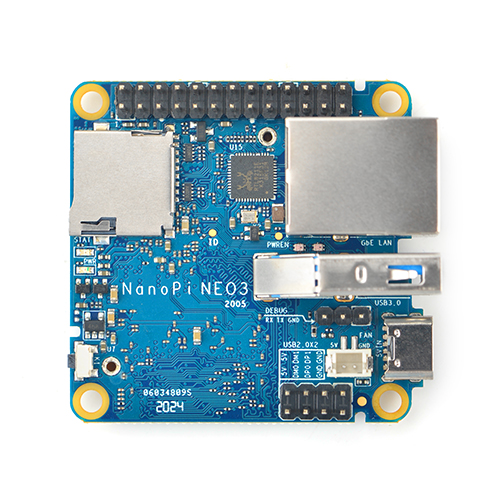
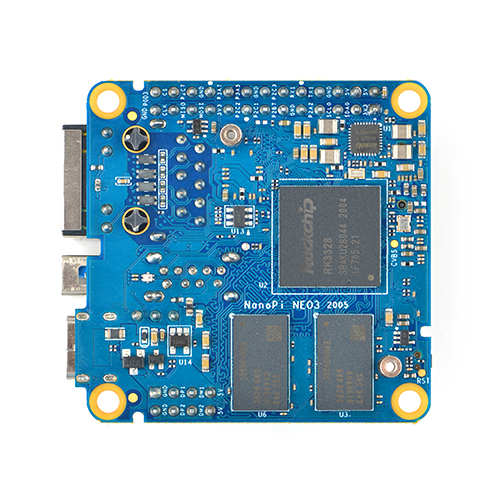
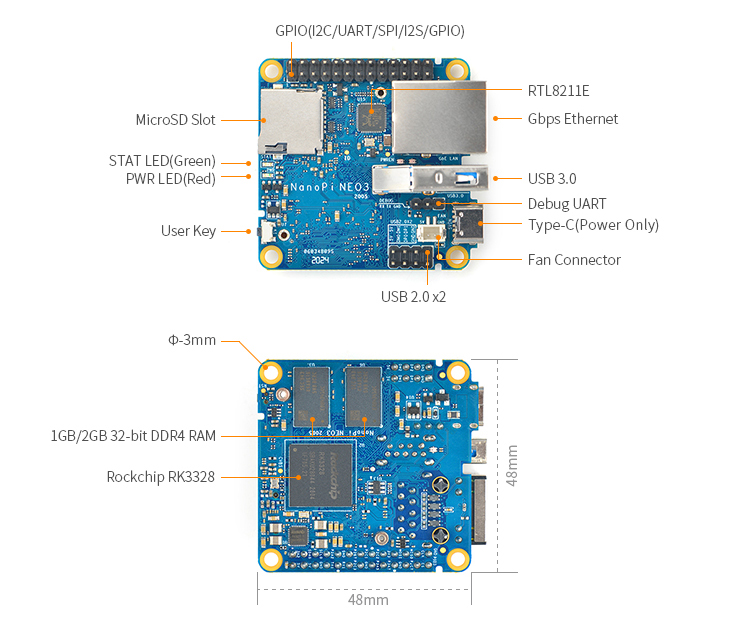
NanoPi NEO3
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 Hardware Spec
- 3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
- 4 Get Started
- 5 Work with FriendlyWrt
- 5.1 Introduction to FriendlyWrt
- 5.2 First boot
- 5.3 Account & Password
- 5.4 Login FriendlyWrt
- 5.5 Recommended security settings
- 5.6 Change LAN IP in LuCI
- 5.7 Safe shutdown operation
- 5.8 Soft Factory Reset
- 5.9 Install Software Packages
- 5.10 Disable IPv6
- 5.11 Configure the function of the user button
- 5.12 Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking
- 5.13 Some common issues of FriendlyWrt
- 5.14 Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature
- 5.15 How to use USB WiFi
- 5.16 Work with Docker Applications
- 5.17 Mount smbfs
- 5.18 Use sdk to compile the package
- 5.19 Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions
- 6 Compile FriendlyWrt
- 7 Work with FriendlyCore
- 8 Make Your Own OS Image
- 9 More OS Support
- 10 Resources
- 11 Regulatory Compliance
1 Introduction
- The NanoPi NEO3 is another fun board developed by FriendlyELEC for makers, hobbyists and fans.
2 Hardware Spec
- Soc: RockChip RK3328, Quad-core 64-bit high-performance Cortex A53
- RAM: 1GB/2GB DDR4
- LAN: 10/100/1000M Ethernet with unique MAC
- USB Host: 1x USB3.0 Type A and 2x USB2.0 on 2.54mm pin header
- MicroSD Slot: MicroSD x 1 for system boot and storage
- LED: Power LED x 1, System LED x 1
- Key: User Button x 1
- Fan: 2Pin JST ZH 1.5mm Connector for 5V Fan
- GPIO: 2.54mm pitch 26 pin-header, include I2C, UART, SPI, I2S, GPIO
- Serial Debug Port: 2.54mm pitch 3 pin-header, 1500000bps
- Power: 5V/1A, via Type-C or GPIO
- PCB Dimension: 48 x 48mm
- Working Temperature: -20℃ to 70℃
- Weight: 22g
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
- GPIO(I2C/UART/SPI/I2S/GPIO)
Pin# Name Linux GPIO Pin# Name Linux GPIO 1 3.3V(OUT) 2 5V(OUT/IN) 3 I2C0_SDA 4 5V(OUT/IN) 5 I2C0_SCL 6 GND 7 GPIO2_A2/IR-RX 66 8 GPIO3_A4/UART1_TX 100 9 GND 10 GPIO3_A6/UART1_RX 102 11 GPIO2_B7/I2S1_MCLK 79 12 GPIO2_C3/I2S1_SDI 83 13 GPIO2_C1/I2S1_LRCK_TX 81 14 GND 15 GPIO2_C2/I2S1_SCLK 82 16 GPIO3_A5/UART1_RTSN 101 17 3.3V(OUT) 18 GPIO3_A7/UART1_CTSN 103 19 GPIO3_A1/SPI_TXD 97 20 GND 21 GPIO3_A2/SPI_RXD 98 22 GPIO2_C7/I2S1_SDO 87 23 GPIO3_A0/SPI_CLK 96 24 GPIO3_B0/SPI_CSN0 104 25 GND 26 GPIO0_D3/SPDIF_TX 27
- USB2.0
Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 GND 2 GND 3 DP1 4 OTG_DP 5 DM1 6 OTG_DM 7 5V 8 5V
- Note:
- For more details refer to the document: NanoPi-NEO3-2005-Schematic.pdf
3.2 Dimensional Diagram
- Refer to the document: pcb file in dxf format
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi NEO3 get the following items ready
- NanoPi NEO3
- MicroSD Card/TF Card: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- TYPC-C 5V/2A power adapter
- A host computer running Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit system
4.2 TF Cards We Tested
To make your NanoPi NEO3 boot and run fast we highly recommend you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD High Speed TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
4.3 Install OS
4.3.1 Download Image Files
Go to download link to download the image files under the officail-ROMs directory and the flashing utility under the tools directory:
Image Files: rk3328-sd-friendlycore-bionic-5.4-arm64-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Based on UbuntuCore 18.04 and Linux-5.4.12 Kernel rk3328-sd-friendlywrt-5.10-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Based on OpenWrt and Linux-5.10 Kernel Flashing Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
4.3.2 Linux
4.3.2.1 Flash to TF
- FriendlyCore / Debian / Ubuntu / OpenWrt / DietPi are all based on a same Linux distribution and their installation methods are the same.
- Extract the Linux image and win32diskimager.rar files. Insert a TF card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your TF card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the TF card.
After it is installed you will see the following window:
- Insert this card into your board's BOOT slot and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and the STAT LED is blinking this indicates your board has successfully booted.
;
5 Work with FriendlyWrt
5.1 Introduction to FriendlyWrt
FriendlyWrt is a customized system made by FriendlyElec based on an OpenWrt distribution. It is open source and well suitable for developing IoT applications, NAS applications etc.
5.2 First boot
For the first boot, the system needs to do the following initialization work:
1)Extended root file system
2)Initial setup(will execute /root/setup.sh)
So you need to wait for a while (about 2~3 minutes) to boot up for the first time, and then set FriendlyWrt, you can enter the ttyd terminal on the openwrt webpage, when the prompt is displayed as root@FriendlyWrt, it means the system has been initialized.
root@FriendlyWrt
5.3 Account & Password
The default password is password (empty password in some versions). Please set or change a safer password for web login and ssh login. It is recommended to complete this setting before connecting NanoPi-NEO3 to the Internet.
5.4 Login FriendlyWrt
Connect the PC to the LAN port of NanoPi-NEO3. If your PC without a built-in ethernet port, connect the LAN port of the wireless AP to the LAN port of NanoPi-NEO3, and then connect your PC to the wireless AP via WiFi , Enter the following URL on your PC's browser to access the admin page:
- http://friendlywrt/
- http://192.168.2.1/
- http://[fd00:ab:cd::1]
The above is the LAN port address of NanoPi-NEO3. The IP address of the WAN port will be dynamically obtained from your main router through DHCP.
5.5 Recommended security settings
The following settings are highly recommended to complete before connecting NanoPi-NEO3 to the Internet。
- Set a secure password
- Only allow access to ssh from lan, change the port
- Check the firewall settings
Set up as you wish.
5.6 Change LAN IP in LuCI
1) Click on Network → Interfaces, then click on the Edit button of the LAN Network;
2) In General Setup tab, input new IP address (for example: 192.168.11.1), click "Save" and then click "Save & Apply";
3) On the pop-up window with the title “Connectivity change“, click "Apply and revert on connectivity loss";
4) Wait a moment, enter the new address in your computer's browser and login to FriendlyWrt;
5.7 Safe shutdown operation
Enter the "Services" -> "Terminal", enter the "poweroff" command and hit enter, wait until the led light is off, and then unplug the power supply.
5.8 Soft Factory Reset
Enter "System"->"Backup/Flash firmware",Click “Perform reset“ Button, Your device's settings will be reset to defaults like when FriendlyWrt was first installed.
You can also do this in the terminal:
firstboot && reboot5.9 Install Software Packages
5.9.1 Set up openwrt official opkg source
sed -i -e 's/mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/downloads.openwrt.org/g' /etc/opkg/distfeeds.conf opkg update
5.9.2 Update Package List
Before install software packages update the package list:
$ opkg update
5.9.3 List Available Packages
$ opkg list
5.9.4 List Installed Packages
$ opkg list-installed
5.9.5 Install Packages
$ opkg install <package names>
5.9.6 Remove Packages
$ opkg remove <package names>
5.10 Disable IPv6
. /root/setup.sh disable_ipv6 reboot
5.11 Configure the function of the user button
By default, the user button is configured to reboot the device, as shown below:
echo 'BTN_1 1 /sbin/reboot' >> /etc/triggerhappy/triggers.d/example.conf
You can change its behavior by changing the configuration file above.
5.12 Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking
- Go to "Network" -> "Interfaces"
- Click "Delete" next to "WAN6", then click "Save & Apply"
- Click "Edit" next to "WAN", in the "Device" drop-down menu, select "Ethernet Adapter: wwan0", in the "Protocol" drop-down menu, select "QMI Cellular" and click "Switch Protocol"
- Click the "Modem Device" drop-down menu, select "/dev/cdc-wdm0", fill in the APN information (e.g. for China Mobile, enter "cmnet")
- Click "Save" to close the dialog, Finally, click "Save & Apply" at the bottom of the page to initiate the dial-up process
- Devices connected to LAN will have access to the Internet, If your device has a WiFi module, you can enable wireless AP functionality on the "Wireless" page and connect to the Internet via devices connected wirelessly
5.13 Some common issues of FriendlyWrt
- Unable to dial up
- Go to "Network" -> "Firewall" and set "Inbound Data", "Outbound Data" and "Forwarding" in "WAN Zone" to "Accept";
- If you still cannot access the Internet, you can try to turn off IPV6;
- Dial-up successful, but no outgoing traffic
- Go to "Services" -> "Terminal" and type "fw4 reload" to try to reload the firewall settings again;
- Unable to power on
- Try to replace the power adapter and cable. It is recommended to use a power supply with specifications above 5V/2A;
- Note that some fast chargers with Type-C interface will have a delay, it may take a few seconds to start providing power;
- When doing secondary routing, the computer cannot connect to the Internet
- If your main network is IPv4, and NanoPi-NEO3 works in IPv6, the computer may not be able to connect to the Internet. It is recommended to turn off IPv6 (the method is described later in this WiKi), or switch the main route to IPv6;
- If you have questions or have better suggestions, please send an email to techsupport@friendlyarm.com;
5.14 Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature
Plug the USB2LCD module to the USB interface ofNanoPi-NEO3 and power on, the IP address and CPU temperature will be displayed on the LCD:

5.15 How to use USB WiFi
5.15.1 Check USB WiFi Device with Command Line Utility
(1) Click on "services>ttyd" to start the command line utility
(2) Make sure no USB devices are connected to your board and run the following command to check if any USB devices are connected or not
lsusb
(3) Connect a USB WiFi device to the board and run the command again
lsusb
You will see a new device is detected. In our test the device's ID was 0BDA:C811
(4) Type your device's ID (in our case it was "0BDA:C811" or "VID_0BDA&PID_C811") in a search engine and you may find a device that matches the ID. In our case the device we got was Realtek 8811CU.
5.15.2 Configure a USB WiFi Device as AP
(1) Connect a USB WiFi device to the NanoPi-NEO3. We recommend you to use the following devices:
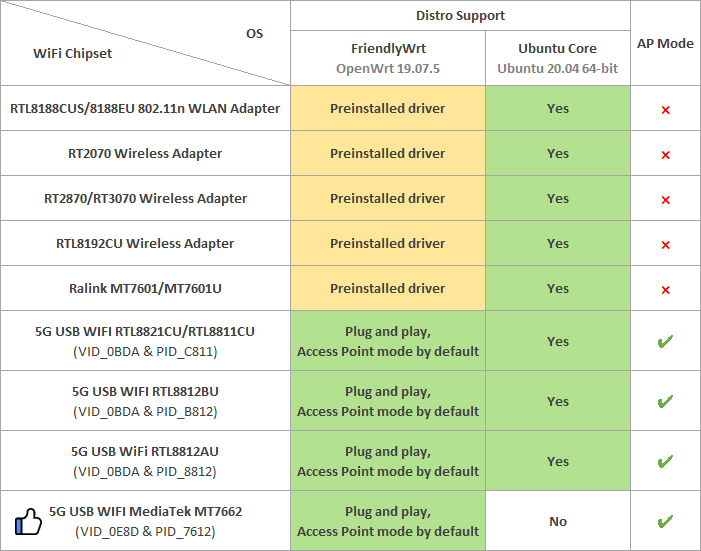
Note: devices that match these VID&PIDs would most likely work.
(2) Click on "System>Reboot" and reboot your NanoPi-NEO3
(3) Click on "Network>Wireless" to enter the WiFi configuration page
(4) Click on "Edit" to edit the configuration
(5) On the "Interface Configuration" page you can set the WiFi mode and SSID, and then go to "Wireless Security" to change the password. By default the password is "password". After you make your changes click on "Save" to save
(6) After you change the settings you can use a smartphone or PC to search for WiFi
5.15.3 Common USB WiFi issues
1) It is recommended to plug in the usb wifi in the off state, then power it on, FriendlyWrt will automatically generate the configuration file /etc/config/wireless, if not, see if there is wlan0 by ifconfig -a, if there is no wlan0, usually there is no driver.
2) If ifconfig -a sees wlan0, but the hotspot is not working properly, try changing the channel and country code, an inappropriate country code can also cause the WiFi to not work.
3) Some USB WiFis (e.g. MTK MT7662) work in CD-ROM mode by default and need to be switched by usb_modeswitch, you can try to add usb_modeswitch configuration to the following directory: /etc/usb_modeswitch.d.
5.15.4 Change the default WiFi hotspot configuration
FriendlyWrt sets the country, hotspot name and other parameters for USB WiFi by default, with the aim of being as plug-and-play as possible, but this does not guarantee that all modules will be compatible with this setting, you can change these behaviors by modifying the following file:
/lib/wifi/mac80211.sh
5.16 Work with Docker Applications
5.16.1 Work with Docker: Install JellyFin
mkdir -p /jellyfin/config mkdir -p /jellyfin/videos docker run --restart=always -d -p 8096:8096 -v /jellyfin/config:/config -v /jellyfin/videos:/videos jellyfin/jellyfin:10.1.0-arm64 -name myjellyfin
After installation, visit port 8096 and here is what you would find:
5.16.2 Work with Docker: Install Personal Nextcloud
mkdir /nextcloud -p docker run -d -p 8888:80 --name nextcloud -v /nextcloud/:/var/www/html/ --restart=always --privileged=true arm64v8/nextcloud
After installtion, visit port 8888.
5.16.3 Expand Docker Storage
- Stop docker service first:
/etc/init.d/dockerd stop
- Rename the original /opt directory, create an empty /opt directory:
mv /opt /opt-old && mkdir /opt
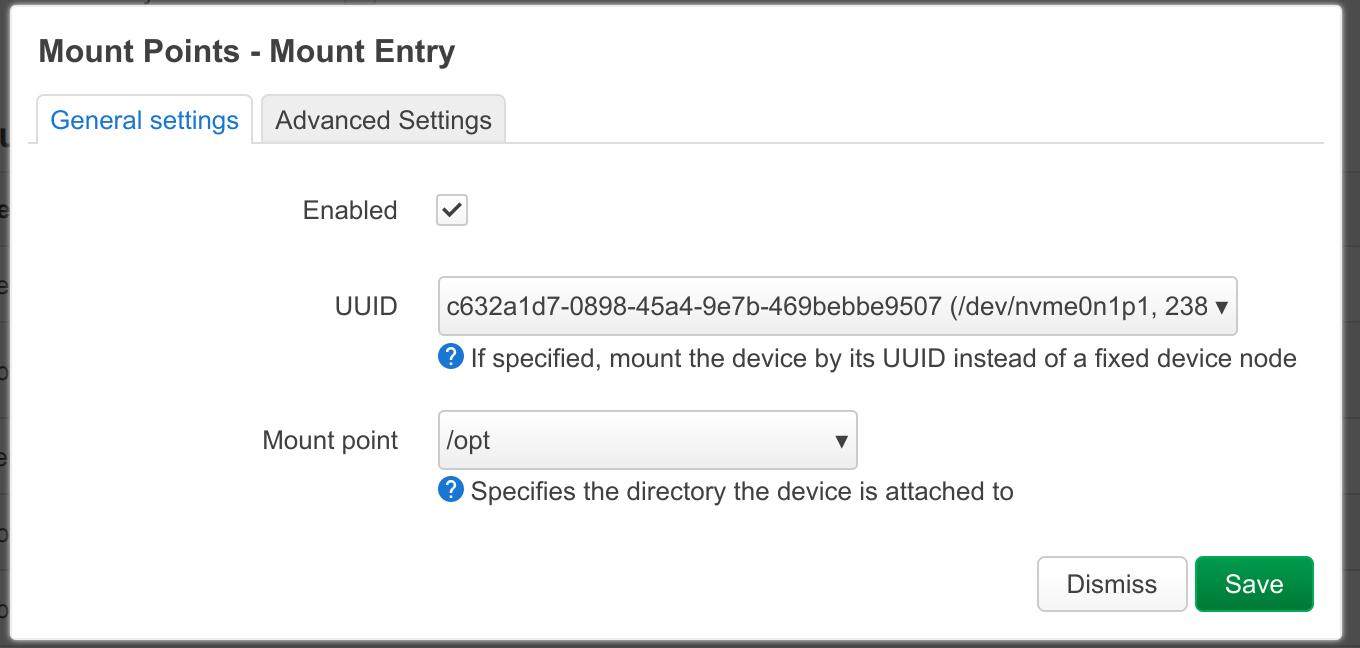
- Format your drive as ext4, and mount it to the /opt directory:
- Enter the command "mount | grep /opt" to check the mount status:
root@FriendlyWrt:~# mount | grep /opt /dev/nvme0n1p1 on /opt type ext4 (rw,relatime) root@FriendlyWrt:~#
- Copy the files from the original /opt directory to the new /opt directory:
cp -af /opt-old/* /opt/ && rm -rf /opt-old
- Reboot the device
reboot
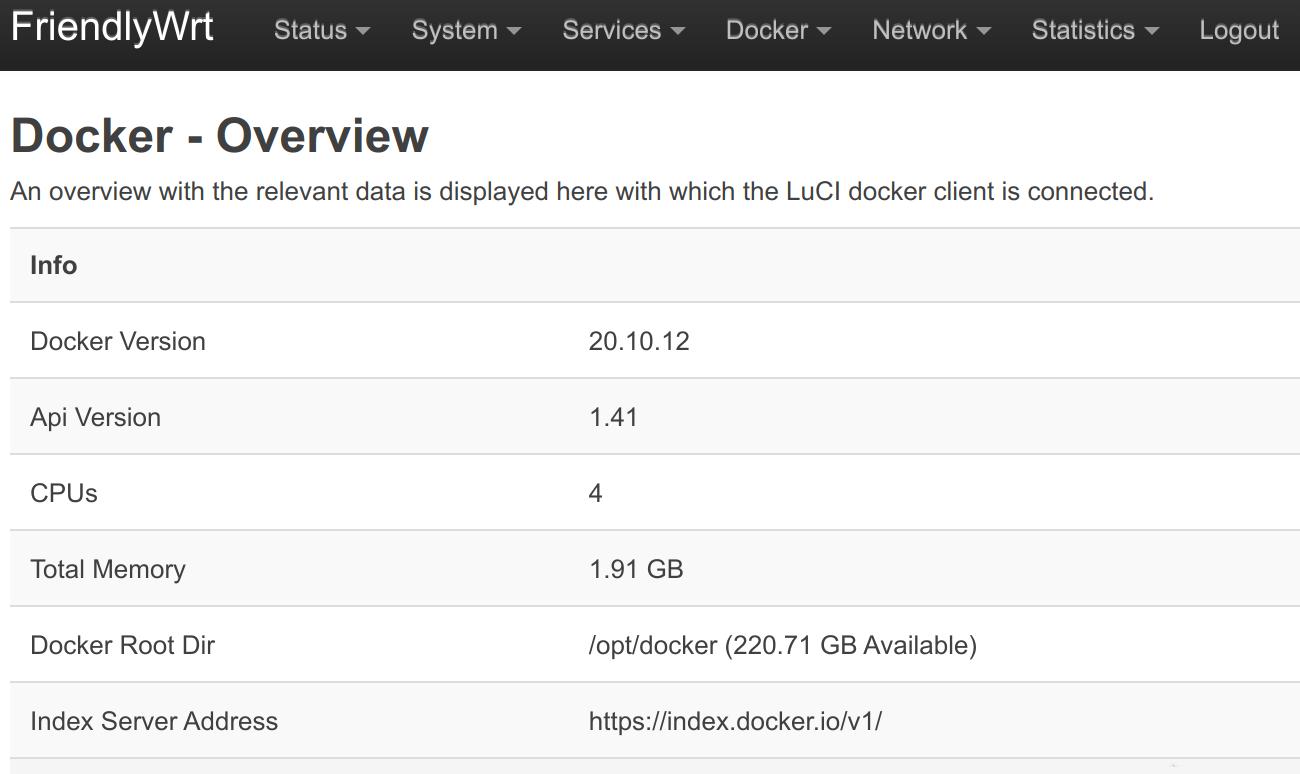
- After reboot, go to the "Docker" -> "Overview" page, check the information in the "Docker Root Dir" line, you can see that the Docker space has been expanded:
5.16.4 Docker FAQ and solutions
5.16.4.1 Unable to access the network services provided by the Docker container
Solution:
- Go to the "Firewall" settings and set "Forwarding" to "Accept";
- Turn off "Software Offload";
5.17 Mount smbfs
mount -t cifs //192.168.1.10/shared /movie -o username=xxx,password=yyy,file_mode=0644
5.18 Use sdk to compile the package
5.18.1 Install the compilation environment
Download and run the following script on 64-bit Ubuntu (version 18.04+): How to setup the Compiling Environment on Ubuntu bionic
5.18.2 Download and decompress sdk from the network disk
The sdk is located in the toolchain directory of the network disk:
tar xvf openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64.tar.xz # If the path is too long, it will cause some package compilation errors, so change the directory name here mv openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64 sdk cd sdk ./scripts/feeds update -a ./scripts/feeds install -a
5.18.3 Compile the package
download the source code of the example (a total of 3 examples are example1, example2, example3), and copy to the package directory:
git clone https://github.com/mwarning/openwrt-examples.git cp -rf openwrt-examples/example* package/ rm -rf openwrt-examples/
Then enter the configuration menu through the following command:
make menuconfigIn the menu, select the following packages we want to compile (actually selected by default):
"Utilities" => "example1" "Utilities" => "example3" "Network" => "VPN" => "example2"
execute the following commands to compile the three software packages:
make package/example1/compile V=99 make package/example2/compile V=99 make package/example3/compile V=99
After the compilation is successful, you can find the ipk file in the bin directory, as shown below:
$ find ./bin -name example*.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk
5.18.4 Install the ipk to NanoPi
You can use the scp command to upload the ipk file to NanoPi:
cd ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/ scp example*.ipk root@192.168.2.1:/root/
Then use the opkg command to install them:
cd /root/ opkg install example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk opkg install example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk opkg install example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk
5.19 Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions
Please refre this link: https://github.com/friendlyarm/Actions-FriendlyWrt
6 Compile FriendlyWrt
6.1 Download Code
mkdir friendlywrt-rk3328 cd friendlywrt-rk3328 repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/friendlywrt_manifests -b master-v19.07.1 -m rk3328.xml --repo-url=https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --no-clone-bundle repo sync -c --no-clone-bundle
6.2 1-key Compile
./build.sh nanopi_neo3.mkAll the components (including u-boot, kernel, and friendlywrt) are compiled and the sd card image will be generated.
7 Work with FriendlyCore
7.1 FriendlyCore User Account
- Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
- Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
7.2 Update Software Packages
$ sudo apt-get update
7.3 Setup Network Configurations
7.3.1 Set static IP address
By default "eth0" is assigned an IP address obtained via dhcp. If you want to change the setting you need to change the following file:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0
For example if you want to assign a static IP to it you can run the following commands:
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.1.231
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.17.3.2 Set a DNS
You also need to modify the following file to add the DNS configuration:
vi /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
For example, set to 192.168.1.1:
[Resolve] DNS=192.168.1.1
Restart the systemd-resolved service with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved.service sudo systemctl enable systemd-resolved.service
7.3.3 Set up to use another network interface
To change the setting of "eth1" you can add a new file similar to eth0's configuration file under the /etc/network/interfaces.d/ directory.
7.4 Setup Wi-Fi
First, use the following command to check if Network-Manager is installed on your system:
which nmcliIf you have installed it, refer to this link to connect to WiFi: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings, If you do not have Network-Manager installed on your system, please refer to the following method to configure WiFi,
By default the WiFi device is "wlan0". You need to create a configuration file under "/etc/network/interfaces.d/" for WiFi:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/wlan0
Here is a sample wlan0 file:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet dhcp
wpa-driver wext
wpa-ssid YourWiFiESSID
wpa-ap-scan 1
wpa-proto RSN
wpa-pairwise CCMP
wpa-group CCMP
wpa-key-mgmt WPA-PSK
wpa-psk YourWiFiPasswordPlease replace "YourWiFiESSID" and "YourWiFiPassword" with your WiFiESSID and password. After save and close the file you can connect to your WiFi source by running the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart networking
After you power on your board it will automatically connect to your WiFi source.
Please note that if you use one TF card to boot multiple boards the WiFi device name will likely be named to "wlan1", "wlan2" and etc. You can reset it to "wlan0" by deleting the contents of the following file and reboot your board:
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
7.5 Install the kernel-header package
sudo dpkg -i /opt/archives/linux-headers-*.deb
8 Make Your Own OS Image
- Please refre this link:
9 More OS Support
9.1 DietPi

DietPi is a highly optimised & minimal Debian-based Linux distribution. DietPi is extremely lightweight at its core, and also extremely easy to install and use.
Setting up a single board computer (SBC) or even a computer, for both regular or server use, takes time and skill. DietPi provides an easy way to install and run favourite software you choose.
For more information, please visit this link https://dietpi.com/docs/.
DietPi supports many of the NanoPi board series, you may download the image file from here:
10 Resources
10.1 Schematics and Datasheets
- Schematics
- Dimensional Diagram
- RK3328 Datasheet Rockchip_RK3328_Datasheet.pdf