:
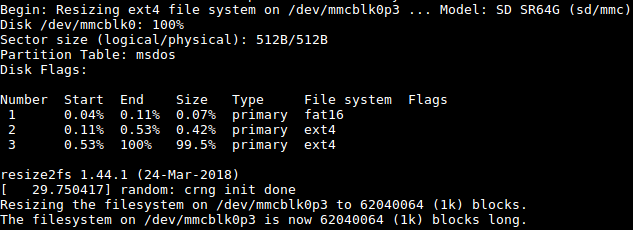
Please wait for this to be done.
- Login via SSH
In FriendlyElec's OpenWrt system the Ethernet(eth0) is configured as WAN.
Before power on your board make sure your board is connected to a master router's LAN with an Ethernet cable and the eth0 will be assigned an IP address by DHCP.
For example, if your eth0 is assigned an IP address 192.168.1.163 you can login with SSH by running the following command:
$ ssh root@192.168.1.163
You can login without a password.
- Login via Web
You can login OpenWrt via a LuCI Web page.
After you go through all the steps in <Login via SSH> and get an IP address e.g. 192.168.1.163 for the Ethernet connection, type this IP address in a browser's address bar and you will be able to login OpenWrt-LuCI:
By default you will login as root without a password, just click on "Login" to login.
7.3 Manage Software Packages
OpenWrt has a package management utility: opkg. You can get its details by running the following command:
$ opkg
Package Manipulation:
update Update list of available packages
upgrade <pkgs> Upgrade packages
install <pkgs> Install package(s)
configure <pkgs> Configure unpacked package(s)
remove <pkgs|regexp> Remove package(s)
flag <flag> <pkgs> Flag package(s)
<flag>=hold|noprune|user|ok|installed|unpacked (one per invocation)
Informational Commands:
list List available packages
list-installed List installed packages
list-upgradable List installed and upgradable packages
list-changed-conffiles List user modified configuration files
files <pkg> List files belonging to <pkg>
search <file|regexp> List package providing <file>
find <regexp> List packages whose name or description matches <regexp>
info [pkg|regexp] Display all info for <pkg>
status [pkg|regexp] Display all status for <pkg>
download <pkg> Download <pkg> to current directory
...These are just part of the manual. Here are some popular opkg commands.
- Update Package List
Before you install a package you'd better update the package list:
$ opkg update
- Check Available Packages
$ opkg list
At the time of writing there are 3241 packages available.
- Check Installed Packages:
$ opkg list-installed
At the time of writing 124 packages have been installed.
- Install/Delete Packages:
$ opkg install <pkgs> $ opkg remove <pkgs>
- Check Files Contained in Installed Packages:
$ opkg files <pkg>
- Install Chinese Language Package for LuCI
$ opkg install luci-i18n-base-zh-cn
- Check Changed Files:
$ opkg list-changed-conffiles
- Reference Links:
7.4 Check System Status
- Check CPU Temperature & Frequency via Commandline
$ cpu_freq
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHzThese messages mean that there are four CPU cores working online simultaneously. Each core's temperature is 26.5 degrees in Celsius, the scheduling policy is on-demand and the working frequency is 624MHz. You can set the frequency by running the following command:
$ cpu_freq -s 1008000
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHzThese messages mean four CPU cores are working online. Each core's temperature is 26.5 degrees. Each core's governor is on demand and the frequency is 480 MHz.
- Check System Status on OpenWrt-LuCI Web Page
After open the OpenWrt-LuCI page, go to "Statistics ---> Graphs" and you will see various system statistics e.g.:
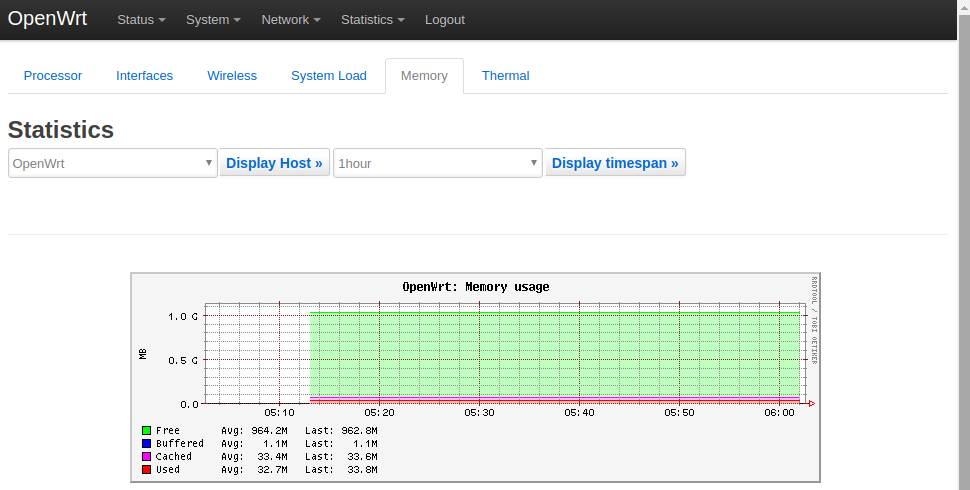
1) System Load:
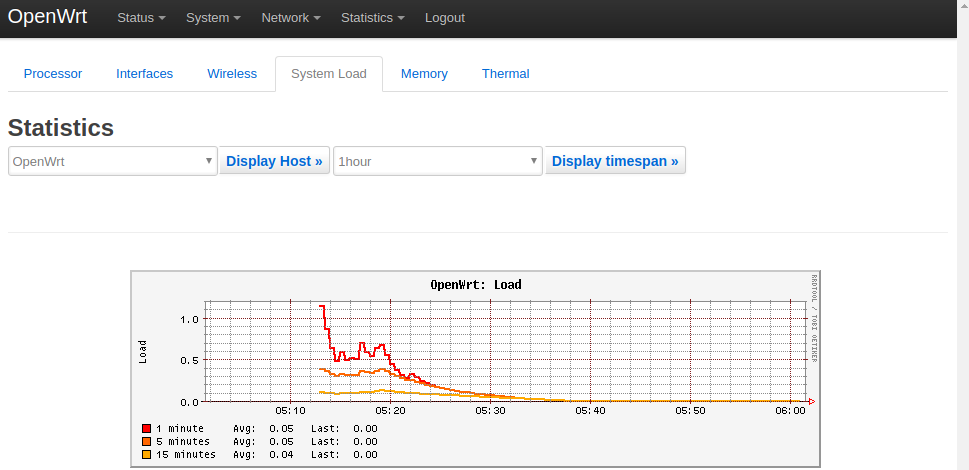
2) RAM:
3) CPU Temperature:
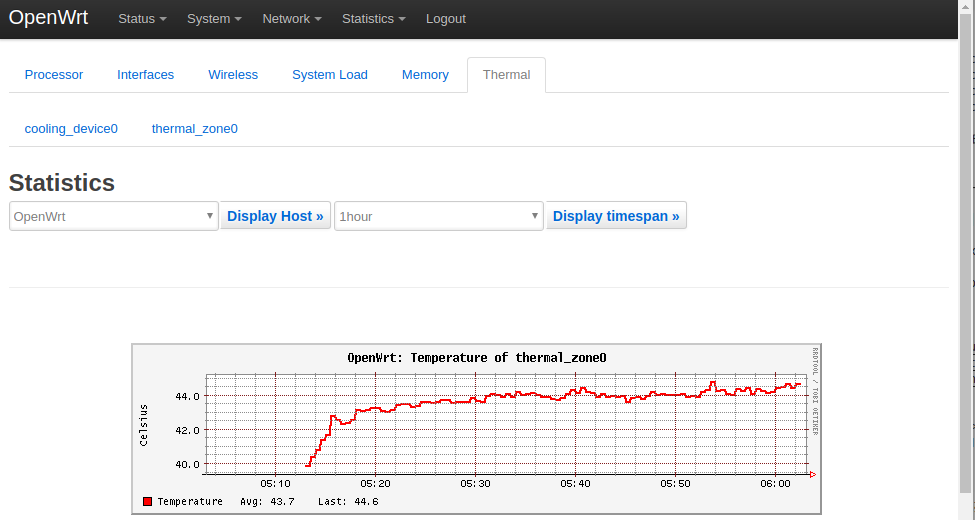
All the statistics listed on the Statistics page are presented by the luci-app-statistics package which uses the Collectd utility to collect data and presents them with the RRDtool utility.
If you want to get more statistics you can install other collectd-mod-* packages.
All collectd-mod-* packages use the same configuration file: /etc/config/luci_statistics.
- Reference Links:
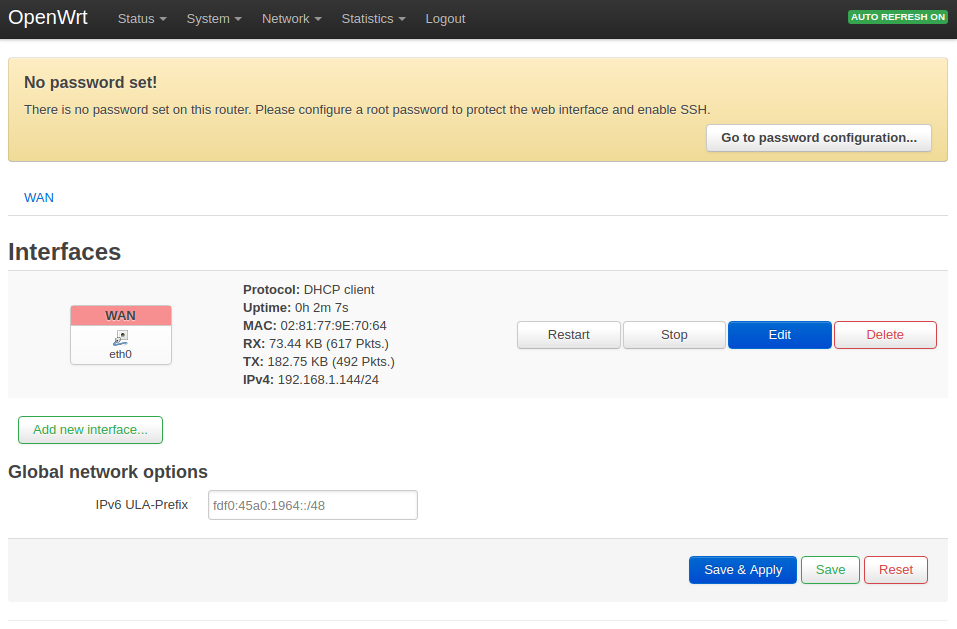
7.5 Check Network->Interfaces Configurations
- After open the OpenWrt-LuCI page, go to "Network" ---> "Interfaces" and you will see the current network's configurations:
- All the configurations listed on the Network->Interfaces page are stored in the "/etc/config/network" file.
7.6 USB WiFi
Currently the NanoPi NEO2 Black only works with a RTL8821CU USB WiFi dongle, plug and play. After this module is connected to the board it will by default work under AP mode and the hotspot's name is "rtl8821cu-mac address" and the password is "password";
7.7 Huawei's WiFi 2 mini(E8372H-155) Module
After this module is connected to the board it will be plug and play. The hotspot's name is "HUAWEI-8DA5". You can connect a device to the internet by connecting to this hotspot.
8 More OS Support
8.1 DietPi

DietPi is a highly optimised & minimal Debian-based Linux distribution. DietPi is extremely lightweight at its core, and also extremely easy to install and use.
Setting up a single board computer (SBC) or even a computer, for both regular or server use, takes time and skill. DietPi provides an easy way to install and run favourite software you choose.
For more information, please visit this link https://dietpi.com/docs/.
DietPi supports many of the NanoPi board series, you may download the image file from here:
9 Make Your Own FriendlyCore
9.1 Mainline U-boot & Linux(64 bit)
Now the NanoPi NEO2 can run a 64-bit Linux kernel with 64-bit Ubuntu Core 16.04. Here is a detailed reference on how to run mainline U-boot and Linux on H5: Mainline U-boot & Linux
9.2 Use Allwinner's BSP
9.2.1 Preparations
Visit this link download link and enter the "sources/nanopi-H5-bsp" directory and download all the source code.Use the 7-zip utility to extract it and a lichee directory and an Android directory will be generated.You can check that by running the following command:
$ ls ./ $ lichee
Or you can get it from our github:
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/h5_lichee.git lichee --depth 1
Note: "lichee" is the project name named by Allwinner for its CPU's source code which contains the source code of U-boot, Linux kernel and various scripts.
9.2.2 Install Cross Compiler
Visit this site download link, enter the "toolchain" directory, download the cross compiler "gcc-linaro-arm-4.6.3.tar.xz" and "gcc-linaro-aarch64.tar.xz" and copy them to the "lichee/brandy/toochain/" directory.
"gcc-linaro-arm-4.6.3.tar.xz"is for compiling u-boot and "gcc-linaro-aarch64.tar.xz" is for compiling Linux kernel.
9.2.3 Compile lichee Source Code
Compilation of the H5's BSP source code must be done under a PC running a 64-bit Linux.The following cases were tested on Ubuntu-14.04 LTS-64bit:
$ sudo apt-get install gawk git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ libgl1-mesa-dev g++-multilib mingw32 tofrodos \ python-markdown libxml2-utils xsltproc zlib1g-dev:i386
Enter the lichee directory and run the following command to compile the whole package:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t all
After this compilation succeeds a u-boot, Linux kernel and kernel modules will be generated.
Note: the lichee directory contains cross-compilers we have setup. When the build.sh script runs it will automatically call these cross-compilers.
The following commands can be used to update the u-boot on an installation TF card:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./fuse.sh -d /dev/sdx -p linux -t u-boot
Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system.
The boot.img and kernel modules are under the "linux-3.10/output" directory. You can copy the new boot.img file to your TF card's boot partition.
9.2.4 Compile U-boot
Note:you need to compile the whole lichee directory before you can compile U-boot individually.
You can run the following commands to compile u-boot individually:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t u-boot
9.2.5 Compile Linux Kernel
Note:you need to compile the whole lichee directory before you can compile Linux kernel individually.
You can run the following commands to compile Linux kernel individually:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t kernel
The boot.img and kernel modules are under the "linux-3.10/output" directory. You can copy the new boot.img file to your TF card's boot partition.
9.2.6 Clean Source Code
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t clean
10 Build Kernel Headers Package
The following commands need to be executed on the development board:
10.1 Software Version
The OS image file name: nanopi-XXX_sd_friendlycore-focal_4.14_arm64_YYYYMMDD.img
$ lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Release: 20.04 Codename: focal $ cat /proc/version Linux version 4.14.111 (root@ubuntu) (gcc version 6.3.1 20170109 (Linaro GCC 6.3-2017.02)) #192 SMP Thu Jun 10 15:47:26 CST 2021
10.2 Install the required packages
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y dpkg-dev libarchive-tools
10.3 Build Kernel Headers Package
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux -b sunxi-4.14.y --depth 1 kernel-h5 cd kernel-h5 rm -rf .git make distclean touch .scmversion make CROSS_COMPILE= ARCH=arm64 sunxi_arm64_defconfig alias tar=bsdtar make CROSS_COMPILE= ARCH=arm64 bindeb-pkg -j4
The following message is displayed to indicate completion:
dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-headers-4.14.111' in '../linux-headers-4.14.111_4.14.111-1_arm64.deb'. dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-libc-dev' in '../linux-libc-dev_4.14.111-1_arm64.deb'. dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-image-4.14.111' in '../linux-image-4.14.111_4.14.111-1_arm64.deb'. dpkg-genchanges: warning: substitution variable ${kernel:debarch} used, but is not defined dpkg-genchanges: info: binary-only upload (no source code included)
10.4 Installation
sudo dpkg -i ../linux-headers-4.14.111_4.14.111-1_arm64.deb
10.5 Testing
To compile the pf_ring module as an example, refer to the documentation: https://www.ntop.org/guides/pf_ring/get_started/git_installation.html.
git clone https://github.com/ntop/PF_RING.git cd PF_RING/kernel/ make
After compiling, use insmod to try to load the module:
sudo insmod ./pf_ring.ko
11 Connect External Modules to NEO2
11.1 DIY NAS Server with 1-bay NAS Dock & NEO2
The 1-bay NAS Dock is an expansion board which can be used to connect an external hard disk to a NanoPi NEO2.It uses JSM568 USB3.0 to SATA IC and communicates with a NanoPi NEO2 via USB interface. It works with a 2.5" SATA hard disk.It uses TI's DC-DC chipset to convert a 12V input to 5V. It has a power switch for users to turn on/off the device.It supports an onboard RTC battery. FriendlyElec migrated mainline Linux-4.14 kernel and Debian-Jessie with OpenMediaVault. Together with FriendlyElec's customized aluminum case you can quickly assemble a storage server. Here is a hardware setup :1-bay NAS Dock v1.2 for NanoPi NEO/NEO2
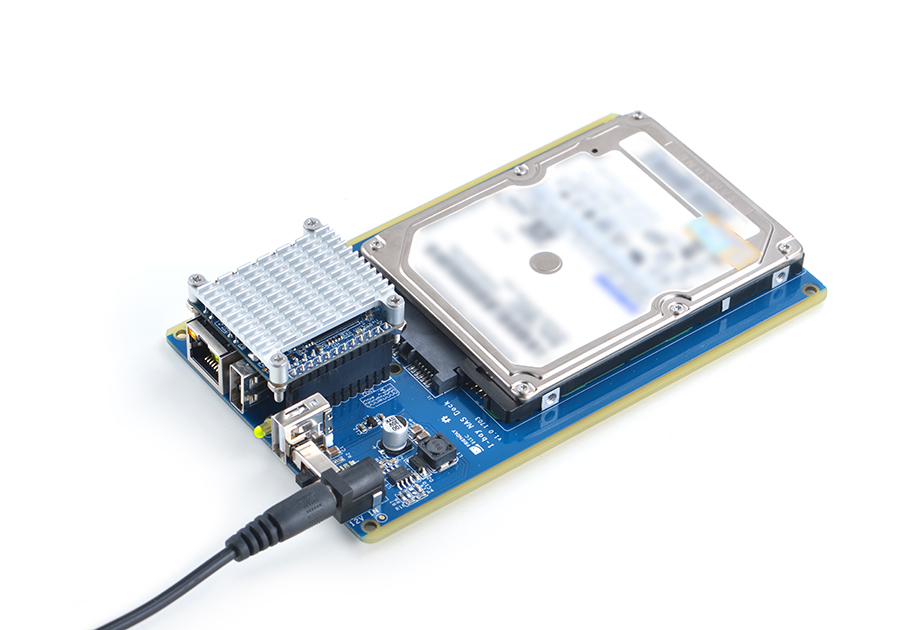

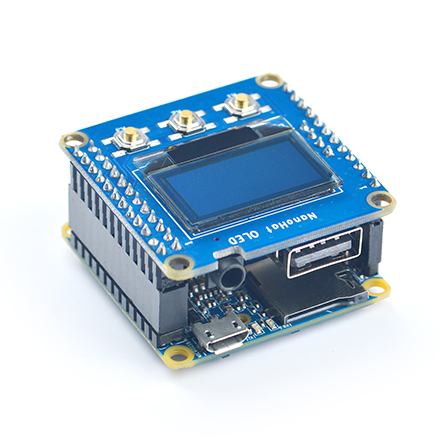
11.2 Connect Python Programmable NanoHat OLED to NEO2
The NanoHat OLED module is a small and cute monochrome OLED module with low power consumption. It has three user buttons. We provide its driver's source code and a user friendly shell interface on which you can check system information and status.A customized aluminum case is made for it. You cannot miss this lovely utility! Here is a hardware setup:NanoHat OLED

11.3 Connect Python Programmable NanoHat Motor to NEO2
The NanoHat Motor module can drive four 5V PWM steering motors and four 12V DC motors or four 5V PWM steering motors and two 12V four-wire step motors.Here is a hardware setup: NanoHat Motor
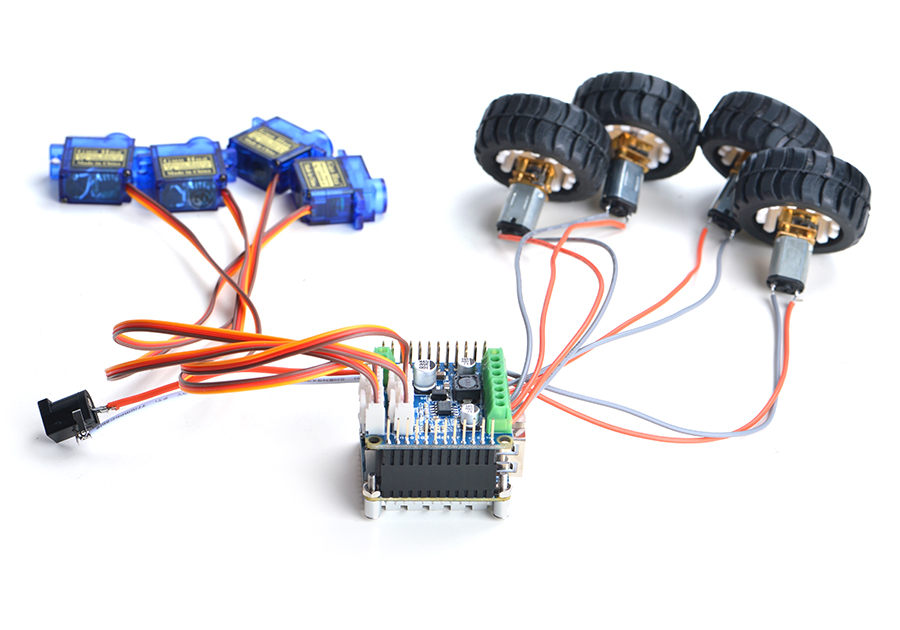
11.4 Connect NanoHat PCM5102A to NEO2
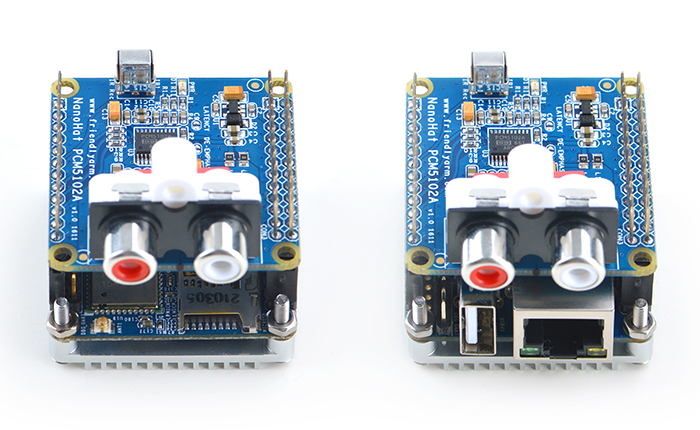
The NanoHat PCM5102A module uses TI's DAC audio chip PCM5102A, a convenient and easy-to-use audio module for hobbyists. Here is a hardware setup:NanoHat PCM5102A
11.5 Connect Arduino Compatible UNO Dock to NEO2
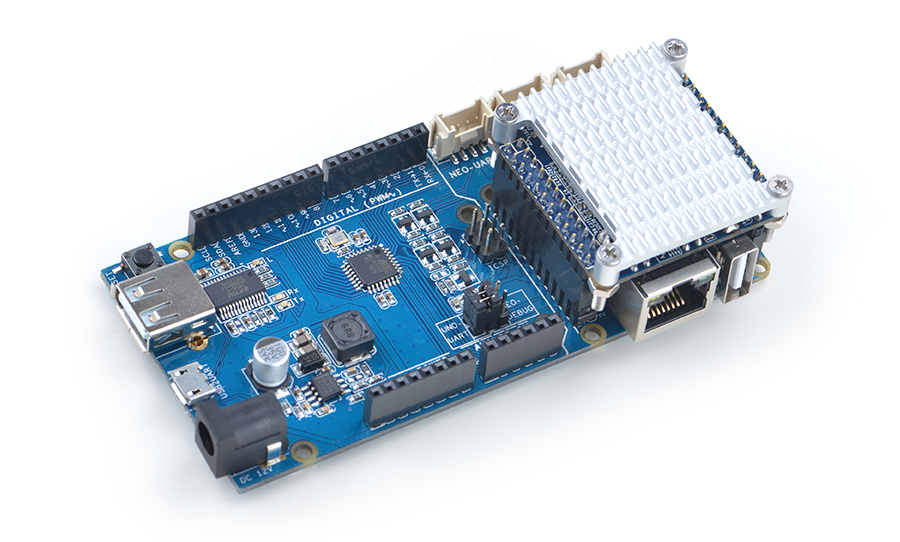
The UNO Dock module is an Arduino board compatible with Arduino UNO and works with Arduino programs.You can use Arduino IDE to run all Arduino programs on the Dock.It also exposes the NanoPi NEO2's pins.It converts 12V power input to 5V/2A output.You can search for various code samples from Ubuntu's ecosystem and run on the Dock. These features make it a powerful platform for IOT projects and cloud related applications. Here is a hardware setup:UNO Dock for NanoPi NEO v1.0
11.6 Connect Power Dock to NEO2
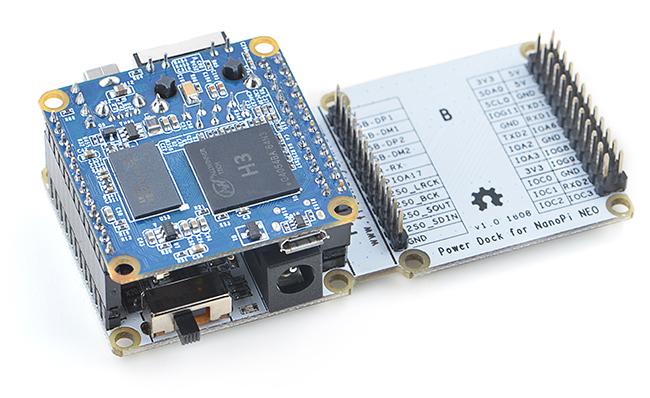
The Power Dock for NanoPi NEO2 is a high efficiency power conversion module. It provides stable and reliable power source. Here is a hardware setup:Power Dock for NanoPi NEO
11.7 Connect NanoHat Proto to NEO2
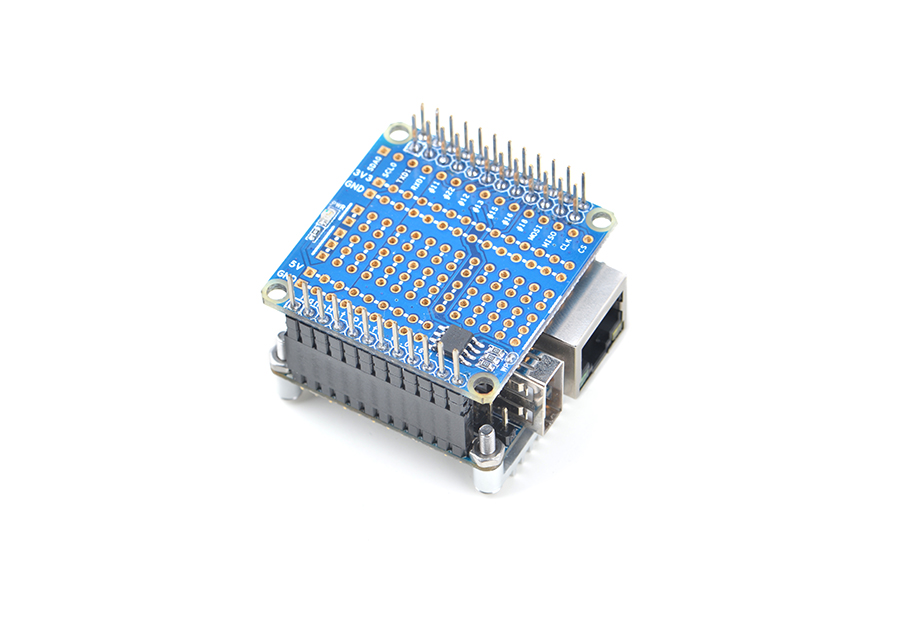
The NanoHat Proto is an expansion board which exposes NEO2's various pins.It has an onboard EEPROM for data storage.Here is a hardware setup:NanoHat Proto
11.8 Connect Matrix - 2'8 SPI Key TFT to NanoPi NEO2
The Matrix-2'8_SPI_Key_TFT module is a 2.8" TFT LCD with resistive touch. It uses the ST7789S IC and XPT2046 resistive touch IC. It has SPI interface and three configurable user keys.Here is its wiki page Matrix - 2'8 SPI Key TFT
12 3D Printing Files
- NanoPi_NEO2_V1.0-1701 3D Printing Files
- [xxx NanoPi_NEO2_V1.1-1711 3D Printing Files]
13 Resources
13.1 Datasheet & Schematics
- Schematics
- Dimensional Diagram
- H5 Datesheet
13.2 Internet resources
14 Hardware Change List
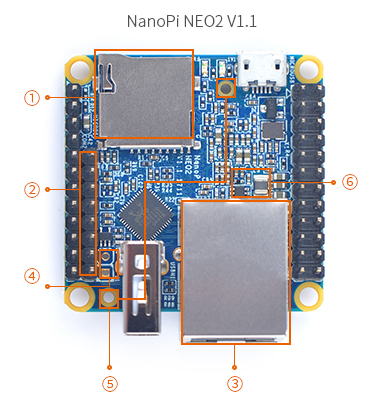
- NanoPi NEO2 Version Compare & List(Hardware)
version NanoPi NEO2 V1.0 NanoPi NEO2 V1.1 Photo TF Card Slot ① Non-Popup TF Card Slot
①Popup TF Card Slot Audio Connector ②NanoPi NEO V1.0 1701's Audio connector is a 2.0mm 5Pin-header
②NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711's Audio connector is a 2.54mm 4Pin-header
RJ45 Gbps Ethernet ③ NanoPi NEO V1.0 1701's Ethernet port is an SMT connector ③ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711's Ethernet port is a pin connector. CVBS Output ④ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711 has a CVBS output which V1.0 doesn't have Mounting Hole ⑤ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711 has two more mounting holes of 1.7 mm in diameter GPIO voltage regulation ⑥ NanoPi NEO V1.1 1711 has 1.1V/1.3V GPIO voltage regulation
15 Update Log
15.1 March-14-2017
- Released English Version
15.2 April-5-2017
- Added sections 5.2 and 5.8
15.3 May-7-2017
- Added sections 7: mainline support for H5
- Added sections 8: support for external modules
15.4 May-17-2017
- Added sections 5.9: WiringNP support for H5
15.5 May-24-2017
- Added section 3: Software Features
15.6 June-4-2017
- Updated section 5.3.1
- Updated section 3: added more OS features
15.7 June-8-2017
- Updated section 3.2: added support for RPi.GPIO_NP
- Added section 6.10: added support for RPi.GPIO_NP
15.8 July-5-2017
- Updated sections 5.3.2, 6.5 and 6.8
- Added section 8.8: connect 2.8"TFT to NEO2
15.9 July-9-2017
- Updated section 7.2
15.10 March-20-2018
- Updated sections 4, 9 and 10
- Added section 11