Difference between revisions of "Matrix - I2C LCD1602 Keypad"
(→Resources) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
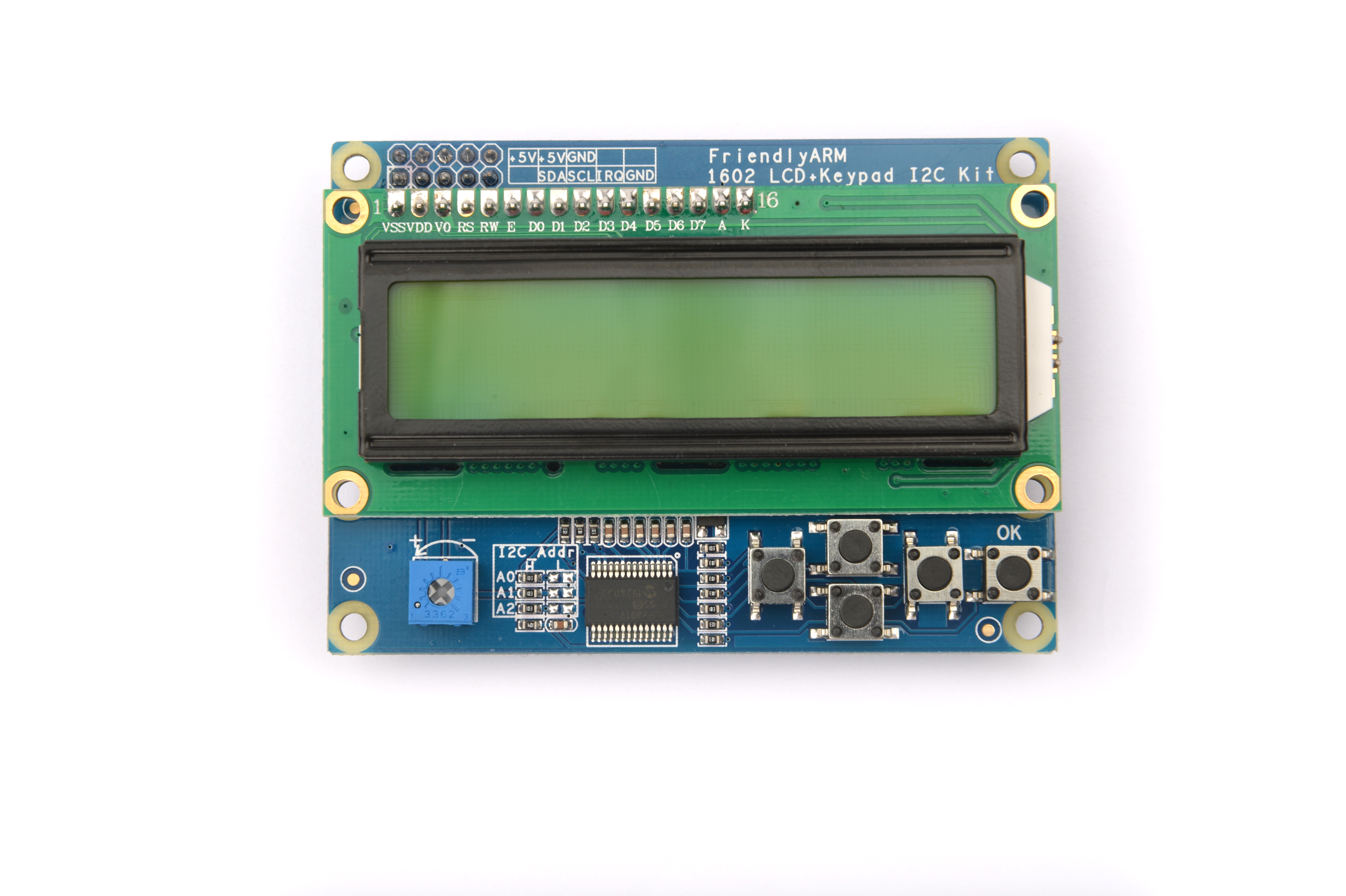
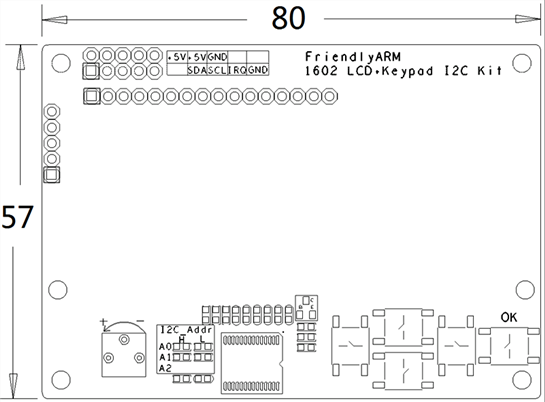
* I2C PCB dimension (mm): 57 x 80 | * I2C PCB dimension (mm): 57 x 80 | ||
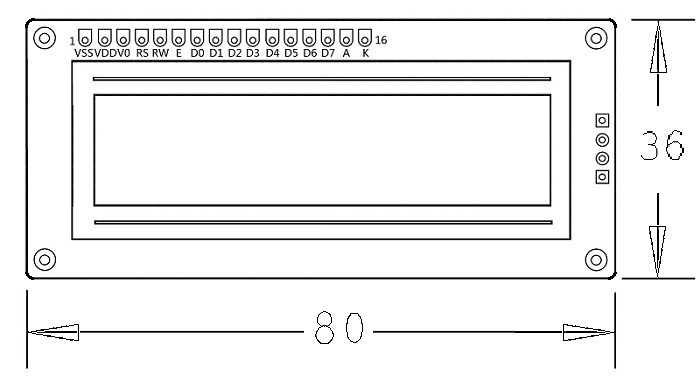
* LCD1602 PCB dimension (mm): 36 x 80 | * LCD1602 PCB dimension (mm): 36 x 80 | ||
| − | [[File:lpdpcb01.png|frameless|400px| | + | [[File:lpdpcb01.png|frameless|400px|IIC Module PCB]] |
[[File:lcdpcb.png|frameless|400px|LCD1602 PCB]] | [[File:lcdpcb.png|frameless|400px|LCD1602 PCB]] | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
===LCD1602=== | ===LCD1602=== | ||
| − | * The connection diagram between the | + | * The connection diagram between the MCP23017 module's Pin0~Pin7 and the LCD module is shown below: |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:图片不正确.png|frameless|400px|1602]] |
* RS is instruction/data register selection. RW is read/write selection. E is enable signal(edge triggering). BL is back light control. D4-D7 are data bits. | * RS is instruction/data register selection. RW is read/write selection. E is enable signal(edge triggering). BL is back light control. D4-D7 are data bits. | ||
* The LCD module is controlled by four data bits through which we can send instructions to control its state. Because it has eight instruction/data bits (DB7 - DB0) when writing each instruction/data we need to write the most significant four bits DB7 - DB4 first and then the least significant four bits DB3 - DB0. | * The LCD module is controlled by four data bits through which we can send instructions to control its state. Because it has eight instruction/data bits (DB7 - DB0) when writing each instruction/data we need to write the most significant four bits DB7 - DB4 first and then the least significant four bits DB3 - DB0. | ||
* Note: the LCD module has 192 most commonly used characters stored in CGROM. When we write a common character e.g "A" it will directly display "A". In addition it can store up to eight user defined characters in RAM called CGRAM. | * Note: the LCD module has 192 most commonly used characters stored in CGROM. When we write a common character e.g "A" it will directly display "A". In addition it can store up to eight user defined characters in RAM called CGRAM. | ||
| + | ==Applications== | ||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi M1=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_nanopi_m1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi 2=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad_nanopi 2.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad_nanopi 2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire.<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_nanopi_m2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_nanopi_m2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPC-T2=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_NanoPC-T2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad || NanoPC-T2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SDA || Pin6 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SCL || Pin5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5V || Pin29 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND || Pin30 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Compile & Run Test Program== | ||
| + | Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git | ||
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compile and install Matrix: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd matrix | ||
| + | $ make && make install | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Run test program: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ matrix-lcd1602_keypad | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Note: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.<br> | ||
| + | Here is what you should observe:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:matrix-lcd1602_keypad_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-lcd1602_keypad_result]] <br> | ||
| + | By default the LCD displays the current time. If you press F1 it will display the IP address. If you press F5 it will display the current time. Users can define the functions of F2, F3 and F4.<br> | ||
| + | If the LCD doesn't show them clearly you can adjust the resistor to highlight the characters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Code Sample== | ||
| + | This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad". Here is its source code: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
| + | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int devFD, board; | ||
| + | int keyValue = 0; | ||
| + | int lastKeyValue = -1; | ||
| + | int showDefault = 1; | ||
| + | int needClear = 1; | ||
| + | time_t lt; | ||
| + | char curTime[TIME_STR_BUFSIZE]; | ||
| + | char preTime[TIME_STR_BUFSIZE]; | ||
| + | int i2cDev = 0; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to init board\n"); | ||
| + | return -1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (argc == 2) | ||
| + | i2cDev = atoi(argv[1]); | ||
| + | if ((devFD = LCD1602KeyInit(i2cDev)) == -1) { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to init LCD1602\n"); | ||
| + | return -1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); | ||
| + | printf("waiting key press...\n"); | ||
| + | while (1) { | ||
| + | keyValue = LCD1602GetKey(devFD); | ||
| + | if (keyValue != lastKeyValue) { | ||
| + | lastKeyValue = keyValue; | ||
| + | } else if (showDefault != 1){ | ||
| + | usleep(1000); | ||
| + | continue; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | switch (keyValue) { | ||
| + | // F1 | ||
| + | case 0x1e: | ||
| + | showDefault = 0; | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F1-IP address"); | ||
| + | if (showIP(devFD, "eth0")) { | ||
| + | if (showIP(devFD, "wlan0")) { | ||
| + | if (showIP(devFD, "usb0")) { | ||
| + | showIP(devFD, "lo"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | // F2 | ||
| + | case 0x1d: | ||
| + | showDefault = 0; | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F2-Your favor"); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, "Come add it"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | // F3 | ||
| + | case 0x1b: | ||
| + | showDefault = 0; | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F3-Your idea"); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, "Come show it"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | // F4 | ||
| + | case 0x17: | ||
| + | showDefault = 0; | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F4-About"); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, "by FriendlyARM"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | // F5 | ||
| + | case 0xf: | ||
| + | showDefault = 1; | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | if (showDefault == 1) { | ||
| + | if (needClear) { | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#Default"); | ||
| + | needClear = 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | memset(curTime, 0, TIME_STR_BUFSIZE); | ||
| + | lt = time(NULL); | ||
| + | strncpy(curTime, ctime(<) + 11, 8); | ||
| + | if(strcmp(curTime, preTime)) { | ||
| + | printf("time:%s\n", curTime); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, curTime); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | memset(preTime, 0, TIME_STR_BUFSIZE); | ||
| + | strcpy(preTime, curTime); | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | needClear = 1; | ||
| + | usleep(1000); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | printf("quit reading key press\n"); | ||
| + | LCD1602KeyDeInit(devFD); | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to [[Matrix API reference manual]] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--- | ||
==Download Matrix Source Code== | ==Download Matrix Source Code== | ||
All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br> | All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 228: | ||
If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples. | If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Connect to NanoPi 2== |
| − | === | + | ===Hardware Connection=== |
| − | + | Please refer to the following connection diagram to connect the Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad to the NanoPi 2:<br> | |
[[File:matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad_nanopi 2.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad_nanopi 2]] | [[File:matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad_nanopi 2.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad_nanopi 2]] | ||
| − | + | Connection Details: | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 88: | Line 247: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Compile Test Program=== |
| − | + | Please login the matrix hub and enter the nanopi2 branch | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ cd matrix | $ cd matrix | ||
| Line 95: | Line 254: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Compile the Matrix code | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean | ||
| Line 101: | Line 260: | ||
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the NanoPi 2.<br> | |
| − | + | Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. The test program is under the "install/usr/bin" directory.<br> | |
| + | The modules are under the "modules" directory. The driver's source code is in github: https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git <br> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Run Test Program=== |
| − | + | Please insert a TF card which is flashed with Debian to a Linux host and mount its boot and rootfs sections.<br> | |
| − | + | We assume the rootfs is mounted to /media/rootfs then please run the following commands to copy the module, library and test program to the card.<br> | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r | ||
| Line 113: | Line 273: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Insert this TF card to your NanoPi 2, power on and run the following command to start the matrix-lcd1602_keypad program.<br> | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ matrix-lcd1602_keypad | $ matrix-lcd1602_keypad | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Note: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to a NanoPi 2.<br> | |
| − | + | Here is what you should expect:<br> | |
[[File:matrix-lcd1602_keypad_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-lcd1602_keypad_result]] <br> | [[File:matrix-lcd1602_keypad_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-lcd1602_keypad_result]] <br> | ||
| − | + | By default the LCD displays the current time. If you press F1 it will display the IP address. If you press F5 it will display the current time. Users can define the functions of F2, F3 and F4. | |
| − | === | + | ===Code Sample=== |
<syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
int main(int argc, char ** argv) | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| Line 215: | Line 375: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
==Connect to NanoPi== | ==Connect to NanoPi== | ||
| Line 488: | Line 647: | ||
==Connect to Arduino== | ==Connect to Arduino== | ||
| − | + | ---> | |
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
| + | [http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/21952b.pdf MCP23017.pdf] <br> | ||
| + | [https://www.openhacks.com/uploadsproductos/eone-1602a1.pdf LCD1602.pdf] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Update Log== | ||
| + | ===Feb-24-2016=== | ||
| + | * Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2 | ||
| + | ===June-19-2016=== | ||
| + | * Re-organized and simplified wiki | ||
Latest revision as of 14:59, 19 June 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
- The Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad module is an easy-to-use display module based on the LCD1602.
- This module integrates the LCD1602 and the MCP23017 module. It has five programmable keys which allow users to control the LCD1602's display and external devices connected to the module.
- It has a potentiometer to adjust the LCD's back light.
- The LCD1602 can display up to 16x2 characters. It has a parallel interface. You can control it via two I2C channels.
- The MCP23017 has a 16-bit remote bidirectional I/O port, high speed I2C interface, three hardware address pins which make it able to connect up to eight devices. It communicates through I2C interface and converts input to parallel signals to the LCD1602.
2 Features
- I2C interface, LCD display and backlight control
- 2.54mm spacing pin
- I2C PCB dimension (mm): 57 x 80
- LCD1602 PCB dimension (mm): 36 x 80
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| IRQ | BUTTON IRQ |
| SDA | I2C SDA |
| SCL | I2C SCL |
| 5V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| GND | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
3.1 MCP23017
- The MCP23017 has a 16-bit remote bidirectional I/O port, high speed I2C interface. These I/O can be configured to inputs and outputs. Each input/output data is kept in its register. It has three hardware address pins which make it able to connect up to eight devices. In addition it has two configurable interrupt pins INTA and INTB.
- The I2C write operation includes the control byte and register address sequence. This sequence is followed by eight bits of data from the master and an Acknowledge (ACK) from the MCP23017. The operation is ended with a Stop (P) or Restart (SR) condition being generated by the master.
- The I2C Read operation includes the control byte sequence. This sequence is followed by another control byte (including the Start condition and ACK) with the R/W bit set (R/W = 1). The MCP23017 then transmits the data contained in the addressed register. The sequence is ended with the master generating a Stop or Restart condition.
- The I2C sequential operation (Write or Read) works this way: instead of transmitting a Stop or Restart condition after a data transfer, the master clocks the next byte pointed to by the address pointer after each data transfer. The sequence is ended with the master sending a Stop or Restart condition.
3.2 LCD1602
- The connection diagram between the MCP23017 module's Pin0~Pin7 and the LCD module is shown below:
- RS is instruction/data register selection. RW is read/write selection. E is enable signal(edge triggering). BL is back light control. D4-D7 are data bits.
- The LCD module is controlled by four data bits through which we can send instructions to control its state. Because it has eight instruction/data bits (DB7 - DB0) when writing each instruction/data we need to write the most significant four bits DB7 - DB4 first and then the least significant four bits DB3 - DB0.
- Note: the LCD module has 192 most commonly used characters stored in CGROM. When we write a common character e.g "A" it will directly display "A". In addition it can store up to eight user defined characters in RAM called CGRAM.
4 Applications
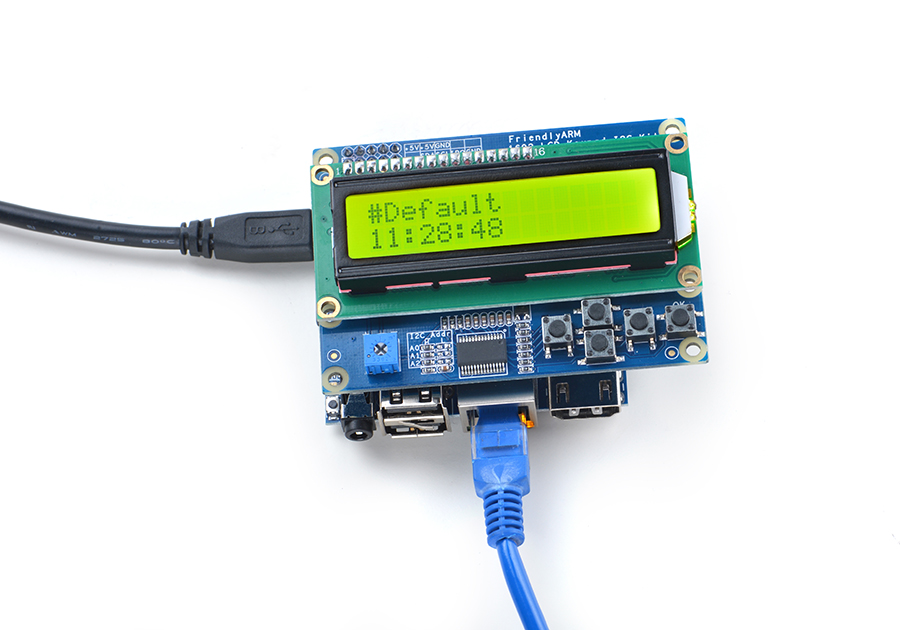
4.1 Connect to NanoPi M1
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:

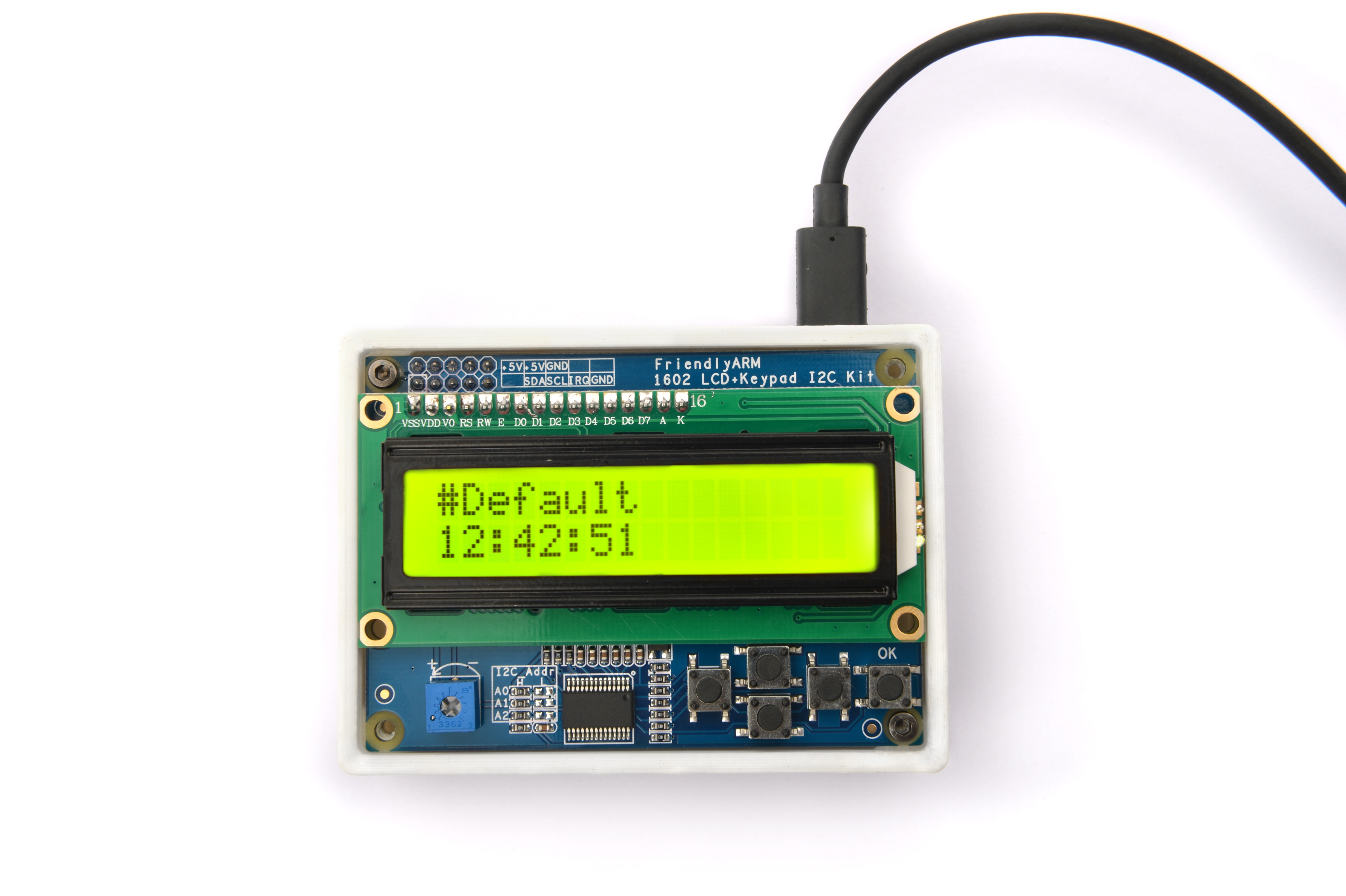
4.2 Connect to NanoPi 2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:

4.3 Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire.
Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_nanopi_m2
4.4 Connect to NanoPC-T2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:
Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad_NanoPC-T2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-I2C_LCD1602_Keypad | NanoPC-T2 |
| SDA | Pin6 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin29 |
| GND | Pin30 |
5 Compile & Run Test Program
Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code:
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated.
Compile and install Matrix:
$ cd matrix $ make && make install
Run test program:
$ matrix-lcd1602_keypadNote: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.
Here is what you should observe:
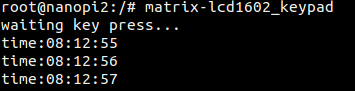
By default the LCD displays the current time. If you press F1 it will display the IP address. If you press F5 it will display the current time. Users can define the functions of F2, F3 and F4.
If the LCD doesn't show them clearly you can adjust the resistor to highlight the characters.
6 Code Sample
This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-i2c_lcd1602_keypad". Here is its source code:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int devFD, board; int keyValue = 0; int lastKeyValue = -1; int showDefault = 1; int needClear = 1; time_t lt; char curTime[TIME_STR_BUFSIZE]; char preTime[TIME_STR_BUFSIZE]; int i2cDev = 0; if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { printf("Fail to init board\n"); return -1; } if (argc == 2) i2cDev = atoi(argv[1]); if ((devFD = LCD1602KeyInit(i2cDev)) == -1) { printf("Fail to init LCD1602\n"); return -1; } LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); printf("waiting key press...\n"); while (1) { keyValue = LCD1602GetKey(devFD); if (keyValue != lastKeyValue) { lastKeyValue = keyValue; } else if (showDefault != 1){ usleep(1000); continue; } switch (keyValue) { // F1 case 0x1e: showDefault = 0; LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F1-IP address"); if (showIP(devFD, "eth0")) { if (showIP(devFD, "wlan0")) { if (showIP(devFD, "usb0")) { showIP(devFD, "lo"); } } } break; // F2 case 0x1d: showDefault = 0; LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F2-Your favor"); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, "Come add it"); break; // F3 case 0x1b: showDefault = 0; LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F3-Your idea"); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, "Come show it"); break; // F4 case 0x17: showDefault = 0; LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#F4-About"); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, "by FriendlyARM"); break; // F5 case 0xf: showDefault = 1; break; } if (showDefault == 1) { if (needClear) { LCD1602KeyClear(devFD); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 0, "#Default"); needClear = 0; } memset(curTime, 0, TIME_STR_BUFSIZE); lt = time(NULL); strncpy(curTime, ctime(<) + 11, 8); if(strcmp(curTime, preTime)) { printf("time:%s\n", curTime); LCD1602KeyDispStr(devFD, 0, 1, curTime); } memset(preTime, 0, TIME_STR_BUFSIZE); strcpy(preTime, curTime); } else { needClear = 1; usleep(1000); } } printf("quit reading key press\n"); LCD1602KeyDeInit(devFD); return 0; }
For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to Matrix API reference manual
7 Resources
8 Update Log
8.1 Feb-24-2016
- Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2
8.2 June-19-2016
- Re-organized and simplified wiki