Matrix - Sound Sensor
Contents
1 Introduction
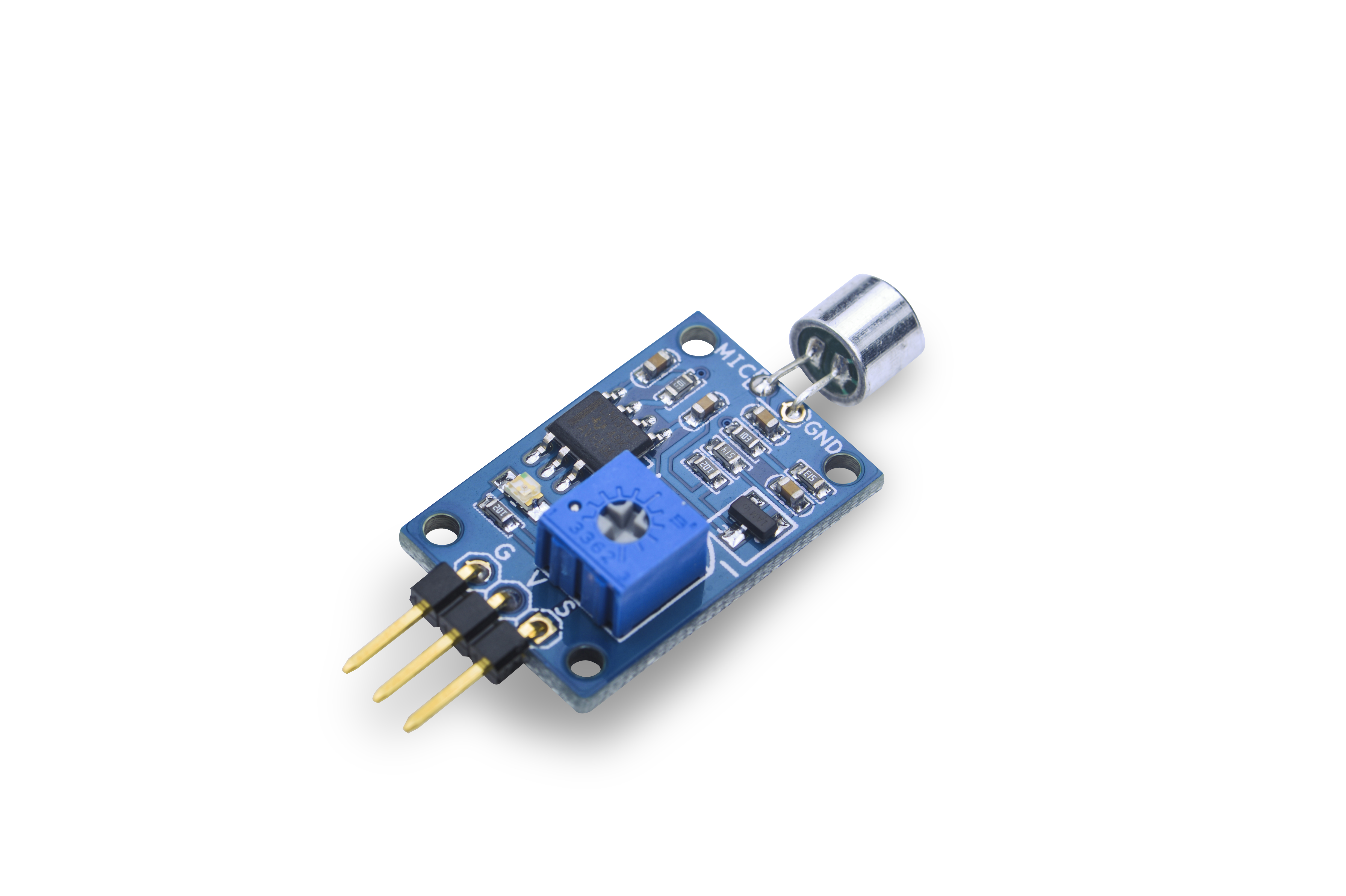
- The Matrix-Sound_Sensor module is used to detect sound.
- The module has a variable resistor which can be used to control the threshold value of a sound level. Only when a sound level's value is greater than this threshold the module can detect it. Turning clockwise increases this threshold value. Turning anticlockwise decreases this value.
- By default this module's output level is high. When it detects sound signals its output level will turn low. When sound signals are not detected its output will turn high again without time delay.
2 Features
- Variable threshold value
- 2.54mm spacing pin interface
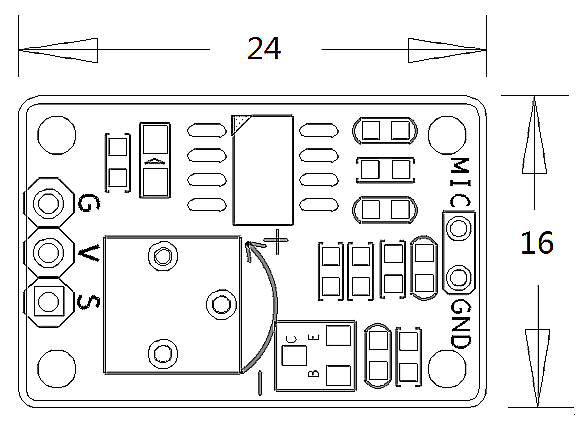
- PCB dimension (mm): 16 x 24
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| S | GPIO |
| V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| G | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
- The module contains an electret condenser microphone. Sound waves impinging on the diaphragm cause the capacitance between it and the back plate to change synchronously, this in turn induces an AC voltage on the back plate.
- This sound sensor functions like a microphone which receives sound waves and convert them to images which show the sound waves' vibration. When it receives a sound wave it will output 1 but cannot measure its strength.
4 Download Matrix Source Code
All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub - https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
Each branch in this hub contains the matrix modules' code samples for a board that the matrix modules can work with.
- The nanopi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi
- The nanopi 2 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi 2
- The tiny4412 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the Tiny4412
- The raspberrypi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the RaspberryPi
Please follow the steps below to get the source code:
Install the git utility on a PC running Ubuntu14.04
$ sudo apt-get install git
Clone the matrix code from GitHub
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples.
5 Connect to NanoPi 2
5.1 Hardware Connection
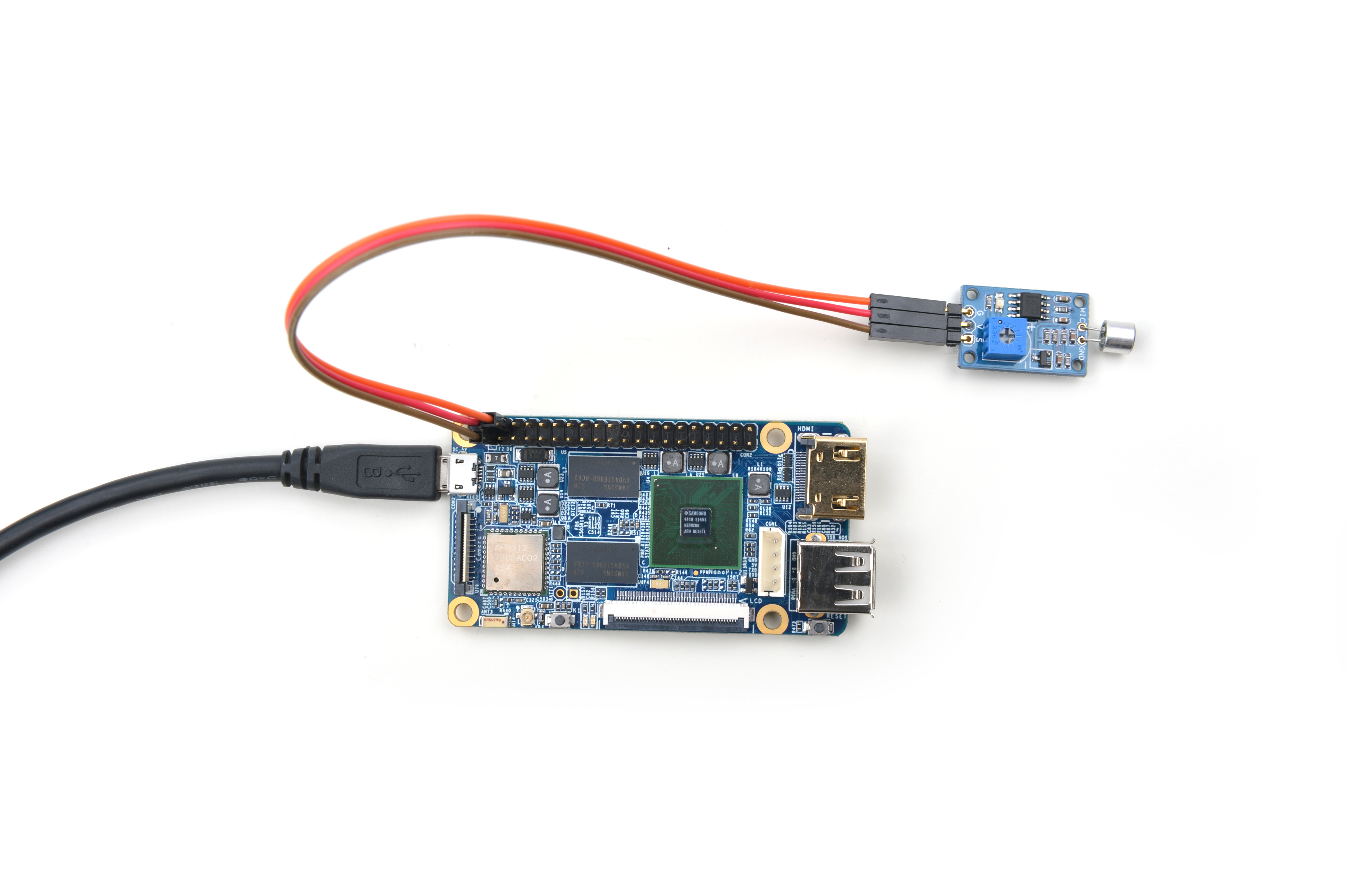
Please refer to the following connection diagram to connect the Matrix-Sound_Sensor to the NanoPi 2:
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Sound_Sensor | NanoPi 2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
5.2 Compile Test Program
Please login the matrix hub and enter the nanopi2 branch
$ cd matrix $ git checkout nanopi2
Compile the matrix code
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the NanoPi 2.
Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. The test program is under the "install/usr/bin" directory.
The modules are under the "modules" directory. The driver's source code is in github: https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git
5.3 运行测试程序
将带有Debian系统的SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs分区。
假设rootfs分区的挂载路径为/media/rootfs,执行以下命令将Matrix的硬件驱动、库文件和测试程序拷贝到NanoPi 2的文件系统上。
$ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/
将SD卡重新插入NanoPi 2,上电启动,在Debian的shell终端中执行以下命令加载硬件驱动。
$ cd /modules $ insmod matrix_gpio_int.ko
运行模块Matrix-Sound_Sensor的测试程序。
$ matrix-sound_sensor运行效果如下:
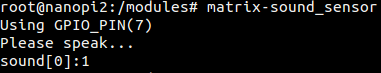
对着模块说话可以被成功检测到,调整模块上的可调电阻可以改变灵敏度。
5.4 代码展示
static struct sensor sound[] = { { GPIO_PIN(7), IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_BOTH, } }; int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int i; int retSize = -1; char value[ARRAY_SIZE(sound)]; int devFD = -1; if (argc == 2) { sound[0].pin = atoi(argv[1]); } printf("Using GPIO_PIN(%d)\n", sound[0].pin); if ((devFD =sensorInit(sound, ARRAY_SIZE(sound))) == -1) { printf("Fail to init sensor\n"); return -1; } printf("Please speak...\n"); if ((retSize = sensorRead(devFD, value, ARRAY_SIZE(sound))) == -1) { printf("Fail to read sensors\n"); } if (retSize > 0) { i = 0; for(i=0; i<retSize; i++) { printf("sound[%d]:%d\n", i, value[i]); } } sensorDeinit(devFD); return 0; }
6 Connect to NanoPi
6.1 Preparations
Please install a Debian on a NanoPi and an appropriate cross compiler on a PC. Please refer to wiki :NanoPi
Compile a NanoPi kernel. Note: please use the kernel's source code from the nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix branch.
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-4.x.y.git $ cd linux-4.x.y $ git checkout nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix $ make nanopi_defconfig $ touch .scmversion $ make
6.2 Hardware Connection
Please refer to the following connection diagram to connect the Matrix-Sound_Sensor to the NanoPi
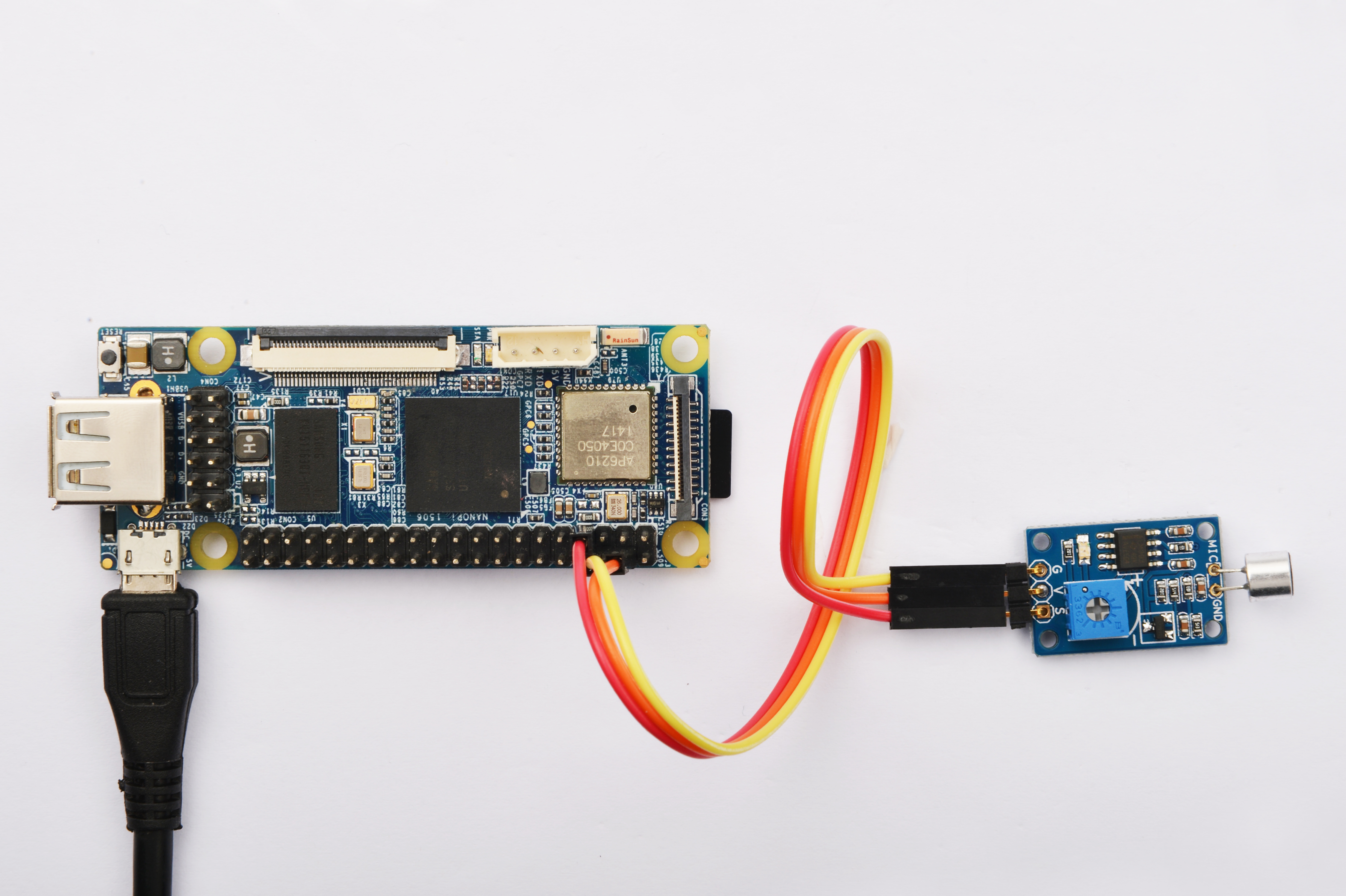
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Sound_Sensor | NanoPi |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
6.3 Compile Test Program
Please login the matrix hub and enter the nanopi branch
$ cd matrix $ git checkout nanopi
Compile the matrix code
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the NanoPi-Debian.
Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. Applications are under the "install/usr/bin" directory. The test program for the "Matrix-Sound_Sensor" module is "matrix-sound_sensor".
6.4 Run Test Program
Please copy the library files and test program to the NanoPi
$ cp install/usr/bin/* nanopi_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* nanopi_rootfs/lib/ -d
Power on the NanoPi and run the following command in Debian's terminal
$ matrix-sound_sensor6.5 Code Sample
static struct sensor sound[] = { { GPIO_PIN1, IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_BOTH, } }; int main(void) { int i; int retSize = -1; char value[ARRAY_SIZE(sound)]; int devFD = -1; if ((devFD =sensorInit(sound, ARRAY_SIZE(sound))) == -1) { printf("Fail to init sensor\n"); return -1; } if (( retSize = sensorRead(devFD, value, ARRAY_SIZE(sound)) ) == -1) { printf("Fail to read sensors\n"); } if (retSize > 0) { i = 0; for(i=0; i<retSize; i++) { printf("sound[%d]:%d\n", i, value[i]); } printf("\n"); } sensorDeinit(devFD); return 0; }
7 Connect to Tiny4412
7.1 Preparations
Please refer to the Tiny4412's user's manual to install a UbuntuCore on the Tiny4412 and install an appropriate cross compiler on a PC.
Note: only the Tiny4412SDK-1506 carrier board can work with this module.
7.2 Hardware Connection
Please refer to the following diagram to connect the Matrix-Sound_Sensor to the Tiny4412
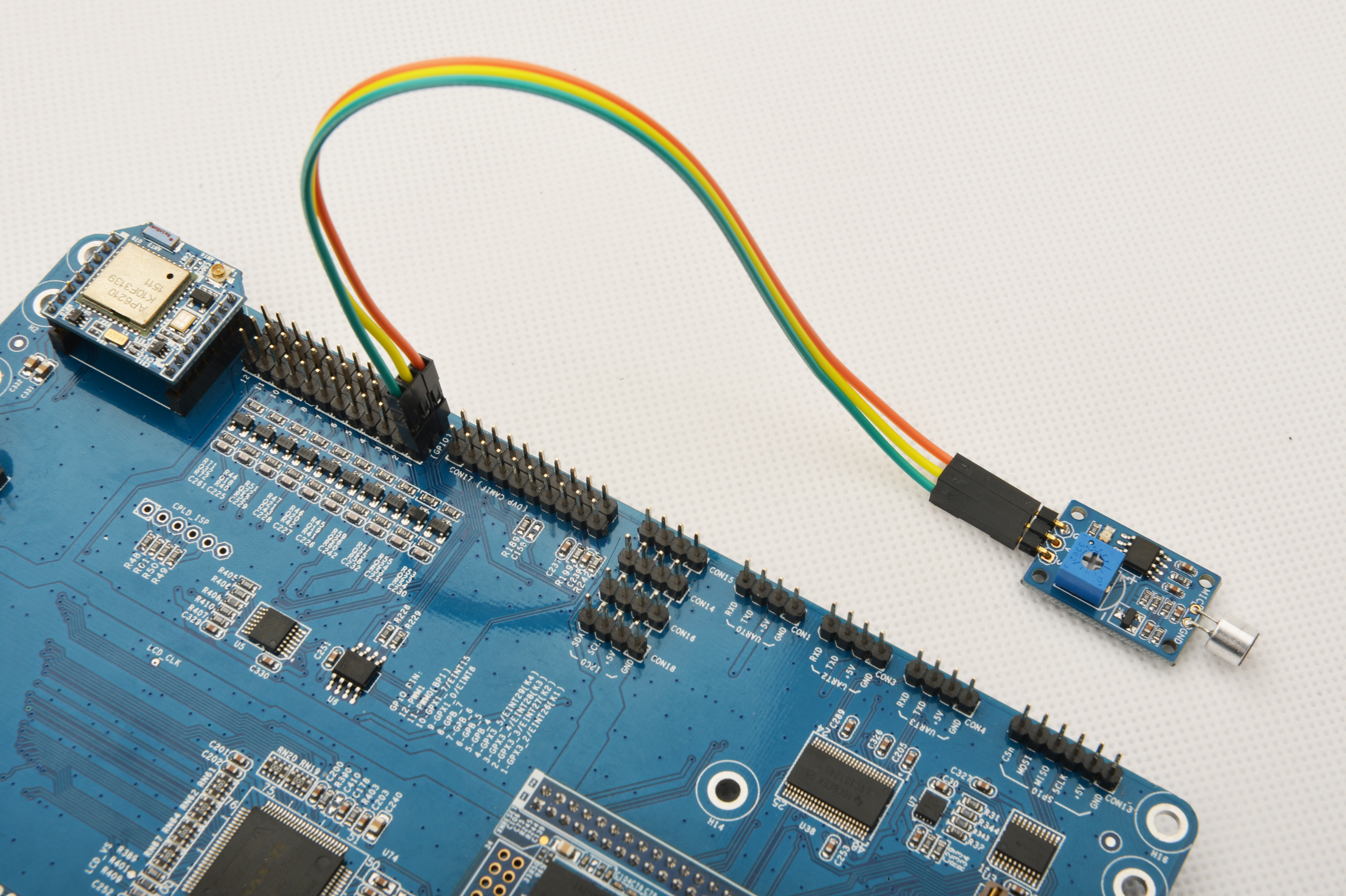
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Sound_Sensor | Tiny4412 |
| S | GPIO1 S |
| V | GPIO1 5V |
| G | GPIO1 GND |
7.3 Compile Test Program
Please login the Matrix hub and enter the matrix-tiny4412 branch
$ cd matrix $ git checkout tiny4412
Compile the matrix code
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- install
Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-4.7.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the Tiny4412-UbuntuCore.
Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. Applications are under the "install/usr/bin" directory. The test program for the "Matrix-Sound_Sensor" module is "matrix-sound_sensor".
7.4 Run Test Program
Please copy the library files and test program to the Tiny4412
$ cp install/usr/bin/* tiny4412_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* tiny4412_rootfs/lib/ -d
Power on the Tiny4412 and run the following command in UbuntuCore's terminal
$ matrix-sound_sensor7.5 Code Sample
static struct sensor sound[] = { { GPIO_PIN1, IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_BOTH, } }; int main(void) { int i; int retSize = -1; char value[ARRAY_SIZE(sound)]; int devFD = -1; if ((devFD =sensorInit(sound, ARRAY_SIZE(sound))) == -1) { printf("Fail to init sensor\n"); return -1; } if (( retSize = sensorRead(devFD, value, ARRAY_SIZE(sound)) ) == -1) { printf("Fail to read sensors\n"); } if (retSize > 0) { i = 0; for(i=0; i<retSize; i++) { printf("sound[%d]:%d\n", i, value[i]); } printf("\n"); } sensorDeinit(devFD); return 0; }
8 Connect to RaspberryPi
9 Connect to Arduino
10 Resources
11 Update Log
11.1 Feb-23-2016
- Added the description for "NanoPi 2 branch" in Section 4
- Added Section 5: Connect to NanoPi 2