|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | [[NanoPC-T6/zh|查看中文]] | + | [[NanoPC-T6 Armbian Installation Guide|English]] |
| − | <!--
| + | ==介绍== |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6-01B.jpg|thumb|Overview]]
| + | 本指南提供了在 NanoPC-T6 上安装和配置 Armbian 的详细说明,主要介绍如下内容: |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6-A01.jpg|thumb|Front]]
| + | * 擦除SPI Nor Flash和eMMC |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6-B01.jpg|thumb|Back]]
| + | * 烧录BootLoader到SPI Nor Flash |
| − | [[File:T6-01.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | * 从NVME引导Armbian系统 |
| − | [[File:T6-02.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:T6-03.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:T6-04.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | -->
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6LTS-01B.jpg|thumb|Overview]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6LTS-A01.jpg|thumb|Front]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6LTS-B01.jpg|thumb|Back]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:T6LTS-01.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:T6LTS-02.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:T6LTS-03.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | <!--
| + | |
| − | [[File:T6LTS-04.jpg|thumb|frameless|250x250px|Case]]
| + | |
| − | -->
| + | |
| − | ==Introduction== | + | |
| − | NanoPC-T6 LTS (as "T6") is a one-for-all high performance open source platform for edge computing, designed and developed by the FriendlyElec team. <br/><br/> | + | |
| − | It has two 2.5G Ethernet ports. It is based on Rockchip's RK3588, and has 4GB/8GB/16G LPDDR4x RAM and an optional 32GB/64GB/256/0GB eMMC flash. It works with systems including OpenMediaVault, FriendlyWrt, Android, Android TV, Debian, Ubuntu etc. It supports GPU and VPU acceleration.<br/><br/>
| + | |
| − | T6 is a compact board of 110 x 80 mm with rich hardware resources and an optional CNC metal case. It has 2 HDMI output ports and 1 HDMI IN port. T6 can play video streams including 8K60p H.265/VP9 , 8K30p H264 etc and record video streams including 4K60p H.265. T6 has one M.2 B-Key slot that supports an M.2 NVME SSD disk, one M.2 E-Key that supports an M.2 2230 WiFi module.<br/><br/>
| + | |
| − | In addition, T6 has one USB 3.0 and two USB 2.0 ports, and one full-featured USB-C port that is powered by DC-12V.<br/><br/>
| + | |
| − | In summary, T6 is well suited for enterprise customers to develop mini machine vision systems with multiple Ethernet ports and for embedded system hobbyists to explore and implement prototype designs.
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ==Hardware Spec== | + | ==前提条件== |
| − | * SoC: Rockchip RK3588
| + | 在开始之前,请确保你具备以下条件: |
| − | ** CPU: Quad-core ARM Cortex-A76(up to 2.4GHz) and quad-core Cortex-A55 CPU (up to 1.8GHz)
| + | * 一块有SPI Nor Flash的NanoPC T6开发板 |
| − | ** GPU: Mali-G610 MP4, compatible with OpenGLES 1.1, 2.0, and 3.2, OpenCL up to 2.2 and Vulkan1.2
| + | * 一条USB-C数据线 |
| − | ** VPU: 8K@60fps H.265 and VP9 decoder, 8K@30fps H.264 decoder, 4K@60fps AV1 decoder, 8K@30fps H.264 and H.265 encoder
| + | * 一块NVMe SSD固态硬盘 |
| − | ** NPU: 6TOPs, supports INT4/INT8/INT16/FP16
| + | * 一台运行Windows的PC |
| − | * RAM: 64-bit 4GB/8GB/16GB LPDDR4X at 2133MHz
| + | |
| − | * eMMC Flash: 32GB/64GB/256GB eMMC, at HS400 mode
| + | |
| − | * Nor Flash: 32MB SPI Nor Flash | + | |
| − | * microSD: support up to SDR104 mode | + | |
| − | * Ethernet: 2 x PCIe 2.5G Ethernet
| + | |
| − | * 1 x USB 3.0 Type-A,
| + | |
| − | * 1 x Full function USB Type‑C™ port, support DP display up to 4Kp60, USB 3.0
| + | |
| − | * 2 x USB 2.0 Type-A
| + | |
| − | * Video input:
| + | |
| − | ** 1 x Standard HDMI input port, up to 4Kp60
| + | |
| − | ** 2 x 4-lane MIPI-CSI, compatible with MIPI V1.2
| + | |
| − | * Video output:
| + | |
| − | ** 2 x Standard HDMI output ports
| + | |
| − | *** compatible with HDMI2.1, HDMI2.0, and HDMI1.4 operation
| + | |
| − | *** one support displays up to 7680x4320@60Hz, another one support up to 4Kp60
| + | |
| − | *** Support RGB/YUV(up to 10bit) format
| + | |
| − | ** 2 x 4-lane MIPI-DSI, compatible with MIPI DPHY 2.0 or CPHY 1.1
| + | |
| − | * Audio:
| + | |
| − | ** 1 x 3.5mm jack for stereo headphone output
| + | |
| − | ** 1 x 2.0mm PH-2A connector for analog microphone input
| + | |
| − | * GPIO:
| + | |
| − | ** 40-pin 2.54mm header connector
| + | |
| − | ** up to 2 x SPIs, 6 x UARTs, 1 x I2Cs, 8 x PWMs, 2 x I2Ss, 28 x GPIOs
| + | |
| − | * M.2 Connectors
| + | |
| − | ** one M.2 M-Key connector with PCIe 3.0 x4 for NVMe SSDs up to 2,500 MB/s
| + | |
| − | ** one M.2 E-key connector with PCIe 2.1 x1 and USB2.0 Host
| + | |
| − | * others:
| + | |
| − | ** 10 Pin 2.54mm header connector including Debug UART(3.3V TTL) and 2 x USB 2.0 Host
| + | |
| − | ** 2 Pin 1.27/1.25mm RTC battery input connector for low power RTC IC HYM8563TS
| + | |
| − | ** one 38Khz IR receiver
| + | |
| − | ** MASK button for eMMC update, reset button, and Power button
| + | |
| − | ** one 5V Fan connector
| + | |
| − | ** USB-C to Debug UART
| + | |
| − | ** 2 x GPIO Controlled LED (SYS, LED1)
| + | |
| − | * Power supply: 5.5*2.1mm DC Jack & 2-Pin 3.5mm pitch connector, 12VDC input.
| + | |
| − | * PCB: 8 Layer, 110x80x1.6mm | + | |
| − | *Ambient Operating Temperature: 0℃ to 70℃ | + | |
| | | | |
| − | ==Diagram, Layout and Dimension== | + | ==下载所需文件== |
| − | ===NanoPC-T6-LTS=== | + | * 访问[https://dl.friendlyelec.com/nanopct6 这里],到 "05_Tools" 目录下载如下文件 "RKDevTool_v3.19_for_window.zip"和"win32diskimager.rar" |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6LTS_Layout-L.jpg|1100px]] | + | * 访问[https://www.armbian.com/nanopct6/ 这里],下载Armbian的固件文件 |
| − | ===NanoPC-T6=== | + | * 访问[http://112.124.9.243/dvdfiles/RK3588/tools/ 这里],下载 "MiniLoaderAll.bin" 和 " rkspi_loader.img.zip" |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T6 Layout-L.jpg|1100px]] | + | 所有步骤目前仅适用于 Windows 系统。 |
| − | ===Layout=== | + | |
| − | <!-- [[File:NanoPC-T6_Layout.jpg|thumb|frameless|300px|NanoPC-T6 Layout]] -->
| + | ==烧写步骤== |
| − | * '''40-pin GPIO'''
| + | ===进入Maskrom模式=== |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | * 通电状态下,按住mask键,再短按reset键 |
| − | |-
| + | * 使用USB Type-C线将NanoPC-T6与电脑相连接 |
| − | |'''Pin#''' || '''GPIO''' || '''SPI''' || '''UART''' || '''I2C''' || '''I2S''' || '''PWM''' ||'''POWER''' ||'''Description'''
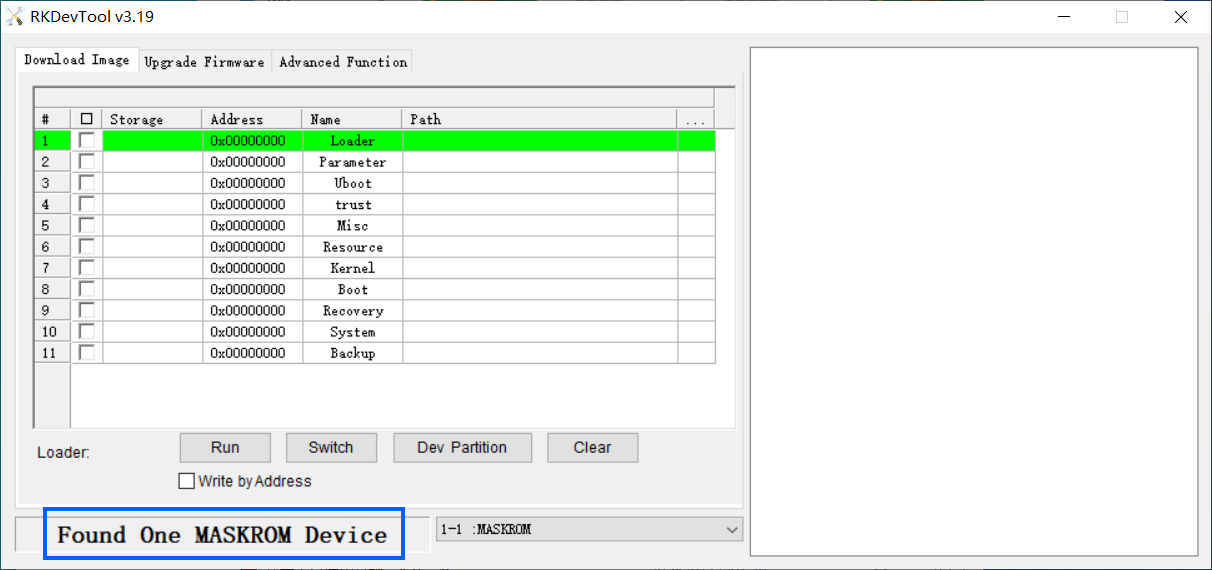
| + | * 在电脑上启动RKDevTool,界面上应显示“Found One MASKROM Device”,如下图所示: |
| | + | [[File:Rkdevtool_found_one_maskrom_device.png|frameless|600px]] |
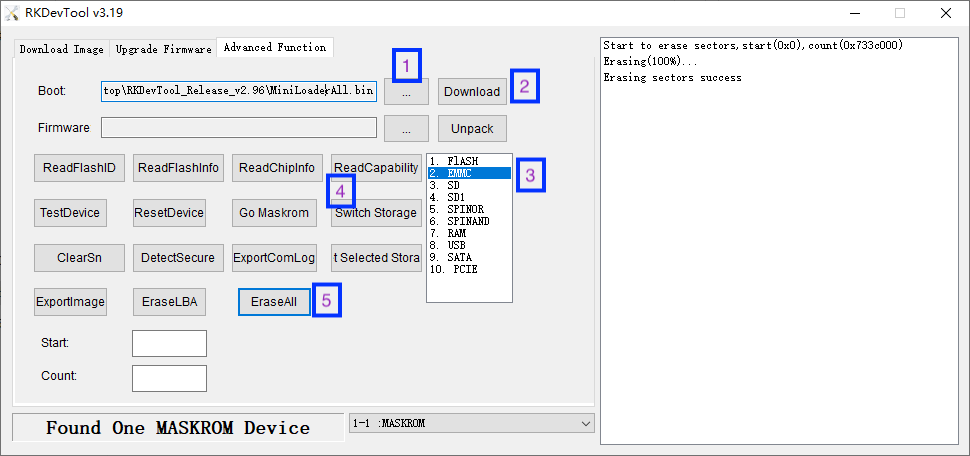
| | + | ===擦除SPI Nor Flash和eMMC=== |
| | + | 为了避免存储设备内有残余的引导数据干扰系统启动,我们先擦除SPI Nor Flash和eMMC,方法如下: |
| | + | * 在RKDevTool界面上点击 "Advanced Function" 选项 |
| | + | * 先在 "Boot" 编辑框中选择 "MiniLoaderAll.bin",然后点击 "Download" 按钮下载并运行 Loader |
| | + | * 选中 "EMMC",点 "Switch Storage",再点击 "ErashAll" 按钮擦除 eMMC |
| | + | [[File:Rkdevtool_erase_emmc.png|frameless|600px]] |
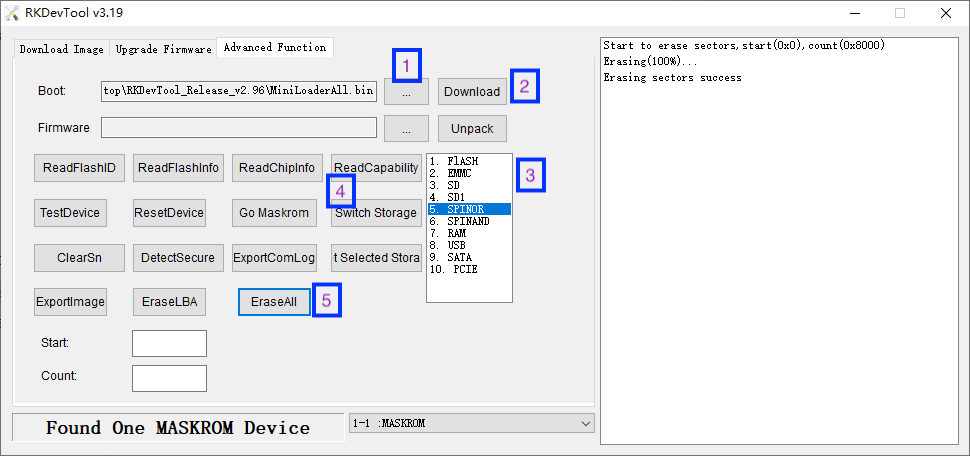
| | + | * 选中 "SPINOR", 点 "Switch Storage",再点击 "ErashAll" 按钮擦除 SPI Nor Flash |
| | + | [[File:Rkdevtool_erase_spinorflash.png|frameless|600px]] |
| | + | |
| | + | ===烧写Boot Loader到SPI Nor Flash=== |
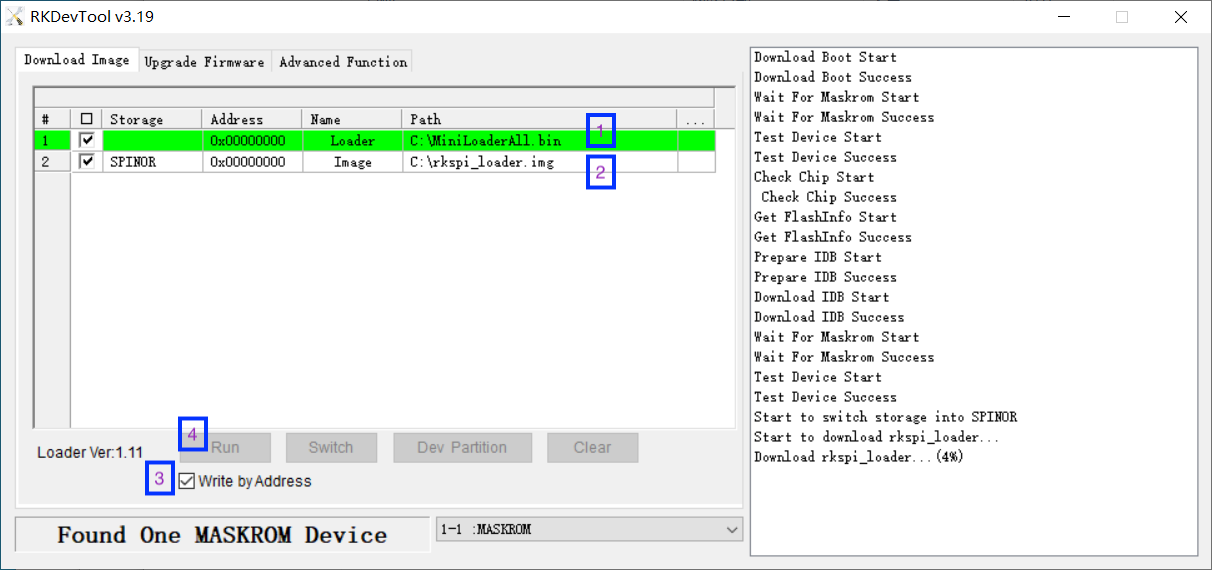
| | + | 参考如下示范图片,在RKDevTool界面上设置烧写的内容: |
| | + | [[File:Rkdevtool_flash_spinor.png|frameless|600px]] |
| | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| | + | ! 步骤 !! 操作 !! 说明 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |1,17 || || || || || || || VCC3V3_SYS_S3 || 3.3V Power Output, 500mA Max | + | | 2 || 选择 loader bin 文件 || (1) 点击蓝色区域,选择 MiniLoaderAll.bin |
| | + | (2) 地址:0x00000000 |
| | + | (3) 存储:空白 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |2,4 || || || || || || || VCC_5V0 || 5V Power Output, 500mA Max | + | | 3 || 选择 UBOOT 文件 || (1) 点击蓝色区域,选择 rkspi_loader.img |
| − | |-
| + | (2) 地址:0x00000000 |
| − | |6,9,14,20,25,30,34,39 || || || || || || || GND || Power and Signal Ground
| + | (3) 存储:SPINOR |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |3 || GPIO1_D7 || || || I2C8_SDA_M2 || || || || pulled up to 3.3V with 2.2K on T6
| + | | 5 || 运行 || 下载 loader.bin,然后将 rkspi_loader.img 写入 SPINOR |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || GPIO1_D6 || || || I2C8_SCL_M2 || || || || pulled up to 3.3V with 2.2K on T6 | + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7 || GPIO3_B2 || || || || I2S2_SDI_M1|| || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |8 || GPIO0_C5 || || UART0_TX_M0 || || || PWM4_M0 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |10 || GPIO0_C4 || || UART0_RX_M0 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || GPIO3_C2 || || || || || PWM14_M0 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12 || GPIO3_B7 || || || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |13 || GPIO3_C3 || || || || ||PWM15_IR_M0|| || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |15 || GPIO1_A7 || || || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |16 || GPIO3_B3 || || || || I2S2_SDO_M1 || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |18 || GPIO3_B4 || || || || I2S2_MCLK_M1|| || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 || GPIO1_B2 || SPI0_MOSI_M2 || UART4_RX_M2 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |21 || GPIO1_B1 || SPI0_MISO_M2 || || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |22 || GPIO1_B5 || SPI0_CS1_M0 || UART7_TX_M2 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |23 || GPIO1_B3 || SPI0_CLK_M2 || UART4_TX_M2 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |24 || GPIO1_B4 || SPI0_CS0_M2 || UART7_RX_M2 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |26 || GPIO1_B0 || || || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |27 || GPIO1_A0 || || UART6_RX_M1 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |28 || GPIO1_A1 || || UART6_TX_M1 || || || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |29 || GPIO3_B5 || || UART3_TX_M1 || || I2S2_SCLK_M1 || PWM12_M0 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |31 || GPIO3_B6 || || UART3_RX_M1 || || I2S2_LRCK_M1 || PWM13_M0 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |32 || GPIO0_C6 || || || || || PWM5_M1 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |33 || GPIO3_B0 || || || || || PWM9_M0 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |35 || GPIO3_A0 || SPI4_MISO_M1 || || || I2S3_MCLK || PWM10_M0 || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |36 || GPIO3_A3 || SPI4_CS0_M1 || UART8_RX_M1 || || I2S3_SDO || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |37 || GPIO3_A4 || SPI4_CS1_M1 || || || I2S3_SDI || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |38 || GPIO3_A1 || SPI4_MOSI_M1 || || || I2S3_SCLK || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |40 || GPIO3_A2 || SPI4_CLK_M1 || UART8_TX_M1 || || I2S3_LRCK || || || 3.3V
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | * '''MIPI-DSI'''
| + | |
| − | :: 0.5mm FPC Connector
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |'''Pin#''' || '''MIPI-DSI0''' || '''MIPI-DSI1''' || '''Description '''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1,2,3 || VCC_5V0 || VCC_5V0 || 5V Power ouput
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |4,7,9,11,15,18,21,24,27,30||GND || GND || Power and Signal Ground
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || I2C5_SDA_M0 || I2C4_SDA_M3 || 3.3V, I2C Data, pulled up to 3.3V with 2.2K on T6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |6 || I2C5_SCL_M0 || I2C4_SCL_M3 || 3.3V, I2C Clock, pulled up to 3.3V with 2.2K on T6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |8 || GPIO3_C0 || GPIO4_A0 || 3.3V, GPIO
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |10 || GPIO3_B1/PWM2_M1 || GPIO3_D5/PWM11_M3 || 3.3V, GPIO/PWM
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12 || GPIO3_A6 || GPIO4_A3 || 3.3V, GPIO
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |13 || /NC || /NC || No Connection
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |14 || GPIO3_C1 || GPIO4_A1 || 3.3V, GPIO
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |16 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D3N || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D3N || MIPI TX Lane3 ouput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |17 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D3P || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D3P || MIPI TX Lane3 ouput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D2N || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D2N || MIPI TX Lane2 ouput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |20 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D2P || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D2P || MIPI TX Lane2 ouput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |22 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D1N || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D1N || MIPI TX Lane1 ouput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |23 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D1P || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D1P || MIPI TX Lane1 ouput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |25 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D0N || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D0N || MIPI TX Lane0 ouput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |26 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_D0P || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_D0P || MIPI TX Lane0 ouput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |28 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_CLKN || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_CLKN || MIPI TX Clock ouput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |29 || MIPI_DPHY0_TX_CLKP || MIPI_DPHY1_TX_CLKP || MIPI TX Clock ouput P
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | * '''MIPI-CSI'''
| + | |
| − | :: 0.5mm FPC Connector
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |'''Pin#''' || '''MIPI-CSI0''' || '''MIPI-CSI1''' || '''Description '''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1,2 || VCC_5V0 || VCC_5V0 || 5V Power ouput
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3,13,15,18,21,24,27,30 || GND || GND || Power and Signal Ground
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |4,5,7 || /NC || /NC || No Connection
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |6 || VCC_1V8_S3 || VCC_1V8_S3 || 1.8V Power ouput, 100mA Max
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |8 || VSYNC_MASTER || VSYNC_SLAVE || Have been Connected together on T6 for sensor synchronization
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |9 || I2C3_SCL_M0 || I2C7_SCL_M0 || 1.8V, I2C Clock, pulled up to 1.8V with 2.2K on T6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |10 || I2C3_SDA_M0 || I2C7_SDA_M0 || 1.8V, I2C Data, pulled up to 1.8V with 2.2K on T6
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || GPIO4_C4 || GPIO2_C1 || 1.8V, GPIO
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12 || GPIO4_C5 || GPIO2_C2 || 1.8V, GPIO
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |14 || MIPI_CAM1_CLKOUT || MIPI_CAM2_CLKOUT || 1.8V, CLock ouput for Sensor
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |16 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D3P || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D3P || MIPI RX Lane3 iuput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |17 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D3N || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D3N || MIPI RX Lane3 iuput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D2P || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D2P || MIPI RX Lane2 iuput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |20 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D2P || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D2N || MIPI RX Lane2 iuput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |22 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D1P || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D1P || MIPI RX Lane1 iuput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |23 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D1N || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D1N || MIPI RX Lane1 iuput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |25 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_CLK0P || MIPI_CSI1_RX_CLK0P || MIPI RX Clock iuput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |26 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_CLK0N || MIPI_CSI1_RX_CLK0N || MIPI RX Clock iuput N
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |28 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D0P || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D0P || MIPI RX Lane0 iuput P
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |29 || MIPI_CSI0_RX_D0N || MIPI_CSI1_RX_D0N || MIPI RX Lane0 iuput N
| + | |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | * '''10 Pin Debug UART & USB 2.0 Header'''
| + | === 引导顺序 === |
| − | :: Debug UART is 3.3V level signals, 1500000bps
| + | 新的引导顺序如下所示: |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| | + | ! 顺序 !! 存储 !! 描述 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |'''Pin#''' ||'''Assignment''' || '''Description ''' ||'''Pin#''' ||'''Assignment''' || '''Description ''' | + | | 1 || SD 卡 || 安全数字卡 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |1 || USB 5V || 5V Power Output(1A Max) || 2 || USB 5V || 5V Power Output(1A Max) | + | | 2 || EMMC || 嵌入式多媒体卡 |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3 || USB_HS2_DM || USB 2.0 Host DM || 4 || USB_HS3_DM || USB 2.0 Host DM
| + | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |5 || USB_HS2_DP || USB 2.0 Host DP || 6 || USB_HS3_DP || USB 2.0 Host DP | + | | 3 || NvME || 非易失性存储器 |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7 || GND || 0V || 8 || GND || 0V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |9 || UART2_TX_M0_DEBUG || Debug UART TX || 10 || UART2_RX_M0_DEBUG || Debug UART RX
| + | |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | *'''About Power'''
| + | 记住不要在 SD 卡和 eMMC 上安装任何操作系统。你可以随时将它们用于数据存储,因为在这些单元上安装操作系统会阻止系统直接从 NvME 驱动器引导。 |
| − | ** Power supply via 5.5*2.1mm DC Jack. 5V~20V, 12V is recommended.
| + | |
| − | **Power Output Capacity
| + | === 刷写 SD 卡 === |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable" | + | 在继续之前,让我们使用 BalenaEtcher 将 Armbian 刷写到 SD 卡上。请按照以下步骤操作: |
| | + | # 打开 BalenaEtcher。 |
| | + | # 选择你之前下载的 Armbian 镜像。 |
| | + | [[File:balenaetcher-screen.png|thumb|center|801x507px]] |
| | + | 刷写后,请记住将 SD 卡从你的 PC 上断开,然后插入 NanoPC T6。 |
| | + | |
| | + | 以下是默认的登录凭据: |
| | + | |
| | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| | + | ! 用户名 !! 密码 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |'''Port''' ||'''Max Output''' || '''Port''' || '''Max Output''' | + | | root || 1234 |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |USB-A 3.0 || 5V/2A || USB-C/DP || 5V/2A
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |M.2 M-Key || 3.3V/3A || M.2 E-Key || 3.3V/3A
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |MIPI-CSI0 || 5V/0.5A || MIPI-CSI1 || 5V/0.5A
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |MIPI-DSI0 || 5V/1A || MIPI-DSI1 || 5V/1A
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |40 Pin GPIO|| 5V/0.5A, 3.3V/0.5A || 10 Pin USB2.0 || 5V/2A
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |USB-A 2.0 || 5V/2A || '''Total''' || '''35W'''
| + | |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | * '''Debug UART Pin Spec (On the old T6 2301)'''
| + | === 从 NanoPC 刷写 NvME 驱动器 === |
| − | :: 3.3V level signals, 1500000bps
| + | 现在你已经进入了你的 NanoPC,你需要直接在 NanoPC 上下载操作系统。你可以从互联网下载,也可以使用 SFTP 传输之前下载的文件。记住,一旦你将操作系统加载到 NvME 驱动器上,你需要重置之前更改的密码。 |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | 要继续加载镜像,请执行以下命令: |
| − | |'''Pin#''' ||'''Assignment''' || '''Description ''' | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | |-
| + | xz -dc Armbian_community_24.5.0-trunk.433_Nanopct6_bookworm_edge_6.8.7_minimal.img.xz | dd of=/dev/nvme0n1 bs=4k status=progress && sync |
| − | |1 || GND || 0V
| + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | |-
| + | 完成后,执行命令 |
| − | |2 || UART2_TX_M0_DEBUG || output
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | |-
| + | shutdown -h now |
| − | |3 || UART2_RX_M0_DEBUG || intput
| + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | |}
| + | 等待 LED 停止闪烁,然后继续移除 SD 卡。 |
| − | *'''About Power (For the old T6 2301)'''
| + | |
| − | ** Power supply via 5.5*2.1mm DC Jack. 5V~20V, 12V is recommended.
| + | == 安装 Proxmox == |
| − | **Power Output Capacity
| + | 要安装 Proxmox,你需要配置一个静态 IP。建议仅安装“标准”软件包选择,因为 Proxmox VE 包含自己的 qemu 和 lxc 包。不需要桌面环境。 |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | === 配置主机名和 IP === |
| − | |'''Port''' ||'''Max Output''' || '''Port''' || '''Max Output'''
| + | 在 /etc/hosts 中为你的 IP 地址添加一个条目,确保你的机器的主机名是可解析的。移除默认条目 127.0.1.1。 |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |USB-A 3.0 || 5V/2A || USB-C/DP || 5V/2A
| + | 示例 /etc/hosts 配置: |
| − | |-
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> |
| − | |M.2 M-Key || 3.3V/3A || M.2 E-Key || 3.3V/3A
| + | 127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost |
| − | |-
| + | 192.168.15.77 prox4m1.proxmox.com prox4m1 |
| − | |MIPI-CSI0 || 5V/0.5A || MIPI-CSI1 || 5V/0.5A
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | # IPv6 行(可选) |
| − | |MIPI-DSI0 || 5V/1A || MIPI-DSI1 || 5V/1A
| + | ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback |
| − | |-
| + | ff02::1 ip6-allnodes |
| − | |GPIO || 5V/0.5A, 3.3V/0.5A || miniPCIe || 3.3V/3A
| + | ff02::2 ip6-allrouters |
| − | |-
| + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | | Total || 35W
| + | 使用以下命令验证设置: |
| − | |}
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | + | hostname --ip-address |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | + | 应返回你的 IP 地址。 |
| | + | |
| | + | === 安装 Proxmox VE === |
| | + | 添加 Proxmox VE 仓库: |
| | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | + | echo 'deb [arch=arm64] https://mirrors.apqa.cn/proxmox/debian/pve bookworm port' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pveport.list |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | + | |
| | + | 添加仓库密钥: |
| | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | + | curl -L https://mirrors.apqa.cn/proxmox/debian/pveport.gpg -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/pveport.gpg |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| | + | 更新仓库和系统: |
| | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | + | apt update && apt full-upgrade |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | *'''RTC'''
| + | 安装 Proxmox VE 包和依赖项: |
| − | ::RTC backup current is 0.25μA TYP (VDD =3.0V, TA =25℃).
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | ::Connector P/N: Molex 53398-0271
| + | apt install ifupdown2 proxmox-ve postfix open-iscsi |
| − | [[File:T6-rtc.png|350px]]
| + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | *'''IR receiver'''
| + | 在安装过程中根据你的偏好配置软件包,特别是用于邮件路由的 postfix。如果不确定,请选择 postfix 配置的 local only。 |
| − | ::Connected to PWM3_IR_M0
| + | |
| − | ::38Khz carrier frequency
| + | |
| − | ::compatible with NEC protocol, User code is 3B4C
| + | |
| − | ::Support FriendlyELEC RC100 IR controller
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ==Get Started==
| + | 安装后,通过 https://youripaddress:8006 访问管理 Web 界面。如果遇到 ifupdown2 错误,运行以下命令: |
| − | ===Essentials You Need===
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | Before starting to use your NanoPC-T6 get the following items ready
| + | systemctl enable --now networking.service |
| − | * NanoPC-T6
| + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | * MicroSD Card/TF Card: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
| + | 然后重试: |
| − | * A DC 12V/2A power
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | * If you need to develop and compile,you need a computer that can connect to the Internet. It is recommended to install Ubuntu 20.04 64-bit system and use the following script to initialize the development environment, or use docker container: <br />
| + | apt install ifupdown2 |
| − | **[https://github.com/friendlyarm/build-env-on-ubuntu-bionic How to setup the Compiling Environment on Ubuntu bionic]<br />
| + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | **[https://github.com/friendlyarm/docker-cross-compiler-novnc docker-cross-compiler-novnc]<br />
| + | 你应该不再收到错误。 |
| − | ===TF Cards We Tested===
| + | |
| − | Refer to: [[Template:TFCardsWeTested/zh|TFCardsWeTested]]
| + | |
| − | {{1500000SerialPortDebugSetting}}
| + | |
| − | ===Install OS=== | + | |
| − | {{Downloads-RK3588|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{BurnLinuxToSD-Rockchip|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{BurnLinuxToEMMC-Rockchip|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{RockchipBootPriority|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{FriendlyWrt21|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | ==Work with Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy) Desktop==
| + | |
| − | ===Introduction to Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop===
| + | |
| − | {{UbuntuJammyDesktop-Intro|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{UbuntuJammyDesktop-Common|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{UbuntuJammyDesktop-WithHDMI|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{Android12|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | ==Work with Debian11 Desktop==
| + | |
| − | ===Introduction to Debian11 Desktop===
| + | |
| − | {{DebianBullseyeDesktop-XFCE-Intro|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{DebianBullseyeDesktop-XFCE-Common|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{DebianBullseyeDesktop-XFCE-WithHDMI|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{DebianBullseyeDesktop-XFCE-HDMIIN|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | ==Work with Debian10 Desktop==
| + | |
| − | * Refer to:
| + | |
| − | ** [[Debian Buster Desktop|Debian Buster]]
| + | |
| − | ==Work with Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal) Desktop==
| + | |
| − | ===Introduction to Ubuntu 20.04 Desktop===
| + | |
| − | {{UbuntuFocalDesktop-Intro|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{UbuntuFocalDesktop-Common|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{OfficialUbuntuCore|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{FriendlyCoreRemoveQt}}
| + | |
| − | ==How to Compile==
| + | |
| − | {{Rockchip-DevEnv|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{RK3588-BuildFromSource|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{RK3588-HWAccess|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{RockchipMiscCustome|RK3588}}
| + | |
| − | {{RockchipCommonLinuxTips|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | {{Template:How to Initialize and Format New SSD And HDD|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | ==Link to Rockchip Resources==
| + | |
| − | {{LinkToRockchipResources|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | |
| − | ==Schematic, PCB CAD File==
| + | |
| − | *NanoPC-T6 2301 Schematic: https://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/9/97/NanoPC-T6_2301_SCH.PDF
| + | |
| − | *NanoPC-T6 LTS 2310 Schematic: https://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/4/44/NanoPC-T6_LTS_2310_SCH.pdf
| + | |
| − | *NanoPC-T6 2301 PCB CAD File:https://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/9/90/NanoPC-T6_2301_DXF.zip
| + | |
| − | *NanoPC-T6 LTS 2310 PCB CAD File: https://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/0/08/NanoPC-T6_LTS_2310_DXF.zip
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ==Update Logs== | + | == 结论 == |
| − | {{RK3588-UpdateLog|NanoPC-T6}}
| + | 完成了,你已经在你的 NanoPC T6 上安装了 Proxmox。下面附上所有有用的链接,以跟踪此移植的开发状态。 |
现在你已经进入了你的 NanoPC,你需要直接在 NanoPC 上下载操作系统。你可以从互联网下载,也可以使用 SFTP 传输之前下载的文件。记住,一旦你将操作系统加载到 NvME 驱动器上,你需要重置之前更改的密码。
要安装 Proxmox,你需要配置一个静态 IP。建议仅安装“标准”软件包选择,因为 Proxmox VE 包含自己的 qemu 和 lxc 包。不需要桌面环境。