NanoPi NEO2
Contents
1 Introduction
- The NanoPI NEO2 is a newly released super tiny ARM board by FriendlyElec. It uses Allwinner’s 64-bit H5 quad-core SoC (ARM Cortex-A53). It has internal hexa-core Mail450 GPU, 512M DDR3 RAM. A UbuntuCore and Armbian image files are ready for it. The NanoPi NEO2 inherits NEO's form factor and has compatible interfaces and ports with NEO.
- In addition in such a small dimension it has Gbps Ethernet and one USB host port. These features make it especially suitable for applications that require high data throughput , speedy data tranmission and high performance. Hobyyists and makers will just love it.
2 Hardware Spec
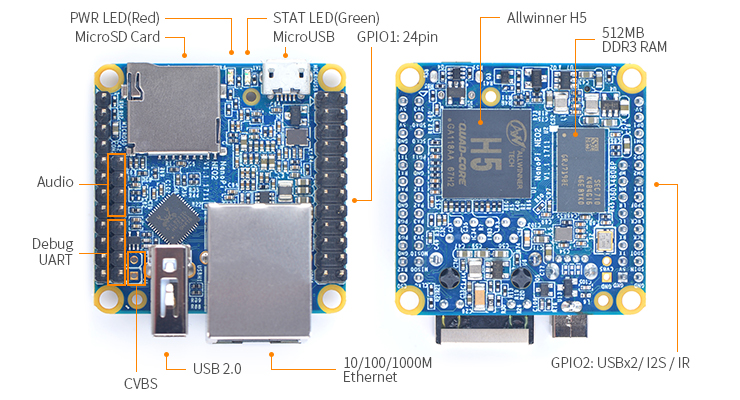
- CPU: Allwinner H5, Quad-core 64-bit high-performance Cortex A53
- DDR3 RAM: 512MB
- Connectivity: 10/100/1000M Ethernet, RTL8211E-VB-CG chip
- USB Host: USB Type A x 1 and USB pin header x 2
- MicroSD Slot: MicroSD x 1 for system boot and storage
- LED: Power LED x 1, System LED(Blue) x 1
- GPIO1: 2.54mm pitch 24 pin-header, compatible with Raspberry Pi's GPIO pin1 - pin 24. It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc
- GPIO2: 2.54mm pitch 12 pin-header. It includes USB, IR receiver, I2S, IO etc
- Serial Debug Port: 2.54mm pitch 4pin-header
- Audio In/Out: 2.0mm pitch 4 pin-header
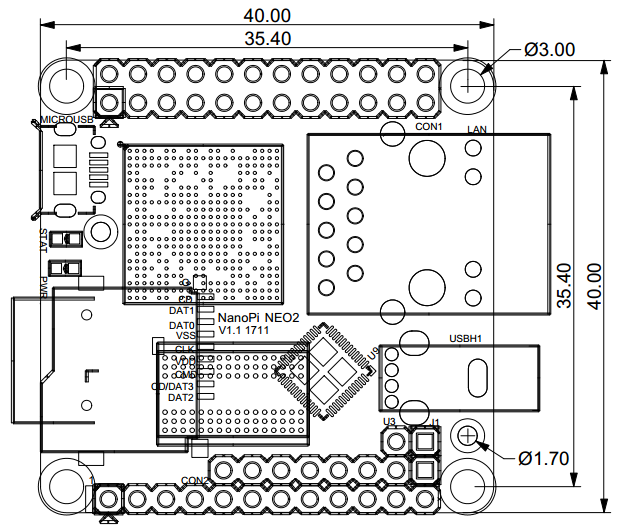
- PCB Dimension: 40 x 40mm
- MicroUSB: Power input(5V/2A) and OTG
- OS/Software: u-boot,Ubuntu Core
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
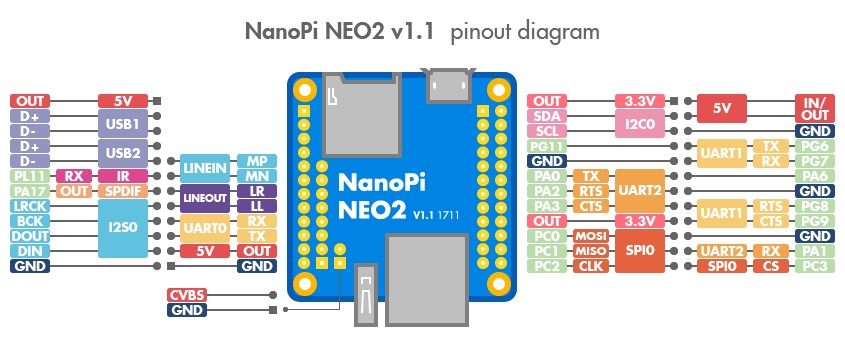
- GPIO Pin Description
Pin# Name Linux gpio Pin# Name Linux gpio 1 SYS_3.3V 2 VDD_5V 3 I2C0_SDA 4 VDD_5V 5 I2C0_SCL 6 GND 7 GPIOG11 203 8 UART1_TX/GPIOG6 198 9 GND 10 UART1_RX/GPIOG7 199 11 UART2_TX/GPIOA0 0 12 PWM1/GPIOA6 6 13 UART2_RTS/GPIOA2 2 14 GND 15 UART2_CTS/GPIOA3 3 16 UART1_RTS/GPIOG8 200 17 SYS_3.3V 18 UART1_CTS/GPIOG9 201 19 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC0 64 20 GND 21 SPI0_MISO/GPIOC1 65 22 UART2_RX/GPIOA1 1 23 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC2 66 24 SPI0_CS/GPIOC3 67
- USB/Audio/IR Pin Descripton
NanoPi-NEO2 Pin# Name Description 1 VDD_5V 5V Power Out 2 USB-DP1 USB1 DP Signal 3 USB-DM1 USB1 DM Signal 4 USB-DP2 USB2 DP Signal 5 USB-DM2 USB2 DM Signal 6 GPIOL11/IR-RX GPIOL11 or IR Receive 7 SPDIF-OUT/GPIOA17 GPIOA17 or SPDIF-OUT 8 PCM0_SYNC/I2S0_LRC I2S/PCM Sample Rate Clock/Sync 9 PCM0_CLK/I2S0_BCK I2S/PCM Sample Rate Clock 10 PCM0_DOUT/I2S0_SDOUT I2S/PCM Serial Data Output 11 PCM0_DIN/I2S0_SDIN I2S/PCM Serial Data Input 12 GND 0V
- Audio
Pin# Name Description 1 MICIN1P Microphone Positive Input 2 MICIN1N Microphone Negative Input 3 LINEOUTR LINE-OUT Right Channel Output 4 GND 0V 5 LINEOUTL LINE-OUT Left Channel Output
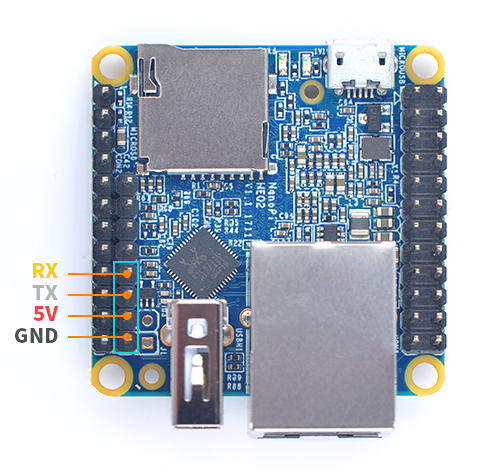
- Debug Port(UART0)
Pin# Name 1 GND 2 VDD_5V 3 UART_TXD0 4 UART_RXD0
- Note
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.6V. It can take power input from the MicroUSB.
- All pins are 3.3V and output current is 5mA
- For more details refer to the document: NanoPi_NEO2-1701-Schematic.pdf
3.2 Dimensional Diagram
- For more details refer to pcb file in dxf format
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi NEO2 get the following items ready
- NanoPi NEO2
- microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must
- A Host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
4.2 TF Cards We Tested
To make your NanoPi NEO2 boot and run fast we highly recommend you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
4.3 Make an Installation TF Card
4.3.1 Get Image File
Get the following files from download link to download image files (under the officail-ROMs directory) and the flashing utility(under the tools directory):
Image Files: nanopi-neo2-core-qte-sd4g.img.zip Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded Image File Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
4.3.2 Make Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded Image Card
Extract the nanopi-neo2-core-qte-sd4g.img.zip and win32diskimager.rar files. Insert a TF card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your TF card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the TF card.
After this writing process is done insert this card into your NanoPi NEO2's TF card slot and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the blue LED is blinking this indicates your NanoPi NEO2 has successfully booted.
5 Work with Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded
5.1 Run Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded
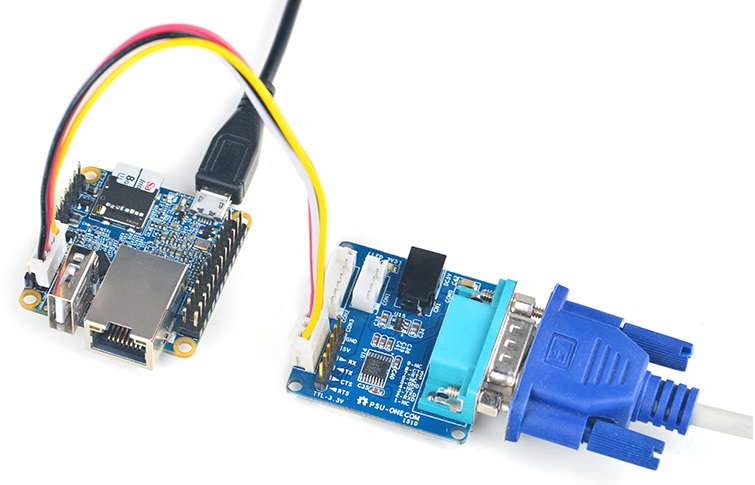
- If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal. Here is a setup where we connect a NanoPi NEO2 to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your NEO2 from either the PSU-ONECOM or the board's MicroUSB:
- The password for both "root" and "fa" is "fa" under Ubuntu-Core
- Update packages:
apt-get update5.2 Ethernet Connection
If a NanoPi NEO2 is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP after it is powered up. If it is not connected via Ethernet or its DHCP is not activated obtaining an IP will fail and system will hang on for about 15 to 60 seconds.In this case you can try obtaining an IP by using the following command:
dhclient eth0
5.3 Login via SSH
The NanoPi NEO2 doesn't have a video output interface. You can log into the board via SSH. In our test the IP address detected by our router was 192.168.1.230 and we ran the following command to log into the NanoPi NEO2:
ssh root@192.168.1.230
The password is fa
5.4 扩展TF卡文件系统
第一次启动系统时,系统会自动扩展文件系统分区,请耐心等待,TF卡的容量越大,需要等待的时间越长,进入系统后执行下列命令查看文件系统分区大小:
df -h
5.5 连接USB WiFi
系统默认已经支持市面上众多常见的USB WiFi,想知道你的USB WiFi是否可用只需将其接在NEO2上即可,已测试过的USB WiFi型号如下:
序号 型号 1 RTL8188CUS 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 NetGear, Inc. WG111v3 54 Mbps Wireless [realtek RTL8187B]
NanoPi NEO2 上电启动并插入上USB WiFi后,通过串口登录到系统,敲入以下命令可以查看到系统是否识别到USB WiFi,如果出现“wlan0”,则证明USB WiFi已被识别到:
ifconfig -a
用vi或在图形界面下用gedit编辑文件 /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf, 在文件末尾填入路由器信息如下所示:
network={ ssid="YourWiFiESSID" psk="YourWiFiPassword" }
其中,YourWiFiESSID和YourWiFiPassword请替换成你要连接的无线AP名称和密码。
保存退出后,执行以下命令即可连接WiFi:
ifdown wlan0 ifup wlan0
如果你的WiFi密码中有特殊字符,或者你不希望明文存放密码,你可以使用wpa_passphrase命令为WiFi密码生成一个密钥(psk),用密钥来代替密码 ,在命令行下,可输入以下命令生成密钥:
wpa_passphrase YourWiFiESSID
在提示输入密码时,输入你的WiFi密码,再打开 /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf 文件你会发现密钥已经被更新,你可以删除明文的密码了。
5.6 连接USB摄像头模块(FA-CAM202)使用
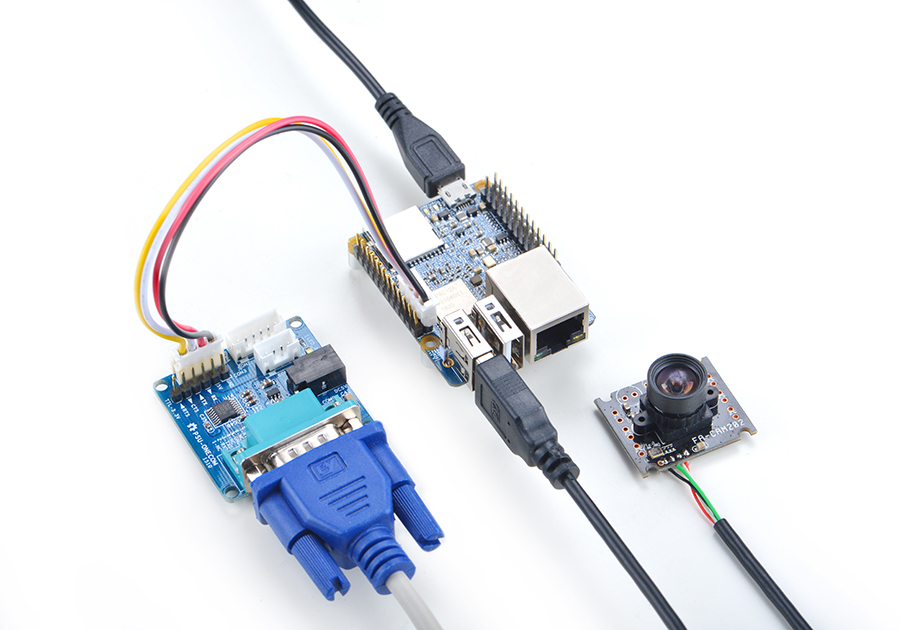
FA-CAM202是一款200万像素的USB摄像头模块,参考维基Matrix - USB_Camera(FA-CAM202)
启动系统,连接网络,以root用户登录终端并编译运行mjpg-streamer:
cd /root/mjpg-streamer apt-get install libjpeg62-dev make ./start.sh
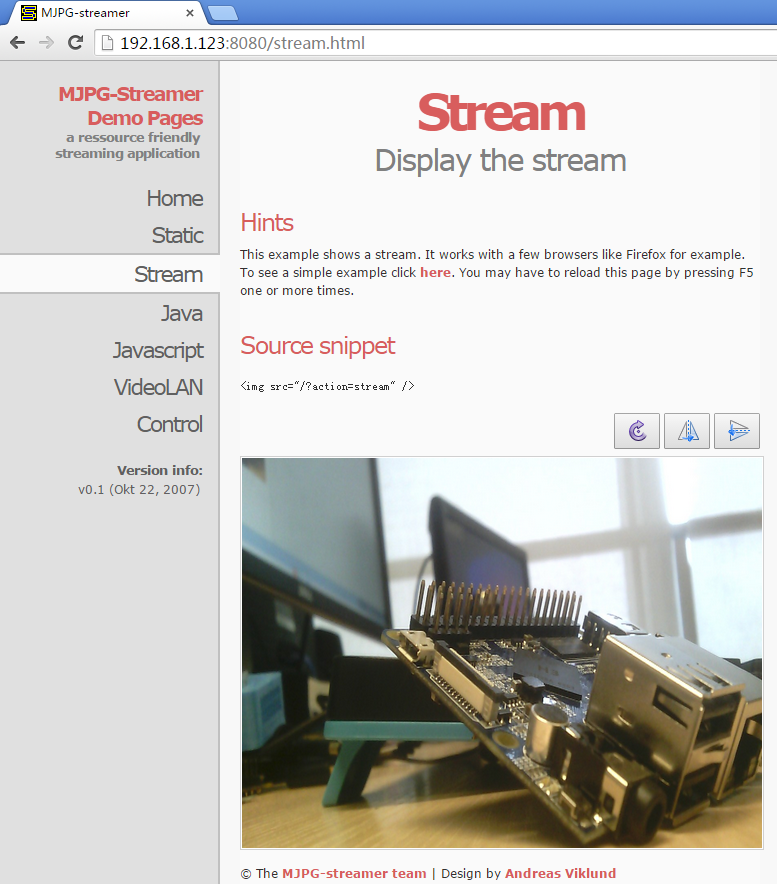
mjpg-streamer是一个开源的网络视频流服务器,在板子上成功运行mjpg-streamer后会打印下列信息:
i: Using V4L2 device.: /dev/video0 i: Desired Resolution: 1280 x 720 i: Frames Per Second.: 30 i: Format............: YUV i: JPEG Quality......: 90 o: www-folder-path...: ./www/ o: HTTP TCP port.....: 8080 o: username:password.: disabled o: commands..........: enabled
假设NEO2的IP地址为192.168.1.123,在PC的浏览器中输入 192.168.1.123:8080 就能浏览摄像头采集的画面了,效果如下:
5.7 命令行查看CPU工作温度
在串口终端执行如下命令,可以快速地获取CPU的当前温度和运行频率等信息:
cpu_freq
6 如何编译Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded系统
6.1 准备工作
访问此处下载地址的sources/nanopi-h5-bsp目录,下载所有压缩文件,使用7-Zip工具解压后得到lichee目录,如下:
ls ./ lichee
也可以从github上克隆lichee源码:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/h5_lichee.git lichee
注:lichee是全志为其CPU的板级支持包所起的项目名称,里面包含了U-boot,Linux等源码和众多的编译脚本。
6.2 安装交叉编译器
访问此处下载地址的toolchain目录,下载压缩包gcc-linaro-arm-4.6.3.tar.xz和gcc-linaro-aarch64.tar.xz。
其中gcc-linaro-arm-4.6.3.tar.xz用于编译U-boot,gcc-linaro-aarch64.tar.xz用于编译Linux内核。下载完成后,将它们拷贝到源码lichee/brandy/toochain/目录下即可。
后面编译U-boot或者Linux内核时,编译脚本会自动解压并使用这两个编译器进行编译。
6.3 编译lichee源码
编译全志 H5 的BSP源码包必须使用64bit的Linux PC系统,并安装下列软件包,下列操作均基于Ubuntu-14.04 LTS-64bit:
sudo apt-get install gawk git gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential \ zip curl libc6-dev libncurses5-dev:i386 x11proto-core-dev \ libx11-dev:i386 libreadline6-dev:i386 libgl1-mesa-glx:i386 \ libgl1-mesa-dev g++-multilib mingw32 tofrodos \ python-markdown libxml2-utils xsltproc zlib1g-dev:i386
编译lichee源码包,执行命令:
cd lichee/fa_tools ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t all
该命令会一次性编译好U-boot、Linux内核和模块。
lichee目录里内置了交叉编译器,当进行源码编译时,会自动使用该内置的编译器,所以无需手动安装编译器。
下列命令可以更新TF卡上的U-boot:
cd lichee/fa_tools/ ./fuse.sh -d /dev/sdx -p linux -t u-boot
/dev/sdx请替换为实际的TF卡设备文件名。
内核boot.img和驱动模块均位于linux-3.10/output目录下,将boot.img拷贝到TF卡的boot分区的根目录即可更新内核。
6.4 编译U-boot
如果你想单独编译U-boot,可以执行命令:
cd lichee/fa_tools/ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t u-boot
6.5 编译Linux内核
如果你想单独编译Linux内核,可以执行命令:
cd lichee/fa_tools/ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t kernel
编译完成后内核boot.img和驱动模块均位于linux-3.10/output目录下,将boot.img拷贝到TF卡的boot分区的根目录即可。
6.6 清理lichee源码
cd lichee/fa_tools/ ./build.sh -b nanopi-neo2 -p linux -t clean
7 3D 打印外壳
8 资源链接
8.1 手册原理图等开发资料
- 原理图
- 尺寸图
- H5芯片手册 Allwinner_H5_Datasheet_V1.0.pdf