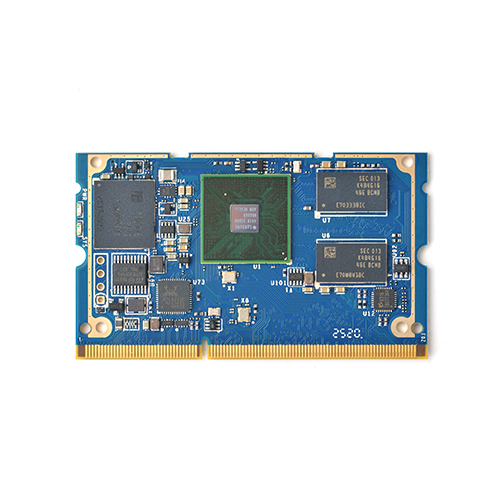
SOM-4418
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 Hardware Spec
- 3 Software Features
- 4 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
- 5 Reference Design
- 6 Notes in Hardware Design
- 7 Get Started
- 8 Work with FriendlyCore
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 System Login
- 8.3 Configure System with npi-config
- 8.4 Develop Qt Application
- 8.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
- 8.6 Extend TF Card's Section
- 8.7 Transfer files using Bluetooth
- 8.8 WiFi
- 8.9 Setup Wi-Fi AP
- 8.10 Bluetooth
- 8.11 Ethernet Connection
- 8.12 Custom welcome message
- 8.13 Modify timezone
- 8.14 Select the system default audio device
- 8.15 Run the X11 application
- 8.16 Run Qt 5.10.0 Demo with GPU acceleration
- 8.17 Run Qt 5.10.0 Demo with OpenGL
- 8.18 Play HD Video with Hardware-decoding
- 8.19 Connect to DVP Camera CAM500B
- 8.20 Power Off and Schedule Power On
- 8.21 Installing and Using OpenCV 4.1.2
- 8.22 Installing and Using Caffe
- 8.23 How to install and use docker (for armhf system)
- 9 Work with Android
- 10 Make Your Own OS Image
- 11 Build Kernel Headers Package
- 12 Installation=
- 13 Access Hardware under Android
- 14 Connect SOM-4418 to FriendlyARM LCD Modules
- 15 Schematics & Mechanical drawing
- 16 Source Code and Image Files Download Links
- 17 Tech Support
- 18 Schematics & Mechanical drawing
- 19 Update Log
- 19.1 2023-01-09
- 19.2 2020-10-26
- 19.3 2019-12-28
- 19.4 2019-11-26
- 19.5 2019-11-14
- 19.6 2019-10-18
- 19.7 2019-09-30
- 19.8 2019-07-18
- 19.9 2019-06-25
- 19.10 2019-06-03
- 19.11 2019-01-24
- 19.12 2018-12-17
- 19.13 March-04-2016
- 19.14 March-09-2016
- 19.15 March-23-2016
- 19.16 March-27-2016
- 19.17 April-08-2016
- 19.18 June-30-2016
- 19.19 Sep-04-2016
- 19.20 Sep-27-2016
- 19.21 Nov-2-2016
- 19.22 Nov-17-2016
- 19.23 Dec-7-2016
- 19.24 June-13-2016
- 19.25 June-20-2016
1 Introduction
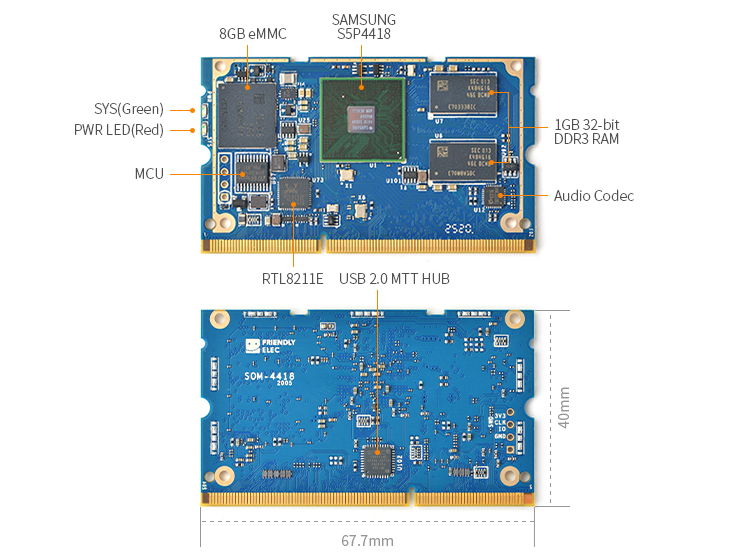
- The SOM-4418 quad core Cortex A9 core board is designed and developed by FriendlyELEC for professional and enterprise users. It uses the Samsung Quad Core Cortex-A9 S5P4418 SoC with dynamic frequency scaling up to 1.4GHz. SOM-4418 has 8G eMMC, 1GB 32bit-DDR3, GigE, and audio codec. To avoid overheat issues the SOM-4418 has a heat sink with mounting posts.
- The SOM-4418 has LVDS and RGB-LCD interface, support resistive touch and capacitive touch.
- The SOM-4418 also has USB HOST, UARTs, I2Cs, SPI, PWM, GPIOs etc.
2 Hardware Spec
- SoC:Samsung S5P4418 Quad Core Cortex-A9 with dynamic frequency scaling up to 1.4G Hz
- PMU Power Management: Implemented by an MCU, support solftware power-off, and RTC alarm power-on functions
- System Memory:1GB 32bit DDR3 RAM
- eMMC:8GB
- Ethernet:Gbps Ethernet Port (RTL8211E) with unique MAC, support WOL(Wake On Lan)
- Video Input: MIPI-CSI
- Video Output: HDMI / LVDS / LCD
- Audio: Build in Codec, 2-Chanel headphone output, one Microphone input
- USB: 4 x USB 2.0 Host(Via USB Hub), 1 x USB 2.0 OTG
- GPIO: 13 x GPIOs, 3 x I2Cs, 1 x SPI, 5 x UARTs, 3 x PWMs, 2 x SDIOs
- LED: 1 x power LED , 1 x SYS LED
- Other Resource: 1 x onboard thermistor, RTC
- Power: DC 5V/1A
- Heat Sink: Aluminum heat sink
- PCB: Six Layer, ENIG
- PCB Dimension: 67.7 mm x 40 mm
- Working Temperature: -40℃ to 70℃
3 Software Features
4 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
4.1 Layout
- 204 Pin Spec
- Socket Type:0.6mm Pitch 204-Pin Standard Type DDR3 SODIMM Socket
Pin# Name Description Pin# Name Description 1 VDD_5V 4.7~5.5V Power Suply input 2 VDD_5V 4.7~5.5V Power Suply input 3 VDD_5V 4 VDD_5V 5 VDD_5V 6 VDD_5V 7 GND 8 GND 9 GND 10 VRTC_IN RTC backup battery(3V)input,backup current is 3.5uA 11 VCC_WIFI_IO(3.3V) MMC1 IO reference power,connect to wifi module IO power input 12 VCC_IO(3.3V) 3.3V out for IO reference 13 MMC1_D0 SDIO1/MMC1, connect to wifi module 14 BOOT_CS Pull low this pin to boot from SD CARD on MMC0 15 MMC1_D1 16 PWRKEY Power key 17 MMC1_D2 18 NRESETIN Hard reset input 19 MMC1_D3 20 AliveGPIO3 GPIO, reserved for RecoveryKey 21 MMC1_CMD 22 EXT_PWR_CTRL Used this pin to control power on/off of the carrier 23 GND 24 MMC0_D0 SDIO0/MMC0, for SD Card 25 MMC1_CLK SDIO1 Clock Out 26 MMC0_D1 27 WL_REG_ON(GPIOB24) GPIOB24, Used as wifi power on control signal 28 MMC0_D2 29 WL_HOST_WAKE(GPIOC17) GPIOC17, Used as wifi wake-up signal 30 MMC0_D3 31 UART1_TX UART1, connect to bluetooth module 32 MMC0_CMD 33 UART1_RX 34 MMC0_CD 35 UART1_nCTS 36 MMC0_CLK 37 UART1_nRTS 38 GND 39 BT_RST_N(GPIOB8) GPIOB8, Used as bluetooth reset 40 MIPI_CSI0_CLKN MIPI CSI Clock 41 BT_WAKE bluetooth wake-up signal 42 MIPI_CSI0_CLKP 43 BT_HOST_WAKE(/NC) Reserved for BT_HOST_WAKE 44 GND 45 LPO_32Khz 32.768kHz output for wifi/bt module 46 MIPI_CSI0_D0N MIPI CSI data0 47 GND 48 MIPI_CSI0_D0P 49 MDI0_P GbE MDI signals 50 GND 51 MDI0_N 52 MIPI_CSI0_D1N MIPI CSI data1 53 MDI1_P 54 MIPI_CSI0_D1P 55 MDI1_N 56 GND 57 GND 58 /NC 59 MDI2_P GbE MDI signals 60 /NC 61 MDI2_N 62 GND 63 MDI3_P 64 /NC 65 MDI3_N 66 /NC 67 GND 68 GND 69 SPEED_LED GbE SPEED LED signal output 70 /NC 71 LINK_LED GbE LINK LED signal output 72 /NC Connector Key 73 GND 74 TP_INT(GPIOC16) I2C signal, connect to touch controller 75 USB_DM4 USB 2.0 host data signal 76 TP_SDA(I2C2_SDA) 77 USB_DP4 78 TP_SCL(I2C2_SCL) 79 GND 80 OneWire(GPIOC15) GPIOC15, used as FriendlyElec LCD OneWire signal 81 USB_DM3 USB 2.0 host data signal 82 GND 83 USB_DP3 84 LCD_CLK RGB LCD Clock signal 85 GND 86 GND 87 USB_DM2 USB 2.0 host data signal 88 LCD_HSYNC RGB LCD horizontal synchronization 89 USB_DP2 90 LCD_VSYNC RGB LCD vertical synchronization 91 GND 92 LCD_DE signal the external LCD that data is valid on the data bus 93 /NC 94 GND 95 /NC 96 LCD_R0 RGB LCD Red data signals 97 GND 98 LCD_R1 99 USB_OTG_D- USB 2.0 OTG data signal 100 LCD_R2 101 USB_OTG_D+ 102 LCD_R3 103 USB_OTG_ID USB 2.0 OTG ID signal 104 LCD_R4 105 VBUS USB 2.0 OTG VBUS 106 LCD_R5 107 VBUS_DRIVE(/NC) Reserved for USB 2.0 OTG VBUS Power Drive Signal 108 LCD_R6 109 HDMI_HPD HDMI Hot plug detect 110 LCD_R7 111 I2C1_SDA I2C1, used as HDMI DDC signal 112 GND 113 I2C1_SCL 114 LCD_G0 RGB LCD Green data signals 115 HDMI_CEC HDMI CEC Signal 116 LCD_G1 117 GND 118 LCD_G2 119 HDMI_TXCN HDMI Clock and data signals 120 LCD_G3 121 HDMI_TXCP 122 LCD_G4 123 GND 124 LCD_G5 125 HDMI_TX0N 126 LCD_G6 127 HDMI_TX0P 128 LCD_G7 129 GND 130 GND 131 HDMI_TX1N 132 LCD_B0 RGB LCD Blue data signals 133 HDMI_TX1P 134 LCD_B1 135 GND 136 LCD_B2 137 HDMI_TX2N 138 LCD_B3 139 HDMI_TX2P 140 LCD_B4 141 GND 142 LCD_B5 143 USB_DM1 USB 2.0 data signal 144 LCD_B6 145 USB_DP1 146 LCD_B7 147 GND 148 GND 149 /NC 150 LVDS_Y3M LVDS signals 151 /NC 152 LVDS_Y3P 153 GND 154 GND 155 /NC 156 LVDS_CLKM 157 /NC 158 LVDS_CLKP 159 GND 160 GND 161 GPIOB31 GPIOs 162 LVDS_Y2M 163 GPIOB30 164 LVDS_Y2P 165 GPIOC7 166 GND 167 GPIOC8 168 LVDS_Y1M 169 GPIOB23 170 LVDS_Y1P 171 GPIOC2 172 GND 173 GPIOC13/PWM1 PWMs 174 LVDS_Y0M 175 GND 176 LVDS_Y0P 177 GPIOC14/PWM2 178 GND 179 GPIOD1/PWM0 180 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC29 SPI 181 I2C2_SDA I2Cs 182 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC31 183 I2C2_SCL 184 SPI0_MISO/GPIOD0 185 I2C0_SDA 186 SPI0_CS/GPIOC30 187 I2C0_SCL 188 GPIOD8/PPM 189 GPIOB27/HP_DETECT GPIOB27, used as Headphone insert detect 190 UART4_TX/GPIOB29 UARTs 191 AUDIO_GND Headphone output return path 192 UART4_RX/GPIOB28 193 HP_R Headphone output R 194 UART3_RX/GPIOD17 195 HP_L Headphone output L 196 UART3_TX/GPIOD21 197 LINEOUT_R(HP_R) Internal connect to HP_R, reserved for line out R in the future 198 UART2_RX 199 LINEOUT_L(HP_L) Internal connect to HP_L, reserver for line out L in the future 200 UART2_TX 201 MICIN_N Microphone input N 202 UART0_RX Used as Debug console 203 MICIN_P Microphone input P 204 UART0_TX
- Note:
- All VDD_5V Must be connected to get the lowest connection resistance.
- All GND Must be connected for good EMC performance and system stability.
- A 4-layer PCB carrier board is highly recommended.
- For more details refer to the document: SOM-4418-2005-Schematic.pdf
5 Reference Design
6 Notes in Hardware Design
6.1 EEPROM
- The board has an EEPROM(model: 24AA025E48T-I/OT) with a unique MAC. This EEPROM is connected to I2C0 and its address is 0x51 therefore some EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0 which will cause conflicts of addresses.
- In our tests these EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0: 24C04, 24C08 and 24C16. There chips which we tested can be connected to I2C0: 24C01, 24C02 and 24C256
- For more details about EEPROM address issues refer to http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/CAT24C01-D.PDF
7 Get Started
7.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your SOM-4418 get the following items ready
- SOM-4418 + Edge-RT300
- TF Coard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB
- A DC 12/2A power
- LCD HD702V (Optional)
- USB keyboard, mouse and possible a USB hub(or a TTL to serial board)
- A host computer running Ubuntu 18.04 64 bit system (Optional)
7.2 Boot from SD Card
Get the following files from here download link:
- Get a 8G SDHC card and backup its data if necessary.
| Image Files | |
| s5p4418-sd-friendlycore-xenial-4.4-armhf-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | FriendlyCore with Qt 5.10.0 (base on Ubuntu core) image file |
| s5p4418-sd-lubuntu-desktop-xenial-4.4-armhf-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | LUbuntu Desktop image file with X Window |
| s5p4418-sd-friendlywrt-4.4-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | FriendlyWrt image file (base on OpenWrt) |
| s5p4418-sd-android7-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | Android7 image file |
| s5p4418-sd-android-kitkat-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | Android4.4 image file with support for 4G LTE |
| s5p4418-sd-android-lollipop-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | Android5.1 image file |
| s5p4418-eflasher-lubuntu-desktop-xenial-4.4-armhf-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | SD card image, which is used to install a lubuntu desktop to eMMC |
| s5p4418-eflasher-friendlywrt-4.4-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | SD card image, which is used to install a FriendlyWrt to eMMC |
| s5p4418-eflasher-android7-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | SD card image, which is used to install a android7 to eMMC |
| s5p4418-eflasher-friendlycore-xenial-4.4-armhf-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | SD card image, which is used to install a friendly-core to eMMC |
| s5p4418-eflasher-android-kitkat-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | SD card image, which is used to install a android4 to eMMC |
| s5p4418-eflasher-android-lollipop-YYYYMMDD.img.zip | SD card image, which is used to install a android5 to eMMC |
| Flash Utility: | |
| win32diskimager.rar | Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd" |
- Uncompress these files. Insert an SD card(at least 4G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Insert this card into your board's boot slot, press and hold the boot key (only applies to a board with onboard eMMC) and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and LED1 is blinking this indicates your board has successfully booted.
7.3 Flash image to eMMC with eflasher
- Download eflasher image file
An image file's name is as : s5p4418-eflasher-OSNAME-YYYYMMDD.img.zip
The "OSNAME" is the name of an OS e.g. android, friendlycore and etc;
This image file is used for making an installation SD card and it contains a Ubuntu core system and a utility EFlasher;
Download s5p4418-eflasher-OSNAME-YYYYMMDD.img.zip to a host PC and get a windows utility win32diskimager.rar as well;
- Make Installation SD Card with eflasher
Extract the package with a 7z utility and you will get a file with an extension ".img". Insert an SDHC card(minimum 8G or above) to a PC running Windows, run the Win32DiskImager utility as administrator, click on "Image File" to select your wanted file, select your SD card and click on "Write" to start flashing the Image to your SD card;
If your PC runs Linux you can command "dd" to extract the package and get an ".img" file and write it to your SD card;
- Operate in GUI Window: Flash OS to eMMC
Insert your SD card to SOM-4418, connect an HDMI monitor or LCD to your board, press and hold the "boot" key beside the Ethernet port, power on the board you will see a pop-up window asking you to select an OS for installation. Select your wanted OS and start installation.
- Operate in Commandline Utility: Flash OS to eMMC
Insert an installation SD card to SOM-4418, log into or SSH to your board and run the following command to start EFlasher:
sudo eflasher7.3.1 Make Installation Card under Linux Desktop
- 1) Insert your SD card into a host computer running Ubuntu and check your SD card's device name
dmesg | tail
Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card has been recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions"
- 2) Downlaod Linux script
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_s5p4418.git
cd sd-fuse_s5p4418
- 3) Here is how to make a Lubuntu desktop SD card
sudo ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx lubuntu
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
When you run the script for the first time it will prompt you to download an image you have to hit “Y” within 10 seconds otherwise you will miss the download
- 4) Run this command to make a complete image file:
sudo ./mkimage.sh lubuntu
More content please refre: Assembling the SD card image yourself
7.4 Extend SD Card Section
- When Debian/Ubuntu is loaded the SD card's section will be automatically extended.
- When Android is loaded you need to run the following commands on your host PC to extend your SD card's section:
sudo umount /dev/sdx? sudo parted /dev/sdx unit % resizepart 4 100 resizepart 7 100 unit MB print sudo resize2fs -f /dev/sdx7
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
7.5 Update SD Card's boot parameters From PC Host
Insert your SD card into a host PC running Linux, if you want to change your kernel command line parameters you can do it via the fw_setevn utility.
Check the current Command Line:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_s5p4418.git
cd sd-fuse_s5p4418/tools
./fw_printenv /dev/sdx | grep bootargs
For example, to disable android SELinux, You can change it this way:
./fw_setenv /dev/sdc bootargs XXX androidboot.selinux=permissive
The "XXX" stands for the original bootargs' value.
7.6 Run Android or Linux (TODO)
- 将制作好SD卡插入SOM-4418,连接HDMI,按住靠近网口的boot按键,最后接电源(5V 2A)拨动开关,SOM-4418会从SD卡启动。你可以看到板上PWR灯常亮,LED1灯闪烁,这说明系统已经开始启动了,同时电视上也将能看到系统启动的画面。
- 要在电视上进行操作,你需要连接USB鼠标和键盘;如果你选购了LCD配件,则可以直接使用LCD上面的触摸屏进行操作。
8 Work with FriendlyCore
8.1 Introduction
FriendlyCore is a light Linux system without X-windows, based on ubuntu core, It uses the Qt-Embedded's GUI and is popular in industrial and enterprise applications.
Besides the regular Ubuntu core's features our FriendlyCore has the following additional features:
- it supports our LCDs with both capacitive touch and resistive touch(S700, X710, HD702, S430, HD101 and S70)
- it supports WiFi
- it supports Ethernet
- it supports Bluetooth and has been installed with bluez utilities
- it supports audio playing
- it supports Qt 5.10.0 EGLES and OpenGL ES1.1/2.0 (Only for S5P4418/S5P6818)
8.2 System Login
- FriendlyCore User Accounts:
Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
The system is automatically logged in as "pi". You can do "sudo npi-config" to disable auto login.
- Update packages
$ sudo apt-get update
8.3 Configure System with npi-config
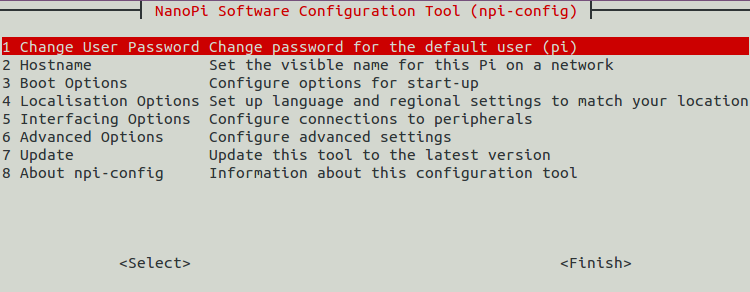
The npi-config is a commandline utility which can be used to initialize system configurations such as user password, system language, time zone, Hostname, SSH switch , Auto login and etc. Type the following command to run this utility.
$ sudo npi-config
Here is how npi-config's GUI looks like:
8.4 Develop Qt Application
Please refer to: How to Build and Install Qt Application for FriendlyELEC Boards
8.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
You can setup a program to autorun on system boot with npi-config:
sudo npi-configGo to Boot Options -> Autologin -> Qt/Embedded, select Enable and reboot.
8.6 Extend TF Card's Section
When FriendlyCore is loaded the TF card's section will be automatically extended.You can check the section's size by running the following command:
$ df -h
8.7 Transfer files using Bluetooth
Take the example of transferring files to the mobile phone. First, set your mobile phone Bluetooth to detectable status, then execute the following command to start Bluetooth search.:
hcitool scan
Search results look like:
Scanning ...
2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 HTC6525LVWThis means that a mobile phone named HTC6525LVW is searched. We write down the MAC address in front of the phone name, and then use the sdptool command to view the Bluetooth service supported by the phone:
sdptool browser 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02
Note: Please replace the MAC address in the above command with the actual Bluetooth MAC address of the mobile phone.
This command will detail the protocols supported by Bluetooth for mobile phones. What we need to care about is a file transfer service called OBEX Object Push. Take the HTC6525LVW mobile phone as an example. The results are as follows:
Service Name: OBEX Object Push Service RecHandle: 0x1000b Service Class ID List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Protocol Descriptor List: "L2CAP" (0x0100) "RFCOMM" (0x0003) Channel: 12 "OBEX" (0x0008) Profile Descriptor List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Version: 0x0100
As can be seen from the above information, the channel used by the OBEX Object Push service of this mobile phone is 12, we need to pass it to the obexftp command, and finally the command to initiate the file transfer request is as follows:
obexftp --nopath --noconn --uuid none --bluetooth -b 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 -B 12 -put example.jpg
Note: Please replace the MAC address, channel and file name in the above command with the actual one.
After executing the above commands, please pay attention to the screen of the mobile phone. The mobile phone will pop up a prompt for pairing and receiving files. After confirming, the file transfer will start.
Bluetooth FAQ:
1) Bluetooth device not found on the development board, try to open Bluetooth with the following command:
rfkill unblock 02) Prompt can not find the relevant command, you can try to install related software with the following command:
apt-get install bluetooth bluez obexftp openobex-apps python-gobject ussp-push8.8 WiFi
For either an SD WiFi or a USB WiFi you can connect it to your board in the same way. The APXX series WiFi chips are SD WiFi chips. By default FriendlyElec's system supports most popular USB WiFi modules. Here is a list of the USB WiFi modules we tested:
Index Model 1 RTL8188CUS/8188EU 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 mi WiFi mt7601 6 5G USB WiFi RTL8821CU 7 5G USB WiFi RTL8812AU
You can use the NetworkManager utility to manage network. You can run "nmcli" in the commandline utility to start it. Here are the commands to start a WiFi connection:
- Change to root
$ su root
- Check device list
$ nmcli devNote: if the status of a device is "unmanaged" it means that device cannot be accessed by NetworkManager. To make it accessed you need to clear the settings under "/etc/network/interfaces" and reboot your system.
- Start WiFi
$ nmcli r wifi on- Scan Surrounding WiFi Sources
$ nmcli dev wifi- Connect to a WiFi Source
$ nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD" ifname wlan0
The "SSID" and "PASSWORD" need to be replaced with your actual SSID and password.If you have multiple WiFi devices you need to specify the one you want to connect to a WiFi source with iface
If a connection succeeds it will be automatically setup on next system reboot.
For more details about NetworkManager refer to this link: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
If your USB WiFi module doesn't work most likely your system doesn't have its driver. For a Debian system you can get a driver from Debian-WiFi and install it on your system. For a Ubuntu system you can install a driver by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install linux-firmware
In general all WiFi drivers are located at the "/lib/firmware" directory.
8.9 Setup Wi-Fi AP
Follow the steps below. Since our OS image by default already has the NetworkManager utility you will be prompted to uninstall it first:
sudo turn-wifi-into-apmode yes
After you uninstall the NetworkManager reboot your board.
After your board is rebooted run the above commands again and you will be prompted to type in a WIFI's name and password. Type in your wanted name and password
If this is successful you will be able to find and connect your board to a WIFI. Login to your board at 192.168.8.1:
ssh root@192.168.8.1
Type in a password. In our system the password is "fa".
To login smoothly via SSH we recommend you turning off WIFI's power save mode by running the following commands:
sudo iwconfig wlan0 power offYou can check your WiFi's mode by running the following command:
sudo cat /sys/module/bcmdhd/parameters/op_mode
Number 2 means your WiFi is in AP mode. You can switch to the Station mode by running the following command:
sudo turn-wifi-into-apmode no8.10 Bluetooth
Search for surrounding bluetooth devices by running the following command:
$ su root
$ hciconfig hci0 up
$ hcitool scanYou can run "hciconfig" to check bluetooth's status.
8.11 Ethernet Connection
If a board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP with DHCP activated after it is powered up. If you want to set up a static IP refer to: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings。
8.12 Custom welcome message
The welcome message is printed from the script in this directory:
/etc/update-motd.d/
For example, to change the FriendlyELEC LOGO, you can change the file /etc/update-motd.d/10-header. For example, to change the LOGO to HELLO, you can change the following line:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal $BOARD_VENDOR
To:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal HELLO
8.13 Modify timezone
For exampe, change to Shanghai timezone:
sudo rm /etc/localtime sudo ln -ls /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
8.14 Select the system default audio device
You can set the system default audio device by following the steps below.
Use the following command to view all the sound card devices in the system (Note: different development boards will have different results):
pi@NanoPi:~$ aplay -l **** List of PLAYBACK Hardware Devices **** card 0: nanopi2audio [nanopi2-audio], device 0: c0055000.i2s-ES8316 HiFi ES8316 HiFi-0 [] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0 card 0: nanopi2audio [nanopi2-audio], device 1: c0059000.spdiftx-dit-hifi dit-hifi-1 [] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
As you can see, the following sound card devices are available on the hardware:
Sound card device Sound card number Description nanopi2audio device 0 3.5mm jack interface nanopi2audio device 1 HDMI
To configure the audio output to the 3.5mm jack, create or modify the configuration file /etc/asound.conf and modify it to the following:
pcm.!default { type hw card 0 device 0 } ctl.!default { type hw card 0 }
To configure to output audio to HDMI, change the device 0 above to device 1.
8.15 Run the X11 application
FriendlyCore system built-in lightweight Xorg,although there is no window manager, you can still run a single X-Windows application,For example, the program to run is ~/YourX11App,use the following command:
. /usr/bin/setqt5env-xcb startx ~/YourX11App -geometry 1280x800
Note that there is a space between "." and /usr/bin/setqt5env-xcb. In addition, the resolution after -geometry should be changed to the actual resolution of your screen.
8.16 Run Qt 5.10.0 Demo with GPU acceleration
Run the following command
$ sudo qt5demo
8.17 Run Qt 5.10.0 Demo with OpenGL
Run the following command
. setqt5env cd $QTDIR cd /examples/opengl/qopenglwidget ./qopenglwidget
For more Qt 5.10.0 examples, please go to:
cd $QTDIR/examples/
8.18 Play HD Video with Hardware-decoding
gst-player is console player, it base on GStreamer, support VPU with Hardware-decoding:
sudo gst-player /home/pi/demo.mp4
The equivalent gsteamer command is as follows:
sudo gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=/home/pi/demo.mp4 ! qtdemux name=demux demux. ! queue ! faad ! audioconvert ! audioresample ! alsasink device="hw:0,DEV=1" demux. ! queue ! h264parse ! nxvideodec ! nxvideosink dst-x=0 dst-y=93 dst-w=1280 dst-h=533
8.19 Connect to DVP Camera CAM500B
The CAM500B camera module is a 5M-pixel camera with DVP interface. For more tech details about it you can refer to Matrix - CAM500B.
Enter the following command to preview the video:
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src device=/dev/video6 ! video/x-raw,format=I420,framerate=30/1,width=1280,height=720 ! nxvideosink
Enter the following command to start recording (VPU hardware encoding):
gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src device=/dev/video6 ! video/x-raw,format=I420,framerate=30/1,width=1280,height=720 ! tee name=t t. \ ! queue ! nxvideosink t. ! queue ! nxvideoenc bitrate=12000000 ! mp4mux ! \ filesink location=result_720.mp4
8.20 Power Off and Schedule Power On
“PMU Power Management” feature helps us to auto power on the board at a specific time, it is implemented by an MCU, support software power-off, and RTC alarm power-up functions.
Here’s a simple guide:
Turn on automatically after 100 seconds. (Time must be greater than 60 seconds.):
$ sudo echo 100 > /sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-3/device/3-002d/wakealarm
After setting up the automatic boot, turn off board with the 'poweroff’ command:
$ sudo poweroff
Cancel automatic boot:
$ sudo echo 0 > /sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-3/device/3-002d/wakealarm
Query the current settings, in the front is current time, followed by the time of automatic booting: If no automatic boot is set, it will display "disabled”.
$ sudo cat /sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-3/device/3-002d/wakealarm
Note that some older versions of hardware may not support this feature, if you don't see this file node in your system:
/sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-3/device/3-002d/wakealarm
your board may be it does not support this feature.
8.21 Installing and Using OpenCV 4.1.2
OpenCV has been pre-installed in FriendlyCore (Version after 20191126) and does not require manual installation.
Please refre this link: https://github.com/friendlyarm/install-opencv-on-friendlycore/blob/s5pxx18/README.md
Quick test:
. /usr/bin/cv-env.sh . /usr/bin/setqt5env-eglfs cd /usr/local/share/opencv4/samples/python python3 turing.py
8.22 Installing and Using Caffe
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/install-caffe-on-friendlycore cd install-caffe-on-friendlycore sudo ./install-caffe.sh
8.23 How to install and use docker (for armhf system)
8.23.1 How to Install Docker
Run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker.io
8.23.2 Test Docker installation
Test that your installation works by running the simple docker image:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/debian-jessie-arm-docker cd debian-jessie-arm-docker ./rebuild-image.sh ./run.sh
9 Work with Android
9.1 Work with 4G Module EC20 under Android5
9.1.1 Hardware Setup
Connect an EC20 module to a USB to miniPCIe board and connect the board to an ARM board's USB Host. Here is a hardware setup:
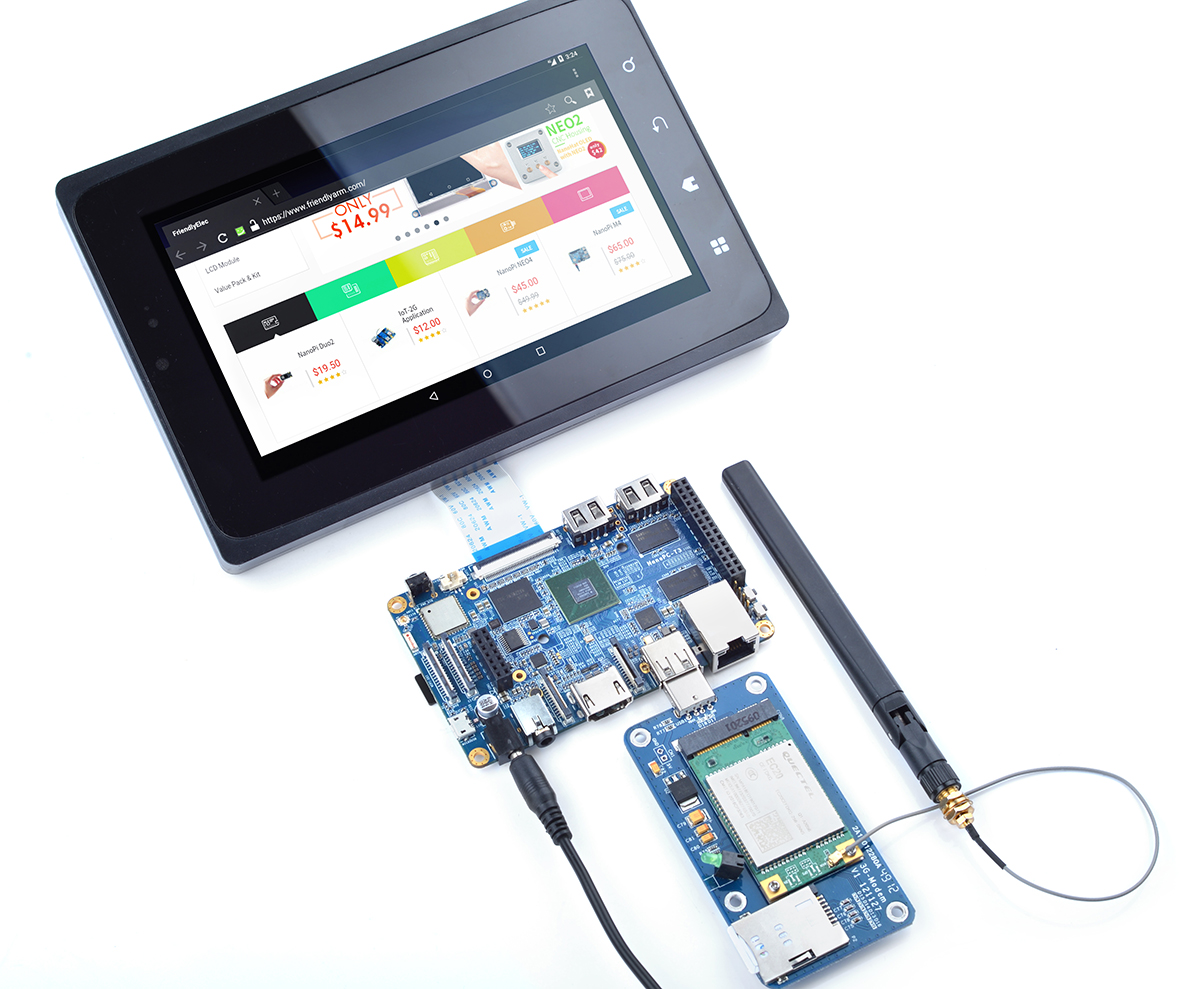

Power on the board and you will be able to surf the internet with the 4G module like using an Android phone.
9.2 Modify the Android boot Logo
Replace the logo.bmp:
/opt/FriendlyARM/smart4418/android/device/friendly-arm/nanopi3/boot/logo.bmp /opt/FriendlyARM/smart4418/android/device/friendly-arm/nanopi2/boot/logo.bmp
Replace the bootanimation.zip:
/opt/FriendlyARM/smart4418/android/device/friendly-arm/nanopi3/bootanimation.zip /opt/FriendlyARM/smart4418/android/device/friendly-arm/nanopi2/bootanimation.zip
Re-compile android.
9.3 Use fastboot command to flash android firmware
Enter the uboot command line mode on the serial terminal when powering on, and then enter the following command:
fastboot 0For S5P4418:
fastboot flash partmap partmap.txt fastboot flash 2ndboot bl1-mmcboot.bin fastboot flash fip-loader loader-mmc.img fastboot flash fip-secure bl_mon.img fastboot flash fip-nonsecure bootloader.img fastboot flash boot boot.img fastboot flash system system.img fastboot flash cache cache.img fastboot flash userdata userdata.img
For S5P6818:
fastboot flash partmap partmap.txt fastboot flash 2ndboot bl1-mmcboot.bin fastboot flash fip-loader fip-loader.img fastboot flash fip-secure fip-secure.img fastboot flash fip-nonsecure fip-nonsecure.img fastboot flash boot boot.img fastboot flash system system.img fastboot flash cache cache.img fastboot flash userdata userdata.img
9.4 Android Keys
Android 5:
vendor/friendly-arm/nanopi3/security/
Android 7:
build/target/product/security/
9.5 Optimizing HDMI Performance on Android 7
9.5.1 Note
By default, the driver initializes two framebuffers, one for the primary LCD display and the other for HDMI. If your project specifically requires the use of HDMI and not the LCD, you can follow the steps outlined in this chapter to make modifications. After making these changes, HDMI will be configured as the primary display, resulting in the initialization of only one framebuffer. This optimization conserves resources and leads to corresponding improvements in UI performance and boot speed.
The content of this chapter is applicable exclusively to S5P6818 running Android 7. For S5P4418, the modification process is similar, with adjustments needed in the corresponding files.
9.5.2 Modify the kernel
You need to modify the kernel Device Tree Source (DTS) to disable the dp_drm_lvds node, as shown below:
--- a/arch/arm64/boot/dts/nexell/s5p6818-nanopi3-common.dtsi +++ b/arch/arm64/boot/dts/nexell/s5p6818-nanopi3-common.dtsi @@ -810,6 +810,7 @@ plane-names = "video", "rgb", "primary"; }; port@1 { + status = "disabled"; reg = <1>; back_color = < 0x0 >; color_key = < 0x0 >; @@ -820,7 +821,7 @@ &dp_drm_lvds { remote-endpoint = <&lcd_panel>; - status = "ok"; + status = "disabled"; display-timing { clock-frequency = <50000000>;
After compilation, you will obtain a new arch/arm64/boot/dts/nexell/s5p6818-nanopi3-rev*.dtb file.
During the testing phase, you can directly update it to the board using adb with the following command:
adb root; adb wait-for-device; adb shell mkdir /storage/sdcard1/; adb shell mount -t ext4 /dev/block/mmcblk0p1 /storage/sdcard1/ adb push arch/arm64/boot/dts/nexell/s5p6818-nanopi3-rev*.dtb /storage/sdcard1/
For a complete firmware update, you will need to replace the files in the device/friendlyelec/nanopi3/boot directory of the Android 7 source code.
9.5.3 Modify env.conf
To modify the device/friendlyelec/nanopi3/boot/env.conf file and add a line
lcdtype HDMI1080P60
This mode needs to match the mode detected by Android 7 after startup; otherwise, it may result in a prolonged black screen state or even no display output. In such cases, you may need to manually set it in the U-Boot command-line environment:
setenv lcdtype HDMI1080P60; saveenv; reset
9.5.4 Modify system.prop
To modify the device/friendlyelec/nanopi3/system.prop file in Android 7
ro.sf.lcd_density=240Alternatively, you can adjust the system property or experiment with different values that you deem more appropriate. You can also use the following command to change the display density under the serial or adb environment and observe if the effect is suitable:
adb shell wm density 2409.5.5 Compiling Android
Follow the instructions in the wiki to compile Android 7 and conduct testing. If you encounter any exceptions, please carefully review the preceding steps.
10 Make Your Own OS Image
10.1 Install Cross Compiler
10.1.1 Install arm-linux-gcc 4.9.3
Download the compiler package:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/prebuilts.git -b master --depth 1 cd prebuilts/gcc-x64 cat toolchain-4.9.3-armhf.tar.gz* | sudo tar xz -C /
Then add the compiler's directory to "PATH" by appending the following lines in "~/.bashrc":
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
Execute "~/.bashrc" to make the changes take effect. Note that there is a space after the first ".":
. ~/.bashrcThis compiler is a 64-bit one therefore it cannot be run on a 32-bit Linux machine. After the compiler is installed you can verify it by running the following commands:
arm-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=arm-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/libexec/gcc/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/4.9.3/lto-wrapper Target: arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf Configured with: /work/toolchain/build/src/gcc-4.9.3/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/sys-root --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-arch=armv7-a --with-tune=cortex-a9 --with-fpu=vfpv3 --with-float=hard ... Thread model: posix gcc version 4.9.3 (ctng-1.21.0-229g-FA)
10.2 Compile Linux kernel for FriendlyCore/Lubuntu/EFlasher
10.2.1 Compile Kernel
- Download Kernel Source Code
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux.git -b nanopi2-v4.4.y --depth 1 cd linux
The SOM-4418's kernel source code is in the "nanopi2-v4.4.y" branch.You need to switch to this branch.
- Compile Ubuntu Kernel
touch .scmversion make ARCH=arm nanopi2_linux_defconfig make ARCH=arm
After your compilation succeeds an "arch/arm/boot/zImage" will be generated and a DTB file(s5p4418-nanopi2-rev*.dtb) will be generated in the "arch/arm/boot/dts/" directory. You can use them to replace the existing zImage and DTB files in the boot partition of your bootable SD card.
10.2.2 Use Your Generated Kernel
- Update kernel in SD card
If you use an SD card to boot Ubuntu you can copy your generated zImage and DTB files to your SD card's boot partition(e.g. partition 1 /dev/sdX1).
- Update kernel in eMMC
If you boot your board from eMMC you can update your kernel file by following the steps below:
1) Usually after OS is loaded eMMC's boot partition (in our example eMMC's device name was /dev/mmcblk0p1) will be automatically mounted and you can verify that by running "mount"
2) Connect your board to a host PC running Ubuntu and copy the zImage and DTB files to eMMC's boot partition
3) Or you can copy your generated kernel file to an external storage card(e.g. an SD card or a USB drive), connect the storage card to your board the move the file from the card to eMMC's boot partition
4) After update is done type "reboot" to reboot your board. Note: don't just directly disconnect your board from its power source or press the reset button to reboot the board. These actions will damage your kernel file
- Generate Your boot.img
Refer to this repo: https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_s5p4418
10.3 Compile Linux kernel for Android7
The Android 7.1.2 source code already contains the pre-compiled kernel. If you need to customize it, you can compile the kernel according to the following guide.
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux.git -b nanopi2-v4.4.y --depth 1 cd linux touch .scmversion make ARCH=arm nanopi2_nougat_defconfig make ARCH=arm
The newly generated kernel is arch/arm/boot/zImage,The new DTB file is also included under the directory arch/arm/boot/dts/.(s5p4418-nanopi2-rev*.dtb).
If you only want to debug the kernel, you can quickly update it with adb:
adb root; adb shell mkdir /storage/sdcard1/; adb shell mount -t ext4 /dev/block/mmcblk0p1 /storage/sdcard1/; adb push arch/arm/boot/zImage arch/arm/boot/dts/s5p4418-nanopi2-rev*.dtb /storage/sdcard1/
If you want to generate boot.img for burning, you can copy the kernel zImage and DTB files to the Android7 source code directory: device/friendlyelec/nanopi2/boot, then recompile Android7.
10.4 Compile U-Boot for Android7/FriendlyCore/Lubuntu/EFlasher
Download the U-Boot source code and compile it. Note that the github's branch is nanopi2-v2016.01:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/u-boot.git cd u-boot git checkout nanopi2-v2016.01 make s5p4418_nanopi2_defconfig make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
After your compilation succeeds a bootloader.img will be generated. If you want to test it flash it to your installation SD card to replace an existing U-Boot v2016.01 file via fastboot, sd-fuse_s5p4418 or eflasher ROM.
For Android7: Copy bootloader.img to Android7 source directory device/friendlyelec/nanopi2/boot, then recompile Android7.
Note: you cannot use mixed U-Boot files. For example you cannot use fastboot to update an existing U-Boot V2014.07 and you cannot use bootloader.img to replace an existing u-boot.bin
10.5 Compile Android 7.1.2
10.5.1 Install Cross Compiler
Install 64 bit Ubuntu 16.04 on your host PC.
sudo apt-get install bison g++-multilib git gperf libxml2-utils make python-networkx zip sudo apt-get install flex curl libncurses5-dev libssl-dev zlib1g-dev gawk minicom sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk sudo apt-get install exfat-fuse exfat-utils device-tree-compiler liblz4-tool
For more details refer to https://source.android.com/source/initializing.html 。
10.5.2 Download Android7 Source Code
There are two ways to download the source code:
- repo archive file on netdisk
Netdisk URL: Click here
File location on netdisk:sources/s5pxx18-android-7.git-YYYYMMDD.tar (YYYYMMDD means the date of packaging)
After extracting the repo package from the network disk, you need to execute the sync.sh script, which will pull the latest code from gitlab:
tar xvf /path/to/netdisk/sources/s5pxx18-android-7.git-YYYYMMDD.tar cd s5pxx18-android-7 ./sync.sh
- git clone from gitlab
SOM-4418 source code is maintained in gitlab, You can download it by running the following command:
git clone https://gitlab.com/friendlyelec/s5pxx18-android-7.git -b master
10.5.3 Compile Android7
cd s5pxx18-android-7 source build/envsetup.sh lunch aosp_nanopi2-userdebug make -j8
After your compilation succeeds the following files will be generated in the "out/target/product/nanopi2/" directory.
filename partition Description bl1-mmcboot.bin raw boot firmware loader-mmc.img raw boot firmware bl_mon.img raw boot firmware bootloader.img raw uboot-v2016.01 env.conf - Uboot environment variable containing Android kernel command line parameters boot.img boot kernel zImage, DTBs; logo; Android ramdisk cache.img cache - userdata.img userdata - system.img system - partmap.txt - Partition description file
11 Build Kernel Headers Package
The following commands need to be executed on the development board:
11.1 Software Version
The OS image file name: s5p4418-sd-friendlycore-xenial-4.4-armhf-YYYYMMDD.img, s5p4418-eflasher-friendlycore-xenial-4.4-armhf-YYYYMMDD.img
pi@NanoPC-T2:~$ lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS Release: 16.04 Codename: xenial pi@NanoPC-T2:~$ cat /proc/version Linux version 4.4.172-s5p4418 (root@jensen) (gcc version 7.5.0 (ctng-1.24.0-108g-FA) ) #1 SMP PREEMPT Wed Mar 24 15:17:25 CST 2021
11.2 Install the required packages
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y dpkg-dev bsdtar
11.3 Build Kernel Headers Package
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux -b nanopi2-v4.4.y --depth 1 kernel-s5pxx18-arm cd kernel-s5pxx18-arm rm -rf .git make distclean touch .scmversion make CROSS_COMPILE= ARCH=arm nanopi2_linux_defconfig alias tar=bsdtar make CROSS_COMPILE= ARCH=arm bindeb-pkg -j4
The following message is displayed to indicate completion:
dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-firmware-image-4.4.172-s5p4418' in '../linux-firmware-image-4.4.172-s5p4418_4.4.172-s5p4418-1_armhf .deb'. dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-headers-4.4.172-s5p4418' in '../linux-headers-4.4.172-s5p4418_4.4.172-s5p4418-1_armhf.deb'. dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-libc-dev' in '../linux-libc-dev_4.4.172-s5p4418-1_armhf.deb'. dpkg-deb: building package 'linux-image-4.4.172-s5p4418' in '../linux-image-4.4.172-s5p4418_4.4.172-s5p4418-1_armhf.deb'. dpkg-genchanges: binary-only upload (no source code included)
12 Installation=
sudo rm -f /lib/modules/4.4.172-s5p4418/build sudo rm -f /lib/modules/4.4.172-s5p4418/source sudo dpkg -i ../linux-headers-4.4.172-s5p4418_4.4.172-s5p4418-1_armhf.deb
12.1 Testing
To compile the pf_ring module as an example, refer to the documentation: https://www.ntop.org/guides/pf_ring/get_started/git_installation.html.
git clone https://github.com/ntop/PF_RING.git cd PF_RING/kernel/ make CROSS_COMPILE=
After compiling, use insmod to try to load the module:
sudo insmod ./pf_ring.ko
13 Access Hardware under Android
FriendlyElec developed a library called “libfriendlyarm-things.so”, for android developer to access the hardware resources on the development board in their android apps, the library is based on Android NDK.
Accessible Modules:
- Serial Port
- PWM
- EEPROM
- ADC
- LED
- LCD 1602 (I2C)
- OLED (SPI)
Interfaces & Ports:
- GPIO
- Serial Port
- I2C
- SPI
Refer to the following url for details:
- Homepage: http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/FriendlyThings
- Examples: https://github.com/friendlyarm/friendlythings-examples
- Guide to API: http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/FriendlyThings_APIs
14 Connect SOM-4418 to FriendlyARM LCD Modules
Supported LCD Model:HD702V
15 Schematics & Mechanical drawing
- PCB Dimension(SOM-4418_2005_dxf.zip)
- Schematic(SOM-4418-2005-Schematic.pdf)
- S5P4418 Datasheet (S5P4418_Datasheet_0.1.pdf)
16 Source Code and Image Files Download Links
17 Tech Support
If you have any further questions please visit our forum http://www.friendlyarm.com/Forum/ and post a message or email us at techsupport@friendlyarm.com. We will endeavor to get back to you as soon as possible.
18 Schematics & Mechanical drawing
- PCB Dimension(SOM-4418_2005_dxf.zip)
- Schematic(SOM-4418-2005-Schematic.pdf)
- S5P4418 Datasheet (S5P4418_Datasheet_0.1.pdf)
19 Update Log
19.1 2023-01-09
19.1.1 FriendlyCore:
- optimized the systemd service
19.2 2020-10-26
- FriendlyCore, Lubuntu:
Fix Bluetooth stability issue
19.3 2019-12-28
- eflasher:
1) Supports flashing only some files, such as updating only the kernel and uboot in emmc
2) Added gui option to disable overlay filesystem
3) Add command line parameters to achieve one-click installation without interaction
4) Fix the issue that the same mac address will appear on different devices after backup and restore image
5) UI interface can now be configured with title, hide interface menus and buttons
19.4 2019-11-26
- FriendlyCore:
Pre-installed OpenCV 4.1.2
19.5 2019-11-14
- Introducing a new system FriendlyWrt:
FriendlyWrt is a customized OpenWrt system developed by FriendlyElec. It is open source and suitable for applications in IoT, NAS etc.
Please refre: http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/How_to_Build_FriendlyWrt
- FriendlyCore, Lubuntu updated as follows:
1) Added support for new 4.3-inch screen YZ43
2) Compile bcmdhd as a module.
- Android7 update is as follows:
1) Added support for new 4.3-inch screen YZ43
2) Optimize the touch experience when using HD900 screen under Android 7 system
3) Optimize the touch experience when using S702 screen under Android 7 system
19.6 2019-10-18
- Android7, FriendlyCore, Lubuntu:
Fixed audio playback issue.
19.7 2019-09-30
- Android7 updated as follows:
1)Added support for Android hardware access library (named FriendlyThing), support access to hardware resources such as GPIO, PWM, RTC, serial port and watchdog, providing open source demo
2) Added support for camera CAM500B (OV5640)
3) Added support for LCD W500 (800x480)
4) Fixed LCD-S430 compatibility issues
- FriendlyCore, FriendlyDesktop updated as follows:
1) Kernel version updated to v4.4.172, same as Android 7
2) Added Docker support, support 32bit and 64bit file systems
3) Kernel configuration items are optimized to enable more features and device drivers
19.8 2019-07-18
- Introducing a new system Android 7.1.2
1) Features similar to the old version of Android 5, support 4G, WiFi, Ethernet, Bluetooth, etc.
2) Kernel version: 4.4.172
3) Known issue: The camera is not working yet
- Android/FriendlyCore/Lubuntu updated as follows:
1) Fix an issue where HD101B can't be touched in some cases
2) Fix GPIO configuration of Power key
3) Solve the problem of too small volume: the volume of the DAC is changed from -20dB to -6dB during playback.
4) Add more models of USB Wi-Fi support, built-in driver rtl8821CU.ko, rtl88XXau.ko
- Updates for Lubuntu only:
1) Modify Lubuntu's Power key behavior to (without pop-ups) shut down directly
2) Add script xrotate.sh to simplify screen rotation settings (Note: screen rotation will lose performance)
- The following updates are only available for NanoPC T2, Smart4418:
Support for reading Ethernet Mac addresses from the onboard EEPROM, only supports the following systems: FriendlyCore, Lubuntu, Android7
19.9 2019-06-25
Linux(Ubuntu 16.04/18.04) uses OverlayFS to enhance filesystem stability.
19.10 2019-06-03
1) Configure LED1 to be in heartbeat mode
2) Fix HDMI 1080P may have no display problem in some cases
3) Fix the issue that mysql cannot be installed under Linux
4) Fix the issue that the 1-wire touch resistance screen cannot be used under lubuntu
19.11 2019-01-24
1) Update uboot-v2014.07, uboot-v2016.01 for HD702V LCD
2) Adjust Qt5 font path
19.12 2018-12-17
- Android5 updated as follows:
1) Add support for 4G network, support module: Quectel EC20
2) Add audio setting UI, you can set the default output to headphones or HDMI
3) Synchronously turn off the backlight of the one-line touch screen when the system Shutdown
- FriendlyCore updated as follows:
1) Add OV5640 camera support
2) Update BL1 to improve system startup stability
- Lubuntu updated as follows:
1) Add Chrome-browser browser, support web page 1080P hardware decoding, support WebGL
2) Set the audio output channel to HDMI by default (can be changed via /etc/asound.conf)
3) Update BL1 to improve system startup stability
4) Fixed some issues regarding the package error in the previous version
5) Adjust DPMS settings, turn off automatic sleep by default
19.13 March-04-2016
- Released English version
19.14 March-09-2016
- Corrected a typo
19.15 March-23-2016
- Added section 11
19.16 March-27-2016
- Corrected expression errors
19.17 April-08-2016
- Added section 6.4.2 and 7.4
- Updated section 6.5
19.18 June-30-2016
- Added section 9 and 10
19.19 Sep-04-2016
- Updated section 5.2.2 and 10.1.1
19.20 Sep-27-2016
- Updated section 5.2.2, 7.5 and 8.2
19.21 Nov-2-2016
- Updated section 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 and 12
19.22 Nov-17-2016
- Added section 10.6
19.23 Dec-7-2016
- Added section 6.6
- Updated section 7.5
19.24 June-13-2016
- Added section 7: added UbuntuCore
- Added section 11.3: added DietPi
19.25 June-20-2016
- Updated sections 6.2 & 6.3: Wireless connection and WiFi AP setting
- Added section 3: software features