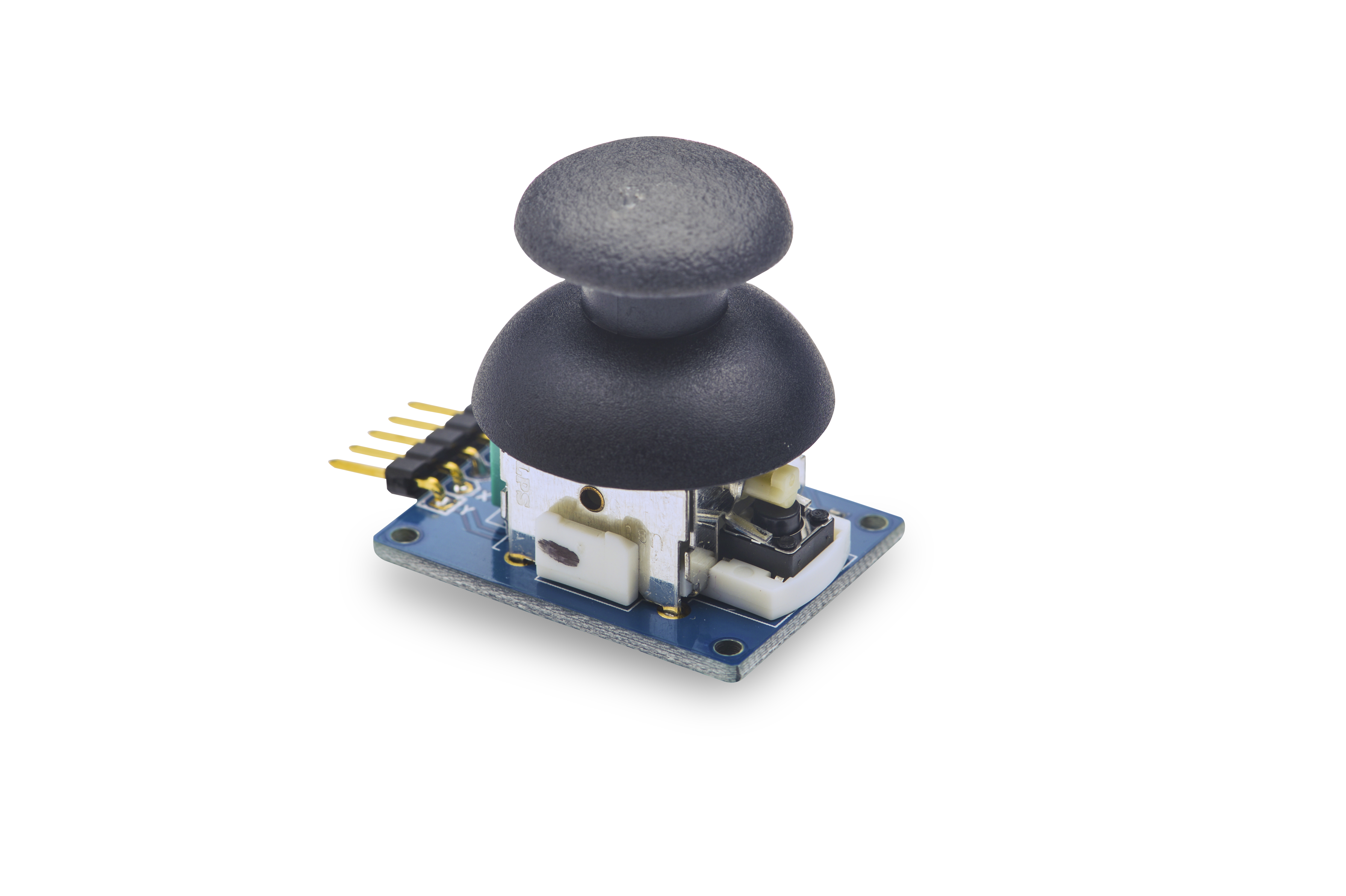
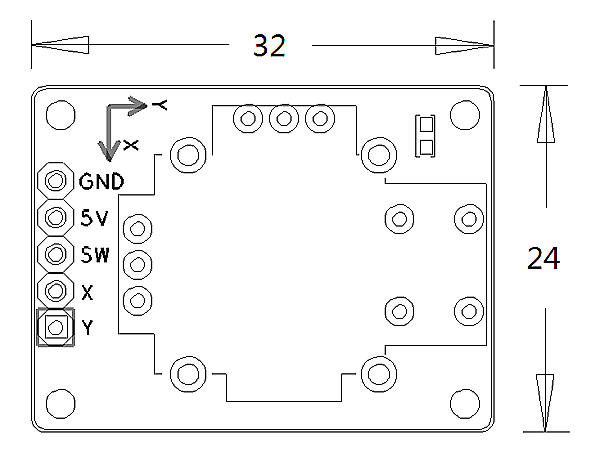
Matrix - Joystick
Contents
1 Introduction
- The matrix-joystick module is a two-axis stick module. It consists of two Sliding rheostats and one button. It has two analog outputs and one digital output. Its positional states can be measured as X and Y axis values as the calibrated resistance of the two potentiometers.
- When you move the joystick the sliding rheostats' resistance will change and the corresponding x/y values will change too. When you push the joystick the SW level will turn low.
2 Features
- X and Y axis, and one button
- 2.54mm spacing pin
- PCB dimension(mm): 24 X 32
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| GND | Ground |
| 5V | Power 5V |
| SW | Button |
| X | X Axis |
| Y | Y Axis |
3 Basic Device Operation
- It has two analog outputs and one digital output. The two analog outputs are measured as X and Y values as the calibrated resistance of the two potentiometers. The digital output is measured as Z value indicating whether or not the button is pressed.
- 为了更加方便地配合扩展板等标准接口,在设计上把 X,Y,Z 轴的电路都单独引出,以控制输入这个操纵杆模块的 x、y、z 的值以及在特定的值下实现某种功能。We extend all three outputs: X, Y and Z.
4 Download Matrix Source Code
All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
Each branch in this hub contains the matrix modules' code samples for a board that the matrix modules can work with.
- The nanopi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi
- The tiny4412 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the Tiny4412
- The raspberrypi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the RaspberryPi
Please follow the steps below to get the source code:
Install the git utility on a PC running Ubuntu14.04
$ sudo apt-get install git
Clone the matrix code from GitHub
$ git clone git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples.
5 Connect to NanoPi
5.1 Preparations
Please install a Debian on a NanoPi and an appropriate cross compiler on a PC. Please refer to wiki: NanoPi
Compile a NanoPi kernel. Note: please use the kernel's source code from the nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix branch.
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-4.x.y.git $ cd linux-4.x.y $ git checkout nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix $ make nanopi_defconfig $ touch .scmversion $ make
5.2 Hardware Connection
Please refer to the following connection diagram to connect the Matrix-Joystick and Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter to the NanoPi
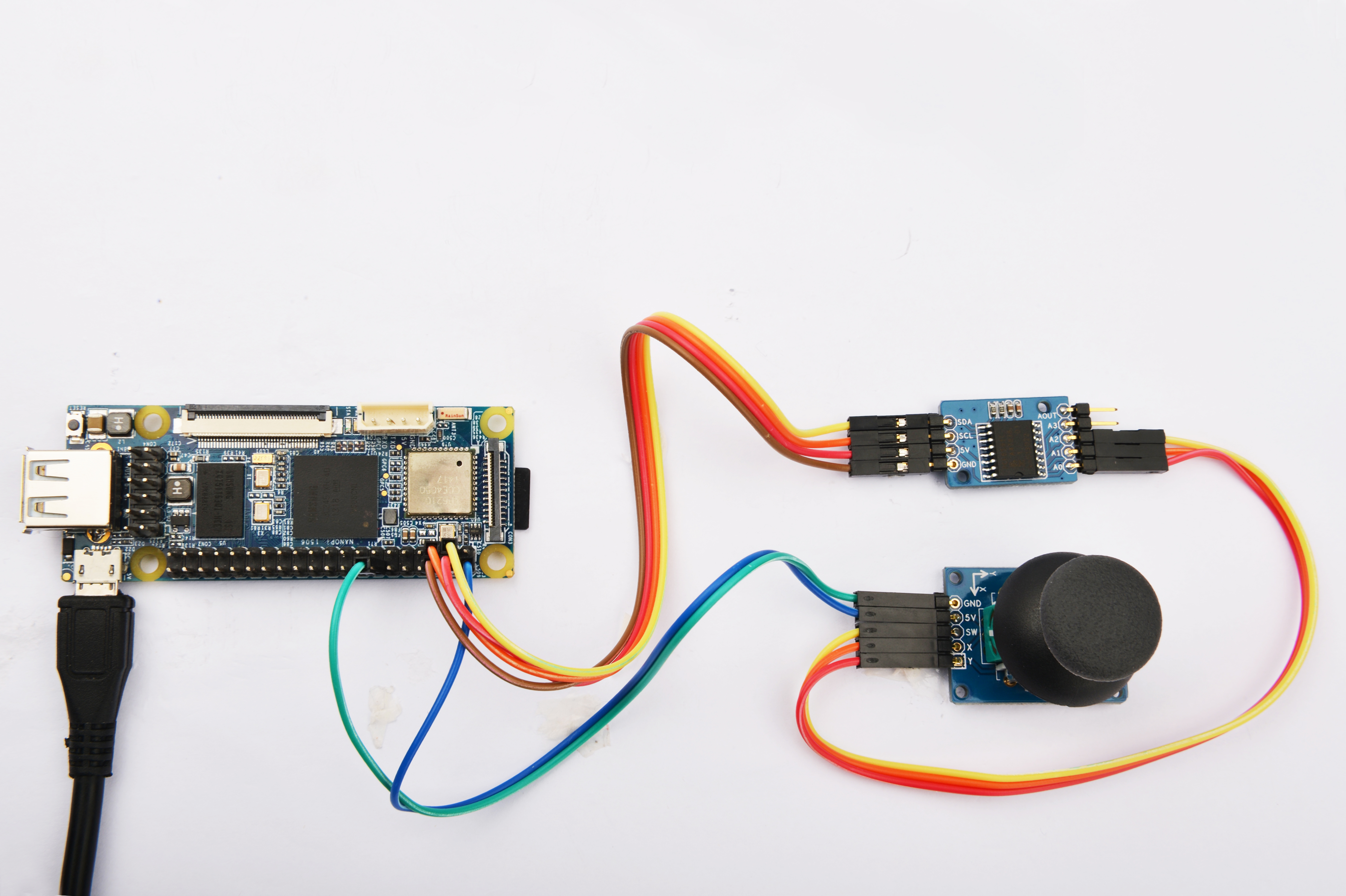
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Joystick | |
| GND | NanoPi Pin14 |
| 5V | NanoPi Pin2 |
| SW | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 |
| X | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 |
| Y | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A0 |
5.3 Compile Test Program
Please login the matrix hub and enter the nanopi branch
$ cd matrix $ git checkout nanopi
Compile the matrix code
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the NanoPi-Debian.
Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. Applications are under the "install/usr/bin" directory. The test program for the "Matrix-Joystick" module is "matrix-joystick".
5.4 Run Test Program
Please copy the library files and test program to the NanoPi
$ cp install/usr/bin/* nanopi_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* nanopi_rootfs/lib/ -d
Power on the NanoPi and run the following command in Debian's terminal
$ matrix-joystick5.5 Code Sample
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int mode = 0x0; if ((devFD = pcf8591Init()) == -1) { printf("Fail to init pcf8591 AD\n"); return -1; } if (pcf8591SetCtrl(devFD, PCF8591_INIT_AD_CONTROL) == -1) { printf("Fail to Set pcf8591 control AD\n"); pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return -1; } int i = 0; int x, y, z; signal(SIGINT, PS2Handler); for (i=0; i<PS2_READ_TIMES; i++) { x = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL0); y = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL1); z = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL2); if (z > SW_TRIGGER) { z = 0; } else { z = 1; } printf("X=%3d Y=%3d Z=%d\n", x, y, z); sleep(1); } pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return 0; }
6 与Tiny4412连接使用
6.1 准备工作
参考Tiny4412光盘里的《友善之臂Ubuntu使用手册》,在Tiny4412上运行UbuntuCore系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。
注意:只能使用Tiny4412SDK-1506的底板。
6.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-Joystick、模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter和Tiny4412
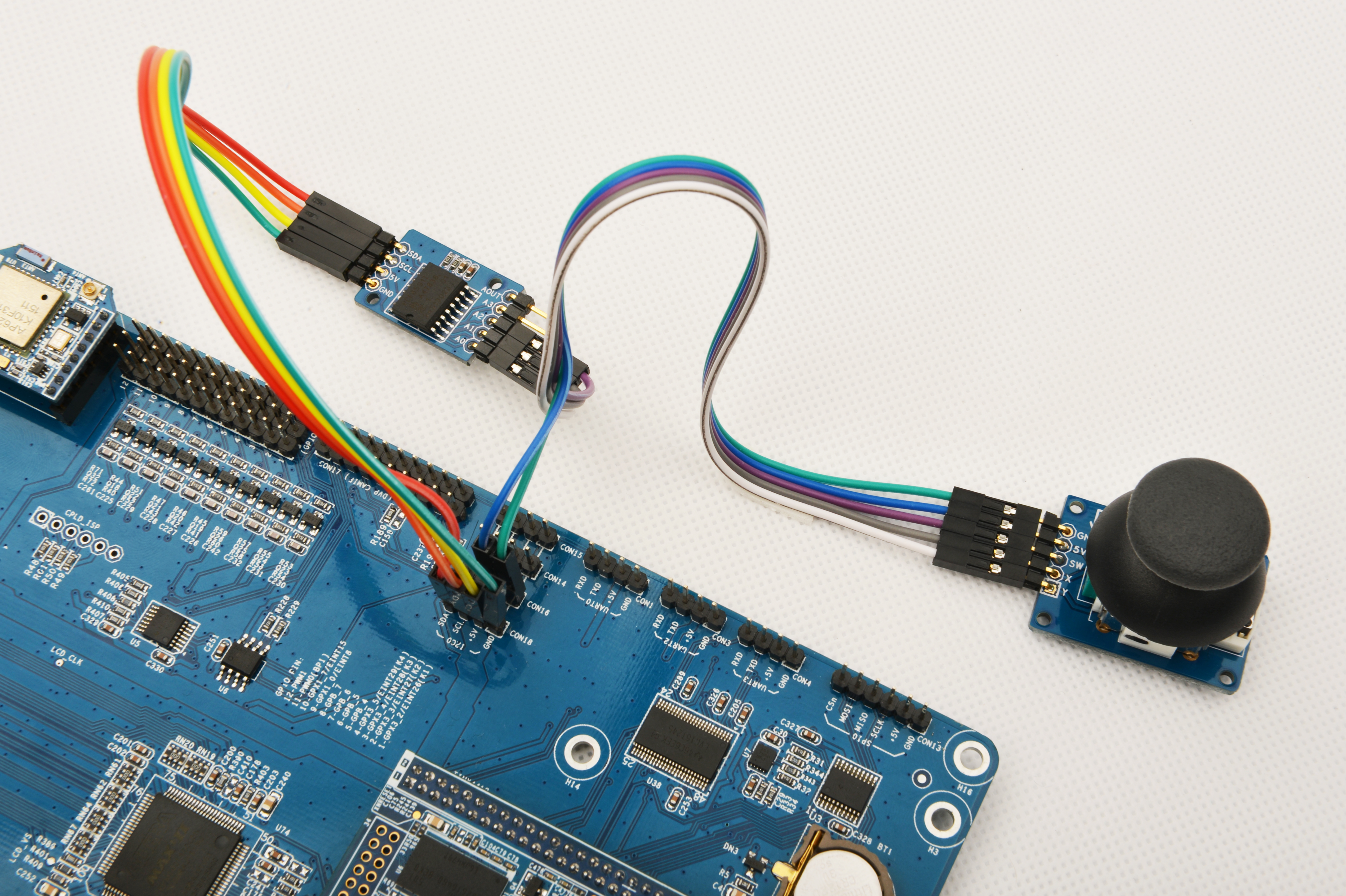
连接说明:
| Matrix-Joystick | |
| GND | Tiny4412 CON16 GND |
| 5V | Tiny4412 CON16 5V |
| SW | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A2 |
| X | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A1 |
| Y | Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter A0 |
6.3 编译测试程序
进入matrix代码仓库,切换到tiny4412分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout tiny4412
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为Tiny4412-UbuntuCore配套的arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-4.7.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-Joystick对应的测试程序为matrix-joystick。
6.4 运行测试程序
拷贝库文件和测试程序到Tiny4412的UbuntuCore的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* tiny4412_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* tiny4412_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动Tiny4412,在UbuntuCore的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-Joystick的测试程序
$ matrix-joystick6.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int mode = 0x0; if ((devFD = pcf8591Init()) == -1) { printf("Fail to init pcf8591 AD\n"); return -1; } if (pcf8591SetCtrl(devFD, PCF8591_INIT_AD_CONTROL) == -1) { printf("Fail to Set pcf8591 control AD\n"); pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return -1; } int i = 0; int x, y, z; signal(SIGINT, PS2Handler); for (i=0; i<PS2_READ_TIMES; i++) { x = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL0); y = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL1); z = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL2); if (z > SW_TRIGGER) { z = 0; } else { z = 1; } printf("X=%3d Y=%3d Z=%d\n", x, y, z); sleep(1); } pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return 0; }