Difference between revisions of "Matrix - Analog to Digital Converter"
(→Resources) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
3. The on-chip D/A converter and a high-gain comparator are used temporarily during an A/D conversion cycle. An A/D conversion cycle is always started after sending a valid read mode address to a PCF8591 device. The A/D conversion cycle is triggered at the trailing edge of the acknowledge clock pulse and is executed while transmitting the result of the previous conversion。 <br> | 3. The on-chip D/A converter and a high-gain comparator are used temporarily during an A/D conversion cycle. An A/D conversion cycle is always started after sending a valid read mode address to a PCF8591 device. The A/D conversion cycle is triggered at the trailing edge of the acknowledge clock pulse and is executed while transmitting the result of the previous conversion。 <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==硬件连接== | ||
| + | ===连接NanoPi M1=== | ||
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_nanopi_m1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 连接说明: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter || NanoPi M1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SDA || Pin3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SCL || Pin5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===连接NanoPi 2=== | ||
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_nanopi_2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 连接说明: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter || NanoPi 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SDA || Pin3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SCL || Pin5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===连接NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire=== | ||
| + | NanoPi M2和NanoPi 2 Fire的40 Pin引脚定义是一模一样的,所以它们操作Matrix配件的步骤是一样的,这里仅以NanoPi M2为例。<br> | ||
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_nanopi_M2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_nanopi_M2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 连接说明: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter || NanoPi M2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SDA || Pin3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SCL || Pin5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===连接NanoPC-T2=== | ||
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_NanoPC-T2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 连接说明: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter || NanoPC-T2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SDA || Pin6 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SCL || Pin5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || Pin29 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || Pin30 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==编译运行测试程序== | ||
| + | 启动开发板并运行Debian系统,进入系统后克隆Matrix代码仓库: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git | ||
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 克隆完成后会得到一个名为matrix的目录。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 编译并安装Matrix: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd matrix | ||
| + | $ make && make install | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 运行测试程序: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ matrix-adc | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br> | ||
| + | 运行效果如下:<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | The channel0 value is 2460 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 当通道0接到5V时,能得到最大值2550,当通道0接到地时,能得到最小值0。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==代码说明== | ||
| + | 所有的开发板都共用一套Matrix代码,本模块的测试示例代码为matrix-analog_to_digital_converter,内容如下: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
| + | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i = 0; | ||
| + | int value = 0; | ||
| + | int channel = 0; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (boardInit() < 0) { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to init board\n"); | ||
| + | return -1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (argc == 2) | ||
| + | channel = atoi(argv[1]); | ||
| + | system("modprobe "DRIVER_MODULE); | ||
| + | signal(SIGINT, intHandler); | ||
| + | for (i=0; i<ADC_READ_TIMES; i++) { | ||
| + | if (pcf8591Read(channel, &value) != -1) { | ||
| + | printf("The channel%d value is %d\n", channel, value); | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to get channel%d value\n", channel); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); | ||
| + | |||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | API说明参考维基:[[Matrix API reference manual/zh|Matrix API reference manual]] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!--- | ||
==Download Matrix Source Code== | ==Download Matrix Source Code== | ||
All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br> | All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br> | ||
| Line 329: | Line 463: | ||
==Connect to Arduino== | ==Connect to Arduino== | ||
| + | ---> | ||
| + | |||
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
Revision as of 09:35, 17 June 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
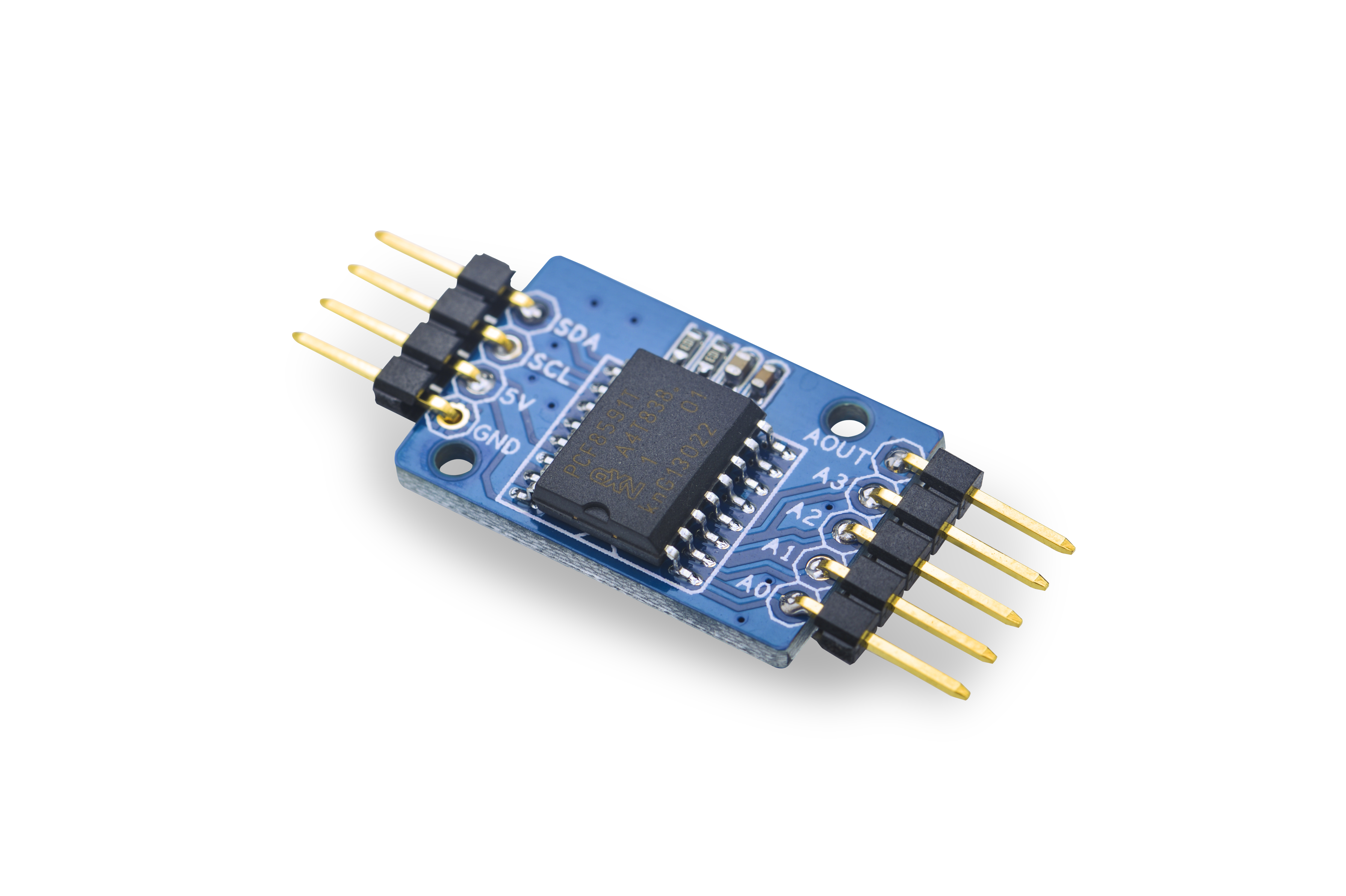
- The Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter is a single-chip, single-supply low-power 8-bit CMOS data acquisition device.
- It utilizes the PCF8591 chip with four analog inputs, one analog output and a serial I2C-bus interface. Three address pins A0, A1 and A2 are used for programming the hardware address, allowing
the use of up to eight devices connected to the I2C-bus without additional hardware. Address, control and data to and from the device are transferred serially via the two-line bidirectional I2C-bus. The maximum conversion rate is given by the maximum speed of the I2C-bus.
- The I2C hardware address is configured to 1001000x
- The operating supply voltage is from 2.5V to 6.0V,Among the 2.54 mm spacing pin header the 5V pin is the supply voltage. If you need 0 - 3.3V analog signals and keep the acquisition resolution you can connect it to a 3.3V supply voltage.
2 Features
- Wide range supply voltage: 2.5V - 6.0V
- I2C interface: 3.3V/5V
- 8-bit A/D x 4
- 8-bit D/A x 1
- Small and easy to be used in various situations
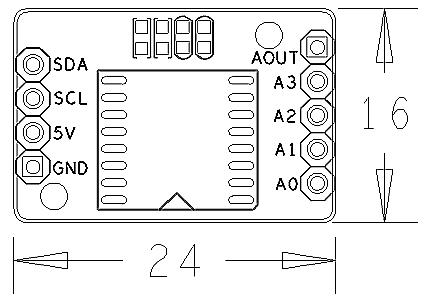
- 2.54 mm spacing pin
- PCB dimension (mm): 16 x 24
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| SDA | I2C SDA |
| SCL | I2C SCL |
| 5V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| GND | Ground |
| AOUT | Analog Output |
| A3 | Analog Input3 |
| A2 | Analog Input2 |
| A1 | Analog Input1 |
| A0 | Analog Input0 |
3 Basic Device Operation
The PCF8591's I2C-bus is for bidirectional, two-line communication between different ICs or modules. The two lines are a Serial DAta line (SDA) and a Serial CLock line (SCL). Both lines must
be connected to a positive supply via a pull-up resistor. Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy. The AINT0 - AINT4 pins are analog inputs which can be configured to single-ended or differential inputs. The supply voltage is 0 - VDD.
1. Each PCF8591 device in an I2C-bus system is activated by sending a valid address to the device. The address consists of a fixed part and a programmable part. The programmable part must be set according to the address pins A0, A1 and A2. The address is always sent as the first byte after the start condition in the I2C-bus protocol. The last bit of the address byte is the read/write-bit which sets the direction of the following data transfer.
2. The second byte sent to a PCF8591 device is stored in its control register and is required to control the device function. The upper nibble of the control register is used for enabling the analog output, and for programming the analog inputs as single-ended or differential inputs. The lower nibble selects one of the analog input channels defined by the upper nibble.
3. The on-chip D/A converter and a high-gain comparator are used temporarily during an A/D conversion cycle. An A/D conversion cycle is always started after sending a valid read mode address to a PCF8591 device. The A/D conversion cycle is triggered at the trailing edge of the acknowledge clock pulse and is executed while transmitting the result of the previous conversion。
4 硬件连接
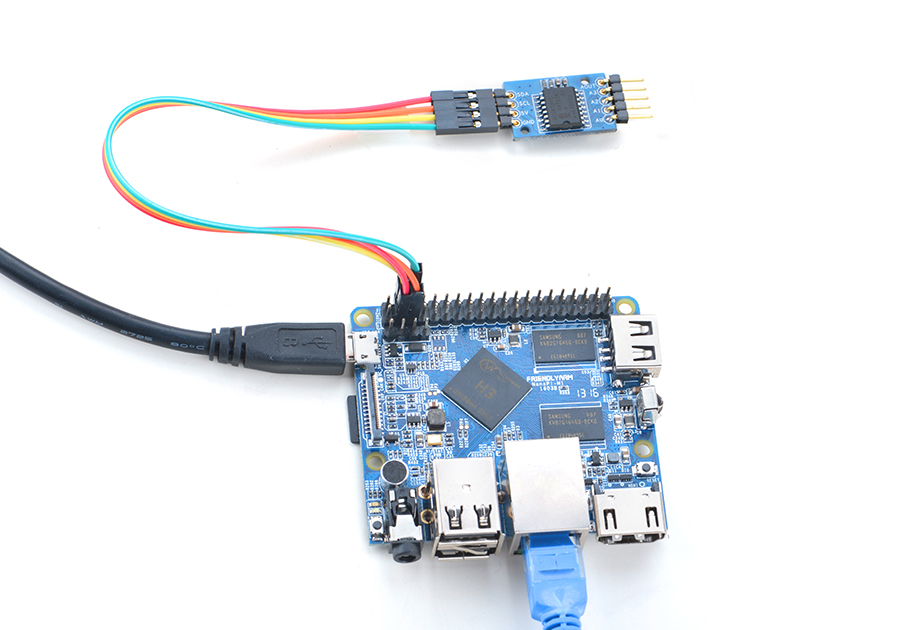
4.1 连接NanoPi M1
连接说明:
| Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter | NanoPi M1 |
| SDA | Pin3 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin4 |
| GND | Pin6 |
4.2 连接NanoPi 2
连接说明:
| Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter | NanoPi 2 |
| SDA | Pin3 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin4 |
| GND | Pin6 |
4.3 连接NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire
NanoPi M2和NanoPi 2 Fire的40 Pin引脚定义是一模一样的,所以它们操作Matrix配件的步骤是一样的,这里仅以NanoPi M2为例。
参考下图连接模块:
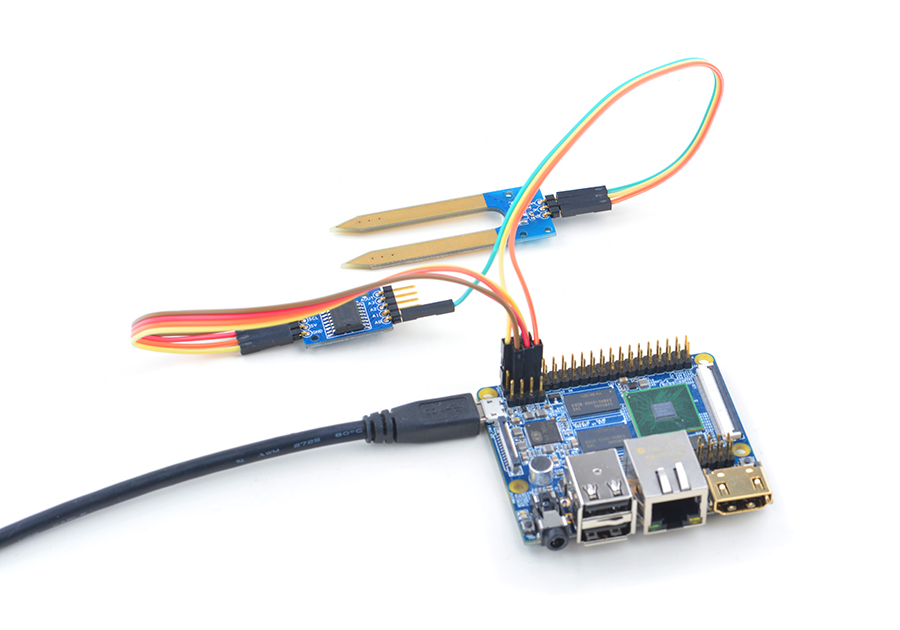
连接说明:
| Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter | NanoPi M2 |
| SDA | Pin3 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin4 |
| GND | Pin6 |
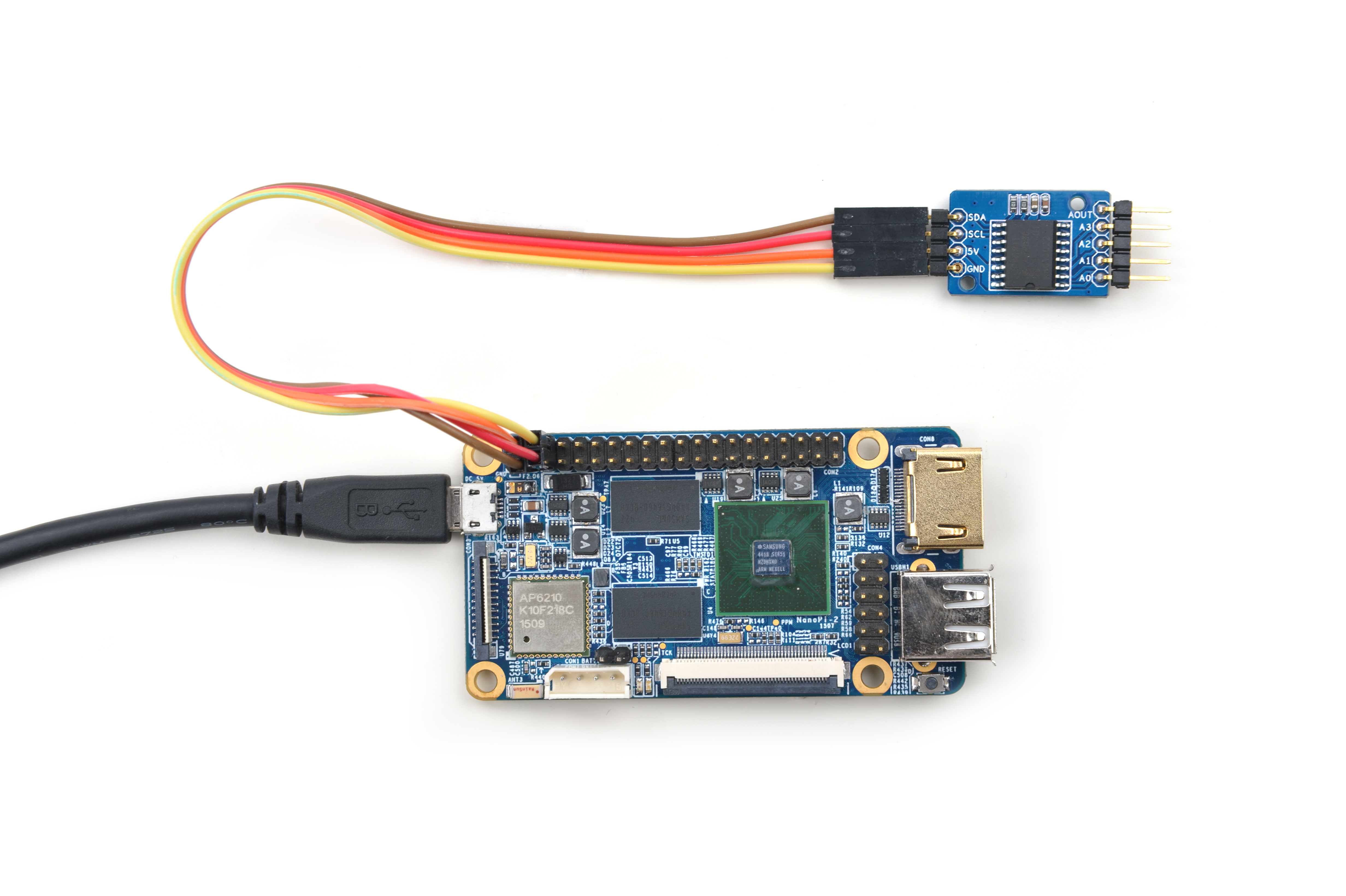
4.4 连接NanoPC-T2
参考下图连接模块:
Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter_NanoPC-T2
连接说明:
| Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter | NanoPC-T2 |
| SDA | Pin6 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin29 |
| GND | Pin30 |
5 编译运行测试程序
启动开发板并运行Debian系统,进入系统后克隆Matrix代码仓库:
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
克隆完成后会得到一个名为matrix的目录。
编译并安装Matrix:
$ cd matrix $ make && make install
运行测试程序:
$ matrix-adc注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。
运行效果如下:
The channel0 value is 2460当通道0接到5V时,能得到最大值2550,当通道0接到地时,能得到最小值0。
6 代码说明
所有的开发板都共用一套Matrix代码,本模块的测试示例代码为matrix-analog_to_digital_converter,内容如下:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int i = 0; int value = 0; int channel = 0; if (boardInit() < 0) { printf("Fail to init board\n"); return -1; } if (argc == 2) channel = atoi(argv[1]); system("modprobe "DRIVER_MODULE); signal(SIGINT, intHandler); for (i=0; i<ADC_READ_TIMES; i++) { if (pcf8591Read(channel, &value) != -1) { printf("The channel%d value is %d\n", channel, value); } else { printf("Fail to get channel%d value\n", channel); } } system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); return 0; }
API说明参考维基:Matrix API reference manual
7 Resources
8 Update Log
8.1 Feb-19-2016
- Added Section 5