Template:FriendlyCoreAllwinnerH3
Contents
1 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
The FA-CAM202 is a 200M USB camera. Connect your board to camera module. Then boot OS, connect your board to a network, log into the board as root and run "mjpg-streamer":
$ cd /root/C/mjpg-streamer $ make $ ./start.sh
You need to change the start.sh script and make sure it uses a correct /dev/videoX node. You can check your camera's node by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install v4l-utils $ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -D Driver Info (not using libv4l2): Driver name : uvcvideo Card type : HC 3358+2100: HC 3358+2100 / USB 2.0 Camera: USB 2.0 Camera Bus info : usb-1c1b000.usb-1 ...
The above messages indicate that "/dev/video0" is camera's device node.The mjpg-streamer application is an open source video steam server. After it is successfully started the following messages will be popped up:
$ ./start.sh i: Using V4L2 device.: /dev/video0 i: Desired Resolution: 1280 x 720 i: Frames Per Second.: 30 i: Format............: YUV i: JPEG Quality......: 90 o: www-folder-path...: ./www/ o: HTTP TCP port.....: 8080 o: username:password.: disabled o: commands..........: enabled
start.sh runs the following two commands:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$(pwd)" ./mjpg_streamer -i "./input_uvc.so -d /dev/video0 -y 1 -r 1280x720 -f 30 -q 90 -n -fb 0" -o "./output_http.so -w ./www"
Here are some details for mjpg_streamer's major options:
-i: input device. For example "input_uvc.so" means it takes input from a camera;
-o: output device. For example "output_http.so" means the it transmits data via http;
-d: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's device node;
-y: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's data format: 1:yuyv, 2:yvyu, 3:uyvy 4:vyuy. If this option isn't defined MJPEG will be set as the data format;
-r: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's resolution;
-f: input device's subparameter. It defines a camera's fps. But whether this fps is supported depends on its driver;
-q: input device's subparameter. It defines the quality of an image generated by libjpeg soft-encoding;
-n: input device's subparameter. It disables the dynctrls function;
-fb: input device's subparameter. It specifies whether an input image is displayed at "/dev/fbX";
-w: output device's subparameter. It defines a directory to hold web pages;
In our case the board's IP address was 192.168.1.230. We typed 192.168.1.230:8080 in a browser and were able to view the images taken from the camera's. Here is what you would expect to observe:
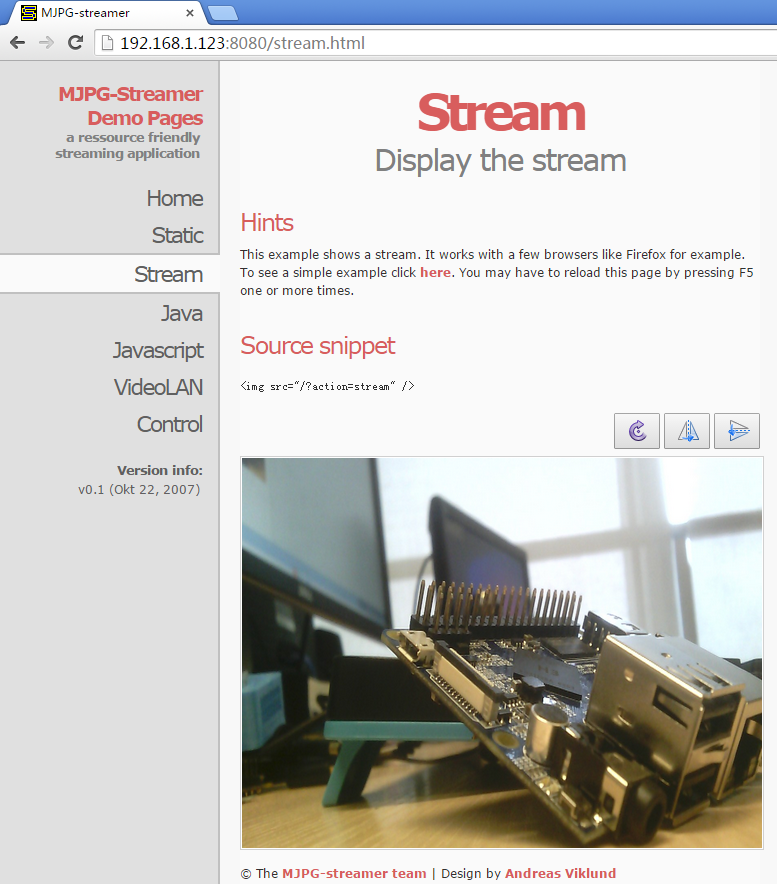
2 Check CPU's Working Temperature
You can get CPU's working temperature by running the following command:
$ cpu_freq
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHzThis message means there are currently four CPUs working. All of their working temperature is 26.5 degree in Celsius and each one's clock is 624MHz.
Set CPU frequency:
$ cpu_freq -s 1008000
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
3 Test Infrared Receiver
Note: Please Check your board if IR receiver exist.
By default the infrared function is disabled you can enable it by using the npi-config utility:
$ npi-config
6 Advanced Options Configure advanced settings
A8 IR Enable/Disable IR
ir Enable/Disable ir[enabled]Reboot your system and test its infrared function by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install ir-keytable $ echo "+rc-5 +nec +rc-6 +jvc +sony +rc-5-sz +sanyo +sharp +mce_kbd +xmp" > /sys/class/rc/rc0/protocols # Enable infrared $ ir-keytable -t Testing events. Please, press CTRL-C to abort.
"ir-keytable -t" is used to check whether the receiver receives infrared signals. You can use a remote control to send infrared signals to the receiver. If it works you will see similar messages as follows:
1522404275.767215: event type EV_MSC(0x04): scancode = 0xe0e43 1522404275.767215: event type EV_SYN(0x00). 1522404278.911267: event type EV_MSC(0x04): scancode = 0xe0e42 1522404278.911267: event type EV_SYN(0x00).
4 Run Qt Demo
Run the following command
$ sudo /opt/QtE-Demo/run.sh
Here is what you expect to observe. This is an open source Qt Demo:
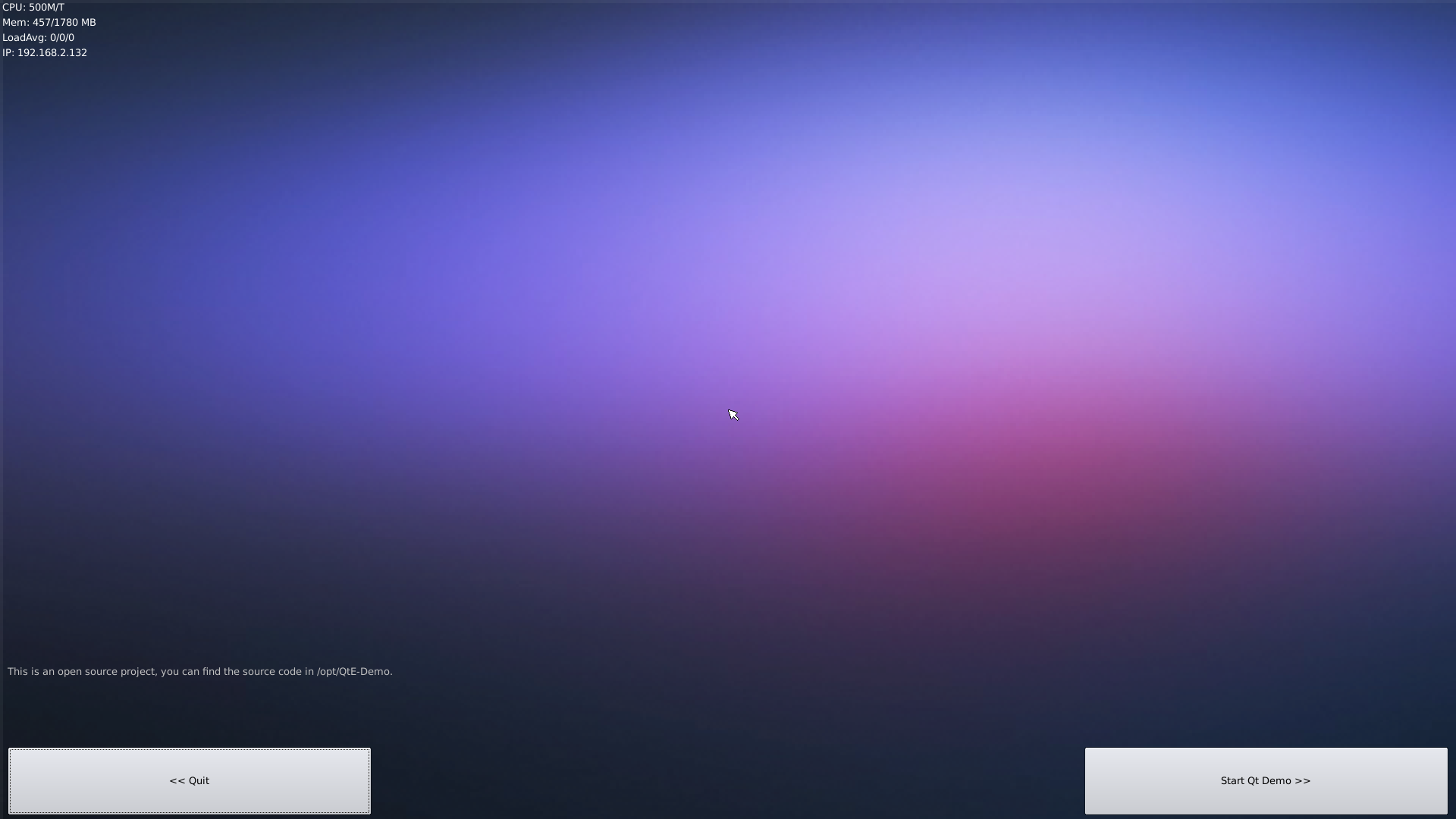
5 How to install and use docker (for armhf system)
5.1 How to Install Docker
Run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker.io
5.2 Test Docker installation
Test that your installation works by running the simple docker image:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/debian-jessie-arm-docker cd debian-jessie-arm-docker ./rebuild-image.sh ./run.sh
6 Using 4G Module EC20 on FriendlyCore
6.1 Step1:Compile the quectel-CM command line tool on the development board
Compile and install quectel-CM into the /usr/bin/ directory by entering the following command:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/quectel-cm.git cd quectel-cm/ make cp quectel-CM /usr/bin/
6.2 Step2:Add udhcpc script
The quectel-CM tool will call the udhcpc script. we need to create a udhcpc script for it. Please create a new file with the editor you are familiar with. The file name is: /usr/share/udhcpc/default.script, the content is as follows:
#!/bin/sh # udhcpc script edited by Tim Riker <Tim@Rikers.org> [ -z "$1" ] && echo "Error: should be called from udhcpc" && exit 1 RESOLV_CONF="/etc/resolv.conf" [ -n "$broadcast" ] && BROADCAST="broadcast $broadcast" [ -n "$subnet" ] && NETMASK="netmask $subnet" case "$1" in deconfig) /sbin/ifconfig $interface 0.0.0.0 ;; renew|bound) /sbin/ifconfig $interface $ip $BROADCAST $NETMASK if [ -n "$router" ] ; then echo "deleting routers" while route del default gw 0.0.0.0 dev $interface ; do : done for i in $router ; do route add default gw $i dev $interface done fi echo -n > $RESOLV_CONF [ -n "$domain" ] && echo search $domain >> $RESOLV_CONF for i in $dns ; do echo adding dns $i echo nameserver $i >> $RESOLV_CONF done ;; esac exit 0
Assign executable permissions with the following command:
chmod 755 /usr/share/udhcpc/default.script
6.3 Step3:Start 4G dialing
Start the dialing by entering the following command:
quectel-CM &If the dialing is successful, the screen will output information such as the IP address, as shown below:
root@NanoPC-T4:~# quectel-CM & [1] 5364 root@NanoPC-T4:~# [05-15_08:23:13:719] WCDMA<E_QConnectManager_Linux&Android_V1.1.34 [05-15_08:23:13:720] quectel-CM profile[1] = (null)/(null)/(null)/0, pincode = (null) [05-15_08:23:13:721] Find /sys/bus/usb/devices/3-1 idVendor=2c7c idProduct=0125 [05-15_08:23:13:722] Find /sys/bus/usb/devices/3-1:1.4/net/wwan0 [05-15_08:23:13:722] Find usbnet_adapter = wwan0 [05-15_08:23:13:723] Find /sys/bus/usb/devices/3-1:1.4/usbmisc/cdc-wdm0 [05-15_08:23:13:723] Find qmichannel = /dev/cdc-wdm0 [05-15_08:23:13:739] cdc_wdm_fd = 7 [05-15_08:23:13:819] Get clientWDS = 18 [05-15_08:23:13:851] Get clientDMS = 2 [05-15_08:23:13:884] Get clientNAS = 2 [05-15_08:23:13:915] Get clientUIM = 1 [05-15_08:23:13:947] Get clientWDA = 1 [05-15_08:23:13:979] requestBaseBandVersion EC20CEFHLGR06A01M1G_OCPU_BETA1210 [05-15_08:23:14:043] requestSetEthMode QMUXResult = 0x1, QMUXError = 0x46 [05-15_08:23:14:075] requestGetSIMStatus SIMStatus: SIM_READY [05-15_08:23:14:107] requestGetProfile[1] cmnet///0 [05-15_08:23:14:139] requestRegistrationState2 MCC: 460, MNC: 0, PS: Attached, DataCap: LTE [05-15_08:23:14:171] requestQueryDataCall IPv4ConnectionStatus: DISCONNECTED [05-15_08:23:14:235] requestRegistrationState2 MCC: 460, MNC: 0, PS: Attached, DataCap: LTE [05-15_08:23:14:938] requestSetupDataCall WdsConnectionIPv4Handle: 0xe16e4540 [05-15_08:23:15:002] requestQueryDataCall IPv4ConnectionStatus: CONNECTED [05-15_08:23:15:036] ifconfig wwan0 up [05-15_08:23:15:052] busybox udhcpc -f -n -q -t 5 -i wwan0 [05-15_08:23:15:062] udhcpc (v1.23.2) started [05-15_08:23:15:077] Sending discover... [05-15_08:23:15:093] Sending select for 10.22.195.252... [05-15_08:23:15:105] Lease of 10.22.195.252 obtained, lease time 7200 [05-15_08:23:15:118] deleting routers SIOCDELRT: No such process [05-15_08:23:15:132] adding dns 221.179.38.7 [05-15_08:23:15:132] adding dns 120.196.165.7
6.4 Test 4G connection
Ping a domain name to see if DNS resolution is already working:
root@NanoPC-T4:~# ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (183.232.231.174) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 183.232.231.174 (183.232.231.174): icmp_seq=1 ttl=56 time=74.3 ms 64 bytes from 183.232.231.174 (183.232.231.174): icmp_seq=2 ttl=56 time=25.1 ms 64 bytes from 183.232.231.174 (183.232.231.174): icmp_seq=3 ttl=56 time=30.8 ms 64 bytes from 183.232.231.174 (183.232.231.174): icmp_seq=4 ttl=56 time=29.1 ms 64 bytes from 183.232.231.174 (183.232.231.174): icmp_seq=5 ttl=56 time=29.2 ms
6.5 Test the speed of 4G
wget -O - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sivel/speedtest-cli/master/speedtest.py | python
The test results obtained are as follows:
Retrieving speedtest.net configuration... Testing from China Mobile Guangdong (117.136.40.167)... Retrieving speedtest.net server list... Selecting best server based on ping... Hosted by ChinaTelecom-GZ (Guangzhou) [2.51 km]: 62.726 ms Testing download speed................................................................................ Download: 32.93 Mbit/s Testing upload speed................................................................................................ Upload: 5.58 Mbit/s