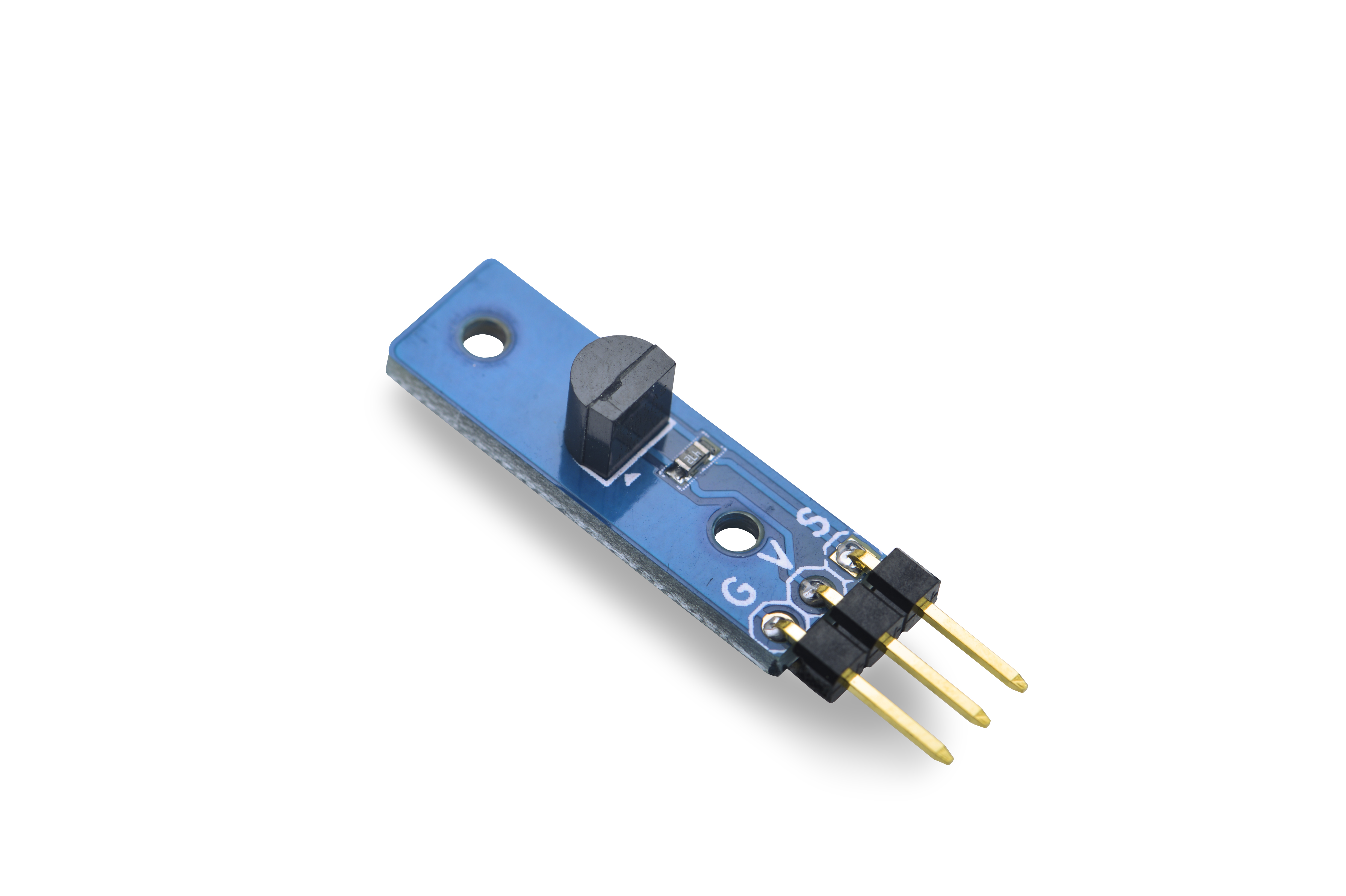
Matrix - Temperature Sensor
Contents
1 Introduction
- The matrix-temperature_sensor module is used to measure temperature.
- We utilitze the DS18B20 chip with the To-92 package in this module. Its unique 1-wire interface requires only 1 port pin for reading/writing. Power for reading, writing, and performing temperature conversions can be derived from the data line itself with no need for an external power source. The DS18B20 can be powered from its data line. Each DS18B20 is assigned a unique ID.
- Its temperature range is -55 degree Celsius to +125 degree Celsius. The thermometer resolution is programmable from 9 to 12 bits. When the measured temperature is between -10 degree Celsius to +85 degree Celsius the accuracy can be at 0.5 degree. Among all three DS18B20 pins V is power, G is ground and S is data.
2 Features
- -55 degree Celsius to +125 degree Celsius
- One wire interface for communication
- Tiny, easy to be deployed in various situations
- 2.54mm spacing pin
- PCB dimension(mm): 8 X 24
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| S | GPIO |
| V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| G | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
The core functionality of the DS18B20 is its direct-to-digital temperature sensor. The resolution of the DS18B20 is configurable (9, 10, 11, or 12 bits), with 12-bit readings the factory default state. This equates to a temperature resolution of 0.5°C, 0.25°C, 0.125°C, or 0.0625°C. Following the issuance of the Convert T [44h] command, a temperature conversion is performed and the thermal data is stored in the scratchpad memory in a 16-bit, sign-extended two’s complement format. The temperature information can be retrieved over the 1-Wire interface by issuing a Read Scratchpad [BEh] command once the conversion has been performed. The data is transferred over the 1-Wire bus, LSB first. The MSB of the temperature register contains the “sign” (S) bit, denoting whether the temperature is positive or negative.
4 Applications
4.1 Connect to NanoPi M1
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:
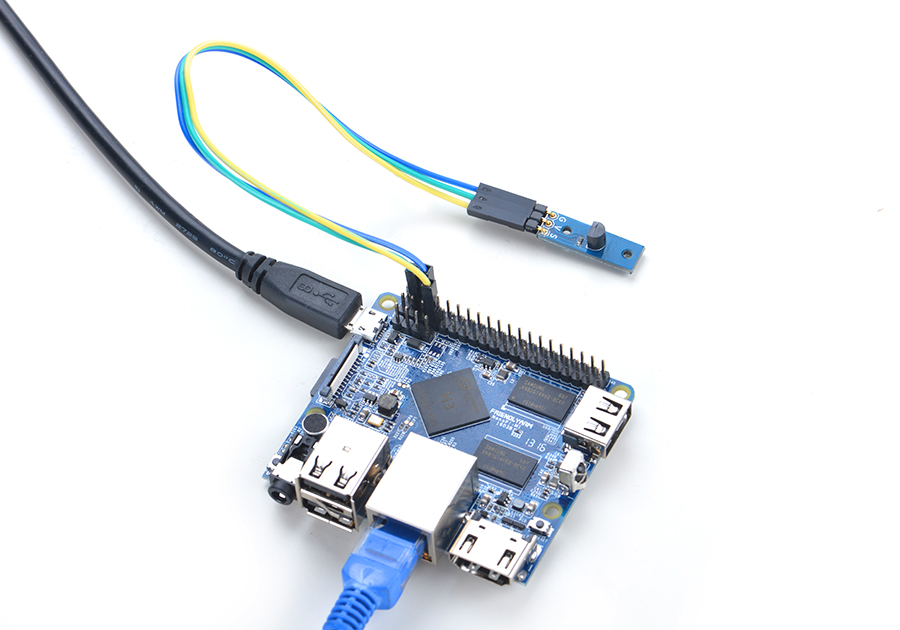
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Temperature_Sensor | NanoPi M1 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.2 Connect to NanoPi 2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:
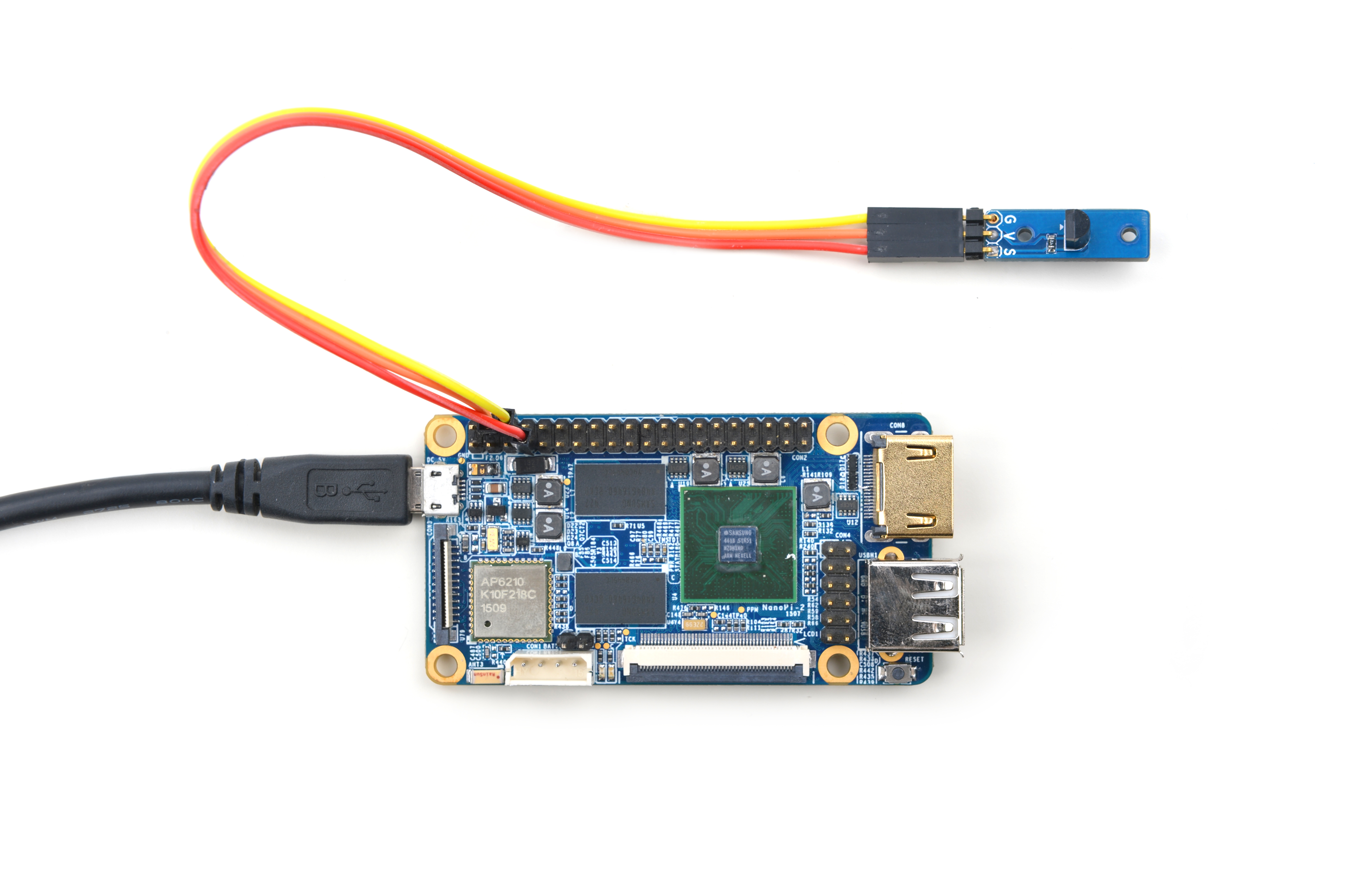
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Temperature_Sensor | NanoPi 2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.3 Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire:
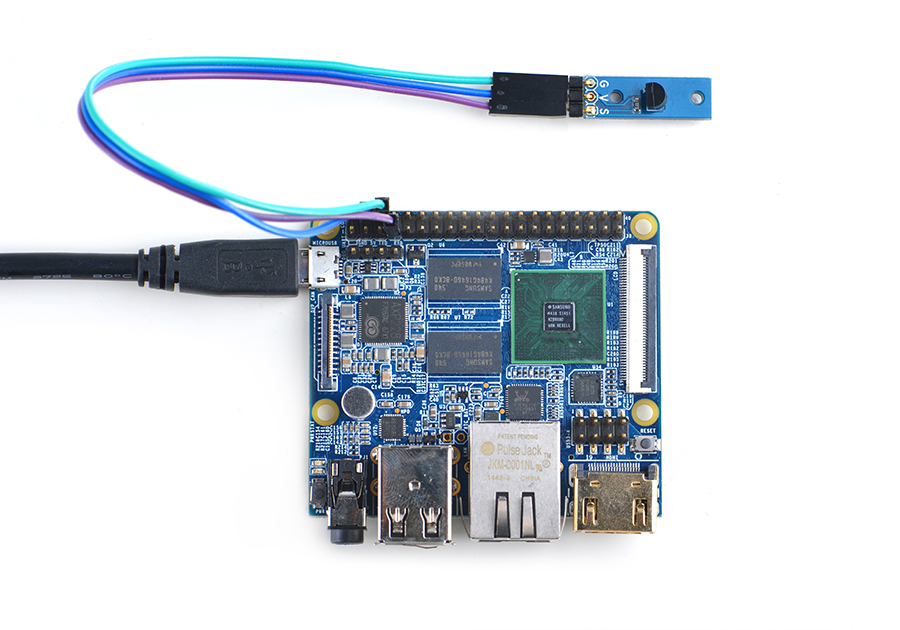
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Temperature_Sensor | NanoPi M2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.4 Connect to NanoPC-T2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:
Matrix-Temperature_Sensor_NanoPC-T2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Temperature_Sensor | NanoPC-T2 |
| S | Pin15 |
| V | Pin29 |
| G | Pin30 |
5 编译运行测试程序
启动开发板并运行Debian系统,进入系统后克隆Matrix代码仓库:
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
克隆完成后会得到一个名为matrix的目录。
编译并安装Matrix:
$ cd matrix $ make && make install
运行测试程序:
$ matrix-temp_sensor注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。
运行效果如下:
The temperature is 27.312 C成功读取温度值。
6 代码说明
所有的开发板都共用一套Matrix代码,本模块的测试示例代码为matrix-temperature_sensor,内容如下:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { char temperature[BUF_SIZE], modStr[BUF_SIZE]; int board; int pin=GPIO_PIN(7); if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { printf("Fail to init board\n"); return -1; } if (board == BOARD_NANOPI_T2) pin = GPIO_PIN(15); if (argc == 2) pin = atoi(argv[1]); sprintf(modStr, "modprobe %s gpio=%d", TEMP_GPIO_DRIVER_MODULE, pintoGPIO(pin)); printf("%s\n", modStr); system(modStr); system("modprobe "TEMP_DRIVER_MODULE); sleep(1); memset(temperature, 0, BUF_SIZE); if (ds18b20Read(temperature) > 0) { printf("The temperature is %.3f C\n", atoi(temperature)/1000.0); } else { printf("Fail to get temperature\n"); } system("rmmod "TEMP_GPIO_DRIVER_MODULE); system("rmmod "TEMP_DRIVER_MODULE); return 0; }
API说明参考维基:Matrix API reference manual
7 Resources
8 Update Log
8.1 Feb-23-2016
- Added the description for "NanoPi 2 branch" in Section 4
- Added Section 5: Connect to NanoPi 2