|
|
| (97 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | ===Linux系统编译===
| |
| − | ====各个OS对应的内核与u-boot版本====
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! 操作系统
| |
| − | ! 内核版本
| |
| − | ! uboot版本
| |
| − | ! 交叉编译器
| |
| − | ! 分区类型
| |
| − | ! 构建工具集
| |
| − | ! 内核代码分支
| |
| − | ! 内核配置
| |
| − | ! uboot代码分支
| |
| − | ! uboot配置
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | buildroot
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" | linux v4.19.y
| |
| − | | rowspan="7" | u-boot <br />v2017.09
| |
| − | | rowspan="7" | 11.3-aarch64
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/blob/kernel-4.19/prebuilt/parameter.template GPT]
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/tree/kernel-4.19 sd-fuse]
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip/tree/nanopi4-v4.19.y nanopi4-v4.19.y]
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" | nanopi4_linux_defconfig
| |
| − | | rowspan="7" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip/tree/nanopi4-v2017.09 nanopi4-v2017.09]
| |
| − | | rowspan="7" | rk3288_defconfig
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlycore-focal-arm64
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlycore-lite-focal-arm64
| |
| − | | rowspan="5" | linux v5.15.y
| |
| − | | rowspan="5" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/blob/kernel-5.15.y/prebuilt/parameter.template GPT]
| |
| − | | rowspan="5" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/tree/kernel-5.15.y<br /> sd-fuse]
| |
| − | | rowspan="5" | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip/tree/nanopi-r2-v5.15.y nanopi-r2-v5.15.y]
| |
| − | | nanopi-r2_linux_defconfig
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlywrt21
| |
| − | | rowspan="4" | nanopi-r2_linux_defconfig<br />+friendlywrt.config
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlywrt21-docker
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlywrt22
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlywrt22-docker
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | * 内核源代码仓库地址:https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip
| |
| − | * u-boot源代码仓库地址:https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip
| |
| − | * 交叉编译工具链存放在如下路径: /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/,使用前需导出到PATH环境变量,例如需要使用11.3-aarch64版本的编译器,使用如下命令:
| |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| |
| − | export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH
| |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| |
| − | * sd-fuse构建工具集可以用于快速编译kernel和uboot、重新打包sd卡固件与卡刷固件等
| |
| − | * 点击表格中的MBR与GPT可查看各系统的分区布局(配置文件)
| |
| − | ====编译内核linux-v4.19.y====
| |
| − | 本节内容适用于如下OS:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | buildroot
| |
| − | | friendlycore-focal-arm64
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | 下载源代码并编译:
| |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| |
| − | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi4-v4.19.y kernel-rockchip
| |
| − | cd kernel-rockchip
| |
| − | export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH
| |
| − | touch .scmversion
| |
| − | # 编译内核
| |
| − | make ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux- nanopi4_linux_defconfig
| |
| − | # make ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux- menuconfig # 启动配置界面
| |
| − | make ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux- nanopi4-images -j$(nproc)
| |
| − | # 编译驱动模块
| |
| − | mkdir -p out-modules
| |
| − | make ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux- INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules -j$(nproc)
| |
| − | make ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux- INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules_install
| |
| − | KERNEL_VER=$(make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 kernelrelease)
| |
| − | rm -rf $PWD/out-modules/lib/modules/${KERNEL_VER}/kernel/drivers/gpu/arm/mali400/
| |
| − | [ ! -f "$PWD/out-modules/lib/modules/${KERNEL_VER}/modules.dep" ] && depmod -b $PWD/out-modules -E Module.symvers -F System.map -w ${KERNEL_VER}
| |
| − | (cd $PWD/out-modules && find . -name \*.ko | xargs aarch64-linux-strip --strip-unneeded)
| |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| |
| − | 编译完会生成如下文件:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | kernel.img
| |
| − | | resource.img
| |
| − | | 驱动模块位于out-modules目录
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | 安装内核: <br>
| |
| − | 请参考 [[#下载uboot与内核到目标板]]<br>
| |
| − | ====编译内核linux-v5.15.y====
| |
| − | 本节内容适用于如下OS:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | friendlywrt21
| |
| − | | friendlywrt21-docker
| |
| − | | friendlywrt22
| |
| − | | friendlywrt22-docker
| |
| − | | friendlycore-lite-focal-arm64
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | 下载源代码并编译:
| |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| |
| − | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi-r2-v5.15.y kernel-rockchip
| |
| − | cd kernel-rockchip
| |
| − | export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH
| |
| − | touch .scmversion
| |
| − | # 编译内核
| |
| − | make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 nanopi-r2_linux_defconfig
| |
| − | # make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 menuconfig # 启动配置界面
| |
| − | make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 -j$(nproc)
| |
| − | # 编译驱动模块
| |
| − | mkdir -p out-modules && rm -rf out-modules/*
| |
| − | make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules -j$(nproc)
| |
| − | make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules_install
| |
| − | KERNEL_VER=$(make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 kernelrelease)
| |
| − | [ ! -f "$PWD/out-modules/lib/modules/${KERNEL_VER}/modules.dep" ] && depmod -b $PWD/out-modules -E Module.symvers -F System.map -w ${KERNEL_VER}
| |
| − | (cd $PWD/out-modules && find . -name \*.ko | xargs aarch64-linux-strip --strip-unneeded)
| |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| |
| − | 打包kernel.img与resource.img:
| |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| |
| − | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/kernel-5.15.y/tools/mkkrnlimg && chmod 755 mkkrnlimg
| |
| − | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/kernel-5.15.y/tools/resource_tool && chmod 755 resource_tool
| |
| − | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/kernel-5.15.y/prebuilt/boot/logo.bmp
| |
| − | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/kernel-5.15.y/prebuilt/boot/logo_kernel.bmp
| |
| − | ./mkkrnlimg arch/arm64/boot/Image kernel.img
| |
| − | ./resource_tool --dtbname arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3328-nanopi*-rev*.dtb logo.bmp logo_kernel.bmp
| |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| |
| − | 完成后会得到如下文件:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | kernel.img
| |
| − | | resource.img
| |
| − | | 驱动模块位于out-modules目录
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | 安装内核: <br>
| |
| − | 请参考 [[#下载uboot与内核到目标板]]<br>
| |
| − | ====编译u-boot v2017.09====
| |
| − | 本节内容适用于如下OS:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | buildroot
| |
| − | | friendlycore-focal-arm64
| |
| − | | friendlywrt21
| |
| − | | friendlywrt21-docker
| |
| − | | friendlywrt22
| |
| − | | friendlywrt22-docker
| |
| − | | friendlycore-lite-focal-arm64
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | 下载源代码并编译:
| |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| |
| − | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/rkbin --single-branch --depth 1 -b friendlyelec
| |
| − | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi4-v2017.09 -j$(nproc)
| |
| − | export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH
| |
| − | cd uboot-rockchip/
| |
| − | ./make.sh nanopi_r2
| |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| |
| − | 编译完成后会生成如下文件:
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | uboot.img
| |
| − | | trust.img
| |
| − | | rk3328_loader_v1.16.250.bin
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | 安装u-boot: <br />
| |
| − | 请参考 [[#下载uboot与内核到目标板]]<br>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ====下载uboot与内核到目标板====
| + | {{BurnLinuxToExtDrive-Rockchip/zh|NanoPC-T4}} |
| − | =====下载至已安装的系统=====
| + | {{BurnLinuxToExtDrive-Rockchip|NanoPC-T4}} |
| − | ======GPT分区======
| + | |
| − | 本节内容适用于如下OS:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | buildroot
| + | |
| − | | friendlycore-focal-arm64 | + | |
| − | | friendlywrt21
| + | |
| − | | friendlywrt21-docker
| + | |
| − | | friendlywrt22
| + | |
| − | | friendlywrt22-docker
| + | |
| − | | friendlycore-lite-focal-arm64
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | linux v4.19内核和linux v5.15内核的系统默认使用GPT分区, 更新GPT分区比较简单,直接dd image文件至相应的分区即可(注意image的大小不要越界),在操作时需要注意存储设备的节点:
| + | |
| − | * SD/TF Card设备节点为 /dev/mmcblk0 <br />
| + | |
| − | * eMMC设备节点为 /dev/mmcblk2 <br />
| + | |
| − | 下面将演示如何将内核更新到eMMC:<br />
| + | |
| − | 使用parted命令查看分区布局:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | parted /dev/mmcblk2 print
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 得到如下输出:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | Model: MMC A3A551 (sd/mmc)
| + | |
| − | Disk /dev/mmcblk2: 31.0GB
| + | |
| − | Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
| + | |
| − | Partition Table: gpt
| + | |
| − | Disk Flags:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
| + | |
| − | 1 8389kB 12.6MB 4194kB uboot
| + | |
| − | 2 12.6MB 16.8MB 4194kB misc
| + | |
| − | 3 16.8MB 21.0MB 4194kB dtbo
| + | |
| − | 4 21.0MB 37.7MB 16.8MB resource
| + | |
| − | 5 37.7MB 79.7MB 41.9MB kernel
| + | |
| − | 6 79.7MB 113MB 33.6MB boot
| + | |
| − | 7 113MB 147MB 33.6MB recovery
| + | |
| − | 8 147MB 31.0GB 30.9GB ext4 rootfs
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 可以看到resource分区位置为4, kernel分区位置为5,用dd命令分别写入resource.img与kernel.img到这两个分区即可, 命令如下:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | dd if=resource.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p4 bs=1M
| + | |
| − | dd if=kernel.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p5 bs=1M
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 如果要更新uboot,则命令为:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | dd if=boot.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p1 bs=1M
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 如果要更新内核驱动模块,将新驱动模块目录上传并替换以下目录下的文件即可:/lib/modules。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | =====打包新的SD卡启动固件或者SD-to-eMMC卡刷固件=====
| + | |
| − | sd-fuse 提供一些工具和脚本, 用于制作SD卡固件, 具体用途如下:<br />
| + | |
| − | * 制作分区镜像文件, 例如将rootfs目录打包成rootfs.img<br />
| + | |
| − | * 将多个分区镜像文件打包成可直接写SD卡的单一镜像文件<br />
| + | |
| − | * 简化内核和uboot的编译, 一键编译内核、第三方驱动, 并更新rootfs.img中的内核模块<br />
| + | |
| − | 请根据所用的内核版本点击对应的链接了解详细的使用方法:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | ! 内核版本
| + | |
| − | ! 构建工具集
| + | |
| − | |- | + | |
| − | | linux v4.19.y
| + | |
| − | | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/tree/kernel-4.19<br /> sd-fuse]
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | | linux v5.15.y
| + | |
| − | | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3328/tree/kernel-5.15.y<br /> sd-fuse]
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | =====线刷=====
| + | |
| − | 不擦除flash的情况下只刷入编译生成的文件即可,需要注意的是uboot编译生成的rk3328_loader需要改名为MiniLoaderAll.bin,如下命令演示刷入uboot与内核,需要先加载parameter.txt,再刷入其他文件:
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool ul MiniLoaderAll.bin
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool di -p parameter.txt
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool di uboot uboot.img
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool di trust trust.img
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool di resource resource.img
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool di kernel kernel.img
| + | |
| − | sudo upgrade_tool RD
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注:upgrade_tool是Rockchip提供的Linux下的命令行工具(Linux_Upgrade_Tool)
| + | |
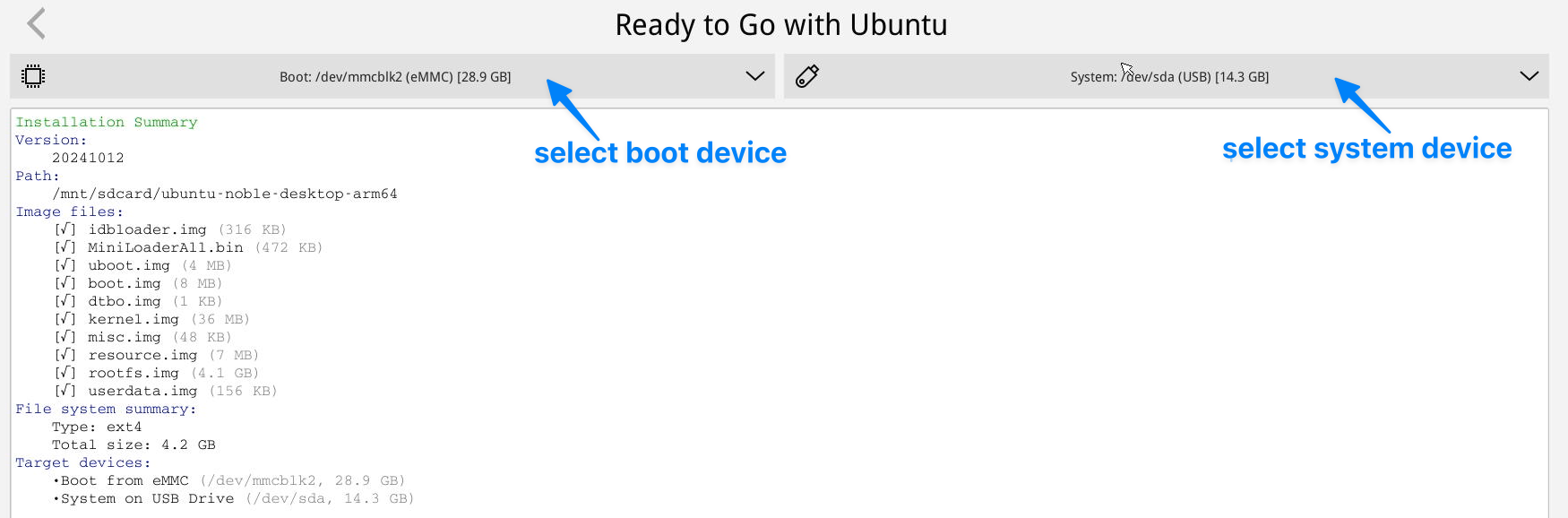
可以通过使用TF卡启动eFlasher系统,将引导和系统分别安装到不同存储设备,但是由于CPU不支持直接从M.2和USB设备引导,所以虽然系统可以安装到M.2和USB设备,但是引导仍然需要安装到eMMC或者TF卡。
操作步骤如下:
You can use a TF card to boot the eFlasher system, allowing the boot and system to be installed on different storage devices. However, since the CPU doesn’t support booting directly from M.2 and USB devices, the system can be installed on M.2 and USB devices, but the boot must still be installed on eMMC or a TF card.
Steps are as follows: