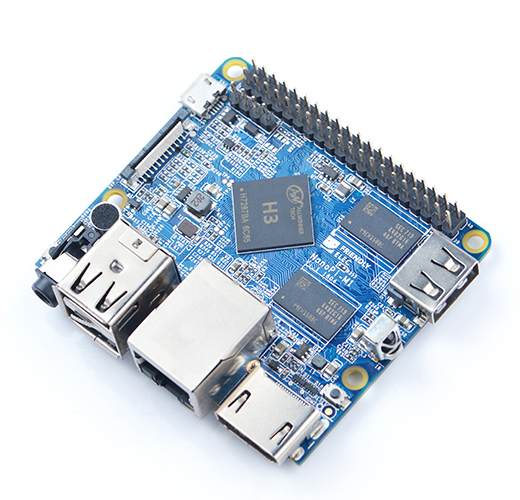
NanoPi M1
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Hardware Spec
- 3 Software Features
- 4 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
- 5 Get Started
- 6 Working with Debian
- 7 Work with FriendlyCore
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 System Login
- 7.3 Configure System with npi-config
- 7.4 Develop Qt Application
- 7.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
- 7.6 Extend TF Card's Section
- 7.7 WiFi
- 7.8 Ethernet Connection
- 7.9 WiringPi and Python Wrapper
- 7.10 Custom welcome message
- 7.11 Modify timezone
- 7.12 Set Audio Device
- 7.13 Connect to DVP Camera CAM500B
- 7.14 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
- 7.15 Check CPU's Working Temperature
- 7.16 Test Infrared Receiver
- 7.17 Run Qt Demo
- 7.18 How to install and use docker (for armhf system)
- 8 Make Your Own Linux System
- 9 Applications under Android
- 10 Make Your Own Android
- 11 Developer Guide
- 12 More OS Support
- 13 Download Link to Image Files
- 14 3D Housing Printing Files
- 15 Matrix Compact Kit B:A Good Kit for Starters
- 16 Resources
- 17 Update Log
1 Introduction
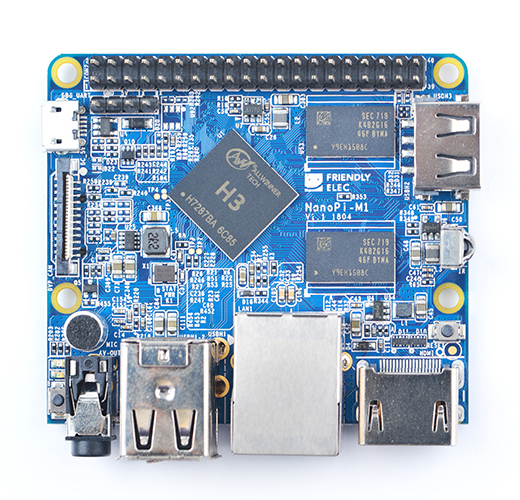
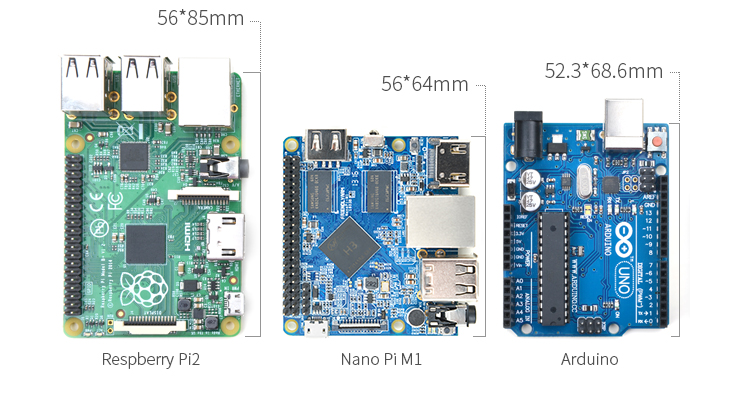
- The NanoPi M1 is an Allwinner H3 based ARM board designed and released by FriendlyARM for hobbyists, makers and electronic fans. It is only two thirds the size of the Raspberry Pi. It is open source. It works with Ubuntu MATE, Debian and etc.
- The NanoPi M1 uses the Allwinner H3 Soc. It integrates Ethernet, IR receiver, video/audio output and supports HDMI and AVOUT. It can be powered via the MicroUSB port
- In such a small board it still integrates rich interfaces and ports. Besides the popular HDMI, Ethernet, USB-Host, USB-OTG, DVP camera interface and AVOUT (audio and video) it has an onboard Microphone, IR receiver, a serial debug port and a Raspberry Pi compatible 40 pin GPIO pin header.
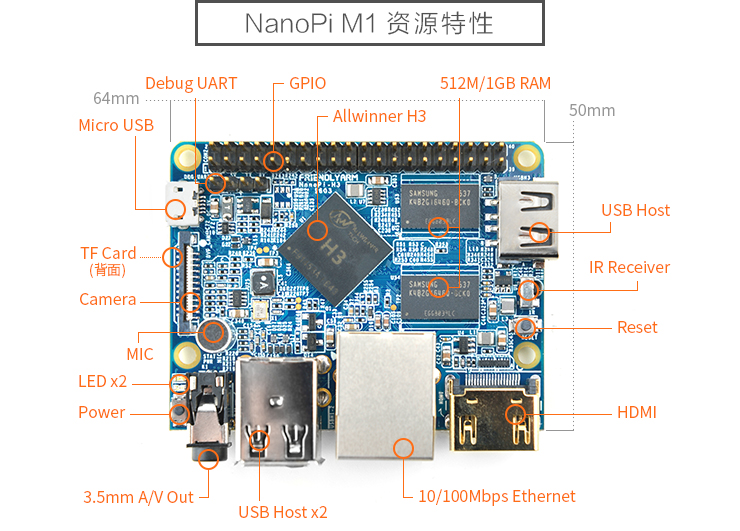
2 Hardware Spec
- CPU: Allwinner H3, Quad-core Cortex-A7@1.2GHz
- GPU: Mali400MP2@600MHz,Supports OpenGL ES2.0
- DDR3 RAM: 512MB/1GB
- Connectivity: 10/100M Ethernet
- Audio: 3.5mm audio jack/Via HDMI
- Microphone: Onboard microphone
- IR Receiver: Onboard IR receiver
- USB Host:Type A, USB 2.0 x 3
- MicroSD Slot x 1
- MicroUSB: for data transmission and power input, OTG
- Video Output: HDMI 1.4 1080P, CVBS
- DVP Camera Interface: 24pin, 0.5mm pitch FPC seat
- Debug Serial Port: 4Pin, 2.54mm pitch pin header
- GPIO: 2.54mm spacing 40pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi's GPIO. It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc
- User Key: GPIO Key x 1, Reset x 1
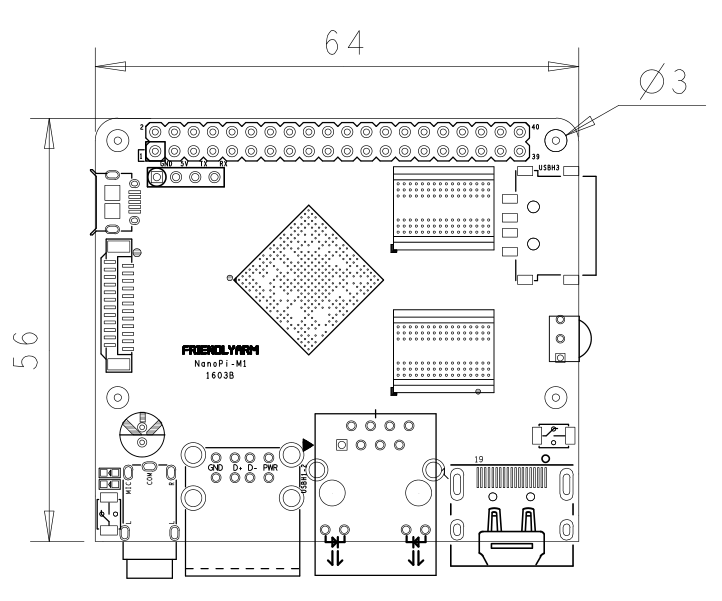
- PC Size: 64 x 56mm
- Power Supply: DC 5V/2A
- Working Temperature: -30℃ to 70℃
- OS/Software: u-boot,Ubuntu MATE,Debian
3 Software Features
3.1 uboot
- mainline uboot released on May 2017
- supports fastboot to update uboot
3.2 UbuntuCore 16.04
- mainline kernel: Linux-4.11.2
- rpi-monitor: check system status and information
- npi-config: system configuration utility for setting passwords, language, timezone, hostname, SSH and auto-login,and enabling/disabling i2c, spi, serial and PWM
- networkmanager: manage network
- system log output from serial port
- auto-login with user account "pi" with access to npi-config
3.3 Debian Jessie
- welcome window with basic system information and status
- npi-config: system configuration utility for setting passwords, language, timezone, hostname,
3.4 Android
- supports USB WiFi
4 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
4.1 Layout
- GPIO Pin Spec
Pin# Name Linux gpio Pin# Name Linux gpio 1 SYS_3.3V 2 VDD_5V 3 I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 4 VDD_5V 5 I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 6 GND 7 GPIOG11 203 8 UART1_TX/GPIOG6 198 9 GND 10 UART1_RX/GPIOG7 199 11 UART2_TX/GPIOA0 0 12 GPIOA6 6 13 UART2_RTS/GPIOA2 2 14 GND 15 UART2_CTS/GPIOA3 3 16 UART1_RTS/GPIOG8 200 17 SYS_3.3V 18 UART1_CTS/GPIOG9 201 19 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC0 64 20 GND 21 SPI0_MISO/GPIOC1 65 22 UART2_RX/GPIOA1 1 23 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC2 66 24 SPI0_CS/GPIOC3 67 25 GND 26 SPDIF-OUT/GPIOA17 17 27 I2C1_SDA/GPIOA19/PCM0_CLK/I2S0_BCK 19 28 I2C1_SCL/GPIOA18/PCM0_SYNC/I2S0_LRCK 18 29 GPIOA20/PCM0_DOUT/I2S0_SDOUT 20 30 GND 31 GPIOA21/PCM0_DIN/I2S0_SDIN 21 32 GPIOA7 7 33 GPIOA8 8 34 GND 35 UART3_CTS/SPI1_MISO/GPIOA16 16 36 UART3_TX/SPI1_CS/GPIOA13 13 37 GPIOA9 9 38 UART3_RTS/SPI1_MOSI/GPIOA15 15 39 GND 40 UART3_RX/SPI1_CLK/GPIOA14 14
- Debug Port(UART0)
Pin# Name 1 GND 2 VDD_5V 3 UART_TXD0/GPIOA4 4 UART_RXD0/GPIOA5/PWM0
- DVP Camera IF Pin Spec
Pin# Name Description 1, 2 SYS_3.3V 3.3V power output, to camera modules 7,9,13,15,24 GND Gound, 0V 3 I2C2_SCL I2C Clock Signal 4 I2C2_SDA I2C Data Signal 5 GPIOE15 Regular GPIO, control signals output to camera modules 6 GPIOE14 Regular GPIO, control signals output to camera modules 8 MCLK Clock signals output to camera modules 10 NC Not Connected 11 VSYNC vertical synchronization to CPU from camera modules 12 HREF/HSYNC HREF/HSYNC signal to CPU from camera modules 14 PCLK PCLK signal to CPU from camera modules 16-23 Data bit7-0 data signals
- Note:
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. When the external device’s power is greater than the MicroUSB’s the external device is charging the board otherwise the board powers the external device. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.6V
- All pins are 3.3V and output current is 5mA. It can drive small loads. No IO pins can drive a load.
- For more details refer to the document: NanoPi-M1-1603B-Schematic.pdf
4.2 Board Dimension
- For more details please refer to: pcb file in dxf
5 Get Started
5.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi M1 get the following items ready
- NanoPi M1
- microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must
- HDMI monitor
- USB keyboard and mouse
- A host computer running Ubuntu 16.04 64 bit system
5.2 TF Cards We Tested
To make your NanoPi M1 boot and run fast we highly recommend you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
5.3 Install OS
5.3.1 Get Image Files
Visit this link download link to download image files and the flashing utility:
Image Files: nanopi-m1_sd_friendlycore-xenial_3.4_armhf_YYYYMMDD.img.zip FriendlyCore (base on UbuntuCore) Image File, kernel:Linux-3.4 nanopi-m1_sd_friendlycore-xenial_4.14_armhf_YYYYMMDD.img.zip FriendlyCore (base on UbuntuCore) Image File, kernel:Linux-4.14 nanopi-m1_sd_debian-jessie_3.4_armhf_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Debian-Desktop Image File, kernel:Linux-3.4 nanopi-m1_sd_debian-jessie_4.14_armhf_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Debian-Desktop Image File, kernel:Linux-4.14 nanopi-m1_sd_android_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Android Image File, kernel:Linux-3.4 Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility for flashing Debian image. Under Linux users can use "dd" PhoenixCard_V310.rar Windows utility for flashing Android image. Attention: the "dd" command under Linux doesn't work for flashing Android image HDDLLF.4.40.exe Windows utility for formatting a TF card
5.3.2 Comparison of Linux-3.4 and Linux-4.14
- Our Linux-3.4 is provided by Allwinner. Allwinner has done a lot of customization work which on one hand contains many features and functions but on the other hand incurs overheat issues. If your application needs to use VPU or GPU you need to use the 3.4 kernel based ROM and use a heat sink together with your board.
- Our Linux-4.14 is based on the mainline kernel. We will keep this kernel with the latest one released by Linus Torvalds. This kernel is stable and doesn't generate heat that much. If your application doesn't need to use VPU or GPU we recommend you to use this kernel.
- For more details about the Linux-4.14 kernel refer to: Building U-boot and Linux for H5/H3/H2+
5.3.3 Android
5.3.3.1 Flash to TF
Note:before make a MicroSD card to an Android image card you need to format this card.
- On a Windows PC run the HDDLLF.4.40 utility as administrator. Insert a TF card(at least 8G) into this PC and format it. After formatting is done take out the TF card, insert it into the PC again and format it with Windows internal format utility to format it to FAT32. After this formatting is done take out the card.
- Extract the the Android image and PhoenixCard_V310.rar . Insert the TF card you made in the previous step into a Windows PC and run the PhoenixCard_V310 utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your TF card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the TF card.
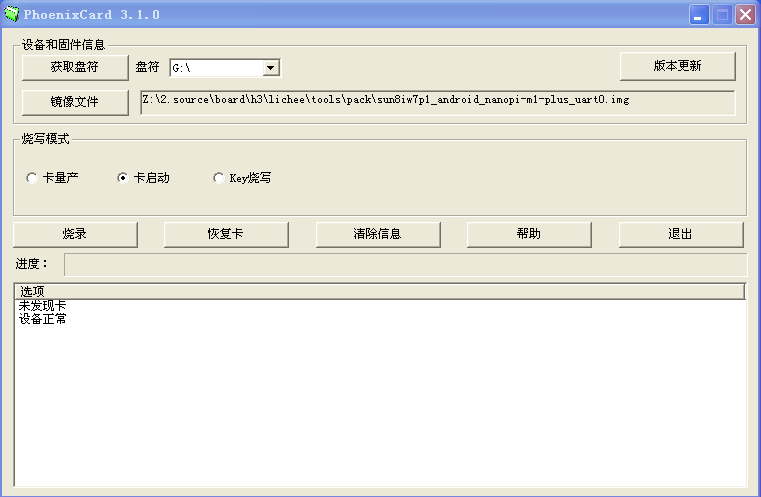
(In the screenshot an Android image file for the NanoPi M1 Plus was selected. You need to select a correct image file for your board.)
- Insert this card into your board' BOOT slot and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the green LED is on and the blue LED is blinking this indicates your board has successfully booted.
6 Working with Debian
6.1 Ethernet Connection
- If the board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on, it will automatically obtain an IP after it is powered up.
6.2 Wireless Connection
Under Debian you can manage your network with NetworkManager.
After Debian boots click on the network icon on the bottom right of the task bar a NetworkManger menu will pop up and all the available networks will be listed. If there is an active wireless network you will see something similar to the following screenshot:
![]()
You can click on a WiFI AP and connect your board to it.
For more details refer to:NetworkManager.
For either an SD WiFi or a USB WiFi you can connect it to your board in the same way. The APXX series WiFi chips are SD WiFi chips. By default FriendlyElec's system supports most popular USB WiFi modules. Here is a list of the USB WiFi modules we tested:
Index Model 1 RTL8188CUS/8188EU 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 mi WiFi mt7601 6 5G USB WiFi RTL8821CU 7 5G USB WiFi RTL8812AU
You can use the NetworkManager utility to manage network. You can run "nmcli" in the commandline utility to start it. Here are the commands to start a WiFi connection:
- Change to root
$ su root
- Check device list
$ nmcli devNote: if the status of a device is "unmanaged" it means that device cannot be accessed by NetworkManager. To make it accessed you need to clear the settings under "/etc/network/interfaces" and reboot your system.
- Start WiFi
$ nmcli r wifi on- Scan Surrounding WiFi Sources
$ nmcli dev wifi- Connect to a WiFi Source
$ nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD" ifname wlan0
The "SSID" and "PASSWORD" need to be replaced with your actual SSID and password.If you have multiple WiFi devices you need to specify the one you want to connect to a WiFi source with iface
If a connection succeeds it will be automatically setup on next system reboot.
For more details about NetworkManager refer to this link: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
If your USB WiFi module doesn't work most likely your system doesn't have its driver. For a Debian system you can get a driver from Debian-WiFi and install it on your system. For a Ubuntu system you can install a driver by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install linux-firmware
In general all WiFi drivers are located at the "/lib/firmware" directory.
6.3 Install Debian Packages
We provide a Debian Jessie image. You can install Jessie's packages by commanding "apt-get". If this is your first installation you need to update the package list by running the following command
apt-get updateYou can install your preferred packages. For example if you want to install an FTP server you can do this:
apt-get install vsftpdNote: you can change your download server by editting "/etc/apt/sources.list". You can get a complete server list from [1]. You need to select the one with "armhf".
6.4 Set Audio Device
If your system has multiple audio devices such as HDMI-Audio, 3.5mm audio jack and I2S-Codec you can set system's default audio device by running the following commands.
- After your board is booted run the following commands to install alsa packages:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libasound2 $ apt-get install alsa-base $ apt-get install alsa-utils
- After installation is done you can list all the audio devices by running the following command. Here is a similar list you may see after you run the command:
$ aplay -l card 0: HDMI card 1: 3.5mm codec card 2: I2S codec
"card 0" is HDMI-Audio, "card 1" is 3.5mm audio jack and "card 2" is I2S-Codec. You can set default audio device to HDMI-Audio by changing the "/etc/asound.conf" file as follows:
pcm.!default { type hw card 0 device 0 } ctl.!default { type hw card 0 }
If you change "card 0" to "card 1" the 3.5mm audio jack will be set to the default device.
Copy a .wav file to your board and test it by running the following command:
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav
You will hear sounds from system's default audio device.
If you are using H3/H5/H2+ series board with mainline kernel, the easier way is using npi-config。
6.5 Login via VNC and SSH
If your board is not connected to a display device you can login to your board from a mobile phone. You need to download and install a "VNC Viewer" from here on a mobile phone and login to the board via VNC at port 1. Its default password is "fa123456".
Here is a screenshot which shows how it looks like when users login to the board from an iPhone via VNC:
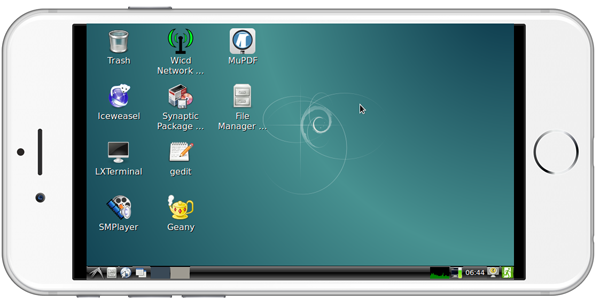
In our case our board's IP address is 192.168.1.230. You can login via SSH by running the following commands:
$ ssh root@192.168.1.230
The password is fa.
6.6 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
The FA-CAM202 is a 200M USB camera.
Refer to this link for more details on how to connect to a FA-CAM202:
Connect NanoPi M1 to DVP Camera CAM500B
In Debian, click on "other"-->"xawtv" on the left bottom of the GUI and the USB Camera application will be started. After enter "welcome to xawtv!" click on "OK" to start exploring.
6.7 Use OpenCV to Access Camera
- The full name of "OpenCV" is Open Source Computer Vision Library and it is a cross platform vision library.
- Make sure your board is connected to the internet and an HDMI monitor, Boot Debian and login.
- Install OpenCV libraries:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libcv-dev libopencv-dev
- Refer to the instructions in the previous sections to make sure the camera works
- Compile and run a code sample(Official Code Sample in C++ provided by the OpenCV organization):
$ cd /home/fa/Documents/opencv-demo $ make $ ./demo
6.8 Connect to DVP Camera CAM500B
The CAM500B camera module is a 5M-pixel camera with DVP interface. For more tech details about it you can refer to Matrix - CAM500B.
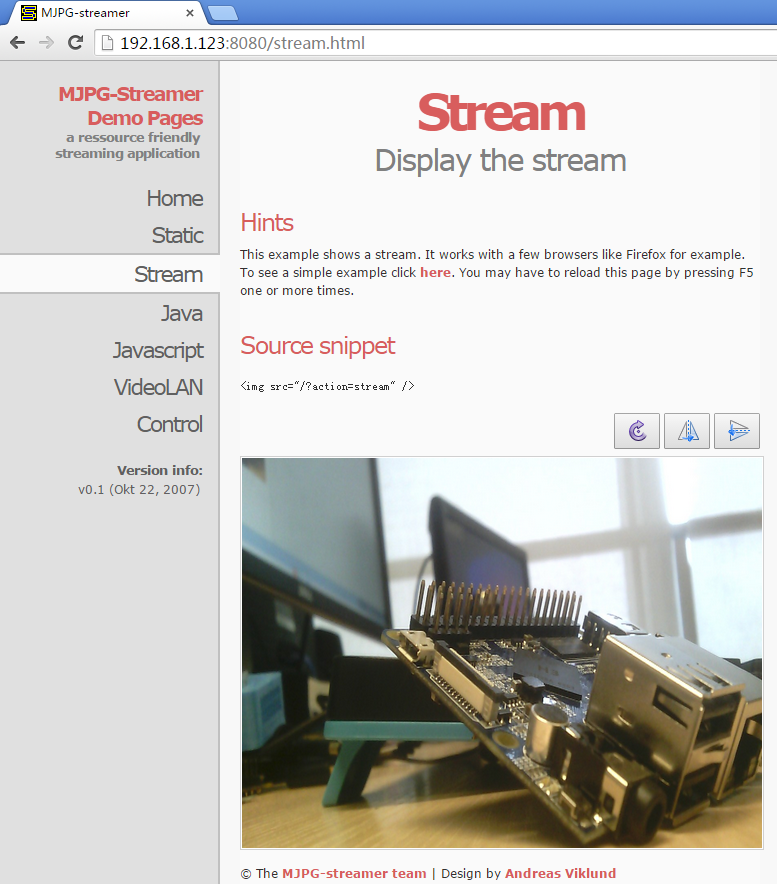
connect your H3 board to a CAM500B. Then boot OS, connect your board to a network, log into the board as root and run "mjpg-streamer":
$ cd /root/mjpg-streamer $ make $ ./start.sh
The mjpg-streamer application is an open source video steam server. After it is successfully started the following messages will be popped up:
i: Using V4L2 device.: /dev/video0 i: Desired Resolution: 1280 x 720 i: Frames Per Second.: 30 i: Format............: YUV i: JPEG Quality......: 90 o: www-folder-path...: ./www/ o: HTTP TCP port.....: 8080 o: username:password.: disabled o: commands..........: enabled
In our case the board's IP address was 192.168.1.230. We typed 192.168.1.230:8080 in a browser and were able to view the images taken from the camera's. Here is what you would expect to observe:
The mjpg-streamer utility uses libjpeg to software-encode steam data. The Linux-4.x based ROM currently doesn't support hardware-encoding. If you use a Linux-3.x based ROM you can use the ffmpeg utility to hardware-encode stream data and this can greatly release CPU's resources and speed up encoding:
$ ffmpeg -t 30 -f v4l2 -channel 0 -video_size 1280x720 -i /dev/video0 -pix_fmt nv12 -r 30 \ -b:v 64k -c:v cedrus264 test.mp4
By default it records a 30-second video. Typing "q" stops video recording. After recording is stopped a test.mp4 file will be generated.
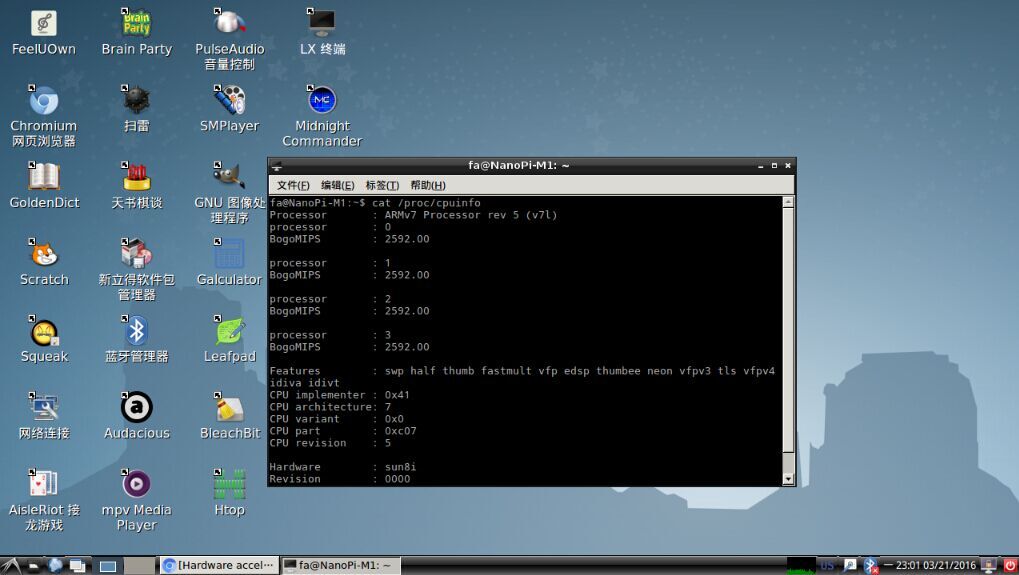
6.9 Check CPU's Working Temperature
You can use the following command to read H3's temperature and frequency
cpu_freq
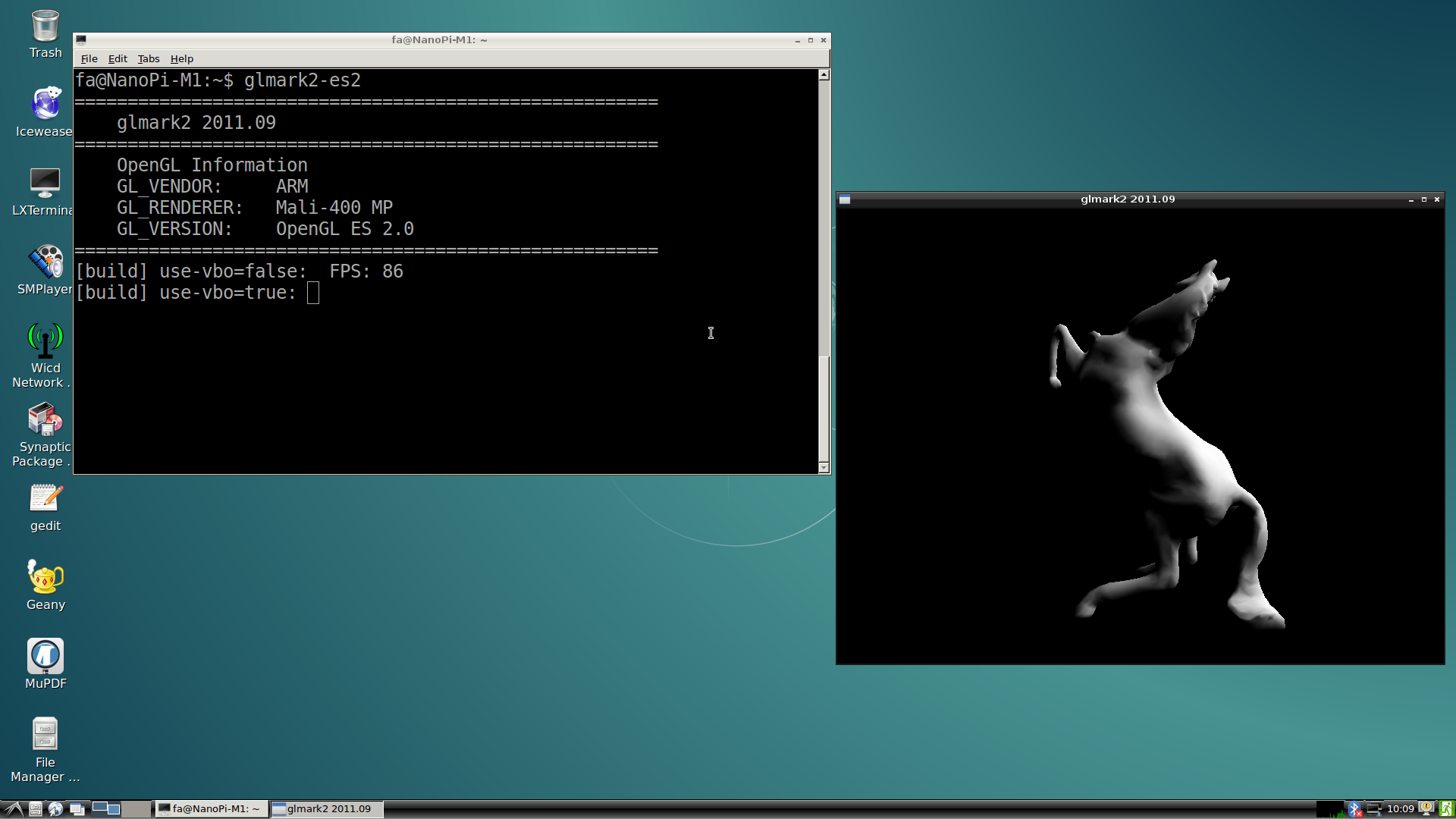
6.10 Test GPU
Note: this function is only supported in Allwinner Linux-3.4.y.
After OS loads please login from a terminal and run the following command:
glmark2-es2
6.11 Test VPU
Note: this function is only supported in Allwinner Linux-3.4.y
Visit this link download link to download files
After OS is loaded login from a terminal and run the following commands:
$ sudo apt-get install mpv $ video_play mpv ./big_buck_bunny_1080p_H264_AAC_25fps_7200K.MP4
In our test it could do hard coding and play 1080P video fluently.
7 Work with FriendlyCore
7.1 Introduction
FriendlyCore is a light Linux system without X-windows, based on ubuntu core, It uses the Qt-Embedded's GUI and is popular in industrial and enterprise applications.
Besides the regular Ubuntu Core's features FriendlyCore has the following additional features:
- it integrates Qt4.8;
- it integrates NetworkManager;
- it has bluez and Bluetooth related packages;
- it has alsa packages;
- it has npi-config;
- it has RPiGPIO, a Python GPIO module;
- it has some Python/C demo in /root/ directory;
- it enables 512M-swap partition;
7.2 System Login
- If your board is connected to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and keyboard.
- If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will
allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB:
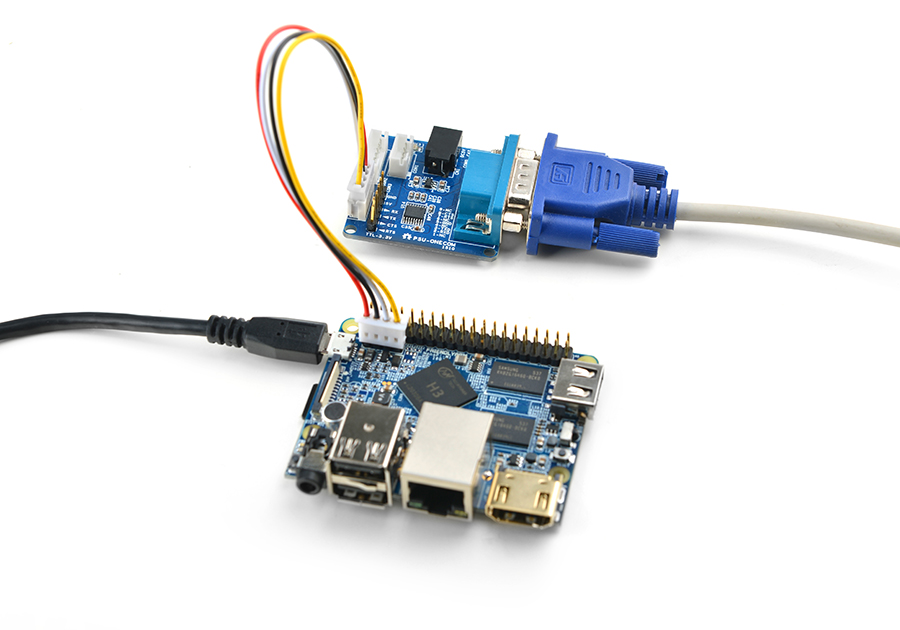
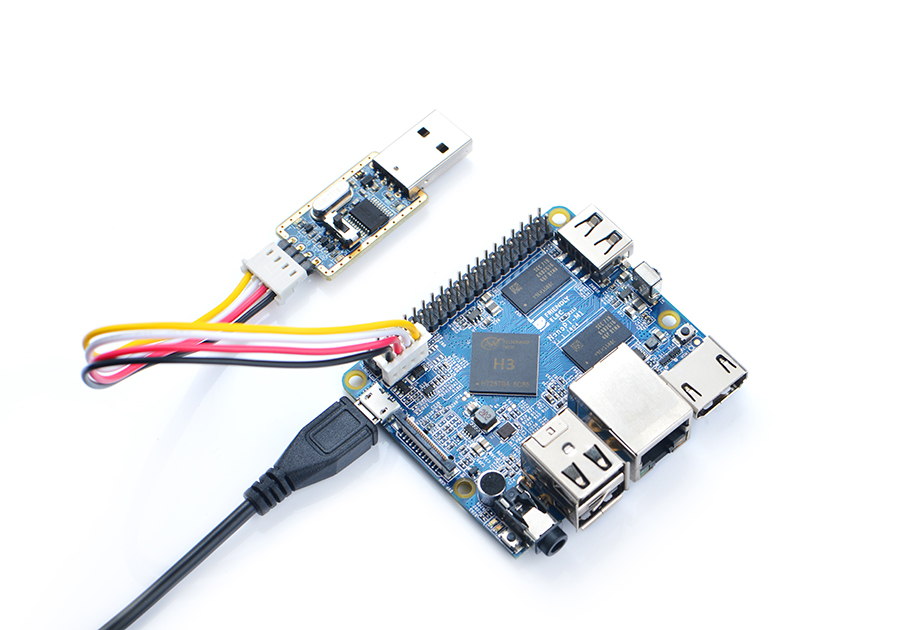
You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too.
Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:
- FriendlyCore User Accounts:
Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
The system is automatically logged in as "pi". You can do "sudo npi-config" to disable auto login.
- Update packages
$ sudo apt-get update
7.3 Configure System with npi-config
The npi-config is a commandline utility which can be used to initialize system configurations such as user password, system language, time zone, Hostname, SSH switch , Auto login and etc. Type the following command to run this utility.
$ sudo npi-config
Here is how npi-config's GUI looks like:
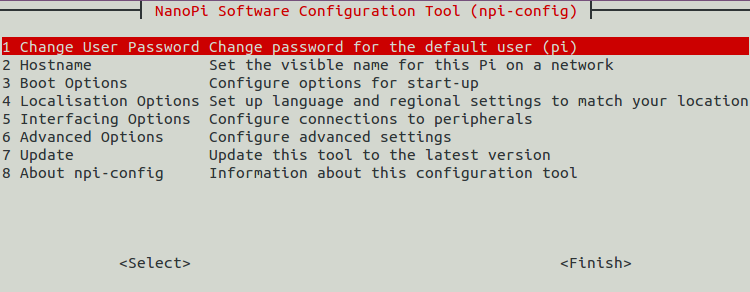
7.4 Develop Qt Application
Please refer to: How to Build and Install Qt Application for FriendlyELEC Boards
7.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
You can setup a program to autorun on system boot with npi-config:
sudo npi-configGo to Boot Options -> Autologin -> Qt/Embedded, select Enable and reboot.
7.6 Extend TF Card's Section
When FriendlyCore is loaded the TF card's section will be automatically extended.You can check the section's size by running the following command:
$ df -h
7.7 WiFi
For either an SD WiFi or a USB WiFi you can connect it to your board in the same way. The APXX series WiFi chips are SD WiFi chips. By default FriendlyElec's system supports most popular USB WiFi modules. Here is a list of the USB WiFi modules we tested:
Index Model 1 RTL8188CUS/8188EU 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 mi WiFi mt7601 6 5G USB WiFi RTL8821CU 7 5G USB WiFi RTL8812AU
You can use the NetworkManager utility to manage network. You can run "nmcli" in the commandline utility to start it. Here are the commands to start a WiFi connection:
- Change to root
$ su root
- Check device list
$ nmcli devNote: if the status of a device is "unmanaged" it means that device cannot be accessed by NetworkManager. To make it accessed you need to clear the settings under "/etc/network/interfaces" and reboot your system.
- Start WiFi
$ nmcli r wifi on- Scan Surrounding WiFi Sources
$ nmcli dev wifi- Connect to a WiFi Source
$ nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD" ifname wlan0
The "SSID" and "PASSWORD" need to be replaced with your actual SSID and password.If you have multiple WiFi devices you need to specify the one you want to connect to a WiFi source with iface
If a connection succeeds it will be automatically setup on next system reboot.
For more details about NetworkManager refer to this link: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
If your USB WiFi module doesn't work most likely your system doesn't have its driver. For a Debian system you can get a driver from Debian-WiFi and install it on your system. For a Ubuntu system you can install a driver by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install linux-firmware
In general all WiFi drivers are located at the "/lib/firmware" directory.
7.8 Ethernet Connection
If a board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP with DHCP activated after it is powered up. If you want to set up a static IP refer to: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings。
7.9 WiringPi and Python Wrapper
- WiringNP: NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with C
- RPi.GPIO : NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with Python
7.10 Custom welcome message
The welcome message is printed from the script in this directory:
/etc/update-motd.d/
For example, to change the FriendlyELEC LOGO, you can change the file /etc/update-motd.d/10-header. For example, to change the LOGO to HELLO, you can change the following line:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal $BOARD_VENDOR
To:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal HELLO
7.11 Modify timezone
For exampe, change to Shanghai timezone:
sudo rm /etc/localtime sudo ln -ls /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
7.12 Set Audio Device
If your system has multiple audio devices such as HDMI-Audio, 3.5mm audio jack and I2S-Codec you can set system's default audio device by running the following commands.
- After your board is booted run the following commands to install alsa packages:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libasound2 $ apt-get install alsa-base $ apt-get install alsa-utils
- After installation is done you can list all the audio devices by running the following command. Here is a similar list you may see after you run the command:
$ aplay -l card 0: HDMI card 1: 3.5mm codec card 2: I2S codec
"card 0" is HDMI-Audio, "card 1" is 3.5mm audio jack and "card 2" is I2S-Codec. You can set default audio device to HDMI-Audio by changing the "/etc/asound.conf" file as follows:
pcm.!default { type hw card 0 device 0 } ctl.!default { type hw card 0 }
If you change "card 0" to "card 1" the 3.5mm audio jack will be set to the default device.
Copy a .wav file to your board and test it by running the following command:
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav
You will hear sounds from system's default audio device.
If you are using H3/H5/H2+ series board with mainline kernel, the easier way is using npi-config。
7.13 Connect to DVP Camera CAM500B
For NanoPi-M1 the CAM500B can work with both Linux-3.4 Kernel and Linux-4.14 Kernel.
The CAM500B camera module is a 5M-pixel camera with DVP interface. For more tech details about it you can refer to Matrix - CAM500B.
connect your board to camera module. Then boot OS, connect your board to a network, log into the board as root and run "mjpg-streamer":
$ cd /root/C/mjpg-streamer $ make $ ./start.sh
You need to change the start.sh script and make sure it uses a correct /dev/videoX node. You can check your camera's node by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install v4l-utils $ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -D Driver Info (not using libv4l2): Driver name : sun6i-video Card type : sun6i-csi Bus info : platform:camera Driver version: 4.14.0 ...
The above messages indicate that "/dev/video0" is camera's device node.The mjpg-streamer application is an open source video steam server. After it is successfully started the following messages will be popped up:
$ ./start.sh i: Using V4L2 device.: /dev/video0 i: Desired Resolution: 1280 x 720 i: Frames Per Second.: 30 i: Format............: YUV i: JPEG Quality......: 90 o: www-folder-path...: ./www/ o: HTTP TCP port.....: 8080 o: username:password.: disabled o: commands..........: enabled
start.sh runs the following two commands:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$(pwd)" ./mjpg_streamer -i "./input_uvc.so -d /dev/video0 -y 1 -r 1280x720 -f 30 -q 90 -n -fb 0" -o "./output_http.so -w ./www"
Here are some details for mjpg_streamer's major options:
-i: input device. For example "input_uvc.so" means it takes input from a camera;
-o: output device. For example "output_http.so" means the it transmits data via http;
-d: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's device node;
-y: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's data format: 1:yuyv, 2:yvyu, 3:uyvy 4:vyuy. If this option isn't defined MJPEG will be set as the data format;
-r: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's resolution;
-f: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's fps. But whether this fps is supported depends on its driver;
-q: input device's subparameter. It defines the quality of an image generated by libjpeg soft-encoding;
-n: input device's subparameter. It disables the dynctrls function;
-fb: input device's subparameter. It specifies whether an input image is displayed at "/dev/fbX";
-w: output device's subparameter. It defines a directory to hold web pages;
In our case the board's IP address was 192.168.1.230. We typed 192.168.1.230:8080 in a browser and were able to view the images taken from the camera's. Here is what you would expect to observe:

The mjpg-streamer utility uses libjpeg to software-encode steam data. The Linux-4.14 based ROM currently doesn't support hardware-encoding. If you use a H3 boards with Linux-3.4 based ROM you can use the ffmpeg utility to hardware-encode stream data and this can greatly release CPU's resources and speed up encoding:
$ ffmpeg -t 30 -f v4l2 -channel 0 -video_size 1280x720 -i /dev/video0 -pix_fmt nv12 -r 30 \ -b:v 64k -c:v cedrus264 test.mp4
By default it records a 30-second video. Typing "q" stops video recording. After recording is stopped a test.mp4 file will be generated.
7.14 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
The FA-CAM202 is a 200M USB camera. Connect your board to camera module. Then boot OS, connect your board to a network, log into the board as root and run "mjpg-streamer":
$ cd /root/C/mjpg-streamer $ make $ ./start.sh
You need to change the start.sh script and make sure it uses a correct /dev/videoX node. You can check your camera's node by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install v4l-utils $ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -D Driver Info (not using libv4l2): Driver name : uvcvideo Card type : HC 3358+2100: HC 3358+2100 / USB 2.0 Camera: USB 2.0 Camera Bus info : usb-1c1b000.usb-1 ...
The above messages indicate that "/dev/video0" is camera's device node.The mjpg-streamer application is an open source video steam server. After it is successfully started the following messages will be popped up:
$ ./start.sh i: Using V4L2 device.: /dev/video0 i: Desired Resolution: 1280 x 720 i: Frames Per Second.: 30 i: Format............: YUV i: JPEG Quality......: 90 o: www-folder-path...: ./www/ o: HTTP TCP port.....: 8080 o: username:password.: disabled o: commands..........: enabled
start.sh runs the following two commands:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$(pwd)" ./mjpg_streamer -i "./input_uvc.so -d /dev/video0 -y 1 -r 1280x720 -f 30 -q 90 -n -fb 0" -o "./output_http.so -w ./www"
Here are some details for mjpg_streamer's major options:
-i: input device. For example "input_uvc.so" means it takes input from a camera;
-o: output device. For example "output_http.so" means the it transmits data via http;
-d: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's device node;
-y: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's data format: 1:yuyv, 2:yvyu, 3:uyvy 4:vyuy. If this option isn't defined MJPEG will be set as the data format;
-r: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's resolution;
-f: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's fps. But whether this fps is supported depends on its driver;
-q: input device's subparameter. It defines the quality of an image generated by libjpeg soft-encoding;
-n: input device's subparameter. It disables the dynctrls function;
-fb: input device's subparameter. It specifies whether an input image is displayed at "/dev/fbX";
-w: output device's subparameter. It defines a directory to hold web pages;
In our case the board's IP address was 192.168.1.230. We typed 192.168.1.230:8080 in a browser and were able to view the images taken from the camera's. Here is what you would expect to observe:

7.15 Check CPU's Working Temperature
You can get CPU's working temperature by running the following command:
$ cpu_freq
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHzThis message means there are currently four CPUs working. All of their working temperature is 26.5 degree in Celsius and each one's clock is 624MHz.
Set CPU frequency:
$ cpu_freq -s 1008000
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
7.16 Test Infrared Receiver
Note: Please Check your board if IR receiver exist.
By default the infrared function is disabled you can enable it by using the npi-config utility:
$ npi-config
6 Advanced Options Configure advanced settings
A8 IR Enable/Disable IR
ir Enable/Disable ir[enabled]Reboot your system and test its infrared function by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install ir-keytable $ echo "+rc-5 +nec +rc-6 +jvc +sony +rc-5-sz +sanyo +sharp +mce_kbd +xmp" > /sys/class/rc/rc0/protocols # Enable infrared $ ir-keytable -t Testing events. Please, press CTRL-C to abort.
"ir-keytable -t" is used to check whether the receiver receives infrared signals. You can use a remote control to send infrared signals to the receiver. If it works you will see similar messages as follows:
1522404275.767215: event type EV_MSC(0x04): scancode = 0xe0e43 1522404275.767215: event type EV_SYN(0x00). 1522404278.911267: event type EV_MSC(0x04): scancode = 0xe0e42 1522404278.911267: event type EV_SYN(0x00).
7.17 Run Qt Demo
Run the following command
$ sudo /opt/QtE-Demo/run.sh
Here is what you expect to observe. This is an open source Qt Demo:
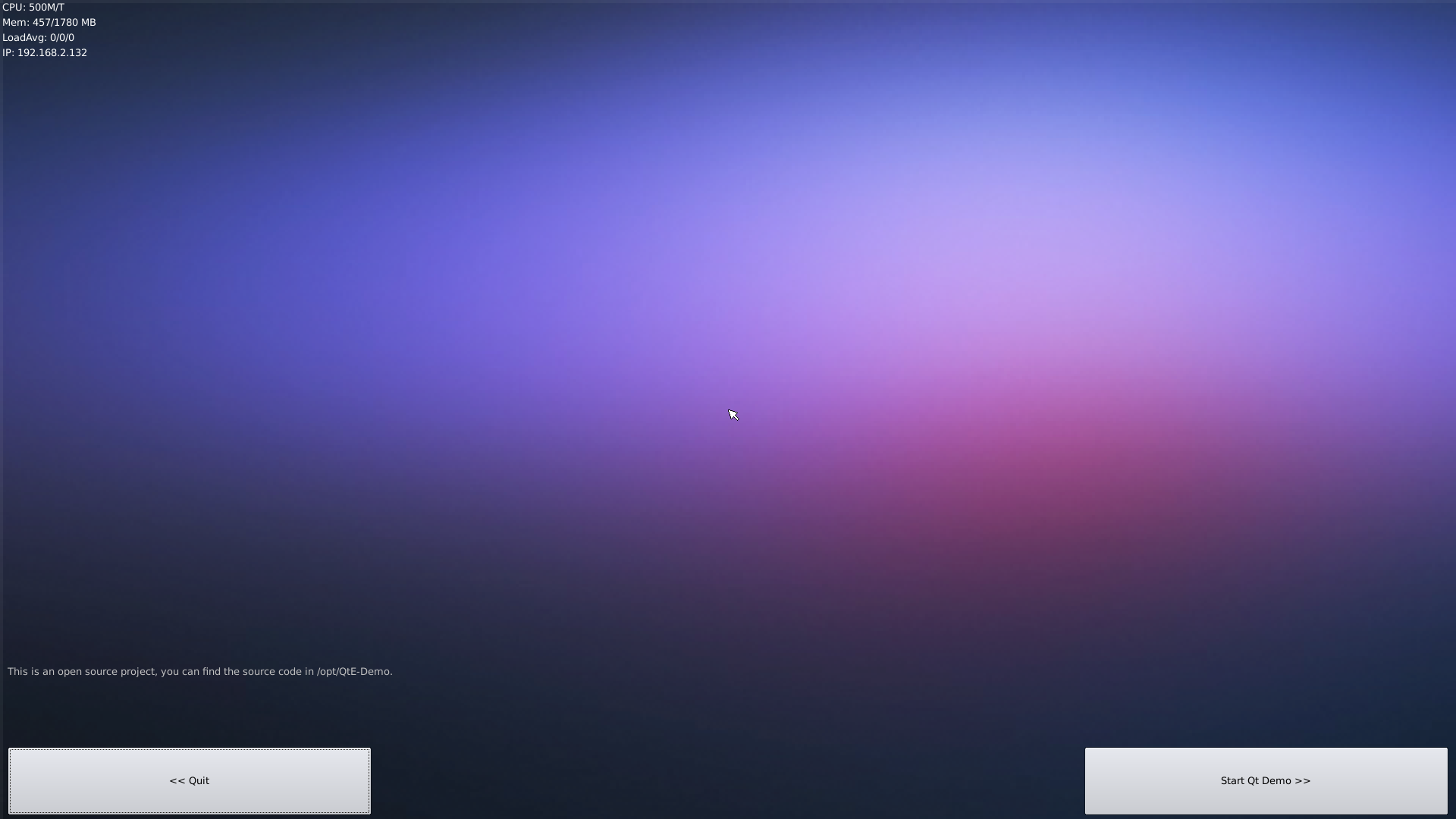
7.18 How to install and use docker (for armhf system)
7.18.1 How to Install Docker
Run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker.io
7.18.2 Test Docker installation
Test that your installation works by running the simple docker image:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/debian-jessie-arm-docker cd debian-jessie-arm-docker ./rebuild-image.sh ./run.sh
8 Make Your Own Linux System
8.1 Make Image Based on Linux-4.14 BSP
The NanoPi M1 supports the Linux-4.14 kernel which is mainly maintained and supported by open source communities. FriendlyElec ported this kernel to the NanoPi M1.
Here is a reference link to more details about how to make image files for Allwinner H3 based on mainline U-boot and Linux-4.14:Building U-boot and Linux for H5/H3/H2+
8.2 Make Image Based on Linux-3.4 BSP
The Linux3.4 BSP is provided by Allwinner. FriendlyElec ported this to the NanoPi M1.
8.2.1 Preparations
Get lichee source:
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/h3_lichee.git lichee --depth 1
Note: "lichee" is the project name named by Allwinner for its CPU's source code which contains the source code of U-boot, Linux kernel and various scripts.
8.2.2 Install Cross Compiler
Visit this site download link, enter the "toolchain" directory, download the cross compiler "gcc-linaro-arm.tar.xz" and copy it to the "lichee/brandy/toochain/" directory.
8.2.3 Compile lichee Source Code
Compilation of the H3's BSP source code must be done under a PC running a 64-bit Linux.The following cases were tested on Ubuntu-14.04 LTS-64bit:
$ sudo apt-get install gawk git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ libgl1-mesa-dev g++-multilib mingw32 tofrodos \ python-markdown libxml2-utils xsltproc zlib1g-dev:i386
Enter the lichee directory and run the following command to compile the whole package:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1 -p linux -t all
After this compilation succeeds a u-boot, Linux kernel and kernel modules will be generated
Note: the lichee directory contains a cross-compiler we have setup. When you compile the source code it will automatically call this cross-compiler.
8.2.4 Compile U-boot
Note:you need to compile the whole lichee directory before you can compile U-boot individually.
You can run the following commands to compile U-boot:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1-plus -p linux -t u-boot
The gen_script.sh script patches the U-boot with Allwinner features. A U-boot without these features cannot work.
Type the following command to update the U-boot on the MicroSD card:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./fuse.sh -d /dev/sdX -p linux -t u-boot
Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system.
8.2.5 Compile Linux Kernel
Note:you need to compile the whole lichee directory before you can compile Linux kernel individually.
If you want to compile the Linux kernel run the following command:
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1 -p linux -t kernel
After the compilation is done a boot.img and its kernel modules will be generated under "linux-3.4/output".
8.2.6 Clean Source Code
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1 -p linux -t clean
9 Applications under Android
9.1 USB WiFi
The rtl8188etv/rtl8188eu USB WiFi modules are supported in Android.
9.2 IR Controller(RC-100)
You can use FriendlyARM's IR controller(RC-100) to navigate the Android system.
Here is a list of the function keys on the RC-100 IR controller
Key Function POWER On/Off F1 Search F2 Open Browser F3 Enable/Disable Mouse UP Move Up DOWN Move Down LEFT Move Left RIGHT Move Right OK OK Volume- Turn Down Volume Mute Mute Volume+ Turn Up Volume SETTING Go to Setting Window HOME Go to Home Window BACK Go Back to the Previous Window
After Android is loaded for the first time you need to follow the prompts on Android's GUI to enter the main window and then press F3 to enable mouse and complete the setup process by navigating "up", "down", "left", "right" and "OK".
9.3 Play 4K Video
Visit this the test-video directory of this link download link and download the 4K video file: 4K-Chimei-inn-60mbps.mp4 and copy it to an SD card or USB drive.
Boot Android on your M1(512M RAM) and insert this SD card or USB drive to your M1. After locate the 4K video file with ESFileExplorer click on and play it with Android's Gallery player.
In our test playing this 4K video file from a USB drive worked better.
10 Make Your Own Android
10.1 Preparations
- Compilation of the H3's BSP source code must be done under a PC running a 64-bit Linux.The following cases were tested on Ubuntu-14.04 LTS-64bit:
$ sudo apt-get install gawk git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ libgl1-mesa-dev g++-multilib mingw32 tofrodos \ python-markdown libxml2-utils xsltproc zlib1g-dev:i386
- Generating an Android image relies on the scripts in the lichee's source code. Therefore you need to clone lichee's source code:
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/h3_lichee.git lichee
Note:lichee is the name of the project in which Allwinner provides support for its CPUs. The lichee source code includes the source code of U-boot, Linux and various scripts. You cannot rename the "lichee" directory.
- Clone Android Source Code:
$ git clone https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/h3_android-4.4 android
Since generating an Android image relies on the scripts in the lichee's source code. Therefore you need to clone the Android source code under the same directory where lichee is located and name the cloned directory "android":
$ ls ./ android lichee
- Install Cross Compiler:
In order to compile the lichee source code you need to visit this site download link, enter the "toolchain" directory, download the cross compiler "gcc-linaro-arm.tar.xz" and copy it to the "lichee/brandy/toochain/" directory.
10.2 Compile Android
- Setup Environment
Run the following commands on a host PC running 64-bit Ubuntu-14.04 LTS-64bit:
$ sudo apt-get install bison g++-multilib git gperf libxml2-utils make python-networkx zip flex libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk minicom
For more details refer to:android_initializing。
- Install JDK
We used the JDK1.6.0_45. You can get it from Oracle: Oracle JDK . In our test we installed it in the /usr/lib/jvm/ directory.
- Compile System
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1 -p android -t all # compile lichee's source code and this will generate a kernel and drivers for Android. $ cd ../../android $ export PATH=/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.6.0_45/bin:$PATH $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1 # compile android's source code and this will generate an Android image file.
After the above commands are finished an Android image "sun8iw7p1_android_nanopi-m1_uart0.img" will be generated under the "lichee/tools/pack/" directory.
10.3 Clean Source Code
$ cd lichee/fa_tools/ $ ./build.sh -b nanopi-m1 -p android -t clean
11 Developer Guide
11.1 CVBS
12 More OS Support
12.1 Ubuntu-MATE
Ubuntu-Mate is a Ubuntu variant and its GUI is Mate-desktop. You can login via SSH when you connect a NanoPi M1 to an HDMI monitor
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it
- Go to this link download link to download the image file nanopi-m1-ubuntu-mate-sd4g.img.zip
- Uncompress it and flash the image file to a TF card with win32diskimager under Windows
- After it is done you can boot your NanoPi M1 with this card
- Login name: "root" or "fa", Password: fa
12.2 DietPi_NanoPiNEO-armv7-(Jessie)
DietPi is an extremely lightweight Debian Jessie OS. Its image file starts at 400MB and nearly 3x lighter than 'Raspbian Lite'.It is pre-installed with DietPi-RAMLog. These features enable users to get the best performance of a device.
The following steps are for reference only. FriendlyElec doesn't provide technical support for them.
Installation guide:
- Download the image file "DietPi_NanoPiNEO-armv7-(Jessie)" from DietPi_NanoPiNEO-armv7-(Jessie)
- Extract the package and use the win32diskimager to write it to a MicroSD card under Windows.
- Insert this MicroSD card to your NanoPi M1 and power up.
Username:root , Password: dietpi
12.3 Debian8(Jacer)
Debian8(Jacer) is a Debian 8 variant developed by a developer "Jacer". It uses Debian 8's desktop and has good support for the Chinese language. Users need to run this OS with an HDMI monitor and can login to the system via SSH.
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
- Please visit here :download link to download its image file Debian8(unofficial-Jacer).rar.
- Uncompress it and flash the image file to a TF card with win32diskimager under Windows.
- After it is done you can boot your NanoPi M1 with this card
- Login name: "fa", Password: fa
Note: When the NanoPi M1 is connected to an HDMI monitor and runs Debian8(Jacer) we don't suggest login to the system as root. If you do that the HDMI monitor will show black instead of a Debian8 GUI;
Debian8(Jacer) is integrated with GPU drivers, H264 and H265 hard decoding code. It defaults to the HDMI 720P configuration. If you want to modify its resolution to 1080P you can set the "HDMI MODE =" setting in the script.fex (under the "/boot" section) to the 1080P definition and use the corresponding script.bin file. For more details refer to the h3disp.sh file;
Debian8(Jacer) supports these WiFi card models: 8192cu, 8188cus, 8188eu, rt3070.
Debian8(Jacer)has the following support too:
- 1.Mali400 GPU driver
- 2.mpv hard decoding H264, H265
- 3.Chromium and flash
- 4.Netease's feeluown
- 5.Games such as Chess and Minesweeper
- 6.retroarch game simulator
- 7.Virtual memory
- 8.Dynamic frequency scaling
- 9.aria2 download utility
- 10.samba
- 11.WiFi cards: 8192cu/8188cus/8188eu/rt3070/rt2800/rt5370
- 12.GIMP utility
- 13.SSH
- 14.xrdp and vnc
- 15.HTML5 media player
- 16.goldendict
- 17.audacious music player
- 18.pulseaudio volume control utility
- 19.USB bluetooth
12.4 Android(Jacer)
Android(Jacer) is an Android4.4.2 variant developed by a developer "Jacer". It uses Android's desktop. Users need to run this OS with an HDMI monitor and can login to the system via SSH.
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
- Download image files and utilities
1. Please visit here :download link to download its image file Android(Beelink_X2_v205k4_for_NanoPiM1).
2. Download Windows utility (HDDLLF.4.40) for formatting a TF card.
3. Download Windows utility (PhoenixCard) for flashing Android image files.
- Make Android TF Card
1. On a Windows PC run the HDDLLF.4.40 utility as administrator. Insert a TF card(at least 4G) into this PC and format it. After formatting is done take out the TF card;
2. Insert it into the PC again and format it with Windows internal format utility to format it to FAT32. After this formatting is done take out the card;
3. Insert the TF card you made in the previous step into a Windows PC and run the PhoenixCard_V310 utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your TF card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the TF card.
Note: none of the above steps should be missed otherwise the TF card you made may not work.
- Boot Android
1. Insert an installation TF card into an M1, power on the board and you will be able to work with it
Android(Jacer) supports these WiFi cards: rtl8188etv, rt8188eus and rt8189.
Android(Jacer) has the following features:
- 1. the menu bar can be set hidden; a power button can be added; dynamic frequency scaling is enabled
- 2. GAAPS
- 3. it supports rtl8188etv/eus 8189 WiFi cards and CSR bluetooth
- 4. relative low working voltage and low working temperature
For details about its full features try it by yourself:)
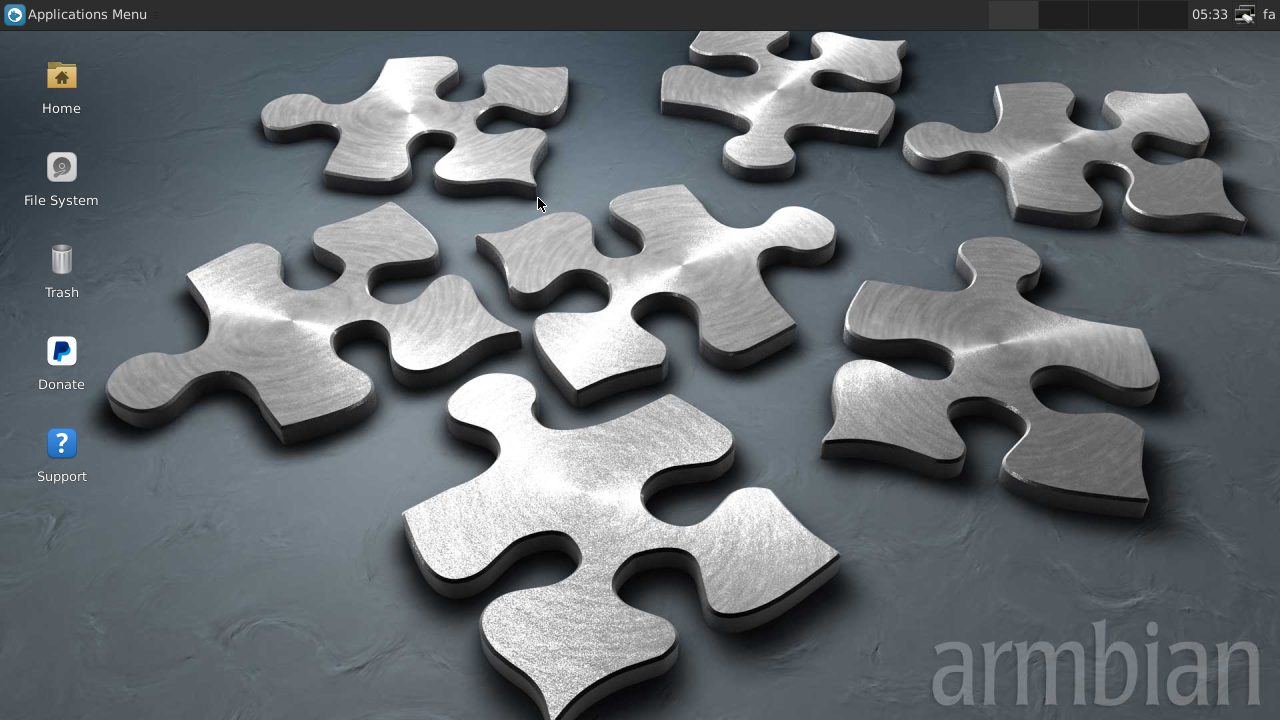
12.5 Armbian
For image download links and instructions visit Armbian's page for the NanoPi M1:armbian-m1
Armbian provides a server and a desktop versions. Here is how the desktop GUI looks like:

12.6 OpenWRT
OpenWRT was migrated to the M1 by one hobbyist "Tom".
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
- Visit download link to download openwrt-sunxi-NanoPi_M1-sdcard-vfat-ext4.img(unofficail-ROMs directory).
- Uncompress the file and you will get openwrt-sunxi-NanoPi_M1-sdcard-vfat-ext4.img.
- Insert a microSD to a host PC running Ubuntu and check the SD card's device name by using the following command
dmesg | tail
Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card is recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions"
- Go to the directory where openwrt-sunxi-NanoPi_M1-sdcard-vfat-ext4.img is located and run the following command to flash the image to your MicroSD card:
dd if=openwrt-sunxi-NanoPi_M1-sdcard-vfat-ext4.img of=/dev/sdx
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
- After it is done insert the card to your board and power on. Here is what you expect to observe.
13 Download Link to Image Files
- Image files: [2]
14 3D Housing Printing Files
- NanoPi M1 3D housing printing files:[3]
15 Matrix Compact Kit B:A Good Kit for Starters
- Matrix - Compact Kit B:click to visit
16 Resources
16.1 User's Manual & Datasheets
- Schematic
- Dimensional Diagram
- Allwinner H3 datasheet Allwinner_H3_Datasheet_V1.2.pdf
16.2 Development Guide
- Matrix Modules & Wiki Sites:
- Button
- LED
- A/D Converter
- Relay
- 3-Axis Digital Accelerometer
- 3-Axis Digital Compass
- Temperature Sensor
- Temperature & Humidity Sensor
- Buzzer
- Joystick
- I2C(PCF8574)+LCD1602
- Sound Sensor
- Ultrasonic Ranger
- GPS
- Matrix - Compact Kit
- Fire Sensor
- CAM500A Camera
- BAll Rolling Switch
- 2'8 SPI Key TFT 2.8" SPI LCD
- IR Counter
- IR Receiver
- L298N Motor Driver
- MQ-2 Gas Sensor
- MQ-3 Gas Sensor
- One_Touch_Sensor
- _Photoresistor
- _Potentiometer
- Pressure & Temperature Sensor
- RGB LED
- RTC
- Rotary Encoder
- Soil Moisture Sensor
- Thermistor
- USB WiFi
- Water Sensor
17 Update Log
17.1 March-22-2016
- Released English Version
17.2 March-29-2016
- Corrected expression errors
17.3 Apr-02-2016
- Rewrote sections 4.3, 5, 6 and 8
17.4 Apr-15-2016
- Added sections 5.10, 5.11, 7 and 9
- Rewrote sections 5.9, 6.2
17.5 Apr-18-2016
- Update Features sections, "DDR3 RAM: 512MB" to "DDR3 RAM: 512MB/1GB"
- Update Board Dimension to 1603B
- Add dxf file and Schematic of 1603B to Resources section
17.6 July-07-2016
- Added sections 7, 9.5, 9.6 and 11
17.7 Sep-08-2016
- Added sections 5.10
- Updated sections 5.11
17.8 Nov-03-2016
- Updated section 5.10
17.9 Dec-09-2016
- Updated section 5.8, 6.1, 8.1 and 8.3
- Added section 7.3
17.10 Jan-30-2017
- Added section 6.2, 8.2 and 9.3
17.11 June-4-2017
- Added section 3: software features
- Added section 10: setup compiler for user space programs
17.12 June-15-2017
- Added section 7: UbuntuCore
- Updated section 10
17.13 July-8-2017
- Updated section 6.8
17.14 March-28-2018
- Added section 11.1
17.15 August-1-2018
- Updated section 10
17.16 Dec-19-2018
- Updated section 8