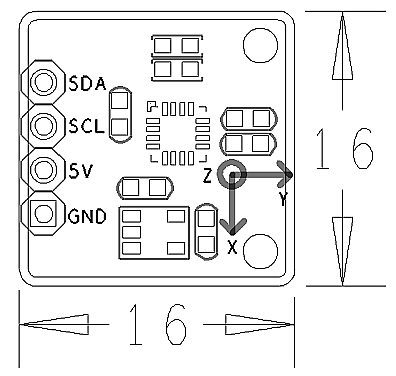
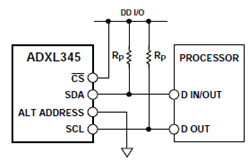
Matrix - 3-Axis Digital Compass
Contents
1 Introduction
- The Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass module is designed to measure the direction and functions like to a compass.
- It utilizes the HMC5883L chip. The HMC5883L includes high-resolution HMC118X series magneto-resistive sensors plus an ASIC containing amplification, automatic degaussing strap drivers, offset cancellation, and a 12-bit ADC that enables 1° to 2° compass heading accuracy. It achieves 2 milli-gauss field resolution in ±8 gauss fields. These sensors’ solid-state construction with very low cross-axis sensitivity is designed to measure both the direction and the magnitude of Earth’s magnetic fields, from milli-gauss to 8 gauss. It has an I2C serial bus interface.
- It integrates a 3.3V power conversion IC allowing it to be powered by an external 5V power source. It can be controlled by an I2C master.
2 Features
- I2C,3.3V
- 1° to 2° compass heading accuracy
- 2.54 mm spacing pin
- PCB Dimension(mm): 16 x 16
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| SDA | I2C SDA |
| SCL | I2C SCL |
| 5V | Power 5V |
| GND | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
- The Honeywell HMC5883L magnetoresistive sensor circuit is a trio of sensors and application specific support circuits to measure magnetic fields. With power supply applied, the sensor converts any incident magnetic field in the sensitive axis directions to a differential voltage output. The magnetoresistive sensors are made of a nickel-iron (Permalloy) thin-film and patterned as a resistive strip element. In the presence of a magnetic field, a change in the bridge resistive elements causes a corresponding change in voltage across the bridge outputs. These resistive elements are aligned together to have a common sensitive axis (indicated by arrows in the pinout diagram) that will provide positive voltage change with magnetic fields increasing in the sensitive direction. Because the output is only proportional to the magnetic field component along its axis, additional sensor bridges are placed at orthogonal directions to permit accurate measurement of magnetic field in any orientation.
- The HMC5883L communicates via a two-wire I2C bus system as a slave device. It has 8-bit read address and 8-bit write address. This device supports standard and fast modes, 100kHz and 400kHz, respectively, but does not support the high speed mode (Hs). The bus bit format is an 8-bit Data/Address send and a 1-bit acknowledge bit. The format of the data bytes (payload) shall be case sensitive ASCII characters or binary data to the HMC5883L slave, and binary data returned. Negative binary values will be in two’s complement form. The default (factory) HMC5883L 8-bit slave address is 0x3C for write operations, or 0x3D for read operations.
- The module has an I2C interface which complies to the I2C standard protocol and the connection diagram is as follows
4 Download Matrix Source Code
All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
Each branch in this hub contains the matrix modules' code samples for a board that the matrix modules can work with.
- The nanopi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi
- The tiny4412 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the Tiny4412
- The raspberrypi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the RaspberryPi
Please follow the steps below to get the source code:
Install the git utility on a PC running Ubuntu14.04
$ sudo apt-get install git
Clone the matrix code from GitHub
$ git clone git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples.
5 与NanoPi连接使用
5.1 准备工作
在NanoPi上运行Debian系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。参考wiki:NanoPi
注意:必须使用nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix分支编译出来的内核。
下载NanoPi内核源代码并编译
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-4.x.y.git $ cd linux-4.x.y $ git checkout nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix $ make nanopi_defconfig $ touch .scmversion $ make
5.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass和NanoPi
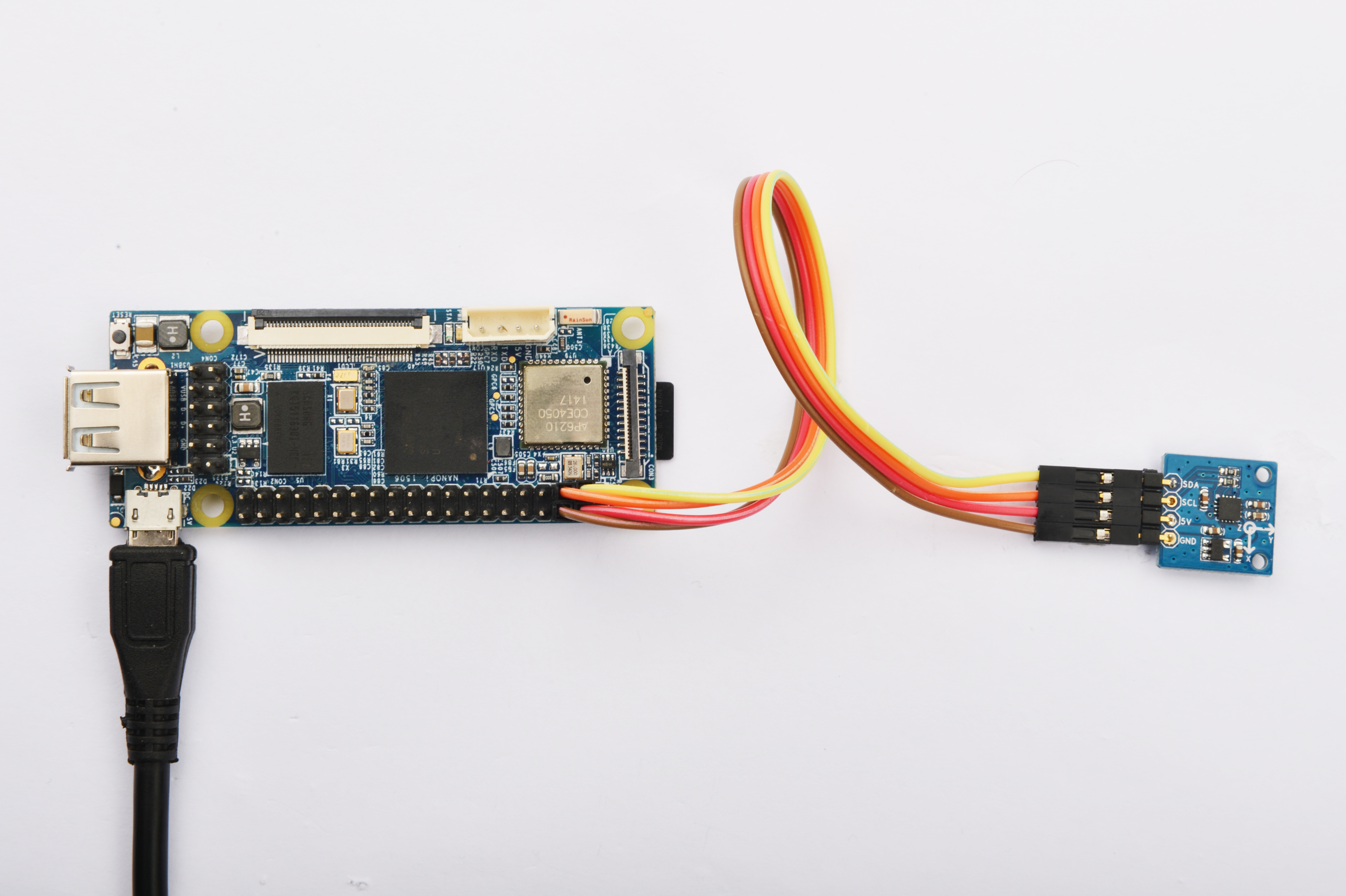
连接说明:
| Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass | NanoPi |
| SDA | Pin3 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin4 |
| GND | Pin6 |
5.3 编译测试程序
进入matrix代码仓库,切换到nanopi分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout nanopi
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi-Debian配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass对应的测试程序为matrix-3_axis_digital_compass。
5.4 运行测试程序
拷贝matrix相关的库文件和测试程序到NanoPi的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* nanopi_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* nanopi_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动NanoPi,在Debian的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass的测试程序
注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件正常连接。
$ matrix-3_axis_digital_compass
5.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int devFD; double angle; if ((devFD = hmc5883Init()) == -1) { printf("Fail to init hmc5883\n"); return -1; } if ((angle = hmc5883Read(devFD)) == -1) { printf("Fail to read hmc5883\n"); hmc5883DeInit(devFD); return -1; } printf("The angle is %f\n", angle); printf("You are heading "); if((angle < 22.5) || (angle > 337.5 )) { printf("South\n"); } else if((angle > 22.5) && (angle < 67.5 )) { printf("South-West\n"); } else if((angle > 67.5) && (angle < 112.5 )) { printf("West\n"); } else if((angle > 112.5) && (angle < 157.5 )) { printf("North-West\n"); } else if((angle > 157.5) && (angle < 202.5 )) { printf("North\n"); } else if((angle > 202.5) && (angle < 247.5 )) { printf("NorthEast\n"); } else if((angle > 247.5) && (angle < 292.5 )) { printf("East\n"); } else if((angle > 292.5) && (angle < 337.5 )) { printf("SouthEast\n"); } hmc5883DeInit(devFD); return 0; }
6 与Tiny4412连接使用
6.1 准备工作
参考Tiny4412光盘里的《友善之臂Ubuntu使用手册》,在Tiny4412上运行UbuntuCore系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。
注意:只能使用Tiny4412SDK-1506的底板。
6.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass和Tiny4412
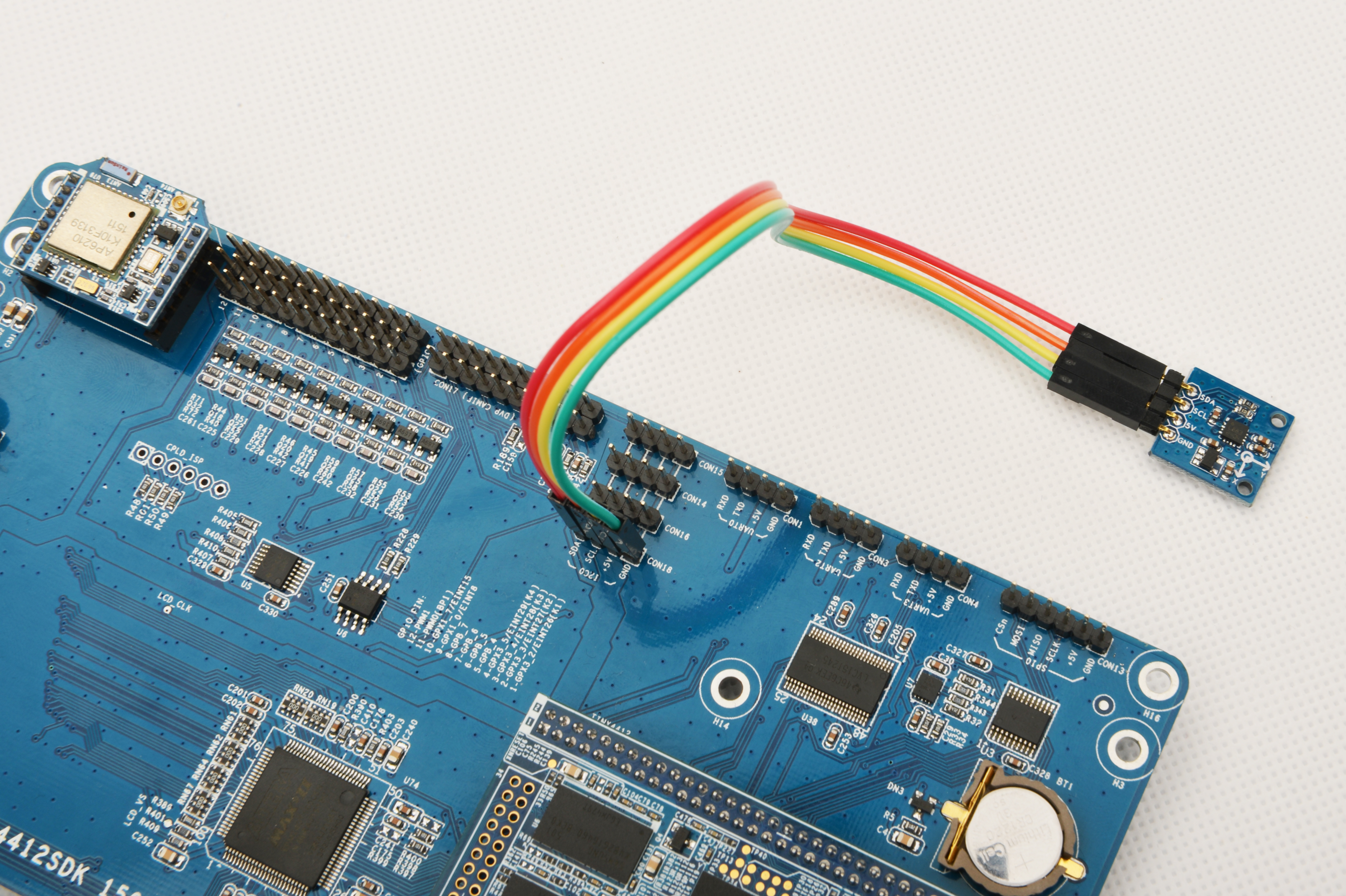
连接说明:
| Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass | Tiny4412 |
| SDA | CON18 SDA |
| SCL | CON18 SCL |
| 5V | CON18 5V |
| GND | CON18 GND |
6.3 编译测试程序
进入matrix代码仓库,切换到tiny4412分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout tiny4412
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为tiny4412-UbuntuCore配套的arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-4.7.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass对应的测试程序为matrix-3_axis_digital_compass。
6.4 运行测试程序
拷贝matrix相关的库文件和测试程序到Tiny4412的UbuntuCore的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* tiny4412_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* tiny4412_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动Tiny4412,在UbuntuCore的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-3_Axis_Digital_Compass的测试程序
注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件正常连接。
$ matrix-3_axis_digital_compass
6.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int devFD; double angle; if ((devFD = hmc5883Init()) == -1) { printf("Fail to init hmc5883\n"); return -1; } if ((angle = hmc5883Read(devFD)) == -1) { printf("Fail to read hmc5883\n"); hmc5883DeInit(devFD); return -1; } printf("The angle is %f\n", angle); printf("You are heading "); if((angle < 22.5) || (angle > 337.5 )) { printf("South\n"); } else if((angle > 22.5) && (angle < 67.5 )) { printf("South-West\n"); } else if((angle > 67.5) && (angle < 112.5 )) { printf("West\n"); } else if((angle > 112.5) && (angle < 157.5 )) { printf("North-West\n"); } else if((angle > 157.5) && (angle < 202.5 )) { printf("North\n"); } else if((angle > 202.5) && (angle < 247.5 )) { printf("NorthEast\n"); } else if((angle > 247.5) && (angle < 292.5 )) { printf("East\n"); } else if((angle > 292.5) && (angle < 337.5 )) { printf("SouthEast\n"); } hmc5883DeInit(devFD); return 0; }