NanoPi R5S
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 Hardware Spec
- 3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
- 4 Get Started
- 4.1 Essentials You Need
- 4.2 TF Cards We Tested
- 4.3 PD Power Adapters We Tested
- 4.4 Configure parameters for serial port
- 4.5 Install OS
- 5 Work with FriendlyWrt
- 5.1 Introduction to FriendlyWrt
- 5.2 First boot
- 5.3 Account & Password
- 5.4 Login FriendlyWrt
- 5.5 Recommended security settings
- 5.6 Change LAN IP in LuCI
- 5.7 Safe shutdown operation
- 5.8 Soft Factory Reset
- 5.9 Install Software Packages
- 5.10 Disable IPv6
- 5.11 Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking
- 5.12 Some common issues of FriendlyWrt
- 5.13 Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature
- 5.14 How to use USB WiFi
- 5.15 Work with Docker Applications
- 5.16 Mount smbfs
- 5.17 Use sdk to compile the package
- 5.18 Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions
- 6 Work with FriendlyCore
- 7 Work with Android
- 8 Work with Debian11 Desktop
- 8.1 Introduction to Debian11 Desktop
- 8.2 Account & Password
- 8.3 View IP address
- 8.4 Connect to Debian via SSH
- 8.5 Update Software Packages
- 8.6 Install x11vnc Server on Debian for Remote Access
- 8.7 Install the kernel-header package
- 8.8 Change time zone
- 8.9 Change startup LOGO and Wallpaper
- 8.10 Soft Factory Reset
- 8.11 Start the program automatically at startup(For example Kodi)
- 8.12 Disable auto-mounting
- 8.13 Setup Chinese language and Input method
- 8.14 Installing Plex Multimedia Server
- 8.15 Install Docker on Debian
- 8.16 How to test NPU
- 8.17 How to test VPU
- 8.18 WiFi Connection
- 8.19 Cancel auto-login
- 8.20 Test OpenGL ES
- 8.21 HDMI/DP LCD Resolution
- 8.22 HiDPI and display scaling
- 8.23 Adjust HDMI overscan
- 8.24 Chromium web browser
- 8.25 Test hardware encoding
- 9 Work with Debian10 Desktop
- 10 Buildroot Linux
- 11 How to Compile
- 12 Using On-Board Hardware Resources
- 13 Backup rootfs and create custom SD image (to burn your application into other boards)
- 14 Connect NVME SSD High Speed Hard Disk
- 15 Common Linux-based operating system operations
- 16 Unbricking Method
- 17 Link to Rockchip Resources
- 18 Schematic, PCB CAD File
- 19 Update Logs
- 19.1 2025-01-23
- 19.2 2024-11-12
- 19.3 2024-10-16
- 19.4 2024-06-14
- 19.5 2024-06-06
- 19.6 2024-04-21
- 19.7 2024-03-15
- 19.8 2024-01-31
- 19.9 2023-12-23
- 19.10 2023-12-01
- 19.11 2023-11-13
- 19.12 2023-10-31
- 19.13 2023-09-09
- 19.14 2023-08-15
- 19.15 2023-07-19
- 19.16 2023-07-01
- 19.17 2023-06-25
- 19.18 2023-06-16
- 19.19 2023-06-09
- 19.20 2023-06-06
- 19.21 2023-06-02
- 19.22 2023-05-26
- 19.23 2023-05-21
- 19.24 2023-05-15
- 19.25 2023-05-05
- 19.26 2023-04-26
- 19.27 2023-03-24
- 19.28 2023-02-10
- 19.29 2023-01-09
- 19.30 2022-12-04
- 19.31 2022-09-06
- 19.32 2022-08-03
- 19.33 2022-07-27
- 19.34 2022-07-04
- 19.35 2022-06-22
- 19.36 2022-06-21
- 19.37 2022-06-15
- 19.38 2022-06-14
- 19.39 2022-05-16
1 Introduction
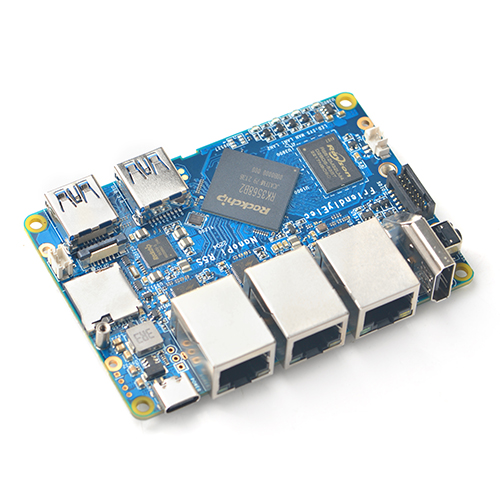
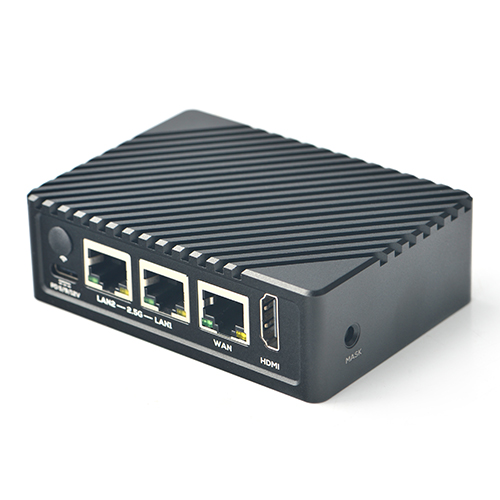
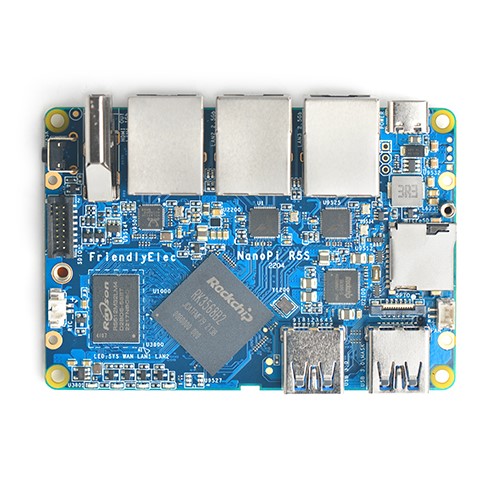
The NanoPi R5S (as “R5S”) is an open-sourced mini IoT gateway device with two 2.5G and one Gbps Ethernet ports, designed and developed by FriendlyElec.It is integrated with a Rockchip RK3568B2 CPU, 2GB/4GB LPDDR4x RAM and 8GB/16GB eMMC flash. It supports booting with TF cards and works with operating systems such as FriendlyWrt etc.
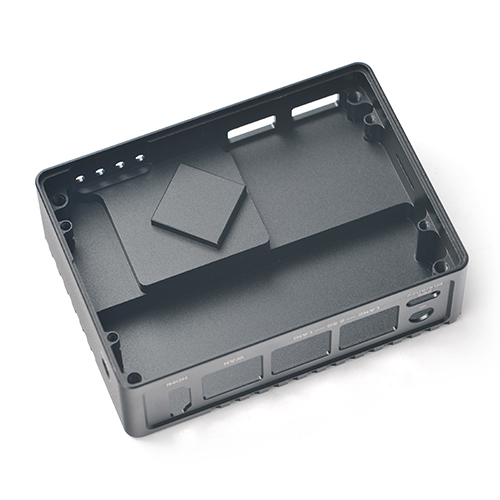
The NanoPi R5S has rich hardware resources with a compact size of 90 x 62 mm. FriendlyElec has released a carefully-designed custom CNC housing for it. It has one HDMI port. It works with Android, Ubuntu Desktop and Buildroot etc and works with headless systems as well. It supports decoding 4K60p H.265/H.264 formatted videos.
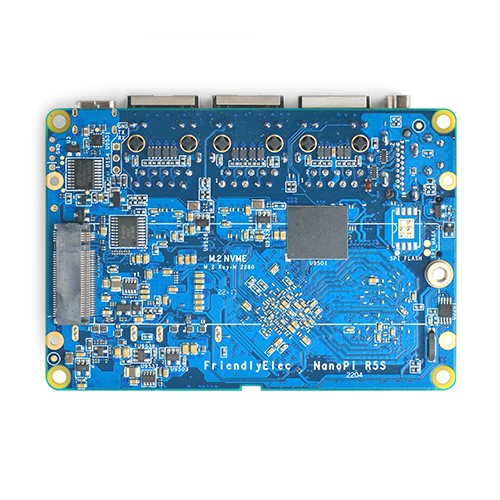
The NanoPi R5S has one M.2 NVME port, two USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports, and supports USB type-C power delivery. It is an ideal portable drive for saving images and videos.
All in all, the NanoPi R5S is a board featured with multiple Ethernet ports, light NAS and video playing. It is a cannot-miss platform with infinite possibilities for geeks, fans and developers.
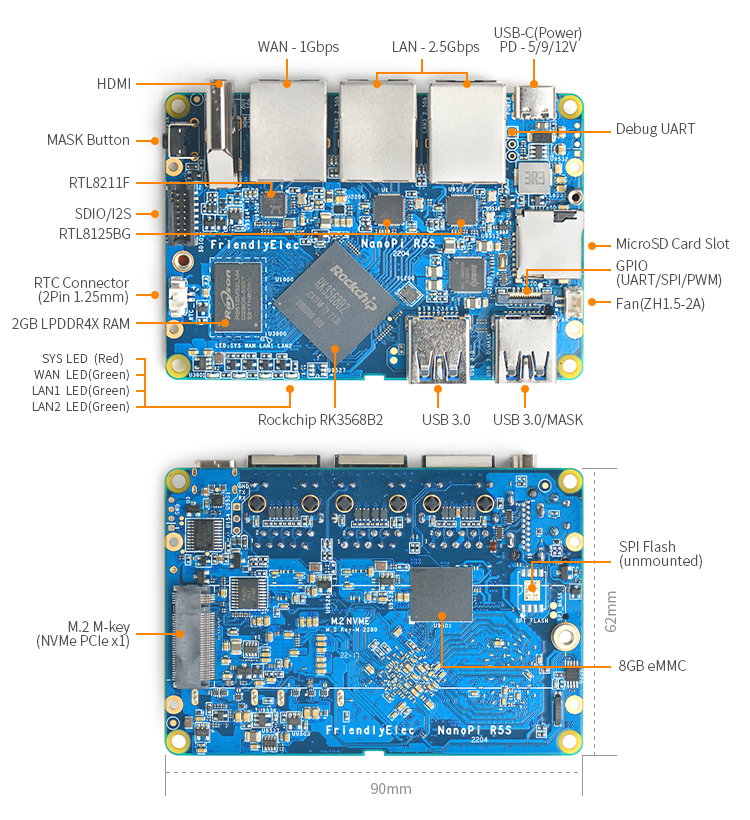
2 Hardware Spec
- SoC: Rockchip RK3568B2
- CPU: Quad-core ARM Cortex-A55 CPU, up to 2.0GHz
- GPU: Mali-G52 1-Core-2EE,supports OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0, and 3.2, Vulkan 1.0 and 1.1, OpenCL 2.0 Full Profile
- VPU: 4KP60 H.265/H.264/VP9 video decoder, 1080P60 H.264/H.265 video encoder
- NPU: Support 0.8T
- RAM: 2GB/4GB LPDDR4X
- Flash: 8GB/16GB eMMC
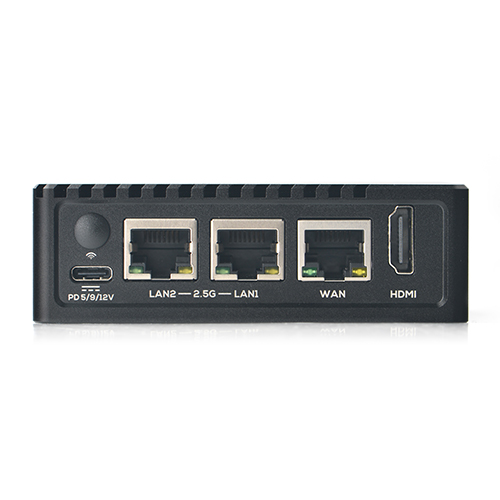
- Ethernet: one Native Gigabit Ethernet, and two PCIe 2.5Gbps Ethernet
- USB: two USB 3.2 Gen 1 Type-A ports
- HDMI:
- support HDMI1.4 and HDMI2.0 operation
- support up to 10 bits Deep Color modes
- support up to 1080p@120Hz and 4096x2304@60Hz
- support 3-D video formats
- PCIe: M.2 Key M, PCIe2.1 x1, support NVME, PCIe WiFi etc
- microSD: support UHS-I
- GPIO:
- 12-pin 0.5mm FPC connector
- up to 1x SPI, up to 3x UARTs, up to 4x PWMs, up to 8x GPIOs
- SD/MMC/SDIO/I2S:
- 2x8-pin 1.27mm connector
- Compatible with SDIO3.0 protocol
- Compatible with SD3.0, MMC ver4.51
- 4bits data bus widths
- 1x I2S with 2x SDO and 3x SDI
- Debug: one Debug UART, 3 Pin 2.54mm header, 3.3V level, 1500000bps
- LEDs: 4 x GPIO Controlled LED (SYS, WAN, LAN1, LAN2)
- others:
- 2 Pin 1.27/1.25mm RTC battery input connector for low power RTC IC HYM8563TS
- MASK button for eMMC update
- one 5V Fan connector
- Power supply: USB-C, support PD, 5V/9V/12V input
- PCB: 8 Layer, 62x90x1.6mm
- Ambient Operating Temperature: 0℃ to 70℃
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
- 12-pin GPIO
Pin# GPIO SPI UART PWM POWER Description 1 VCC3V3_SYS 3.3V power output 2 VCC3V3_SYS 3.3V power output 3 GPIO3_C3 SPI1_CLK_M1 UART5_RX_M1 3.3V level 4 GND 5 GPIO3_C2 SPI1_MISOI_M1 UART5_TX_M1 3.3V level 6 GPIO3_A1 SPI1_CS0_M1 3.3V level 7 GPIO3_C1 SPI1_MOSI_M1 3.3V level 8 GND 9 GPIO4_C5 UART9_TX_M1 PWM12_M1 3.3V level 10 GPIO4_C6 UART9_RX_M1 PWM13_M1 3.3V level 11 GPIO3_C4 UART7_TX_M1 PWM14_M0 3.3V level 12 GPIO3_C5 UART7_RX_M1 PWM15_IR_M0 3.3V level
- 2x8-pin SDIO/I2S
Pin# GPIO SD/MMC/SDIO I2S POWER Description 1 VCC5V0_SYS 5V power output 2 VCC5V0_SYS 5V power output 3 GPIO3_C6 SDMMC2_D0_M0 I2S1_MCLK_M1 1.8V level 4 GPIO3_C7 SDMMC2_D1_M0 I2S1_SCLK_TX_M1 1.8V level 5 GND 6 GND 7 GPIO3_D0 SDMMC2_D2_M0 I2S1_LRCK_TX_M1 1.8V level 8 GPIO3_D3 SDMMC2_CLK_M0 I2S1_SDI1_M1 1.8V level 9 GND 10 GND 11 GPIO3_D1 SDMMC2_D3_M0 I2S1_SDO0_M1 1.8V level 12 GPIO3_D2 SDMMC2_CMD_M0 I2S1_SDI0_M1 1.8V level 13 GND 14 GND 15 GPIO3_D5 SDMMC2_PWREN_M0 I2S1_SDI3_M1 1.8V level 16 GPIO3_D4 SDMMC2_DET_M0 I2S1_SDI2_M1 1.8V level
- Debug UART Pin Spec
- 3.3V level signals, 1500000bps
Pin# Assignment Description 1 GND 0V 2 UART2DBG_TX output 3 UART2DBG_RX intput
- USB Port
- Each USB 3.2 Gen 1 port has 1.4A overcurrent protection.
- RTC
- RTC backup current is 0.25μA TYP (VDD =3.0V, TA =25℃).
- Connector P/N: Molex 53398-0271
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi-R5S get the following items ready
- NanoPi-R5S
- MicroSD Card/TF Card: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- USB C PD Charger (10W & above)
- If you need to develop and compile,you need a computer that can connect to the Internet. It is recommended to install Ubuntu 20.04 64-bit system and use the following script to initialize the development environment, or use docker container:
4.2 TF Cards We Tested
Refer to: TFCardsWeTested
4.3 PD Power Adapters We Tested
Refer to: PD Power Adapters We Tested
4.4 Configure parameters for serial port
Use the following serial parameters:
| Baud rate | 1500000 |
| Data bit | 8 |
| Parity check | None |
| Stop bit | 1 |
| Flow control | None |
4.5 Install OS
4.5.1 Downloads
4.5.1.1 Official image
Visit download link to download official image files (in the "01_Official images" directory).
The table below lists all official images, the word 'XYZ' in image filename meaning:
- sd: Use it when you need to boot the entire OS from the SD card
- eflasher: Use it when you need to flash the OS to eMMC via TF card
- usb: Use it when you need to flash the OS to eMMC via USB
| Icon | Image Filename | Version | Description | Kernel Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
rk3568-XYZ-debian-bookworm-core-6.1-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | bookworm | Debian 11 Core, command line only | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-debian-bullseye-minimal-6.1-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | bullseye | Debian 11 Desktop, LXDE desktop, no pre-installed recommended software, supports hardware acceleration | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-debian-bullseye-desktop-6.1-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | bullseye | Debian 11 Desktop, LXDE desktop, pre-installed mpv, smplayer and chromium brower, supports hardware acceleration | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-ubuntu-focal-desktop-6.1-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | focal | Ubuntu 20.04 Desktop, LXQT desktop, pre-installed mpv, smplayer and chromium brower, supports hardware acceleration | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-friendlycore-focal-6.1-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | focal | FriendlyCore,command line only, pre-installed Qt5, based on Ubuntu core 20.04 | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-androidtv-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | 12 | Android 12 TV | 5.10.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-android12-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | 12 | Android 12 Tablet | 5.10.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-openmediavault-6.1-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | Shaitan | OpenMediaVault NAS system, base on Debian 12 | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-proxmox-6.1-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | 8.2.7 | Proxmox VE OS (Preview), base on Debian 12 | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-friendlywrt-24.10-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | 24.10 | FriendlyWrt, based on OpenWrt 24.10 | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-friendlywrt-24.10-docker-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | 24.10 | FriendlyWrt with Docker, based on OpenWrt 24.10 | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-friendlywrt-23.05-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | 23.05 | FriendlyWrt, based on OpenWrt 23.05 | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-XYZ-friendlywrt-23.05-docker-YYYYMMDD.img.gz | 23.05 | FriendlyWrt with Docker, based on OpenWrt 23.05 | 6.1.y |
| Other Image | ||||
| |
FriendlyWrt (Github Actions) | 24.10,23.05 | FriendlyWrt | 6.1.y |
| |
Alpine-Linux (Github Actions) | - | Alpine-Linux | 6.1.y |
| |
rk3568-eflasher-multiple-os-YYYYMMDD-25g.img.gz | - | It contains multiple OS image files, making it convenient for testing different operating systems, this image disables automatic flashing at startup; you will need to manually select the OS to flash. | |
4.5.1.2 Tools (optional)
Visit download link to download tools (in the "05_Tools" directory).
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| win32diskimager.rar | This program is designed to write a raw disk image to a removable device or backup a removable device to a raw image file |
| SD Card Formatter | A program (application) that allows easy and quick clear the SD card |
| RKDevTool_Release_v2.84.zip | Rockchip flashing tool, for USB upgrade |
4.5.2 Flashing the OS to the microSD card
Follow the steps below:
- Get an 8G microSD card;
- Visit download linkto download image files (in the "01_Official images/01_SD card images" directory);
- Download the win32diskimager tool (in the "05_Tools" directory), or use your preferred tool;
- Extract the .gz format compressed file to get the .img format image file;
- Run the win32diskimager utility under Windows as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Take out the SD and insert it to NanoPi-R5S's microSD card slot;
- Power on NanoPi-R5S and it will be booted from your TF card, some models may require pressing the Power button to start;
4.5.3 Install OS to eMMC
4.5.3.1 Option 1: Install OS via TF Card
This method firstly boots a mini Linux from a TF card and then automatically runs an EFlasher utility to install the OS to eMMC. You can connect your system to an HDMI monitor and watch its progress.
This is optional. You can watch its progress by observing its LEDs as well:
Progress |
SYS LED(Red) |
LAN LED(Green) |
WAN LED(Green) |
|---|---|---|---|
Power On |
Solid On |
Off |
Off |
System Boot |
Slow Flashing |
Off |
Off |
Installation in Progress |
Fast Flashing |
Off |
Off |
Installation Done |
Slow Flashing |
Solid On |
Solid On |
By default, flashing starts automatically upon power-up, so be sure to back up the data in eMMC. If you don't want it to start automatically, you can use image file with a filename containing the words 'multiple-os' and manually select the OS you want to flash on the interface.
4.5.3.1.1 Flash Official OS to eMMC
Follow the steps below:
- Get an SDHC card with a minimum capacity of 8G
- Visit download linkto download image files (in the "01_Official images/02_SD-to-eMMC images" directory) and win32diskimager tool (in the "05_Tools" directory);
- Extract the .gz format compressed file to get the .img format image file;
- Run the win32diskimager utility under Windows as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Eject your SD card and insert it to NanoPi-R5S’s microSD card slot.
- Turn on NanoPi-R5S, it will boot from the SD card and automatically run EFlasher to install the OS to the board’s eMMC.
- After flashing is complete, eject the SD card from NanoPi-R5S, NanoPi-R5S will automatically reboot and boot from eMMC.
4.5.3.1.2 Flash third party OS (Image file) to eMMC
- Auto Install (Default Behavior)
1) Download an “eflasher” firmware from network drive(in the "01_Official images/02_SD-to-eMMC images" directory), extract it and install it to a TF card ;
2) Eject and insert the TF card to your PC, after a “FriendlyARM” device shows up(Under Linux, it is a “FriendlyARM” directory), copy the image file ending with .raw or .gz into the directory (Note: if your file is in .img format, please rename it to .raw format).
3) Open the eflasher.conf file on the TF card, set “autoStart=” to the name of your image file, such as:
autoStart=openwrt-rockchip-armv8_nanopi-ext4-sysupgrade.img.gzIn addition to third-party image, official image files which with the '-sd-' word in the filename are also supported, for example: rk3NNN-sd-friendlywrt-24.10-YYYYMMDD.img.gz
4) Eject the TF card, insert the TF card to NanoPi-R5S, power it on it will automatically install your firmware. You can watch the installation progress by observing the LEDs’ status.
4.5.3.2 Option 2: Install OS on Web Page
Get a TF card which has been installed with FriendlyWrt, log in FriendlyWrt on the web page, click on “System” ->”eMMC Tools”. Click on “Select file” to select your wanted image file, either an official image (filename containing '-sd-') or a third party image. The file should be a “.gz” or “.img” file.
After a file is selected, click on “Upload and Write” to start installing an OS.
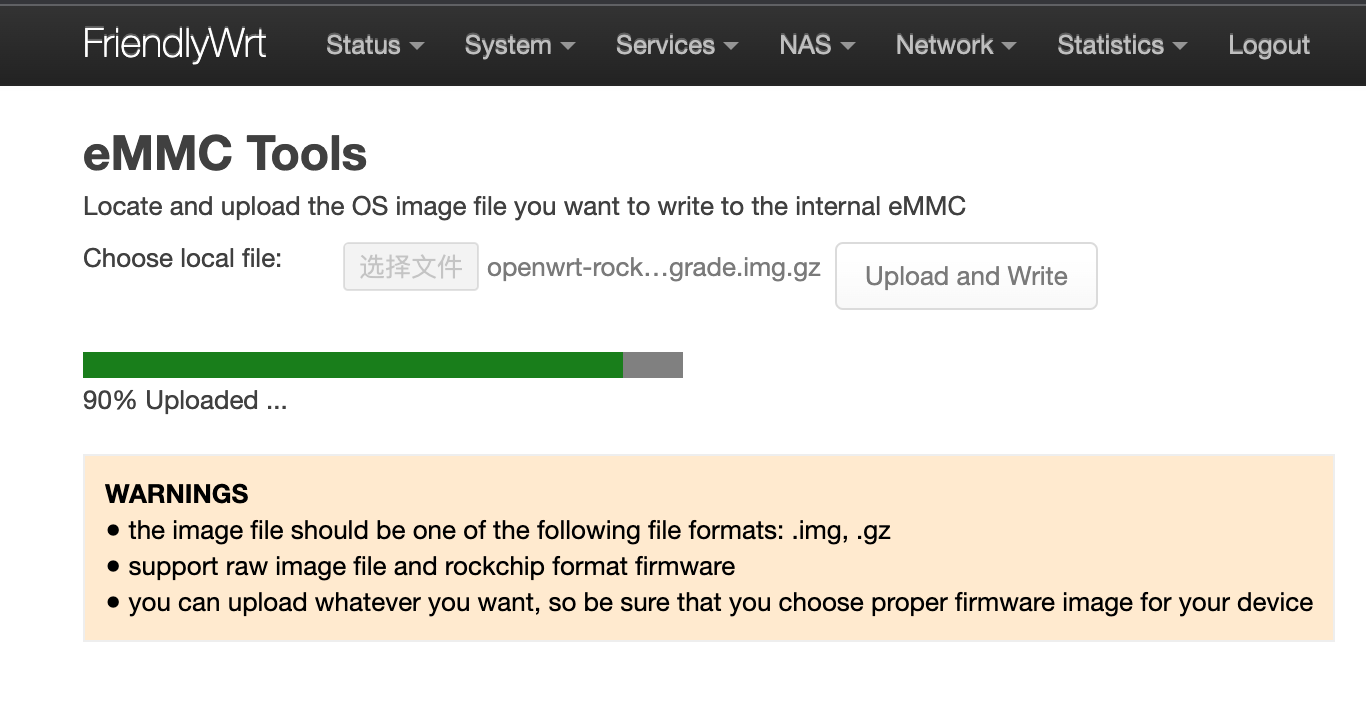
After installation is done, eject the SD card, the system will automatically reboot and load the OS from eMMC. After the OS begins to load, if the system LED is flashing and the network LED is on, it means the the OS has loaded successfully. If the OS is FriendlyWrt, you can click on “Go to Homepage” to enter the homepage.
For official OS, you need select the file with the filename containing '-sd-', for example: rk3NNN-sd-friendlywrt-24.10-YYYYMMDD.img.gz, the compression file only supports the .gz format. If the file is too large, you can compress it into .gz format before uploading.
4.5.3.3 Option 3: Install OS via USB
4.5.3.3.1 Step 1: Install USB Driver and Tools/Utilities
Download a driver file DriverAssitant_v5.12.zip under the “tools” directory from network drive, extract and install it.
Under the same directory, download a utility RKDevTool_Release_v2.84.zip and extract it.
4.5.3.3.2 Step 2: Connect NanoPi-R5S to PC and Enter Installation Mode
1) Press and hold the “Mask” key, power on the board. After the status LED has been on for at least 3 seconds, release the Mask key;
2) Use a USB A-to-A cable, connect NanoPi-R5S to a PC as follows;
4.5.3.3.3 Step 3: Install image to eMMC
A firmware in general is packaged in either of the two options: the first is an whole image (ie, update.img) which is often offered by third party developers, the second is that an image is packaged and placed in multiple partition images. FriendlyElec offers an image in the latter option.
- Option 1: Install whole image (ie, update.img)
On a PC which has the extracted RKDevTool_Release_v2.84 utility, go to the RKDevTool_Release_v2.84 directory, run the RKDevTool.exe file. If everything works, you will see a “Found a new Maskrom device” message on the utility;
Go to “Upgrade Firmware(升级固件)”, click on “Firmware(固件)”, select your wanted image file, and click on “Upgrade(升级)” to install. After installation is done, your board will reboot automatically and load the system from eMMC;
- Option 2: Install OS that is packaged & placed in multiple partition images
Go to network drive to download your needed package and extract it (in the "01_Official images/03_USB upgrade images).
After it is extracted, you will see some utilities and a configuration file under the directory. double click on RKDevTool.exe, you will see a “Found a new Maskrom device” message on the utility. Click on the “Execute”, wait a moment and it will be installed. After installation is done your system will automatically reboot and load the system from eMMC.
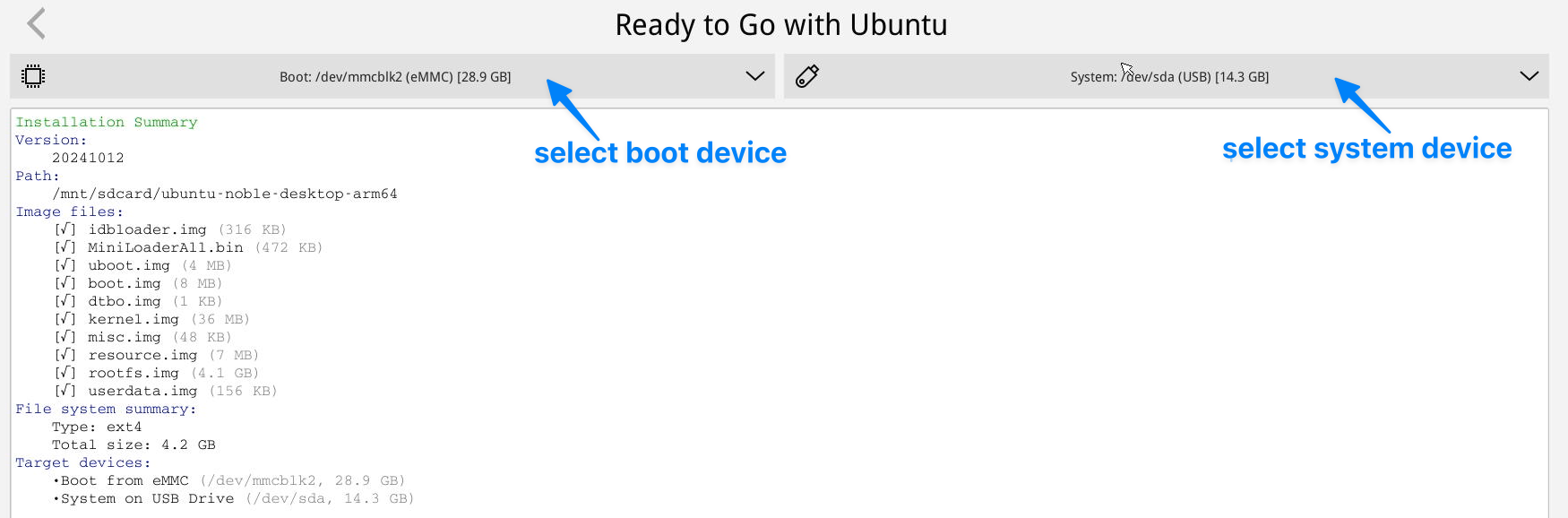
4.5.4 Installing the System to M.2 or USB Drive
You can use a TF card to boot the eFlasher system, allowing the boot and system to be installed on different storage devices. However, since the CPU doesn’t support booting directly from M.2 and USB devices, the system can be installed on M.2 and USB devices, but the boot must still be installed on eMMC or a TF card.
Steps are as follows:
- Prepare a TF card with a capacity of 32GB or larger.
- Visit [the download link here](http://download.friendlyelec.com/NanoPiR5S) to download the firmware file named XXXX-eflasher-multiple-os-YYYYMMDD-30g.img.gz (located in the “01_Official images/02_SD-to-eMMC images” directory).
- Flash the firmware to the TF card, connect the storage device you intend to use on NanoPi-R5S, insert the TF card and power on, we need to perform the operations in the eFlasher GUI. If your NanoPi-R5S does not have a display interface, you can use VNC; refer to Using VNC to Operate eFlasher.
- In the eFlasher GUI, select the OS to install, and in the OS settings interface, choose the destination for boot installation (typically eMMC), then choose the destination for system installation (options include eMMC, M.2 hard drive, USB storage, etc.), as shown below:
- If no eMMC is available, the TF card can serve as the boot by inserting another TF card into the USB port via a USB card reader and selecting it as the boot destination, enabling booting from the TF card with the system stored on the M.2 or USB drive.
- After flashing, eject the SD card from NanoPi-R5S. If booting from eMMC, NanoPi-R5S will automatically restart into the newly flashed system. If boot installation is on a TF card, power off, insert the boot TF card, and power on again.
- For a more detailed installation guide, please refer to this link.
5 Work with FriendlyWrt
5.1 Introduction to FriendlyWrt
FriendlyWrt is a customized system made by FriendlyElec based on an OpenWrt distribution. It is open source and well suitable for developing IoT applications, NAS applications etc.
5.2 First boot
For the first boot, the system needs to do the following initialization work:
1)Extended root file system
2)Initial setup(will execute /root/setup.sh)
So you need to wait for a while (about 2~3 minutes) to boot up for the first time, and then set FriendlyWrt, you can enter the ttyd terminal on the openwrt webpage, when the prompt is displayed as root@FriendlyWrt, it means the system has been initialized.
root@FriendlyWrt
5.3 Account & Password
The default password is password (empty password in some versions). Please set or change a safer password for web login and ssh login. It is recommended to complete this setting before connecting NanoPi-R5S to the Internet.
5.4 Login FriendlyWrt
Connect the PC to the LAN port of NanoPi-R5S. If your PC without a built-in ethernet port, connect the LAN port of the wireless AP to the LAN port of NanoPi-R5S, and then connect your PC to the wireless AP via WiFi , Enter the following URL on your PC's browser to access the admin page:
- http://friendlywrt/
- http://192.168.2.1/
- http://[fd00:ab:cd::1]
The above is the LAN port address of NanoPi-R5S. The IP address of the WAN port will be dynamically obtained from your main router through DHCP.
5.5 Recommended security settings
The following settings are highly recommended to complete before connecting NanoPi-R5S to the Internet。
- Set a secure password
- Only allow access to ssh from lan, change the port
- Check the firewall settings
Set up as you wish.
5.6 Change LAN IP in LuCI
1) Click on Network → Interfaces, then click on the Edit button of the LAN Network;
2) In General Setup tab, input new IP address (for example: 192.168.11.1), click "Save" and then click "Save & Apply";
3) On the pop-up window with the title “Connectivity change“, click "Apply and revert on connectivity loss";
4) Wait a moment, enter the new address in your computer's browser and login to FriendlyWrt;
5.7 Safe shutdown operation
Enter the "Services" -> "Terminal", enter the "poweroff" command and hit enter, wait until the led light is off, and then unplug the power supply.
5.8 Soft Factory Reset
Enter "System"->"Backup/Flash firmware",Click “Perform reset“ Button, Your device's settings will be reset to defaults like when FriendlyWrt was first installed.
You can also do this in the terminal:
firstboot && reboot5.9 Install Software Packages
5.9.1 Set up openwrt official opkg source
sed -i -e 's/mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/downloads.openwrt.org/g' /etc/opkg/distfeeds.conf opkg update
5.9.2 Update Package List
Before install software packages update the package list:
$ opkg update
5.9.3 List Available Packages
$ opkg list
5.9.4 List Installed Packages
$ opkg list-installed
5.9.5 Install Packages
$ opkg install <package names>
5.9.6 Remove Packages
$ opkg remove <package names>
5.10 Disable IPv6
. /root/setup.sh disable_ipv6 reboot
5.11 Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking
- Go to "Network" -> "Interfaces"
- Click "Delete" next to "WAN6", then click "Save & Apply"
- Click "Edit" next to "WAN", in the "Device" drop-down menu, select "Ethernet Adapter: wwan0", in the "Protocol" drop-down menu, select "QMI Cellular" and click "Switch Protocol"
- Click the "Modem Device" drop-down menu, select "/dev/cdc-wdm0", fill in the APN information (e.g. for China Mobile, enter "cmnet")
- Click "Save" to close the dialog, Finally, click "Save & Apply" at the bottom of the page to initiate the dial-up process
- Devices connected to LAN will have access to the Internet, If your device has a WiFi module, you can enable wireless AP functionality on the "Wireless" page and connect to the Internet via devices connected wirelessly
5.12 Some common issues of FriendlyWrt
- Unable to dial up
- Go to "Network" -> "Firewall" and set "Inbound Data", "Outbound Data" and "Forwarding" in "WAN Zone" to "Accept";
- If you still cannot access the Internet, you can try to turn off IPV6;
- Dial-up successful, but no outgoing traffic
- Go to "Services" -> "Terminal" and type "fw4 reload" to try to reload the firewall settings again;
- Unable to power on
- Try to replace the power adapter and cable. It is recommended to use a power supply with specifications above 5V/2A;
- Note that some fast chargers with Type-C interface will have a delay, it may take a few seconds to start providing power;
- When doing secondary routing, the computer cannot connect to the Internet
- If your main network is IPv4, and NanoPi-R5S works in IPv6, the computer may not be able to connect to the Internet. It is recommended to turn off IPv6 (the method is described later in this WiKi), or switch the main route to IPv6;
- If you have questions or have better suggestions, please send an email to techsupport@friendlyarm.com;
5.13 Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature
Plug the USB2LCD module to the USB interface ofNanoPi-R5S and power on, the IP address and CPU temperature will be displayed on the LCD:

5.14 How to use USB WiFi
5.14.1 Check USB WiFi Device with Command Line Utility
(1) Click on "services>ttyd" to start the command line utility
(2) Make sure no USB devices are connected to your board and run the following command to check if any USB devices are connected or not
lsusb
(3) Connect a USB WiFi device to the board and run the command again
lsusb
You will see a new device is detected. In our test the device's ID was 0BDA:C811
(4) Type your device's ID (in our case it was "0BDA:C811" or "VID_0BDA&PID_C811") in a search engine and you may find a device that matches the ID. In our case the device we got was Realtek 8811CU.
5.14.2 Configure a USB WiFi Device as AP
(1) Connect a USB WiFi device to the NanoPi-R5S. We recommend you to use the following devices:
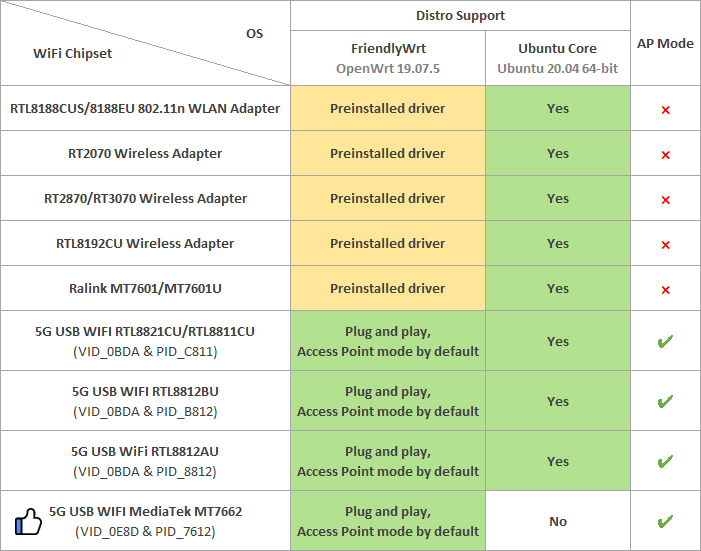
Note: devices that match these VID&PIDs would most likely work.
(2) Click on "System>Reboot" and reboot your NanoPi-R5S
(3) Click on "Network>Wireless" to enter the WiFi configuration page
(4) Click on "Edit" to edit the configuration
(5) On the "Interface Configuration" page you can set the WiFi mode and SSID, and then go to "Wireless Security" to change the password. By default the password is "password". After you make your changes click on "Save" to save
(6) After you change the settings you can use a smartphone or PC to search for WiFi
5.14.3 Common USB WiFi issues
1) It is recommended to plug in the usb wifi in the off state, then power it on, FriendlyWrt will automatically generate the configuration file /etc/config/wireless, if not, see if there is wlan0 by ifconfig -a, if there is no wlan0, usually there is no driver.
2) If ifconfig -a sees wlan0, but the hotspot is not working properly, try changing the channel and country code, an inappropriate country code can also cause the WiFi to not work.
3) Some USB WiFis (e.g. MTK MT7662) work in CD-ROM mode by default and need to be switched by usb_modeswitch, you can try to add usb_modeswitch configuration to the following directory: /etc/usb_modeswitch.d.
5.14.4 Change the default WiFi hotspot configuration
FriendlyWrt sets the country, hotspot name and other parameters for USB WiFi by default, with the aim of being as plug-and-play as possible, but this does not guarantee that all modules will be compatible with this setting, you can change these behaviors by modifying the following file:
/lib/wifi/mac80211.sh
5.15 Work with Docker Applications
5.15.1 Work with Docker: Install JellyFin
mkdir -p /jellyfin/config mkdir -p /jellyfin/videos docker run --restart=always -d -p 8096:8096 -v /jellyfin/config:/config -v /jellyfin/videos:/videos jellyfin/jellyfin:10.1.0-arm64 -name myjellyfin
After installation, visit port 8096 and here is what you would find:
5.15.2 Work with Docker: Install Personal Nextcloud
mkdir /nextcloud -p docker run -d -p 8888:80 --name nextcloud -v /nextcloud/:/var/www/html/ --restart=always --privileged=true arm64v8/nextcloud
After installtion, visit port 8888.
5.15.3 Expand Docker Storage
- Stop docker service first:
/etc/init.d/dockerd stop
- Rename the original /opt directory, create an empty /opt directory:
mv /opt /opt-old && mkdir /opt
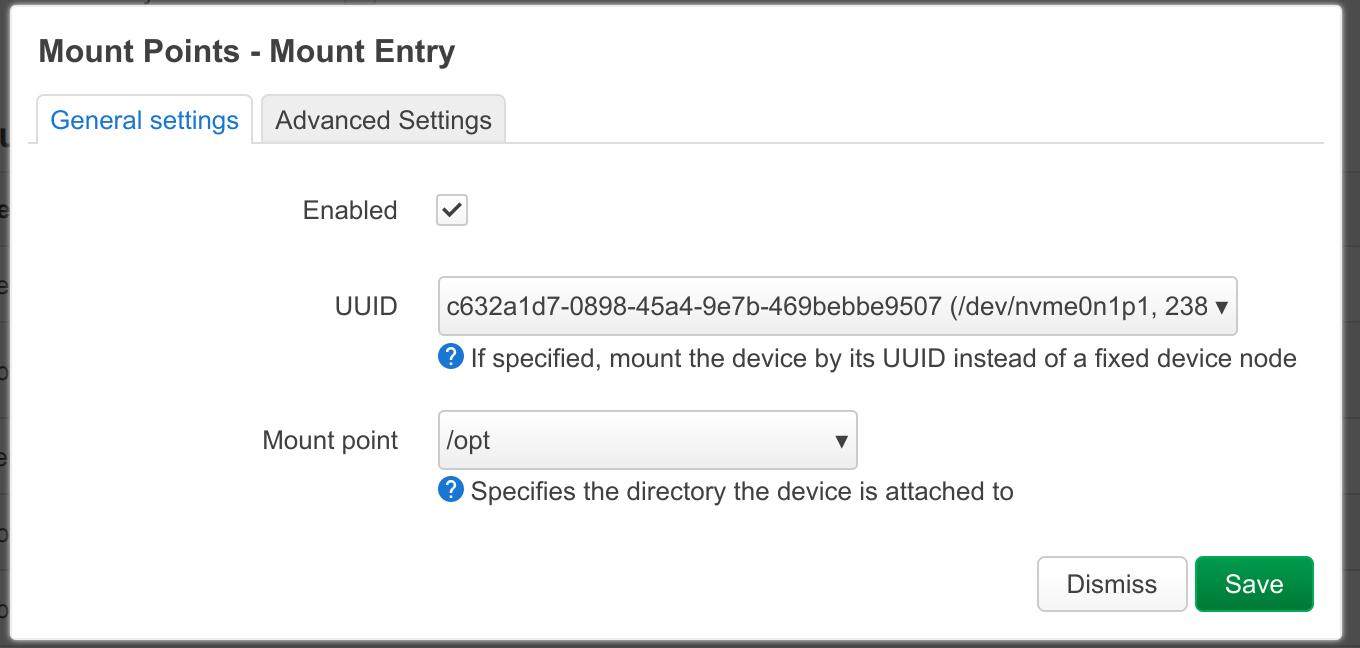
- Format your drive as ext4, and mount it to the /opt directory:
- Enter the command "mount | grep /opt" to check the mount status:
root@FriendlyWrt:~# mount | grep /opt /dev/nvme0n1p1 on /opt type ext4 (rw,relatime) root@FriendlyWrt:~#
- Copy the files from the original /opt directory to the new /opt directory:
cp -af /opt-old/* /opt/ && rm -rf /opt-old
- Reboot the device
reboot
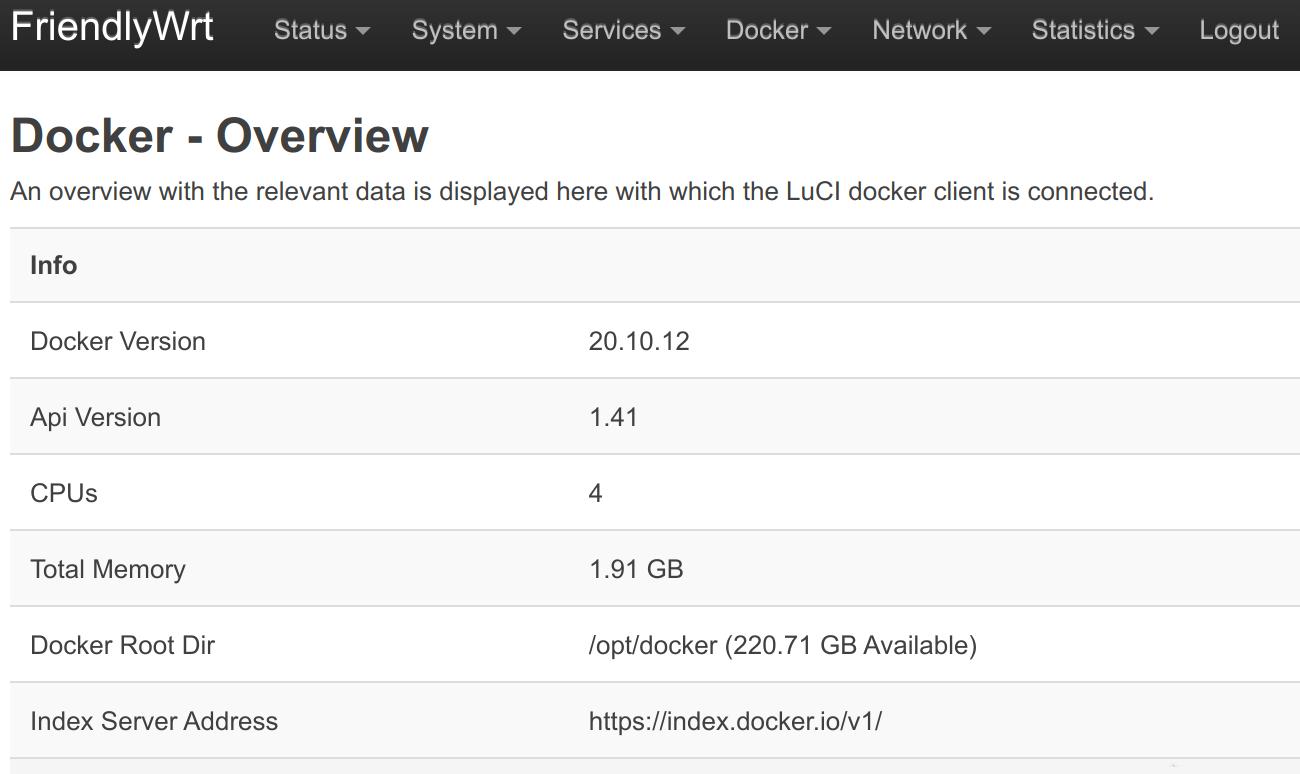
- After reboot, go to the "Docker" -> "Overview" page, check the information in the "Docker Root Dir" line, you can see that the Docker space has been expanded:
5.15.4 Docker FAQ and solutions
5.15.4.1 Unable to access the network services provided by the Docker container
Solution:
- Go to the "Firewall" settings and set "Forwarding" to "Accept";
- Turn off "Software Offload";
5.16 Mount smbfs
mount -t cifs //192.168.1.10/shared /movie -o username=xxx,password=yyy,file_mode=0644
5.17 Use sdk to compile the package
5.17.1 Install the compilation environment
Download and run the following script on 64-bit Ubuntu (version 18.04+): How to setup the Compiling Environment on Ubuntu bionic
5.17.2 Download and decompress sdk from the network disk
The sdk is located in the toolchain directory of the network disk:
tar xvf openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64.tar.xz # If the path is too long, it will cause some package compilation errors, so change the directory name here mv openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64 sdk cd sdk ./scripts/feeds update -a ./scripts/feeds install -a
5.17.3 Compile the package
download the source code of the example (a total of 3 examples are example1, example2, example3), and copy to the package directory:
git clone https://github.com/mwarning/openwrt-examples.git cp -rf openwrt-examples/example* package/ rm -rf openwrt-examples/
Then enter the configuration menu through the following command:
make menuconfigIn the menu, select the following packages we want to compile (actually selected by default):
"Utilities" => "example1" "Utilities" => "example3" "Network" => "VPN" => "example2"
execute the following commands to compile the three software packages:
make package/example1/compile V=99 make package/example2/compile V=99 make package/example3/compile V=99
After the compilation is successful, you can find the ipk file in the bin directory, as shown below:
$ find ./bin -name example*.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk
5.17.4 Install the ipk to NanoPi
You can use the scp command to upload the ipk file to NanoPi:
cd ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/ scp example*.ipk root@192.168.2.1:/root/
Then use the opkg command to install them:
cd /root/ opkg install example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk opkg install example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk opkg install example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk
5.18 Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions
Please refre this link: https://github.com/friendlyarm/Actions-FriendlyWrt
6 Work with FriendlyCore
6.1 FriendlyCore User Account
- Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
- Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
6.2 Update Software Packages
$ sudo apt-get update
6.3 Setup Network Configurations
6.3.1 Set static IP address
By default "eth0" is assigned an IP address obtained via dhcp. If you want to change the setting you need to change the following file:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0
For example if you want to assign a static IP to it you can run the following commands:
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.1.231
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1The other two ethernet ports are set up with static IP addresses, as follows:
eth1: 192.168.2.1
eth2: 192.168.3.1 (Note: if there are three network ports)
6.3.2 Set a DNS
You also need to modify the following file to add the DNS configuration:
vi /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
For example, set to 192.168.1.1:
[Resolve] DNS=192.168.1.1
Restart the systemd-resolved service with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved.service sudo systemctl enable systemd-resolved.service
6.3.3 Set up to use another network interface
To change the setting of "eth1" you can add a new file similar to eth0's configuration file under the /etc/network/interfaces.d/ directory.
6.4 Setup Wi-Fi
First, use the following command to check if Network-Manager is installed on your system:
which nmcliIf you have installed it, refer to this link to connect to WiFi: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings, If you do not have Network-Manager installed on your system, please refer to the following method to configure WiFi,
By default the WiFi device is "wlan0". You need to create a configuration file under "/etc/network/interfaces.d/" for WiFi:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/wlan0
Here is a sample wlan0 file:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet dhcp
wpa-driver wext
wpa-ssid YourWiFiESSID
wpa-ap-scan 1
wpa-proto RSN
wpa-pairwise CCMP
wpa-group CCMP
wpa-key-mgmt WPA-PSK
wpa-psk YourWiFiPasswordPlease replace "YourWiFiESSID" and "YourWiFiPassword" with your WiFiESSID and password. After save and close the file you can connect to your WiFi source by running the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart networking
After you power on your board it will automatically connect to your WiFi source.
Please note that if you use one TF card to boot multiple boards the WiFi device name will likely be named to "wlan1", "wlan2" and etc. You can reset it to "wlan0" by deleting the contents of the following file and reboot your board:
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
6.4.1 WiFi models supported
6.4.1.1 M.2 WiFi Module
- RTL8822CE
6.4.1.2 Usb Dongle
- RTL8821CU (Vid: 0BDA, Pid: C811) (Test sample:TP-Link TL-WDN5200H)
- RTL8812AU (Vid: 0BDA, Pid: 8812)
- MediaTek MT7662 (Vid: 0E8D, Pid: 7612) (Test sample:COMFAST CF-WU782AC V2)
6.5 Install the kernel-header package
sudo dpkg -i /opt/archives/linux-headers-*.deb
6.6 Config status LEDs
First determine whether the system already exists the leds initialization service:
sudo systemctl status ledsIf the leds service already exists, change the default behavior of the LEDs by editing the following file:
/etc/init.d/leds.sh
Since there is no leds service in the early firmware, you need to refer to the following guide to manually configure the LEDs. First, set the following kernel modules to be automatically loaded at boot:
modprobe ledtrig-netdev echo ledtrig-netdev > /etc/modules-load.d/ledtrig-netdev.conf
Put the following into the autorun script to associate the status leds with the ethernet interface, and you can configure it to behave in other ways by referring to these content:
echo netdev > /sys/class/leds/wan_led/trigger echo eth0 > /sys/class/leds/wan_led/device_name echo 1 > /sys/class/leds/wan_led/link echo netdev > /sys/class/leds/lan1_led/trigger echo eth1 > /sys/class/leds/lan1_led/device_name echo 1 > /sys/class/leds/lan1_led/link echo netdev > /sys/class/leds/lan2_led/trigger echo eth2 > /sys/class/leds/lan2_led/device_name echo 1 > /sys/class/leds/lan2_led/link
Execute the following commands:
su root cd / rm -rf usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-5.10.0-rk64one usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-5.10.0-rk64one-sdk usr/bin/setqt5env* usr/bin/qt5demo etc/qt5 rm -rf opt/{qt5-browser,Qt5_CinematicExperience,qt5-multi-screen-demo,qt5-nmapper,qt5-player,qt5-smarthome,QtE-Demo,qt5-qml-image-viewer,dual-camera}
7 Work with Android
Android include the following features:
- There are two versions, TV and Tablet;
- Support infrared remote control (only for models with Ir Receiver);
- Support Bluetooth remote control (requires USB or M.2 Bluetooth module);
- Support wired network;
- Support WiFi (requires external USB or M.2 WIFI module);
- Support video hard decoding;
7.1 WiFi models supported by Android
7.1.1 M.2 WiFi Module
- RTL8822CE
7.1.1.1 Usb Dongle
- RTL8821CU (Vid: 0BDA, Pid: C811) (Test sample:TP-Link TL-WDN5200H)
- RTL8812AU (Vid: 0BDA, Pid: 8812)
- MediaTek MT7662 (Vid: 0E8D, Pid: 7612) (Test sample:COMFAST CF-WU782AC V2)
7.2 Bluetooch models supported by Android
7.2.1 Bluetooth Adapters
- RTL8822CE
- RTL8761B
- CSR8510 A10 Bluetooth Dongle 0a12:0001
(Note: unsupported device ID 0x2B89:0x8761)
7.2.2 Bluetooth Remote
- Amazon Fire TV Remote
7.3 How to use ADB
7.3.1 USB connection
Please note: After turning on the ADB, the USB3 port will work in Device mode, if you need to connect a device such as a USB stick, you need to turn off the ADB and restart the board
In general, ADB is disabled by default, please follow the steps below to enable it:
- Connect your development board to your computer using a USB A-to-A data cable, referring to the figure below, be sure to connect it to the USB port closest to the edge:
7.3.2 For Android Tablet
- Go to Settings -> About tablet -> tap the "Build number" at the bottom of the screen 7 times in a row;
- Go to Settings -> System -> Advance -> Developer options, check USB-Debugging, and then reboot;
- To use ADB over the network, you need to connect to WiFi first, then enable Wireless debugging. In the prompt "Allow wireless debugging on the network", select "Always allow on this network", and then click "Allow".
7.3.3 For Android TV
- Click the Settings icon -> Device Preferences -> About -> tap the "Android TV OS build" at the bottom of the screen 7 times in a row;
- Click the Settings icon -> Device Preferences -> Developer options, check USB-Debugging, and then reboot;
- To use ADB over the network, on Android TV, which supports both WiFi and wired networks, enable network ADB by checking "Internet ADB" on the "Developer options" UI.
7.3.4 Using ADB
- Install ADB drivers and commands based on your operating system;
- Normally, the Android status bar will prompt "USB debugging connected", indicating that ADB has been enabled. Enter the following command on your computer to check the connection:
$ adb devices List of devices attached 27f7a63caa3faf16 device
- Enter adb shell:
$ adb shell
nanopi3:/ $7.3.5 Using ADB over the network
- On an Android Tablet, go to Settings -> System -> Advance -> Developer options, then click on Wireless debugging to view the IP address and port.
- The default network ADB port for Android TV is 5555.
Assuming the IP address and port displayed on the Wireless debugging interface are 192.168.1.167:45055, the ADB commands are as follows:
- To connect to the device:
$ adb connect 192.168.1.167:45055
connected to 192.168.1.167:45055
- To enter ADB shell:
$ adb shell
nanopi3:/ $If there are multiple devices, use the -s parameter to specify the device's IP and port, as shown below:
$ adb -s 192.168.1.167:45055 shell nanopi3:/ $
7.4 How to Change Default Launcher in Android TV
- Refer to the previous section to enable adb
- For example, install the third-party launcher Emotn UI via APK, visit the website https://app.emotn.com/ui/ to download the APK, and then install it using ADB:
$ adb install com.oversea.aslauncher_1.0.9.0_5094.apk
Performing Streamed Install
Success- After the installation is complete, launch it, and then enter the following ADB command to obtain its package name:
$ adb shell dumpsys window | grep mCurrentFocus mCurrentFocus=Window{7a950fb u0 com.oversea.aslauncher/com.oversea.aslauncher.ui.main.MainActivity}
- As you can see, the package name of Emotn UI is com.oversea.aslauncher, set it as the default launcher:
$ adb shell pm set-home-activity com.oversea.aslauncher Success
- Then comes the critical step, you need to disable the native launcher using the following command:
$ adb shell pm disable-user --user 0 com.google.android.tvlauncher Package com.google.android.tvlauncher new state: disabled-user
- Finally, restart the device to see the effect, the device should boot directly into Emotn UI:
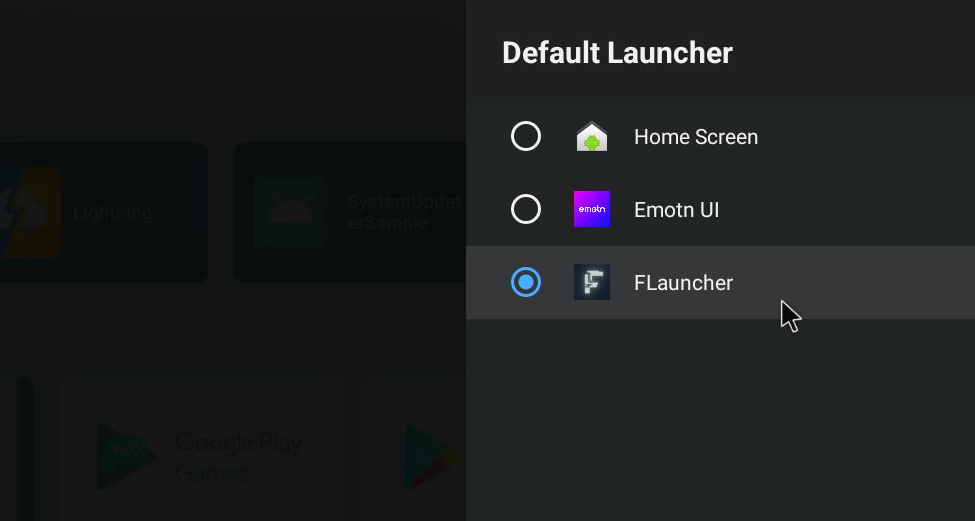
$ adb shell reboot- From now on, if you want to install another launcher, you can switch between them through the GUI. for example, after installing FLauncher, you can enter the following settings interface to set FLauncher as the default launcher: Settings -> Device Preferences -> Advanced setting -> Default Launcher:
7.5 Wired networks on Android
- Any network port can connect to the network via DHCP
- If you want to configure a static IP, only eth0 interface is supported
- Some applications may have compatibility issues and report no network connection error, but the network is actually connected
7.6 EC20 4G LTE module on Android
EC20 support is disabled by default, you can check the status with the following command, if the EC20 is disabled, the number 1 will be displayed:
su
getprop persist.vendor.radio.no_modem_boardTo enable EC20, use the following command (takes effect after a reboot):
su setprop persist.vendor.radio.no_modem_board 0
8 Work with Debian11 Desktop
8.1 Introduction to Debian11 Desktop
Debian11 Desktop is a light-weighted debian desktop system,it has the following features:
- Uses Xfce as default desktop;
- Mali GPU-based OpenGL support;
- Support Rockhip MPP video hard coding and hard decoding;
- Pre-installed mpv and smplayer, both support 4K video hardware decoding;
- Pre-installed Chromium browser, support vpu/gpu hardware acceleration (video hard decoding limited to h264/mp4 format);
- Compatible with Plex Server and Docker;
8.2 Account & Password
Regular Account:
User Name: pi
Password: pi
Root:
the root user account is disabled by default, you may configure the root password through the 'sudo passwd root' command.
8.3 View IP address
Since the Debian Bullseye hostname is the hardware model by default, you can use the ping command to get the IP address:ping NanoPi-R5S
8.4 Connect to Debian via SSH
Run the following commandssh pi@NanoPi-R5S
The default password is: pi
8.5 Update Software Packages
$ sudo apt-get update
8.6 Install x11vnc Server on Debian for Remote Access
8.6.1 Install x11vnc server
The following command to install x11vnc server:
sudo apt-get install x11vnc
8.6.2 Set your password
sudo x11vnc -storepasswd /etc/x11vnc.pwd
8.6.3 Setup x11vnc server with systemd auto start up
Create service configuration file:
sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/x11vnc.service
Let’s copy and paste the following configuration into our newly create service file:
[Unit] Description=Start x11vnc at startup. Requires=display-manager.service After=syslog.target network-online.target Wants=syslog.target network-online.target [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/bin/x11vnc -display :0 -forever -loop -noxdamage -repeat -rfbauth /etc/x11vnc.pwd -rfbport 5900 -shared -capslock -nomodtweak ExecStop=/usr/bin/x11vnc -R stop Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
The following commands to reload the systmd system and to enable and start the x11vnc service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable x11vnc.service sudo systemctl start x11vnc
8.6.4 Testing remote access
Start the VNC client software, input IP:5900 to connect:
8.7 Install the kernel-header package
sudo dpkg -i /opt/archives/linux-headers-*.deb
try to compile a kernel module:
sudo apt update sudo apt install git gcc make bc git clone https://github.com/RinCat/RTL88x2BU-Linux-Driver.git cd RTL88x2BU-Linux-Driver make -j$(nproc) sudo make install sudo modprobe 88x2bu
8.8 Change time zone
8.8.1 Check the current time zone
timedatectl
8.8.2 List all available time zones
timedatectl list-timezones
8.8.3 Set the time zone (e.g. Shanghai)
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
8.9 Change startup LOGO and Wallpaper
8.9.1 Change startup LOGO
Replace the following two files in the kernel source code directory and recompile the kernel:
kernel/logo.bmp
kernel/logo_kernel.bmp
Or use the script to operate, as shown below:
- Download scripts:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3568.git -b kernel-6.1.y --single-branch cd sd-fuse_rk3568
- Compile kernel and repackage firmware
convert files/logo.jpg -type truecolor /tmp/logo.bmp convert files/logo.jpg -type truecolor /tmp/logo_kernel.bmp sudo LOGO=/tmp/logo.bmp KERNEL_LOGO=/tmp/logo_kernel.bmp ./build-kernel.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 sudo ./mk-sd-image.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 sudo ./mk-emmc-image.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64
Note: If your system is not debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64, please specify according to the actual situation
8.9.2 Change Wallpaper
Modify the following configuration file:
/home/pi/.config/xfce4/xfconf/xfce-perchannel-xml/xfce4-desktop.xml
8.10 Soft Factory Reset
Execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo firstboot && sudo reboot
8.11 Start the program automatically at startup(For example Kodi)
Put the desktop file in the ~/.config/autostart/ directory, for example:
mkdir ~/.config/autostart/ cp /usr/share/applications/kodi.desktop ~/.config/autostart/
8.12 Disable auto-mounting
sudo systemctl mask udisks2 sudo reboot
8.13 Setup Chinese language and Input method
8.13.1 Setup Chinese language
Enter the following command and select 'zh_CN.UTF-8':
sudo dpkg-reconfigure localesAdd environment variables to .bashrc:
echo "export LC_ALL=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export LANGUAGE=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> ~/.bashrc
Reboot device:
sudo reboot8.13.2 Installing Chinese input method
Enter the following command to install fcitx and Pinyin input method:
sudo apt update sudo apt-get install fcitx fcitx-pinyin sudo apt-get install im-config sudo apt-get install fcitx-table* sudo apt-get install fcitx-ui-classic fcitx-ui-light sudo apt-get install fcitx-frontend-gtk2 fcitx-frontend-gtk3 fcitx-frontend-qt4 sudo apt-get remove --purge scim* ibus* sudo reboot
After reboot, press Ctrl+Space to switch between Chinese and English input methods, and the input method icon will appear in the upper right corner, right-click the input method icon in the upper right corner to switch input methods in the pop-up menu, as shown below:
8.14 Installing Plex Multimedia Server
Visit the Plex website: https://www.plex.tv/media-server-downloads/
On the download page, select the category "Plex Media Server", choose "Linux" for the platform and "Ubuntu(16.04+)/Debian(8+) - ARMv8" for the version,
After downloading the deb package, use the dpkg command to install the package:
sudo dpkg -i plexmediaserver_1.31.0.6654-02189b09f_arm64.deb
After installation, login to the Plex server by typing the following URL into your computer browser: http://IP地址:32400/web/
8.15 Install Docker on Debian
Please refer to: How to Install Docker on Debian
8.16 How to test NPU
Please refer to: NPU
8.17 How to test VPU
Please refer to: VPU
8.18 WiFi Connection
8.18.1 Gui
Click on the icon on the top right in the Debian's main window, select your wanted WiFi hotspot and proceed with prompts
8.18.2 Console
Please visit: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
8.19 Cancel auto-login
Edit file:
sudo vim /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf
Comment out the following two lines (insert # in front of them):
autologin-user=pi
autologin-user-timeout=08.20 Test OpenGL ES
You can test it by clicking on the Terminator icon to start a commandline utility in the System Tools and run the following commands:
glmark2-es2
8.21 HDMI/DP LCD Resolution
Open the system's menu and go to Settings -> Display to customize your settings.
8.22 HiDPI and display scaling
Xfce supports HiDPI scaling which can be enabled using the settings manager: Go to Settings Manager > Appearance > Settings > Window Scaling and select 2 as the scaling factor.
Or Edit this file: ~/.config/xfce4/xfconf/xfce-perchannel-xml/xsettings.xml
8.23 Adjust HDMI overscan
Open the command line terminal and enter the command to operate, Note:
1) You need to login to the desktop;
2) If you are using ssh terminal, please use the same username as the desktop login. The default is pi. You cannot use the root user. you also need to assign the DISPLAY variable:
export DISPLAY=:0.0
8.23.1 Query which resolutions the display supports
xrandr -q8.23.2 Set resolution
For example set to 1920X1080@60Hz:
xrandr --output HDMI-1 --mode 1920x1080 --refresh 60
8.23.3 Adjust the HDMI overscan
For example, the transformation scaling horizontal coordinates by 0.8, vertical coordinates by 1.04 and moving the screen by 35 pixels right and 19 pixels down:
xrandr --output HDMI-1 --transform 0.80,0,-35,0,1.04,-19,0,0,1
8.23.4 Automatic adjustment at boot
Edit ~/.config/autostart/lxrandr-autostart.desktop,Write the full xrandr command to the key at the beginning of "Exec= as shown below:
[Desktop Entry] Type=Application Name=LXRandR autostart Comment=Start xrandr with settings done in LXRandR Exec=sh -c 'xrandr --output HDMI-1 --mode 1920x1080 --refresh 50 --transform 1.04,0,-35,0,1.05,-30,0,0,1'
8.24 Chromium web browser
8.24.1 GPU
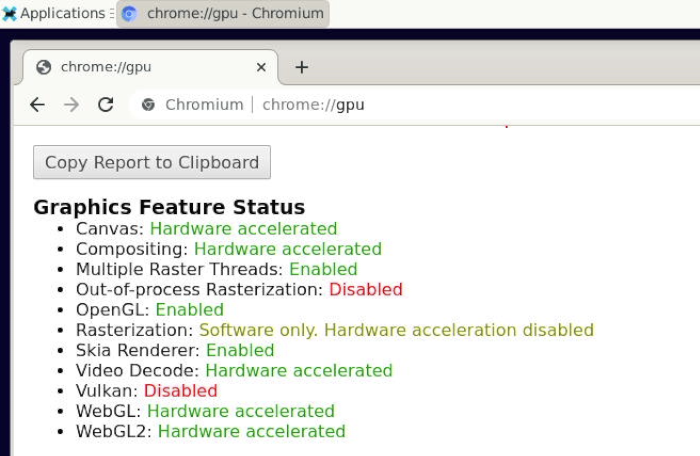
Chromium web browser has enabled hardware acceleration by default, supports WebGL, and can view hardware acceleration details by entering the URL chrome://gpu, as shown below:
8.24.2 VPU
Play a video in the browser, then use fuser on the command line to view the mpp device node to confirm that the vpu interface is being called:
pi@FriendlyElec:~$ fuser /dev/mpp_service /dev/mpp_service: 3258
If there is no content output from the fuser command, it means software decoding.
8.25 Test hardware encoding
mpi_enc_test -w 1920 -h 1080 -t 7 -f 0 -o test.h264 -n 300 export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/0 ffplay test.h264
8.25.1 Check Supported Hardware Decoding Formats
Enter about://gpu in your browser's address bar and scroll to the bottom of the page to view the "Video Acceleration Information" table.
After playing a video, enter about://media-internals in your browser's address bar to check if hardware decoding was enabled for the most recent playback.
9 Work with Debian10 Desktop
- Refer to:
10 Buildroot Linux
Buildroot is a simple, efficient and easy-to-use tool to generate embedded Linux systems through cross-compilation. It contains a boot-loader, kernel, rootfs, various libraries and utilities(e.g. qt, gstreamer, busybox etc).
FriendlyELEC's Buildroot is based on Rockchip's version which is made with linux-sdk and maintained with git. FriendlyELEC's version is synced with Rockchip's version;
- Rockchip's Buildroot: https://github.com/rockchip-linux/buildroot
- Buildroot's official site: https://buildroot.org
For a more detailed description of the Buildroot system, please refer to: Buildroot
11 How to Compile
11.1 Setup Development Environment
11.1.1 Method 1: Using docker to cross-compile
Please refre to docker-cross-compiler-novnc
11.1.2 Method 2: Setup build environment on the host machine
11.1.2.1 Install required packages
Install and run requirements ubuntu 20.04, install required packages using the following commands:
sudo apt-get -y update sudo apt-get install -y sudo curl sudo bash -c \ "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/build-env-on-ubuntu-bionic/master/install.sh)"
The following cross-compilers will be installed:
| Version | Architecture | Compiler path | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.9.3 | armhf | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 | Can be used to build 32-bit ARM applications |
| 6.4 | aarch64 | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/6.4-aarch64 | Can be used to build kernel 4.4 |
| 11.3 | aarch64 | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64 | Can be used to build kernel 4.19 or higher and U-Boot |
11.1.2.2 Setting the compiler path
Based on the table in the previous section, select the appropriate version of the compiler and add the compiler's path to PATH. For example, if you want to use the 11.3 cross-compiler, edit ~/.bashrc using vi and add the following content to the end:
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
Run the ~/.bashrc script to make it effective in the current commandline. Note: there is a space after ".":
. ~/.bashrcTo verify if the installation was successful:
$ aarch64-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=aarch64-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/libexec/gcc/aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu/11.3.0/lto-wrapper Target: aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu Configured with: /home/cross/arm64/src/gcc/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64 --exec_prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu/sysroot --enable-languages=c,c++ --enable-fix-cortex-a53-843419 --with-arch=armv8-a+crypto+crc --with-cpu=cortex-a53 --with-pkgversion=ctng-1.25.0-119g-FA --with-bugurl=http://www.friendlyelec.com/ --enable-objc-gc --enable-__cxa_atexit --disable-libmudflap --disable-libgomp --disable-libssp --disable-libquadmath --disable-libquadmath-support --disable-libsanitizer --disable-libmpx --with-gmp=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --with-mpfr=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --with-mpc=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --with-isl=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --enable-lto --enable-threads=posix --disable-libstdcxx-pch --enable-clocale=gnu --enable-libstdcxx-time=yes --with-default-libstdcxx-abi=new --enable-gnu-indirect-function --enable-gnu-unique-object --enable-default-pie --enable-linker-build-id --with-linker-hash-style=gnu --enable-plugin --enable-gold --with-libintl-prefix=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --disable-multilib --with-local-prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu/sysroot --enable-long-long --enable-checking=release --enable-link-serialization=2 Thread model: posix Supported LTO compression algorithms: zlib gcc version 11.3.0 (ctng-1.25.0-119g-FA)
11.2 Build Openwrt/Friendlywrt
11.2.1 Download Code
Two versions are available, please choose as required:
11.2.1.1 FriendlyWrt 24.10
mkdir friendlywrt24-rk3568 cd friendlywrt24-rk3568 git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --depth 1 tools tools/repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/friendlywrt_manifests -b master-v24.10 \ -m rk3568.xml --repo-url=https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --no-clone-bundle tools/repo sync -c --no-clone-bundle
11.2.1.2 FriendlyWrt 23.05
mkdir friendlywrt23-rk3568 cd friendlywrt23-rk3568 git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --depth 1 tools tools/repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/friendlywrt_manifests -b master-v23.05 \ -m rk3568.xml --repo-url=https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --no-clone-bundle tools/repo sync -c --no-clone-bundle
11.2.2 First compilation step
./build.sh rk3568.mk # or rk3568-docker.mk
All the components (including u-boot, kernel, and friendlywrt) are compiled and the sd card image will be generated, then execute the following command to generate the image file for installing the system into the emmc:
./build.sh emmc-imgAfter making changes to the project, the sd card image needs to be repackaged by running the following command:
./build.sh sd-img11.2.3 Secondary compilation steps
cd friendlywrt make menuconfig rm -rf ./tmp make -j${nproc} cd ../ ./build.sh sd-img ./build.sh emmc-img
11.2.4 Build u-boot only
./build.sh uboot11.2.5 Build kernel only
./build.sh kernel11.2.6 Build friendlywrt only
./build.sh friendlywrtOr go to the friendlywrt directory and follow the standard openwrt commands. If you get an error with the above command, try using the following command to compile in a single thread:
cd friendlywrt make -j1 V=s
11.3 Build Buildroot
please refer to: Buildroot
11.4 Build Other Linux
11.4.1 Kernel and u-boot versions
| Operating System | Kernel Version | U-boot version | Cross-compiler | Partition type | Packaging Tool | Kernel branch | Kernel configuration | U-boot branch | U-boot configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| buildroot | linux v5.10.y | u-boot v2017.09 |
11.3-aarch64 | GPT | sd-fuse | nanopi5-v5.10.y_opt | nanopi5_linux_defconfig | nanopi5-v2017.09 | nanopi5_defconfig |
| openmediavault-arm64 | linux v6.1.y | GPT | sd-fuse | nanopi6-v6.1.y | nanopi5_linux_defconfig | ||||
| friendlycore-focal-arm64 | GPT | ||||||||
| debian-bookworm-core-arm64 | |||||||||
| debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 | |||||||||
| debian-bullseye-minimal-arm64 | |||||||||
| ubuntu-focal-desktop-arm64 | |||||||||
| friendlywrt21 | nanopi5_linux_defconfig friendlywrt.config | ||||||||
| friendlywrt21-docker | |||||||||
| friendlywrt23 | |||||||||
| friendlywrt23-docker |
- Kernel git repo:https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip
- U-boot git repo:https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip
- The cross-compile toolchain is located in the path: /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/
- The sd-fuse is a helper script to make bootable SD card image.
11.4.2 Build kernel linux-v6.1.y
Clone the repository to your local drive then build:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi6-v6.1.y kernel-rockchip cd kernel-rockchip export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH touch .scmversion # Configuring the Kernel # Load default configuration make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 nanopi5_linux_defconfig # Optionally, load configuration for FriendlyWrt # make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 nanopi5_linux_defconfig friendlywrt.config # Optionally, if you want to change the default kernel config # make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 menuconfig # Start building kernel make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 nanopi5-images -j$(nproc) # Start building kernel modules mkdir -p out-modules && rm -rf out-modules/* make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules -j$(nproc) make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules_install KERNEL_VER=$(make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 kernelrelease) [ ! -f "$PWD/out-modules/lib/modules/${KERNEL_VER}/modules.dep" ] && depmod -b $PWD/out-modules -E Module.symvers -F System.map -w ${KERNEL_VER} (cd $PWD/out-modules && find . -name \*.ko | xargs aarch64-linux-strip --strip-unneeded)
The generated files:
| kernel.img | resource.img | |
The kernel modules are located in the out-modules directory |
Run your build:
Please refre to #Running the build
11.4.3 Build u-boot v2017.09
Clone the repository to your local drive then build:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/rkbin --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi5 git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi5-v2017.09 export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH cd uboot-rockchip/ ./make.sh nanopi5
After the compilation, the following files will be generated:
| uboot.img | rk356x_spl_loader_xx.yy.zzz.bin (aka MiniLoaderAll.bin) |
Run your build:
Please refre to #Running the build
11.4.4 Running the build
11.4.4.1 Install to target board
RK3568 uses GPT partitions by default, you can use the dd command, but be careful to choose the right output device:
- The SD/TF Card device node: /dev/mmcblk0
- The eMMC device node: /dev/mmcblk2
Use the 'parted' command to view the partition layout:
parted /dev/mmcblk2 print
Sample outputs:
Model: MMC A3A551 (sd/mmc) Disk /dev/mmcblk2: 31.0GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 8389kB 12.6MB 4194kB uboot 2 12.6MB 16.8MB 4194kB misc 3 16.8MB 21.0MB 4194kB dtbo 4 21.0MB 37.7MB 16.8MB resource 5 37.7MB 79.7MB 41.9MB kernel 6 79.7MB 113MB 33.6MB boot 7 113MB 147MB 33.6MB recovery 8 147MB 31.0GB 30.9GB ext4 rootfs
as shown above, the resource partition is located at 4 and the kernel partition is located at 5. Use the dd command to write the resource.img and kernel.img files to these partitions, the commands are as follows:
dd if=resource.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p4 bs=1M dd if=kernel.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p5 bs=1M
If you want to update u-boot:
dd if=uboot.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p1 bs=1M
To update new driver modules, copy the newly compiled driver modules to the appropriate directory under /lib/modules.
11.4.4.2 Packaging and creating an SD image
To create a new OS image file, you need to use the "sd-fuse" packaging tool.
"sd-fuse" is a collection of scripts that can be used to create bootable SD card images for FriendlyElec boards. Its main features include:
- Creation of root filesystem images from a directory
- Building of bootable SD card images
- Simple compilation of kernel, U-Boot, and third-party drivers
Please click on the following link to find out more:
| Kernel version | Packaging Tool |
|---|---|
| linux v6.1.y | sd-fuse_rk3568 |
11.4.4.3 USB flashing
11.4.4.3.1 Linux
Reboot the board and enter loader mode with the following command:
sudo reboot loaderTo flash U-Boot and kernel using the "upgrade_tool_v2.17_for_linux" tool, please use the following command:
sudo upgrade_tool di -k kernel.img sudo upgrade_tool di -re resource.img sudo upgrade_tool di -u uboot.img sudo upgrade_tool RD
Note: "upgrade_tool" is a command-line tool provided by Rockchip for Linux operating systems (Linux_Upgrade_Tool).
11.5 Build the code using scripts
11.5.1 Download scripts and image files
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3568.git --single-branch -b kernel-6.1.y cd sd-fuse_rk3568 tar xvzf /path/to/netdrive/03_Partition\ image\ files/friendlycore-focal-arm64-images.tgz
11.5.2 Compile the kernel
Download the kernel source code and compile it. the relevant image files in the friendlycore-focal-arm64 directory will be automatically updated, including the kernel modules in the file system:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --depth 1 -b nanopi6-v6.1.y kernel-rk3568 KERNEL_SRC=$PWD/kernel-rk3568 ./build-kernel.sh friendlycore-focal-arm64
11.5.3 Compile the kernel headers
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --depth 1 -b nanopi6-v6.1.y kernel-rk3568 MK_HEADERS_DEB=1 BUILD_THIRD_PARTY_DRIVER=0 KERNEL_SRC=$PWD/kernel-rk3568 ./build-kernel.sh friendlycore-focal-arm64
11.5.4 Compile the uboot
Download the uboot source code and compile it. the relevant image files in the friendlycore-focal-arm64 directory will be automatically updated:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip --depth 1 -b nanopi5-v2017.09 UBOOT_SRC=$PWD/uboot-rockchip ./build-uboot.sh friendlycore-focal-arm64
11.5.5 Generate new image
Repackage the image file in the friendlycore-focal-arm64 directory into sd card image:
./mk-sd-image.sh friendlycore-focal-arm64After the command is completed, the image is in the out directory, you can use the dd command to make the SD boot card, for example:
dd if=out/rk3568-sd-friendlycore-focal-5.10-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img of=/dev/sdX bs=1M
11.6 Building AOSP from source
11.6.1 Hardware and Software Requirements
- Your computer should have at least 16GB of RAM and 300GB of disk space. We recommend using a machine with 32GB of RAM and a large-capacity, high-speed SSD, and we do not recommend using virtual machines.
- If you encounter compilation errors, they may be caused by problems with the compilation environment. We recommend using the following Docker container for compilation: docker-cross-compiler-novnc.
11.6.2 Download source from the netdrive
Netdisk URL: Click here
File location on netdisk:"07_Source codes/rk35xx-android12-xxxxxxx-YYYYMMDD.tgz" (YYYYMMDD represents the date of the package, and xxxxxxx represents the final commit-id)
Unzip and fetch updates:
tar xzf '/path/to/netdisk/07_Source codes/rk35xx-android12-xxxxxxx-YYYYMMDD.tgz' cd rk35xx-android12 git pull
11.6.3 Tablet profile build (First Build)
echo "ROCKCHIP_DEVICE_DIR := device/rockchip/rk356x/nanopi5" > .rockchip_device.mk # export INSTALL_GAPPS_FOR_TESTING=yes # include google apps . setenv.sh ./build.sh -FMu
11.6.4 TV profile build (First Build)
echo "ROCKCHIP_DEVICE_DIR := device/rockchip/rk356x/nanopi5_box" > .rockchip_device.mk # export INSTALL_GAPPS_FOR_TESTING=yes # include google apps . setenv.sh ./build.sh -FMu
11.6.5 Second build
# export INSTALL_GAPPS_FOR_TESTING=yes # include google apps . setenv.sh make ./build.sh -Mu
11.6.6 Running your AOSP build
After the Android compilation is completed, the image file will be stored in the rockdev/Image-aosp_nanopi3 subdirectory of the Android source code directory.
11.6.6.1 USB Flashing
Use the rockchip tool to flash the following file: rockdev/Image-aosp_nanopi3/update.img
11.6.6.2 SD-to-eMMC Flashing
Refer to the following steps:
1) Insert the SD card of the eflasher system into the host;
2) Copy the files in the rockdev/Image-aosp_nanopi3 directory to the android12 or androidtv directory in the FRIENDLYARM partition of the SD card:
sudo cp -af parameter.txt config.cfg MiniLoaderAll.bin uboot.img \ dtbo.img vbmeta.img boot.img recovery.img \ misc.img pcba_small_misc.img pcba_whole_misc.img \ baseparameter.img super.img /media/$USER/FriendlyARM/android12
3) Insert the SD card into NanoPi-R5S and re-flash;
11.6.7 Pack the new SD Image
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3568.git SDFUSE=$PWD/sd-fuse_rk3568 mkdir $SDFUSE/android12 cd /path/to/rk35xx-android12/rockdev/Image-aosp_nanopi3 cp -af parameter.txt config.cfg MiniLoaderAll.bin uboot.img \ dtbo.img vbmeta.img boot.img recovery.img \ misc.img pcba_small_misc.img pcba_whole_misc.img \ baseparameter.img super.img $SDFUSE/android12 cd $SDFUSE/ ./mk-sd-image.sh android12 tar xvzf /path/to/netdrive/03_Partition\ image\ files/emmc-flasher-images.tgz ./mk-emmc-image.sh android12
For more information, please refer to #Packaging and creating an SD image
12 Using On-Board Hardware Resources
12.1 Using VPU
Please refer to NPU
12.2 Using NPU
Please refer to NPU
12.3 DTS files
Please refer to DTS files
13 Backup rootfs and create custom SD image (to burn your application into other boards)
13.1 Backup rootfs
Run the following commands on your target board. These commands will back up the entire root partition:
sudo passwd root su root cd / tar --warning=no-file-changed -cvpzf /rootfs.tar.gz \ --exclude=/rootfs.tar.gz --exclude=/var/lib/docker/runtimes \ --exclude=/etc/firstuser --exclude=/etc/friendlyelec-release \ --exclude=/usr/local/first_boot_flag --one-file-system /
Note: if there is a mounted directory on the system, an error message will appear at the end, which can be ignored.
13.2 Making a bootable SD card from a root filesystem
Run the following script on your Linux PC host, we'll only mention "debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 os" for brevity, but you can apply the same process for every linux OS.
su root git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3568 --single-branch -b kernel-6.1.y cd sd-fuse_rk3568 tar xvzf /path/to/netdrive/03_Partition\ image\ files/debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64-images.tgz tar xvzf /path/to/netdrive/03_Partition\ image\ files/emmc-eflasher-images.tgz scp pi@BOARDIP:/rootfs.tar.gz /rootfs.tar.gz mkdir rootfs tar xvzfp rootfs.tar.gz -C rootfs --numeric-owner --same-owner ./build-rootfs-img.sh rootfs debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 ./mk-sd-image.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 ./mk-emmc-image.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 autostart=yes
14 Connect NVME SSD High Speed Hard Disk
14.1 Detection of SSD
root@FriendlyELEC:~# cat /proc/partitions major minor #blocks name 1 0 4096 ram0 259 0 125034840 nvme0n1
If there is a nvme0n1 device node it means an SSD is recognized.
14.2 Partition of SSD
To mount an SSD under Linux we re-partition it as one section by running the following command:
(echo g; echo n; echo p; echo 1; echo ""; echo ""; echo w; echo q) | fdisk /dev/nvme0n1
If you want to re-partition it to multiple sections you can run "fdisk /dev/nvme0n1". For more detail about this command refer to the fdisk's manual.
14.3 Format Section to EXT4
After an SSD is successfully partitioned you can check its sections by running "cat /proc/partitions". The /dev/nvme0n1p1 section is used to store data:
root@FriendlyELEC:~# cat /proc/partitions major minor #blocks name 1 0 4096 ram0 259 0 125034840 nvme0n1 259 2 125033816 nvme0n1p1
The following command formats a section to ext4:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/nvme0n1p1
14.4 Auto Mount SSD on System Startup
Before we mount an SSD's section you need to know its Block ID. You can check it by running "blkid":
blkid /dev/nvme0n1p1 /dev/nvme0n1p1: UUID="d15c4bbf-a6c3-486f-8f81-35a8dbd46057" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="887628f0-01"
Add a "Block ID" to "/etc/fstab" and here is what it looks like
UUID=<Block ID> /media/nvme ext4 defaults 0 0
You need to replace <Block ID> with the UUID obtained by running "blkid". To mount the SSD in our example we made the "/etc/fstab" file as follows:
UUID=d15c4bbf-a6c3-486f-8f81-35a8dbd46057 /media/nvme ext4 defaults 0 0
We want to mount an SSD to "/media/nvme" but this directory doesn't exist. Therefore we create it and change its access right by running the following commands:
mkdir -p /media/nvme chmod 777 /media/nvme
Run "mount" to check if the SSD is mounted successfully:
mount /media/nvme
You can reboot your board to check if your SSD will be automatically mounted:
reboot
15 Common Linux-based operating system operations
15.1 Using ADB on Linux Systems
15.1.1 Enabling ADB in Buildroot System
Enable on Startup
mv /etc/init.d/K50usbdevice.sh /etc/init.d/S50usbdevice.sh reboot
Enable Temporarily
usbdevice-wrapper start
15.1.2 Enabling ADB in Ubuntu and Debian Systems
Enable on Startup
sudo systemctl enable usbdevice sudo reboot
Enable Temporarily
usbdevice-wrapper start
15.1.3 How to Connect
When using ADB, the port connected to the computer is the same as the USB flashing port.
15.2 Install Kernel Headers
To install the .deb file located in the /opt/archives directory:
sudo dpkg -i /opt/archives/linux-headers-*.deb
To download and update the kernel header files online:
wget http://112.124.9.243/archives/rk3568/linux-headers-$(uname -r)-latest.deb
sudo dpkg -i ./linux-headers-latest.deb
You can visit http://112.124.9.243/archives/rk3568 to see which kernel deb packages are available.
15.3 Update Kernel to Latest Version
This will update the kernel to the latest version and update the kernel and resource partitions, as well as the kernel modules:
wget http://112.124.9.243/archives/rk3568/linux-image-$(uname -r)-latest.deb
sudo dpkg -i ./linux-image-latest.deb
sudo reboot
15.4 Setting Kernel Boot Parameters (eMMC Only)
Flash the firmware file XXXX-eflasher-multiple-os-YYYYMMDD-30g.img.gz to a TF card, then insert the TF card into your computer. Windows will usually recognize the TF card partition automatically (formatted as exFAT). For Linux or Mac users, manually mount the first partition of the TF card. Assuming the TF card’s device name is /dev/sdX, mount /dev/sdX1.
Edit the info.conf configuration file in the OS directory on the TF card, adding the bootargs-ext parameter. For example:
bootargs-ext=rockchipdrm.fb_max_sz=2048To remove a specified parameter, set it to empty. For example, to remove the userdata parameter:
bootargs-ext=userdata=After editing, use this TF card to flash the system to eMMC.
To set kernel boot parameters during the creation of a mass production card, refer to the following script (example for RK3588):
https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3588/blob/kernel-6.1.y/test/test-custom-bootargs.sh
16 Unbricking Method
If the ROM is not installed correctly, causing the development board to become bricked, and you might not have the opportunity to reinstall the ROM via an SD card, you need to enter Maskrom mode to unbrick it by erasing the storage device.
16.1 Windows Users
16.1.1 Download Required Files
- Get the necessary tools: Visit here, find RKDevTool_v3.19_for_window.zip and DriverAssitant_v5.12.zip in the 05_Tools directory, and download them to your local machine.
- Install Rockchip USB driver and RKDevTool: Extract DriverAssitant_v5.12.zip to install the Rockchip USB driver, and extract RKDevTool_v3.19_for_window.zip to obtain the Rockchip flashing tool RKDevTool.
- Get the loader: Visit here, enter the tools directory corresponding to your CPU model, and download MiniLoaderAll.bin.
16.1.2 Enter Maskrom Mode to Erase the Storage Device
- Remove the SD card, USB device, and other peripherals from the development board
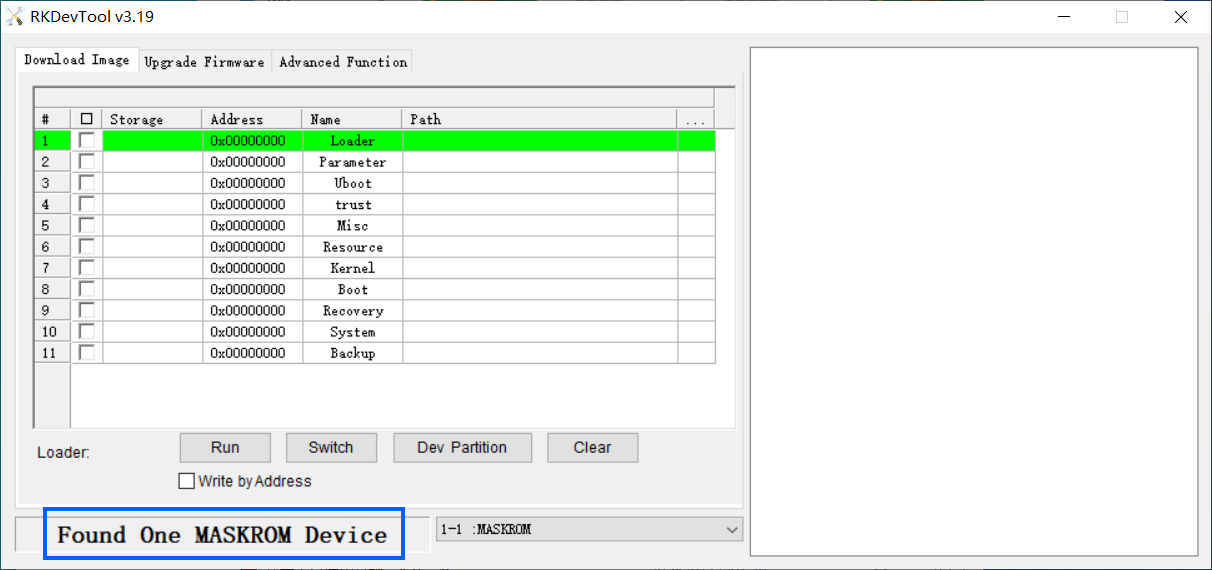
- Start RKDevTool on your computer.
- Press and hold the “Mask” key, power on the board. After the status LED has been on for at least 3 seconds, release the Mask key
- Use a USB A-to-A cable, connect NanoPi-R5S to a PC as follows
- You will see Found One MASKROM Device displayed at the bottom of the RKDevTool interface, as shown below:
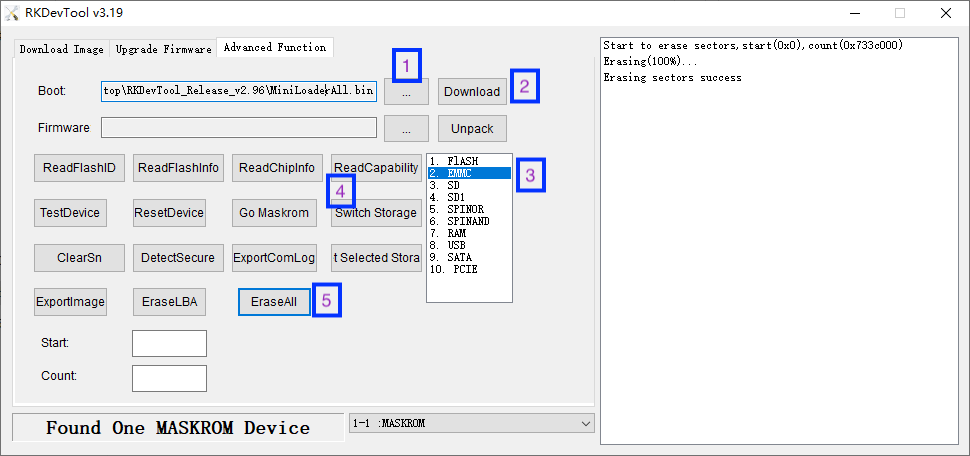
- Click the Advanced Function tab in the RKDevTool interface.
- In the Boot text box, select MiniLoaderAll.bin, then click the Download button.
- Select EMMC, click Switch Storage, then click the EraseAll button to erase the eMMC.
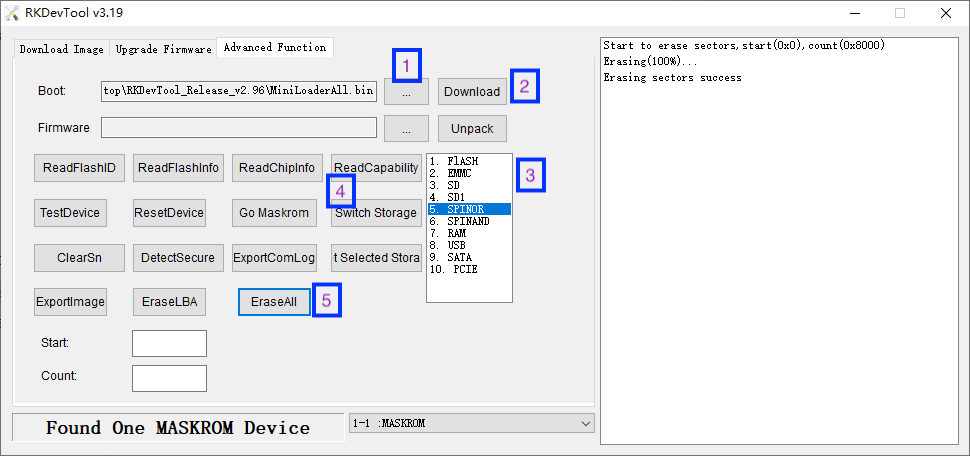
- (Optional): If your NanoPi-R5S has SPI Nor Flash, select SPINOR, click Switch Storage, then click the EraseAll button to erase the SPI Nor Flash.
- At this point, NanoPi-R5S is restored to its initial state and can be normally booted via SD card or eMMC.
16.2 Linux Users
16.2.1 Download the Required Files
- Get the necessary tools: Visit here and find upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux.tgz in the 05_Tools directory and download it locally.
- Get the loader: Visit here, enter the tools directory corresponding to your CPU model, and download MiniLoaderAll.bin.
16.2.2 Installation for upgrade_tool
Using the following commands:
tar xzf upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux.tgz cd upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux sudo cp upgrade_tool /usr/local/sbin/ sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/sbin/upgrade_tool
16.2.3 Enter Maskrom Mode to Erase the Storage Device
- Connect NanoPi-R5S to the computer using a USB data cable.
- Disconnect the power from NanoPi-R5S, hold down the MASK button, connect the power, and release the button after 4 seconds.
- Check the connection with the following command:
upgrade_tool LD
A result similar to "DevNo=1 Vid=0x2207,Pid=0x350b,LocationID=13 Mode=Maskrom SerialNo=" indicates that the device has been detected.
- Erase the eMMC with the following command:
upgrade_tool EF MiniLoaderAll.bin
- (Optional): If your NanoPi-R5S has SPI Nor Flash, erase the SPI Nor Flash with the following commands:
upgrade_tool DB MiniLoaderAll.bin upgrade_tool SSD # Select 5, SPINOR dd if=/dev/zero of=zero.img bs=1M count=16 # For 16M NOR FLASH upgrade_tool WL 0 zero.img
- At this point, NanoPi-R5S has been restored to its initial state and can boot the system normally via SD card or eMMC.
16.3 Mac Users
Our tests found that upgrade_tool_v2.25 does not work properly on macOS. Therefore, we recommend using Windows or Linux unless an updated version of upgrade_tool becomes available.
17 Link to Rockchip Resources
18 Schematic, PCB CAD File
- Schematic: NanoPi_R5S_2204_SCH.PDF
- PCB CAD File:NanoPi_R5S_2204_DXF.zip
19 Update Logs
19.1 2025-01-23
19.1.1 Linux Kernel
- Synchronized upstream kernel update to version 6.1.99
- Updated rknpu driver to version v0.9.8 (Document: NPU)
19.1.2 Debian/Ubuntu/OpenMediaVault/ProxmoxVE
- Updated Debian Bullseye system to linux-5.10-gen-rkr9 (including updates mpp, xserver, rkaiq, gstreamer-rockchip, rga2, libv4l-rkmpp, libmali, and related packages)
- Updated Rockchip hardware-related packages for Ubuntu Focal Desktop system (same as Debian Bullseye)
- Integrated hardware acceleration packages such as mpp, gstreamer, rknn, and libmali into the Core system without a desktop environment
- Update Chromium to the new stable version (130) for Debian 11 and Ubuntu 20 systems
19.2 2024-11-12
- Improved ramdisk and eflasher for more flexibility and reliability when installing the system on external storage
19.3 2024-10-16
19.3.1 New System
- Added Proxmox VE system
19.3.2 Linux Kernel
- KVM is enabled by default in the kernel
19.3.3 Linux System
- Updated Buildroot system to linux-5.10-gen-rkr8
- Updated Debian Bullseye system to linux-5.10-gen-rkr8 (updated packages such as mpp/xserver/rkaiq/gstreamer-rockchip/rga2/libv4l-rkmpp, etc.)
- Updated Rockchip-related software packages in Ubuntu Focal Desktop system (same as Debian Bullseye)
- Upgraded Chromium to the new version (stable version 129), improving performance by 50% compared to the previous version, with support for GPU acceleration and hardware video decoding, as well as HiDPI resolution
- Updated FriendlyWrt to version openwrt-23.05.05
19.3.4 Others
- Eflasher firmware flashing now supports selecting the target storage device, allowing the Linux system root partition to be installed on M.2 SSD or USB drive (but still requires eMMC/TF card for boot)
- Eflasher can customize kernel boot parameters via configuration file
- Updated ramdisk to support btrfs filesystem (can use sd-fuse_rk3568 to package btrfs firmware)
- Updated ramdisk to improve compatibility for filesystem repair
19.4 2024-06-14
19.4.1 Android
- Added support for PWM fan
- Improved HDMI output compatibility
- Added support for Intel RealSense Depth Camera, enable it by setting the CONFIG_USB_VIDEO_CLASS_REALSENSE option in the kernel
- Updated support for Android video decoding
19.5 2024-06-06
19.5.1 Linux Kernel
- Synchronize upstream kernel updates to 6.1.57.
- Add support for NVMe hardware monitoring, temperature of NVMe devices can be viewed through the /sys/class/hwmon node.
- Refactor rknpu (v0.9.3) as a module for easier updates or version changes.
- Introduce a simple driver for querying input power voltage (node: /sys/class/power_supply/simple-vin/voltage_now).
- Add support for Intel RealSense Depth Camera, enable it by configuring the kernel option CONFIG_USB_VIDEO_CLASS_REALSENSE.
- Fixed the RGA3 issue.
- Modified kernel LSM to add apparmor,selinux.
19.5.2 Debian11 Desktop
- Synchronize upstream Debian version to linux-5.10-gen-rkr7.1.
- Update core libraries such as libmali, mpp, rga2, npu, gstreamer, etc., to newer versions.
- Update web browser Chromium to a new version.
19.5.3 Ubuntu Focal Desktop
- Add support for multiple languages (including Chinese).
- Fix potential issue of no display when connecting a screen after boot.
- Update core libraries such as libmali, mpp, rga2, npu, gstreamer, etc., to newer versions.
19.5.4 Other
- sd-fuse_rk3568 Support packaged image on arm64 platform
19.6 2024-04-21
19.6.1 OpenMediaVault
- Update to 7.0.5-1
- Update to Debian12
19.7 2024-03-15
19.7.1 Ubuntu focal desktop
- Fix the bluetooth issue
19.8 2024-01-31
19.8.1 Debian/Ubuntu/FriendlyCore/Buildroot
- Add adb support
19.8.2 Android 12 & Android TV
- Add wifidisplay (no hdcp) support
- Add Wi-Fi direct support for rtl8822ce and rtl8812au
19.8.3 FriendlyWrt
- Add wireless repeater mode support for rtl8822ce
19.9 2023-12-23
19.9.1 Android 12 & Android TV
- Fix the UsbCamera preview abnormal issue
- Fix connection for ps5/dualshock controller
- Improve support for non-16:9 resolutions in HDMI output
- Update SDK to Rockchip Android 12.1 rkr14.2
19.9.2 FriendlyWrt
- Fix an issue that unable to use eMMC tools for large-capacity eMMC
19.10 2023-12-01
19.10.1 FriendlyWrt
- Update to openwrt-23.05.2
19.11 2023-11-13
19.11.1 Debian/Ubuntu/FriendlyCore
- Updated npu driver to 0.9.2, fixed known issues
19.12 2023-10-31
19.12.1 Add a new system
- Add NAS system OpenMediaVault, base on Debian 11 with kernel 6.1
19.12.2 Debian/Ubuntu/FriendlyCore
- Update to kernel 6.1
19.12.3 FriendlyWrt
- Update to kernel 6.1
- Update to openwrt-23.05
19.13 2023-09-09
19.13.1 Android 12
- Add hardware library support (Click to view details)
- Add support for OTA and virtual A/B partitions
19.14 2023-08-15
- Update buildroot to linux-5.10-gen-rkr5.1
19.15 2023-07-19
19.15.1 Ubuntu Focal Desktop
- Add Ubuntu 20.04 desktop, with LXQT lightweight desktop
19.15.2 Debian/Ubuntu/Android
- Fix RTL9210 enclosures slowdown issue
19.15.3 FriendlyCore
- Fixed HDMI display issue
19.16 2023-07-01
19.16.1 Debian11
- Update to rockchip bsp linux-5.10-gen-rkr5, improve xserver and video playback performance
- Update kernel to 5.10.160
- Fix some known issues
19.17 2023-06-25
19.17.1 Debian11
- Update mpp/ffmpeg/gsteamer-rockchip/libv4l-rkmpp/libdrm-cursor packages
19.17.2 Android TV & Android 12
- Update to rockchip android-12.1-mid-rkr14
- Upgrade kernel to 5.10.160
- Add support for MediaTek MT7921 wireless card (WiFi only)
19.18 2023-06-16
19.18.1 Debian11
- Merge changes from upsteam version rockchip linux-5.10-gen-rkr4.1
- Improved UI performance and video playback performance
- Add support for MediaTek MT7921 wireless card
- Fix some known issues
19.19 2023-06-09
19.19.1 FriendlyWrt
- Add support for MediaTek MT7921 wireless card
19.20 2023-06-06
19.20.1 Android TV & Android 12
- Auto expand storage space for SD boot
19.21 2023-06-02
19.21.1 Android TV
- Fix home button issue
19.22 2023-05-26
19.22.1 Debian11
- Optimized r8125 performance and stability
19.22.2 FriendlyWrt
- Updated v22.03 to openwrt-22.03.5
- Updated v21.02 to openwrt-21.02.7
- Optimized r8125 performance and stability
19.23 2023-05-21
19.23.1 Debian11
- Update to Rockchip sdk version linux-5.10-gen-rkr4
- Switch desktop to LXDE
19.24 2023-05-15
19.24.1 FriendlyCore Focal
- Add Qt 5.10 support
19.25 2023-05-05
19.25.1 Android
- Add USB bluetooth dongle support (rtl8761bu)
- Add M.2 RTL8822CE bluetooth support
19.26 2023-04-26
19.26.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Upgrade v22.03 to openwrt-22.03.4
- Upgrade v21.02 to openwrt-21.02.6
19.27 2023-03-24
- Fix the issue that Android Tablet and Android TV cannot start
19.28 2023-02-10
19.28.1 Android update
- First release android tv for rk3568
- android support direct boot from sd card
- Fix the problem that in some cases hdmi has no signal output and needs to be plugged in once to recover
- Support enable adb function through android interface
19.28.2 Added Debian11
There are three versions:
- Debian11 Core: Command-line only
- Debian11 Minimal: With Xfce desktop, lite version
- Debian11 Desktop: With Xfce desktop, full version
19.29 2023-01-09
19.29.1 Android:
- Fixed the problem that Android12 could not run on NanoPi-R5C
- Add support for USB WiFi module and M.2 WiFi module (Model: RTL8822CE/RTL8812AU/MediaTek MT7662)
- Update SDK to Rockchip android-12.1-mid-rkr12
19.29.2 FriendlyCore:
- optimized the systemd service
19.30 2022-12-04
19.30.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Fix the issue that the storage space cannot be expanded
- Improve stability of the eMMC Tools
- Add support for NanoPi-R5C
19.31 2022-09-06
19.31.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Added Fullcone NAT support
- upgrade to 22.03.0
19.32 2022-08-03
19.32.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Upgrade FriendlyWrt to the latest version 22.03-rc6
19.33 2022-07-27
19.33.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Add NAS menu category
- Add wg driver module
- Tweak configuration, docker version and non-docker version have exactly the same features, the difference is only docker
19.34 2022-07-04
19.34.1 FriendlyWrt & FriendlyCore:
- Improved pci-e stability
19.34.2 Debian 10(buster) Desktop (New)
- Uses LXDE as default desktop
- Pre-installed mpv, smplayer and chromium brower
- Supports hardware acceleration
19.35 2022-06-22
19.35.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Upgrade kernel to 5.10.110
19.36 2022-06-21
19.36.1 FriendlyWrt:
19.36.1.1 eMMC Tools
- Add support for burning firmware packaged in rockchip firmware format
- Add an eMMC erase action when burning firmware to enhance compatibility
19.37 2022-06-15
19.37.1 FriendlyCore:
- eth1, eth2 ports initialized with static IPs 192.168.2.1, 192.168.3.1
- Added interrupt settings for NICs
19.38 2022-06-14
19.38.1 FriendlyWrt:
- Optimised network performance, fixed poor tx performance in previous version of software
- Improved package compatibility
- Add support for "Restore factory settings"
- eMMC Tools adds checksum for gz format firmware files
- FriendlyWrt official stable version 21.02.3 is available, version 22.03.0 is still available
- Some other detailed adjustments: Set time zone to Shanghai by default, remove lcd2usb, improve security settings, tune sysctl parameters, fix docker firewall settings, etc.
19.39 2022-05-16
Initial Release