Difference between revisions of "APITestPage"
From FriendlyELEC WiKi
(updated by API) |
(updated by API) |
||
| (166 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{BurnLinuxToExtDrive-Rockchip/zh|NanoPC-T4}} | |
| − | + | {{BurnLinuxToExtDrive-Rockchip|NanoPC-T4}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |- | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |- | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 09:58, 29 October 2024
1 安装系统到M.2或USB硬盘
可以通过使用TF卡启动eFlasher系统,将引导和系统分别安装到不同存储设备,但是由于CPU不支持直接从M.2和USB设备引导,所以虽然系统可以安装到M.2和USB设备,但是引导仍然需要安装到eMMC或者TF卡。
操作步骤如下:
- 准备一张32G或以上容量的TF卡;
- 访问此处的下载地址下载文件名为XXXX-eflasher-multiple-os-YYYYMMDD-30g.img.gz的固件(位于"01_系统固件/02_SD卡刷机固件(SD-to-eMMC)"目录);
- 将固件写入TF卡,在NanoPC-T4上连接好存储设备,插入TF卡上电开机,接下来要在界面上操作,如果没有显示设备,可以使用VNC代替,请参考使用VNC操作eFlasher;
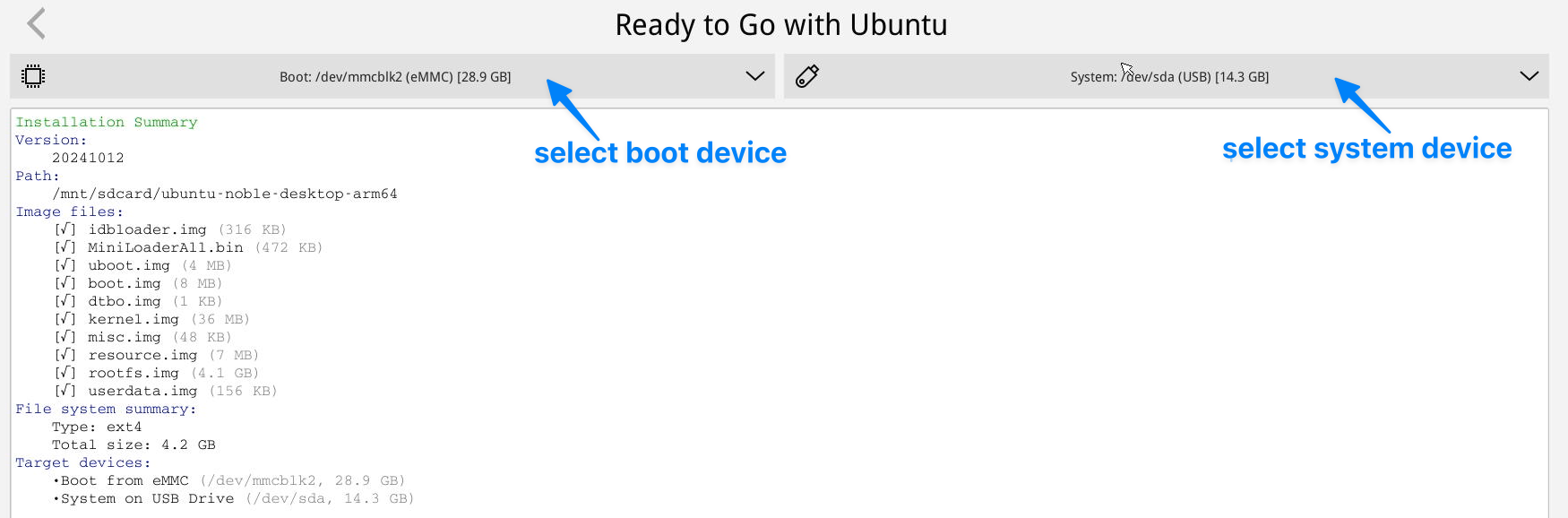
- 在eFlasher界面上,首先选择要安装的OS,然后选择引导安装的目的地 (通常选eMMC),以及选择系统安装的目的地(可以选eMMC,M.2硬盘,USB存储设备等),如下图所示:
- 没有eMMC时可使用TF卡作为引导,方法是将另一个TF卡通过USB读卡器插入USB端口,然后选择USB设备作为引导安装目的地,从而实现从TF卡引导,但系统存放在M.2或USB硬盘的目的;
- 烧写完成后,从NanoPC-T4弹出SD卡,引导在eMMC的情况下,NanoPC-T4会自动重启至你刚刚烧写的系统,如果引导安装在TF卡,则需要拨掉电源,插入TF引导卡再上电开机;
- 更详细的安装指南请参考此处;
2 Installing the System to M.2 or USB Drive
You can use a TF card to boot the eFlasher system, allowing the boot and system to be installed on different storage devices. However, since the CPU doesn’t support booting directly from M.2 and USB devices, the system can be installed on M.2 and USB devices, but the boot must still be installed on eMMC or a TF card.
Steps are as follows:
- Prepare a TF card with a capacity of 32GB or larger.
- Visit [the download link here](http://download.friendlyelec.com/APITestPage) to download the firmware file named XXXX-eflasher-multiple-os-YYYYMMDD-30g.img.gz (located in the “01_Official images/02_SD-to-eMMC images” directory).
- Flash the firmware to the TF card, connect the storage device you intend to use on NanoPC-T4, insert the TF card and power on, we need to perform the operations in the eFlasher GUI. If your NanoPC-T4 does not have a display interface, you can use VNC; refer to Using VNC to Operate eFlasher.
- In the eFlasher GUI, select the OS to install, and in the OS settings interface, choose the destination for boot installation (typically eMMC), then choose the destination for system installation (options include eMMC, M.2 hard drive, USB storage, etc.), as shown below:
- If no eMMC is available, the TF card can serve as the boot by inserting another TF card into the USB port via a USB card reader and selecting it as the boot destination, enabling booting from the TF card with the system stored on the M.2 or USB drive.
- After flashing, eject the SD card from NanoPC-T4. If booting from eMMC, NanoPC-T4 will automatically restart into the newly flashed system. If boot installation is on a TF card, power off, insert the boot TF card, and power on again.
- For a more detailed installation guide, please refer to this link.