|
|
| (221 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | [[Android Hardware Programming for RK3399|English]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==简介==
| + | {{BurnLinuxToExtDrive-Rockchip/zh|NanoPC-T4}} |
| − | 友善电子开发了一个名为libfriendlyarm-hardware.so的函数库,用于Android应用程序访问开发板上的硬件资源,该函数库基于Android-NDK技术开发,提供便利的硬件访问接口,开发者无需掌握过多的嵌入式知识便可使用,有效提高开发进度。<br /><br />
| + | {{BurnLinuxToExtDrive-Rockchip|NanoPC-T4}} |
| − | 本篇文章仅适用于RK3399开发板,包括 NanoPi-NEO4, NanoPi-M4 和 NanoPC-T4。<br />
| + | |
| − | 其他平台也有相应的支持,请移步这里查看:[[Android Thing: Android Hardware Programming]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==支持如下RK3399官方Android BSP==
| + | |
| − | * Android 7.1.2
| + | |
| − | * Android 8.1
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==支持如下RK3399硬件资源==
| + | |
| − | * Serial Port
| + | |
| − | * GPIO
| + | |
| − | * ADC
| + | |
| − | * PWM
| + | |
| − | * I2C
| + | |
| − | * RTC
| + | |
| − | * Watch dog
| + | |
| − | * SPI
| + | |
| − | 等等, 接口包括I2C, SPI, GPIO常用的接口。<br />
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T4+OLED.jpg|frameless|450px|Smart4418SDK+OLED]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==支持的开发板==
| + | |
| − | * NanoPi-NEO4
| + | |
| − | * NanoPi-M4
| + | |
| − | * NanoPC-T4
| + | |
| − | * 其他开发板请移步这里查看:[[Android Thing: Android Hardware Programming]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==开源Android示例==
| + | |
| − | 所有硬件访问的示例程序均已集成到 Android 的源代码当中,位于 Android7.1.2 和 Android8.1 源代码的以下目录:vendor/friendlyelec/apps,也可以单独网上下载,下表中列出各个 Demo 的源代码地址:
| + | |
| − | ===Android8.1===
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="2"| '''Android8.1示例'''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Serial Port
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/SerialPortDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |GPIO
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/GPIO_LED_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |ADC
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/ADCDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |PWM
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/PWMDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |I2C
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/I2C_LCD1602_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |RTC
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/RTC_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Watch dog
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/WatchDogDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |SPI
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-android-8.1/tree/master/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/SPI_OLED_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | ===Android7.1.2===
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="2"| '''Android7.1.2示例'''
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Serial Port
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/SerialPortDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |GPIO
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/GPIO_LED_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |ADC
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/ADCDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |PWM
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/PWMDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |I2C
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/I2C_LCD1602_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |RTC
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/RTC_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Watch dog
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/WatchDogDemo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |SPI
| + | |
| − | |style="width: 90%;"|
| + | |
| − | https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/rk3399-nougat/tree/nanopc-t4-nougat/vendor/friendlyelec/apps/SPI_OLED_Demo
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==如何在自已的程序中使用硬件访问库==
| + | |
| − | ===Step1) 集成libfriendlyarm-hardware.so到你的工程目录===
| + | |
| − | 克隆以下仓库到本地:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/android-libfriendlyarm-hardware.git
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 接着复制 libs 目录下的所有内容到你的工程目录下,然后在你的Android项目的src目录下创建com/friendlyarm目录,将java/AndroidSDK目录拷贝进去即可,最后的目录的结构看上去是这样的 (注:AndroidStudio的项目可能会稍有不同,但大致如此):<br />
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | YourProject/
| + | |
| − | ├── AndroidManifest.xml
| + | |
| − | ├── libs
| + | |
| − | │ ├── arm64-v8a
| + | |
| − | │ │ └── libfriendlyarm-hardware.so
| + | |
| − | │ └── armeabi
| + | |
| − | │ └── libfriendlyarm-hardware.so
| + | |
| − | ├── src
| + | |
| − | │ └── com
| + | |
| − | │ └── friendlyarm
| + | |
| − | │ ├── AndroidSDK
| + | |
| − | │ │ ├── BoardType.java
| + | |
| − | │ │ ├── FileCtlEnum.java
| + | |
| − | │ │ ├── GPIOEnum.java
| + | |
| − | │ │ ├── HardwareControler.java
| + | |
| − | │ │ ├── SPIEnum.java
| + | |
| − | │ │ ├── SPI.java
| + | |
| − | │ │ └── WatchDogEnum.java
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 使用以下方法导入它们,主要的接口都集中在 HardwareControler.java文件中:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="java">
| + | |
| − | import com.friendlyarm.AndroidSDK.HardwareControler;
| + | |
| − | import com.friendlyarm.AndroidSDK.SPIEnum;
| + | |
| − | import com.friendlyarm.AndroidSDK.GPIOEnum;
| + | |
| − | import com.friendlyarm.AndroidSDK.FileCtlEnum;
| + | |
| − | import com.friendlyarm.AndroidSDK.BoardType;
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | ===Step2) 让你的app拥有system权限===
| + | |
| − | 你的app需要拥有system权限,才能访问硬件资源; <br />
| + | |
| − | 请参考下面的方法修改你 app 的 AndroidManifest.xml 和 Android.mk这两个文件; <br />
| + | |
| − | 并且最好将你的app放到Android源码中去编译,这一步不是必需的,但是建议这么做,如果你的app在外部编译,你需要对apk进行签名才能让你的app拥有system权限(新手不太建议,过程比较繁琐)。<br />
| + | |
| − | ====修改AndroidManifest.xml====
| + | |
| − | 在应用程序的AndroidManifest.xml中的manifest节点中加入以下属性:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | android:sharedUserId="android.uid.system"
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | ====修改Android.mk====
| + | |
| − | 编写一个Android.mk文件(最简单的方法就是拷贝示例中的Android.mk文件),修改Android.mk文件,加入LOCAL_CERTIFICATE := platform这一行:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="java">
| + | |
| − | LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
| + | |
| − | include $(CLEAR_VARS)
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(call all-subdir-java-files)
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | LOCAL_PACKAGE_NAME := 你的项目名
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | LOCAL_CERTIFICATE := platform
| + | |
| − | LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
| + | |
| − | LOCAL_CFLAGS := -lfriendlyarm-hardware
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | include $(BUILD_PACKAGE)
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | ===Step3) 在 Android源代码中编译你的app===
| + | |
| − | 先在 Android源代码根目录调用 setenv.sh 导出环境变量,然后进入你的 app 目录,使用mm命令编译; <br />
| + | |
| − | 例子:编译 GPIO_LED_Demo: <br />
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | cd rk3399-android-8.1
| + | |
| − | . setenv.sh
| + | |
| − | cd vendor/friendlyelec/apps/GPIO_LED_Demo
| + | |
| − | mm
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==RK3399平台Android硬件资源的程序访问==
| + | |
| − | ===Serial Port===
| + | |
| − | 目前可用的串口是UART4,设备名称为/dev/ttyS4,其他串口资源如下表所示,你也可以使用USB转串口来扩展:
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |串口设备 || 串口资源占用情况
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |UART0 || 已被蓝牙占用
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |UART1 || 已被千兆以太网占用
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |UART2 || 已被作为调试串口
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |UART3 || 已被千兆以太网占用
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |UART4 || 空闲,设备名称为 /dev/ttyS4 (注:需使用20180618之后的ROM)
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Android硬件库为串口API:
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" | '''接口名称'''
| + | |
| − | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" |'''参数与返回值说明'''
| + | |
| − | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" |'''功能说明'''
| + | |
| − | |- | + | |
| − | |
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="java">
| + | |
| − | int openSerialPortEx(
| + | |
| − | String devName,
| + | |
| − | long baud,
| + | |
| − | int dataBits,
| + | |
| − | int stopBits,
| + | |
| − | String parityBit,
| + | |
| − | String flowCtrl
| + | |
| − | )
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | ||
| + | |
| − | 参数说明:<br />
| + | |
| − | devName: 串口设备文件名,可选的值有:<br />
| + | |
| − | /dev/ttyS4<br />
| + | |
| − | baud: 波特率 <br />
| + | |
| − | dataBits: 数据位 (取值 5~8,一般用8 )<br />
| + | |
| − | stopBits: 停止位 (取值 1~2,一般用1 )<br />
| + | |
| − | parityBit: 奇偶校验位(取值为单个字母,O表示奇校验,E表示偶校验,N表示无校验)<br />
| + | |
| − | flowCtrl: 数据流控制(取值为单个字母,H表示硬件流控制,S表示软件流控制,N表示不使用数据流控制)<br />
| + | |
| − | 返回值说明:<br />
| + | |
| − | 成功打开串口时,将返回串口的文件描述符,用该描述符可进行 read、write和select等操作,如果打开失败,则返回 -1<br />
| + | |
| − | ||
| + | |
| − | 打开指定的串口设备,并返回文件描述符。
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 串口的读写使用以下通用接口:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="c">
| + | |
| − | HardwareControler.select //轮询串口是否有数据可写或可读
| + | |
| − | HardwareControler.read //读取串口数据
| + | |
| − | HardwareControler.write //写数据到串口
| + | |
| − | HardwareControler.close //关闭设备
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | ===GPIO===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===ADC===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===PWM===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===I2C===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===RTC===
| + | |
| − | 可以直接使用cat和echo操作/sys/class/rtc/rtc0/下面的接口。
| + | |
| − | 比如查看当前RTC的日期和时间:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/date
| + | |
| − | # 2018-10-20
| + | |
| − | cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/time
| + | |
| − | # 08:20:14
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 设置开机时间,如设置120秒后开机:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | #120秒后定时开机
| + | |
| − | echo +120 > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Watch dog===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===SPI===
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==开发资料==
| + | |
| − | * 中文API文档:https://github.com/friendlyarm/AndroidHardwareAccess/blob/master/友善电子Android硬件开发指南.pdf
| + | |
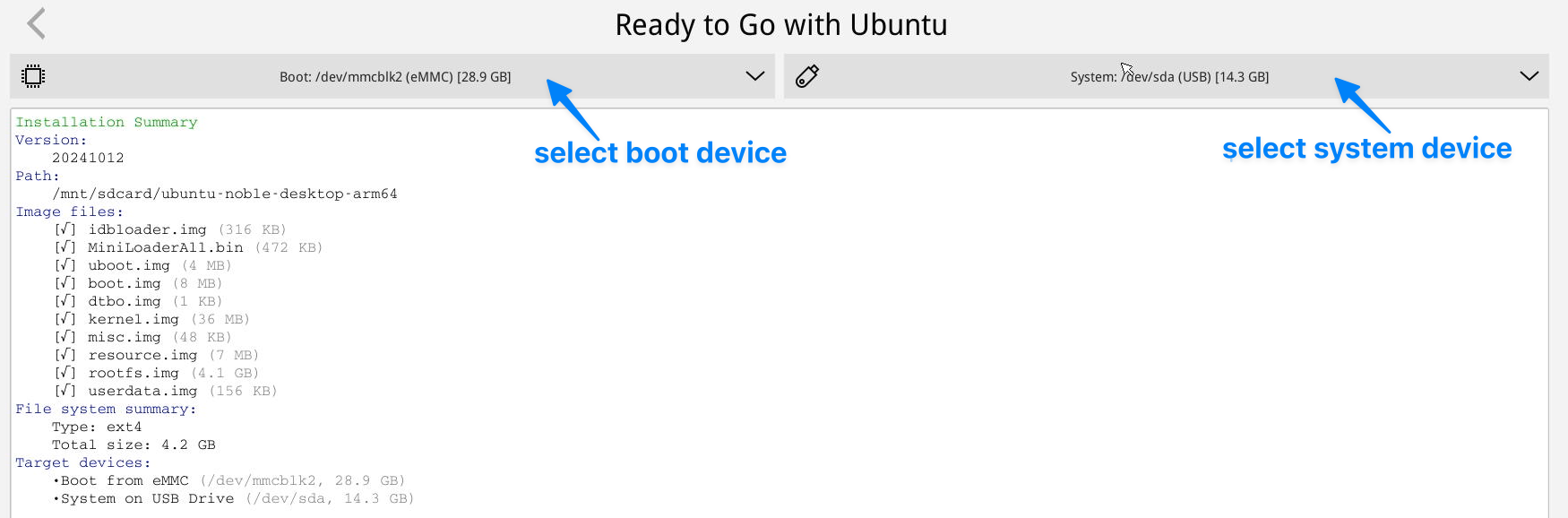
可以通过使用TF卡启动eFlasher系统,将引导和系统分别安装到不同存储设备,但是由于CPU不支持直接从M.2和USB设备引导,所以虽然系统可以安装到M.2和USB设备,但是引导仍然需要安装到eMMC或者TF卡。
操作步骤如下:
You can use a TF card to boot the eFlasher system, allowing the boot and system to be installed on different storage devices. However, since the CPU doesn’t support booting directly from M.2 and USB devices, the system can be installed on M.2 and USB devices, but the boot must still be installed on eMMC or a TF card.
Steps are as follows: