Template:OpenWrt1
Contents
[hide]1 Work with OpenWrt
1.1 Introduction
OpenWrt is a highly extensible GNU/Linux distribution for embedded devices.Unlike many other distributions for routers, OpenWrt is built from the ground up to be a full-featured, easily modifiable operating system for embedded devices. In practice, this means that you can have all the features you need with none of the bloat, powered by a modern Linux kernel. For more details you can refer to:OpenWrt Website.
1.2 System Login
- 串口登录
如果您需要进行内核开发,最好选购一个串口配件,连接了串口,则可以通过串口终端对开发板进行操作。
使用串口模块能有效地提升开发效率,以下是串口模块的连接方法:
接上串口后,您可以选择从串口模块的DC口或者从MicroUSB口 (如果有) 进行供电。
也可以使用USB转串口模块调试,请注意需要使用5V/2A电源给开发板MicroUSB供电。
默认会以 root 用户自动登录,并且没有设置root用户的密码,你可以使用 passwd 命令来设置 root 用户的密码。
第一次运行系统时,系统会自动拓展TF卡上文件系统分区到最大可用空间:
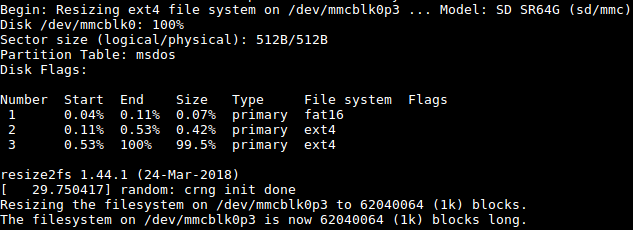
请耐心等待文件系统扩展完成。
- SSH登录
- Web登录
OpenWrt系统支持通过LuCI Web界面进行访问和配置。
默认用户名为root,无需密码,直接点击"Login"按键即可登录。
1.3 Manage Software Packages
OpenWrt has a package management utility: opkg. You can get its details by running the following command:
$ opkg
Package Manipulation:
update Update list of available packages
upgrade <pkgs> Upgrade packages
install <pkgs> Install package(s)
configure <pkgs> Configure unpacked package(s)
remove <pkgs|regexp> Remove package(s)
flag <flag> <pkgs> Flag package(s)
<flag>=hold|noprune|user|ok|installed|unpacked (one per invocation)
Informational Commands:
list List available packages
list-installed List installed packages
list-upgradable List installed and upgradable packages
list-changed-conffiles List user modified configuration files
files <pkg> List files belonging to <pkg>
search <file|regexp> List package providing <file>
find <regexp> List packages whose name or description matches <regexp>
info [pkg|regexp] Display all info for <pkg>
status [pkg|regexp] Display all status for <pkg>
download <pkg> Download <pkg> to current directory
...These are just part of the manual. Here are some popular opkg commands.
- Update Package List
Before you install a package you'd better update the package list:
$ opkg update
- Check Available Packages
$ opkg list
At the time of writing there are 3241 packages available.
- Check Installed Packages:
$ opkg list-installed
At the time of writing 124 packages have been installed.
- Install/Delete Packages:
$ opkg install <pkgs> $ opkg remove <pkgs>
- Check Files Contained in Installed Packages:
$ opkg files <pkg>
- Install Chinese Language Package for LuCI
$ opkg install luci-i18n-base-zh-cn
- Check Changed Files:
$ opkg list-changed-conffiles
- Reference Links:
1.4 查看系统状态
- 命令行查看CPU温度和频率
$ cpu_freq
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=26548C governor=ondemand freq=624000KHz上述信息表示当前有4个CPU核在线, 温度均约为26.5摄氏度, 运行的策略均为根据需求来决定运行频率, 当前的运行频率均为624MHz,设置频率的命令如下:
$ cpu_freq -s 1008000
Aavailable frequency(KHz):
480000 624000 816000 1008000
Current frequency(KHz):
CPU0 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU1 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU2 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHz
CPU3 online=1 temp=36702C governor=userspace freq=1008000KHzThese messages mean four CPU cores are working online. Each core's temperature is 26.5 degrees. Each core's governor is on demand and the frequency is 480 MHz.
- OpenWrt-LuCI Web界面查看系统状态
登录OpenWrt-LuCI界面后,点击顶部的 Statistics ---> Graphs,可以查看系统的各种软硬件状态信息(即statistics),例如:
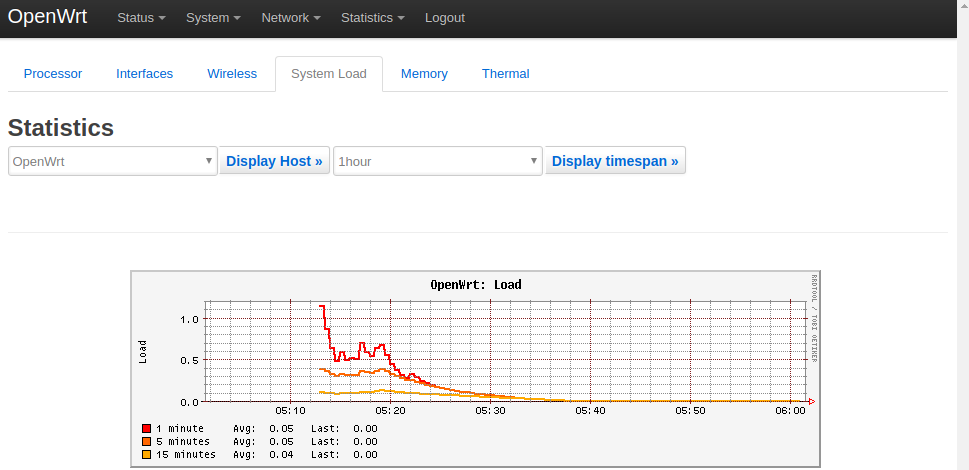
1) System Load:
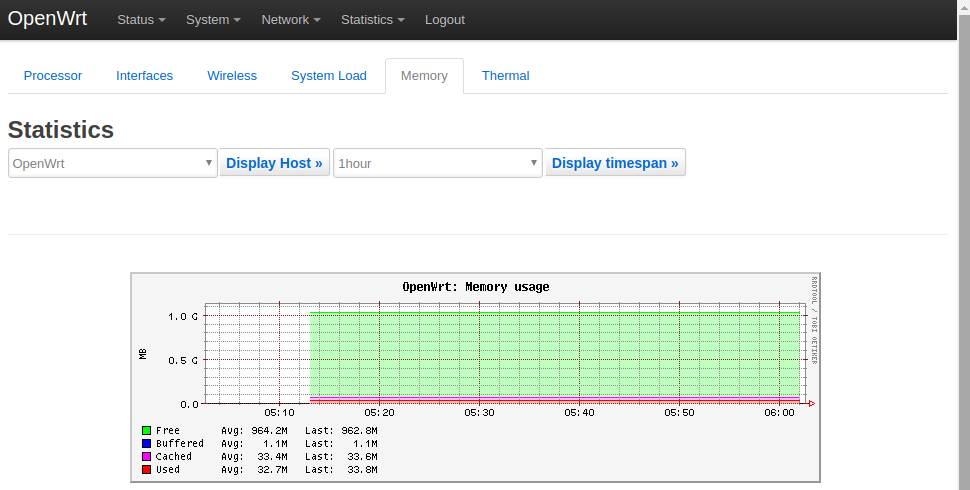
2) RAM:
3) CPU Temperature:
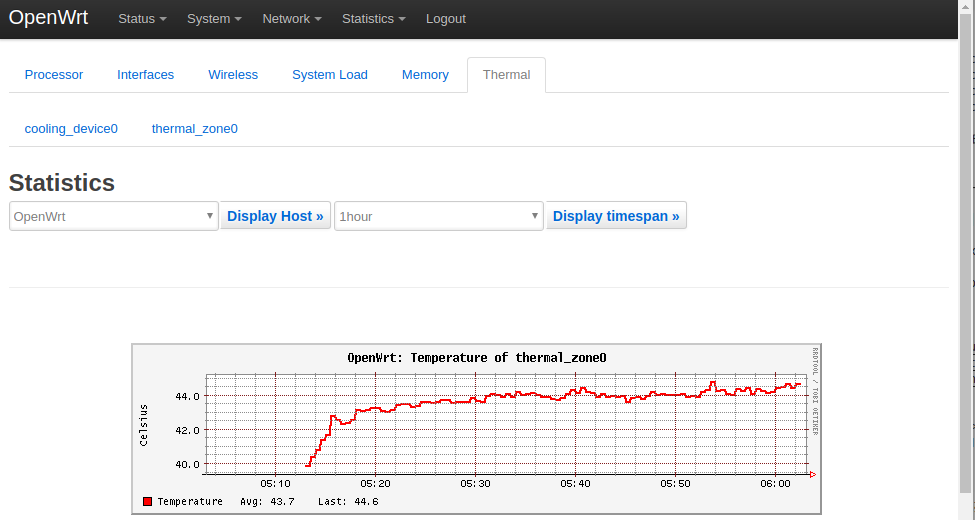
Statistics界面对应软件包luci-app-statistics,luci-app-statistics软件包用Collectd工具收集状态数据并且用RRDtool工具将数据渲染为图表。
你可以通过安装额外的collectd-mod-*软件包去使能更多的statistics.
All collectd-mod-* packages use the same configuration file: /etc/config/luci_statistics.
- Reference Links:
1.5 查看Network->Interfaces的配置
- 登录OpenWrt-LuCI界面后,点击顶部的 Network ---> Interfaces ,可以查看当前的网络设置:
- Network->Interfaces界面的配置保存在/etc/config/network中。
}
- Reference Link:
NanoPi-R1
1.6 Check BUTTON Configuration
FriendlyElec's OpenWrt uses the triggerhappy utility to configure buttons. By default if a button is pressed it will trigger the system to reboot.If the system needs to be rebooted to recover from some errors it is recommended to press the button to reboot the system instead of directly powering off the system.
The triggerhappy utility uses the "/etc/triggerhappy/triggers.d/example.conf" configuration file.
- Reference Link: