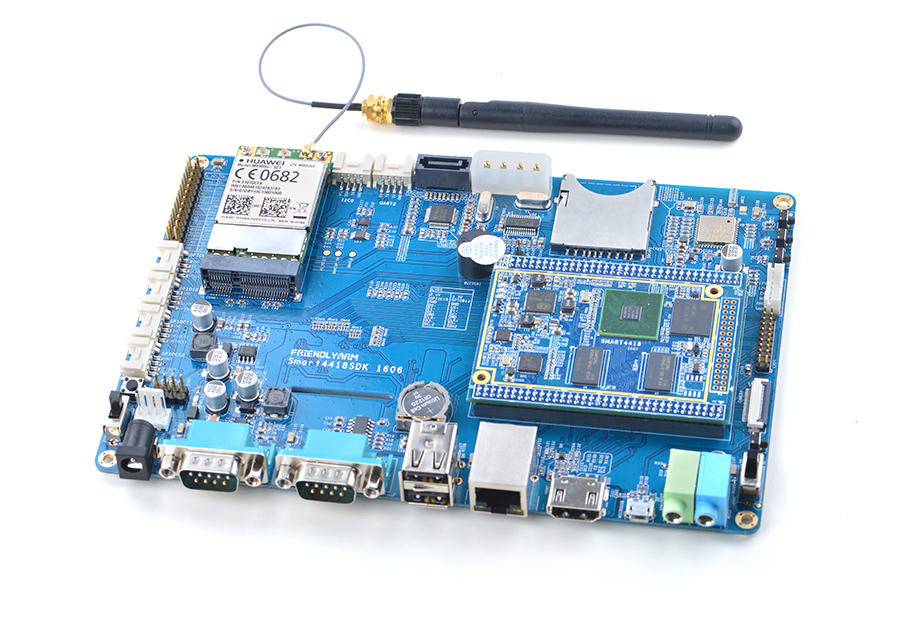
Smart6818
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 Features
- 3 Pin Spec
- 4 Board Dimension
- 5 Notes in Hardware Design
- 6 Carrier Board
- 7 Get Started
- 8 Working with Debian
- 9 Make Your Own OS Image
- 10 Connect Smart6818 to External Modules
- 11 More OS Support
- 12 Resources
- 13 Update Log
- 14 Introduction
- 15 Features
- 16 Pin Spec
- 17 Board Dimension
- 18 Notes in Hardware Design
- 19 Carrier Board
- 20 Get Started
- 21 Working with Debian
- 22 Make Your Own OS Image
- 23 Connect Smart6818 to External Modules
- 24 More OS Support
- 25 Resources
- 26 Update Log
1 Introduction
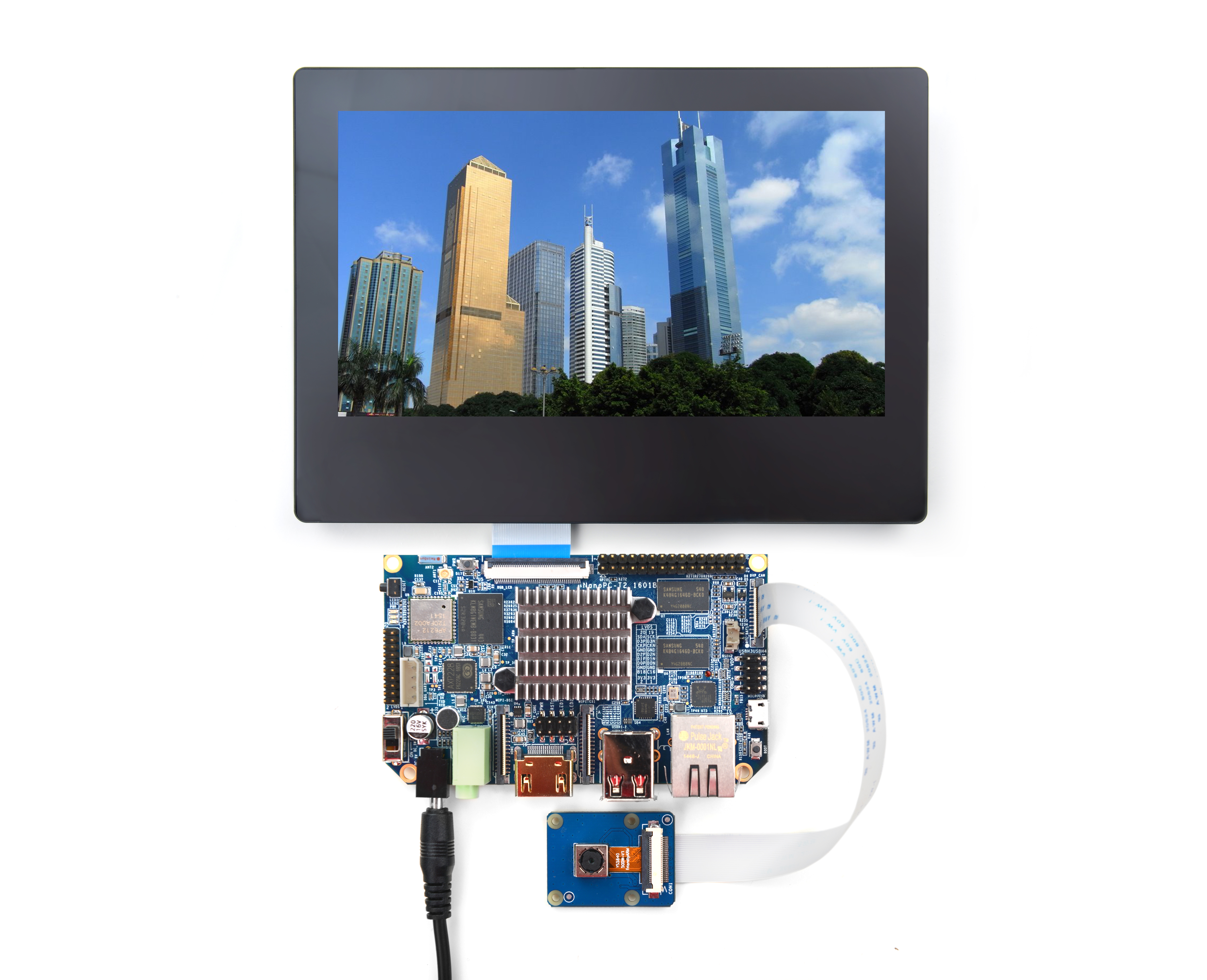
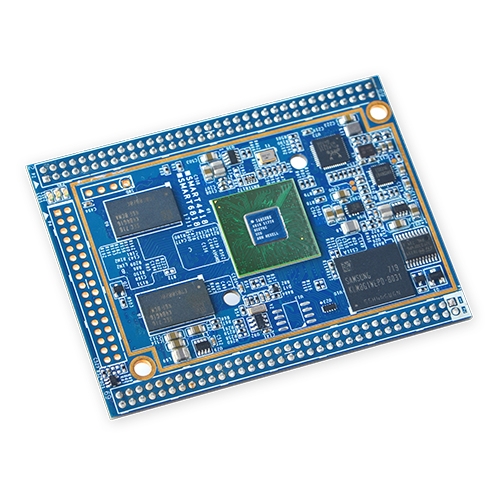
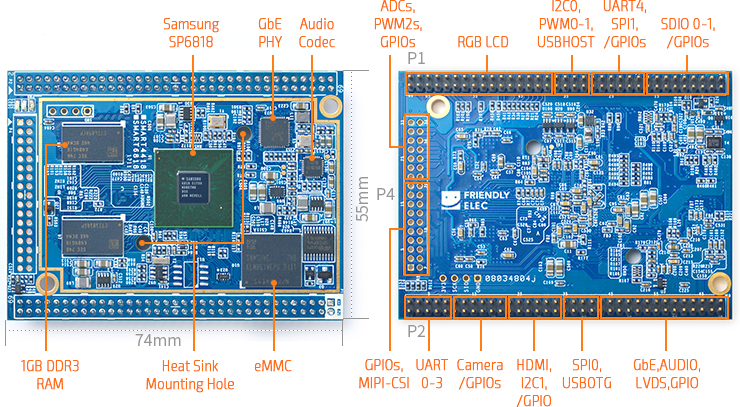
- The Smart6818 CPU board is a Octa-Core Cortex-A53 CPU board designed and developed by FriendlyELEC for industrial applications. As a successor of the Smart210 CPU board it uses the Samsung Octa-Core Cortex-A53 S5P6818 SoC with dynamic frequency scaling up to 1.4GHz. The standard Smart6818 CPU board has 1GB DDR3 RAM and 8GB eMMC. It support software power-off, and RTC alarm power-on functions. In addition its Gbps Ethernet and audio jack make it suitable for various industrial applications.
- The Smart6818 CPU board has 2.0mm pitch double row pin headers(P1, P2 and P4) containing 174 pins in total. These pins contain most popular interface pins. By default we have P1 and P2 soldered on the board and leave P4 for users' applications. It works with various FriendlyELEC LCDs e.g. 3.5"LCD, 4.3"LCD, 5"LCD, 7"LCD and 10.1"LCD.
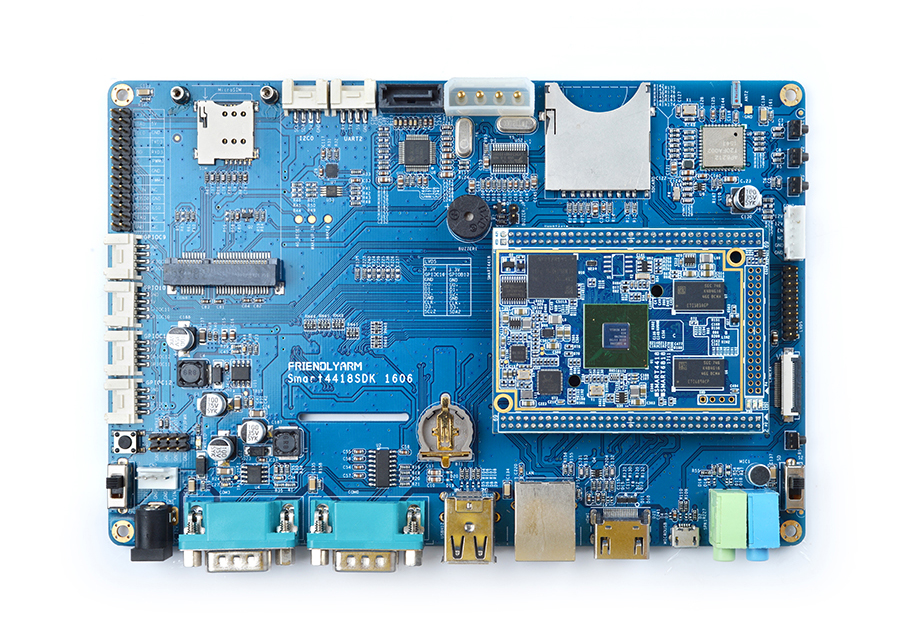
- In addition we have a Smart4418/6818SDK carrier board which enables the Smart6818 CPU board's Gbps Ethernet.In addition, Smart6818 is pin to pin compatible to the Smart4418 CPU board.
- For more details about the Smart4418/6818 SDK carrier board V1606 refer to Smart4418/6818SDK 1606.
2 Features
- SoC: Samsung S5P6818 Octa-Core Cortex-A53, 400M Hz - 1.4G Hz
- PMU Power Management: Implemented by an MCU, support software power-off, and RTC alarm power-on functions
- DDR3 RAM: 1GB 32bit DDR3 RAM
- Ethernet: Gbps Ethernet(RTL8211E) with unique MAC
- eMMC: 8GB
- Audio: 1 x audio codec chip, 1 x onboard Microphone and 1 x audio jack
- LED: 1 x Power LED, 2 x GPIO LED
- PCB Dimension: 74 x 55 mm, Six-Layer
- Power: DC 5V, up to 2A
- Temperature measuring range: -40℃ to 80℃
- OS/Software: u-boot, Android5.1/4.4, Debian8, ubuntu-core
- 3 x 2.0mm pitch double row pin header, 174 pins in total:
- USB 2.0 - Host x1, OTG x1
- Video output/Display - RGB Parallel I/F (24-bit), LVDS and HDMI 1.4a
- Video input - DVP Camera interface, ITU-R BT 601/656 8-bit and MIPI-CSI
- Audio input - Microphone
- Audio output - Audio jack (with headset detection) and HDMI audio
- Ethernet - 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet x 1
- ADC - CPU internal ADC, 7 channels, 12-bit, range: 0 ~ 1.8V
- External interface - SDIO/MMC x2, SPI x2, I2C x3, UART x5, PWM x3, GPIOs x24
- Others - Power key input, RESET input, RESET output, RTC battery input
3 Pin Spec
P1 P2 Pin# Name Pin# Name Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 VDD_5V 2 DGND 1 UART0_TX 2 UART0_RX 3 RTC_BATT 4 GPIOB8 3 UART1_TX 4 UART1_RX 5 NRESETIN 6 GPIOC17 5 UART2_TX 6 UART2_RX 7 MMC0_CMD 8 MMC1_CMD 7 UART3_TX 8 UART3_RX 9 MMC0_CLK 10 MMC1_CLK 9 UART1_nCTS 10 UART1_nRTS 11 MMC0_D0 12 MMC1_D0 11 CAM0_D0 12 CAM0_D1 13 MMC0_D1 14 MMC1_D1 13 CAM0_D2 14 CAM0_D3 15 MMC0_D2 16 MMC1_D2 15 CAM0_D4 16 CAM0_D5 17 MMC0_D3 18 MMC1_D3 17 CAM0_D6 18 CAM0_D7 19 MMC0_CD 20 GPIOB24 19 CAM0_PCLK 20 CAM0_VSYNC 21 PWRKEY 22 SPI1_CS/GPIOC10 21 CAM0_HYNC 22 GPIOB14 23 GPIOB28/UART4_RX 24 SPI1_MISO/GPIOC11 23 GPIOB16 24 HDMI_TX1P 25 GPIOB29/UART4_TX 26 SPI1_MOSI/GPIOC12 25 HDMI_TX0P 26 HDMI_TX1N 27 GPIOB30 28 SPI1_CLK/GPIOC9 27 HDMI_TX0N 28 HDMI_TXCP 29 GPIOC15 30 GPIOC16 29 HDMI_TX2P 30 HDMI_TXCN 31 GPIOB31 32 GPIOB18 31 HDMI_TX2N 32 HDMI_HPD 33 GPIOD1/PWM0 34 I2C0_SCL 33 I2C1_SDA 34 I2C1_SCL 35 GPIOC13/PWM1 36 I2C0_SDA 35 USB_OTG_ID 36 SPI0_CS 37 USB_HOST_D- 38 I2C2_SCL 37 USB_OTG_D- 38 SPI0_MISO 39 USB_HOST_D+ 40 I2C2_SDA 39 USB_OTG_D+ 40 SPI0_MOSI 41 LCD_B0 42 LCD_B1 41 VBUS_5V 42 SPI0_CL 43 LCD_B2 44 LCD_B3 43 LVDS_CLKP 44 GPIOB25 45 LCD_B4 46 LCD_B5 45 LVDS_CLKM 46 DGND 47 LCD_B6 48 LCD_B7 47 LVDS_Y0P 48 LAN_MDI1_N 49 LCD_G0 50 LCD_G1 49 LVDS_Y0M 50 LAN_MDI1_P 51 LCD_G2 52 LCD_G3 51 LVDS_Y1P 52 LAN_MDI0_N 53 LCD_G4 54 LCD_G5 53 LVDS_Y1M 54 LAN_MDI0_P 55 LCD_G6 56 LCD_G7 55 LVDS_Y2P 56 LINK_LED 57 LCD_R0 58 LCD_R1 57 LVDS_Y2M 58 SPEED_LED 59 LCD_R2 60 LCD_R3 59 LVDS_Y3P 60 DGND 61 LCD_R4 62 LCD_R5 61 LVDS_Y3M 62 HP_DETECT 63 LCD_R6 64 LCD_R7 63 HP-R 64 HP-L 65 LCD_VSYNC 66 LCD_HSYNC 65 LAN_MDI2_P 66 LAN_MDI3_P 67 LCD_CLK 68 LCD_DE 67 LAN_MDI2_N 68 LAN_MDI3_N 69 DGND 70 BOOT_CS 69 Mic-P 70 Mic-N
P4 Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 MIPICSI_DP0 2 GPIOD8/PPM 3 MIPICSI_DN0 4 GPIOC7 5 MIPICSI_DP1 6 GPIOC8 7 MIPICSI_DN1 8 GPIOC24 9 MIPICSI_DP2 10 GPIOC28 11 MIPICSI_DN2 12 GPIOC0 13 MIPICSI_DP3 14 GPIOC1 15 MIPICSI_DN3 16 GPIOC2 17 MIPICSI_DPCLK 18 GPIOC3 19 MIPICSI_DNCLK 20 DGND 21 GPIOB9 22 ADC1 23 GPIOB26 24 ADC3 25 GPIOC4 26 ADC4 27 AliveGPIO3 28 ADC5 29 PWREN_SYS 30 ADC6 31 GPIOC14/PWM2 32 ADC7 33 NRESETOUT 34 DGND
- Note:
- VDD_5V: Supply voltage, range:4.7 ~ 5.6V. We recommend a 5V/1.2A(MAX) power. You can lower the clock to decrease the power consumption. When the clock is lowered by 200MHz the power consumption roughly decreases 0.5W .
- BOOT_CS: Boot chip selection. When it is not connected or pulled up the board boots from eMMC otherwise it boots from SD card
- NRESETIN: Reset input. Activated when it is low. A reset signal is input to CPU from this pin
- NRESETOUT: Reset output. Activated when it is low. CPU's reset signal outputs to this pin.
- RTC_BATT: RTC's input, direct connection to a 3V power source. If the CPU board is powered on the RTC seat is powered by 3.3V external power otherwise when the CPU board is not powered on it is powered by the RTC battery.
- ADC1~7: CPU internal ADC, 12-bit, 7 channels 1~7, range:0 ~ 1.8V
- 10/100M Ethernet mode: LAN_MDI1_N/P=RX-/+, LAN_MDI0_N/P=TX-/+, four pins connected to RJ45
- 10/100/1000M Ethernet mode: LAN_MDI0_N/P~LAN_MDI3N/P, all eight pins connected to RJ45
- For more details refer to our carrier board's design:Smart210/4418 SDK
- For more details about the Smart4418 SDK carrier board V1606 refer to Smart4418SDK 1606.
- Smart6818 Schematic in pdf
4 Board Dimension
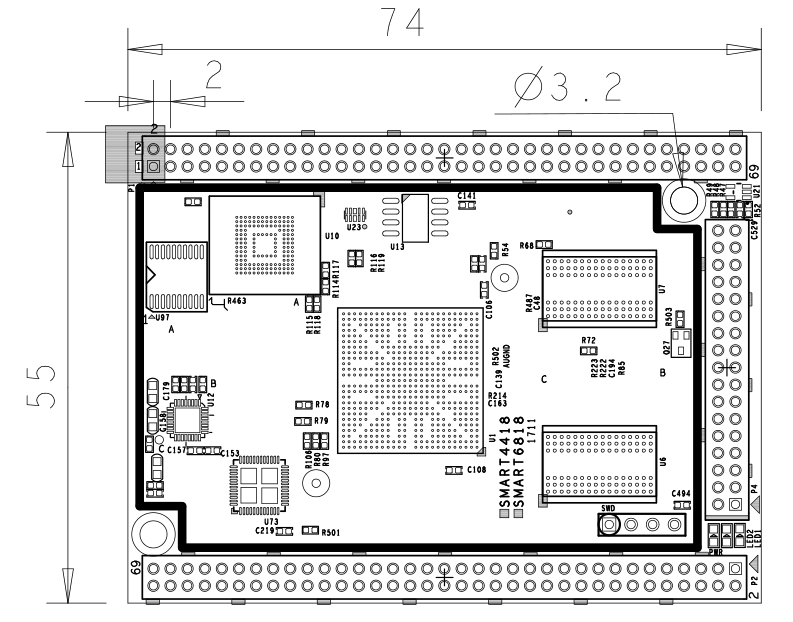
- For more details refer to the dxf file:Smart6818-1711-Drawing(dxf).zip
5 Notes in Hardware Design
5.1 EEPROM
- The Smart6818 CPU board has an EEPROM(model: 24AA025E48T-I/OT) with a unique MAC. This EEPROM is connected to I2C0 and its address is 0x51 therefore some EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0 which will cause conflicts of addresses.
- In our tests these EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0: 24C04, 24C08 and 24C16. There chips which we tested can be connected to I2C0: 24C01, 24C02 and 24C256
- For more details about EEPROM address issues refer to http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/CAT24C01-D.PDF
6 Carrier Board
7 Get Started
7.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your Smart6818 get the following items ready
- Smart6818 CPU board and Smart210/4418 SDK carrier board
- Standard SD card: Class10 or above 8GB SDHC card
- A DC 12V/2A power is a must
- HDMI monitor or LCD
- USB keyboard and mouse
- A host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
7.2 Make an Installation SD Card
7.2.1 Boot Smart6818 from SD Card
Get the following files from here download link:
- Get a 8G SDHC card and backup its data if necessary
Image Files s5p4418-debian-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Debian image file with X Window s5p4418-debian-wifiap-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Debian image file with X Window and WiFi configured as AP s5p4418-kitkat-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Android4.4 image file with support for 4G LTE s5p4418-android-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Android5.1 image file s5p4418-core-qte-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Ubuntu core with Qt Embedded Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
- Uncompress these files. Insert an SD card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator,On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Insert this card into your Smart6818's boot slot, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 12V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and LED1 is blinking this indicates your Smart6818 has successfully booted.
7.2.2 Flash Image to Smart6818's eMMC
- Download eflasher
Get the eflasher utility s5p4418-eflasher-sd8g-xxx-full.img.7z
This package includes a Ubuntu Core, Debian, Android 5 and Android 4.4 image files;
Get the Windows utility: win32diskimager.rar;
- Flash eflasher Image
Extract the .7z package and you will get .img files.Insert an SD card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
If your PC runs Linux you can use the dd command to flash a .img file to the SD card;
- Flash image to eMMC
Insert this card into your Smart6818 SDK carrier board, connect the board to an HDMI monitor or an LCD, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 12V/2A power source) the board. After your board is powered on you will see multiple OS options and you can select an OS to start installation.
7.2.3 Make Installation Card under Linux Desktop
- 1) Insert your SD card into your host PC running Ubuntu and check your SD card's device name
dmesg | tail
Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card has been recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions"
- 2) Downlaod Linux script
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_nanopi2.git cd sd-fuse_nanopi2
- 3) Make Android SD Card
su ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
When you run the script for the first time it will prompt you to download an image you have to hit “Y” within 10 seconds otherwise you will miss the download
- 4) Here is how to make a Debian SD card
./fusing.sh /dev/sdx debian
7.2.4 Extend Smart6818's SD Card Section
- When Debian/Ubuntu boots it will automatically extend its SD card's section. On its initial booting the system will extend the root file system and other sections.
- Under Android users need to extend the section by using the following commands:
sudo umount /dev/sdx? sudo parted /dev/sdx unit % resizepart 4 100 resizepart 7 100 unit MB print sudo resize2fs -f /dev/sdx7
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
7.2.5 LCD/HDMI Resolution
When system boots our uboot will check whether it is connected to an LCD or an HDMI monitor. If it recognizes an LCD it will configure its resolution. Our uboot defaults to the HDMI 720P configuration.
If you want to modify the LCD resolution you can modify file "arch/arm/plat-s5p4418/nanopi2/lcds.c" in the kernel and recompile it.
If your Smart6818 is connected to an HDMI monitor and it runs Android it will automatically set the resolution to an appropriate HDMI mode by checking the "EDID". If your Smart6818 is connected an HDMI monitor and it runs Debian by default it will set the resolution to HDMI 720P. If you want to modify the HDMI resolution to 1080P modify your kernel's configuration as explained above.
7.3 Update Image Files in SD Card From PC Host
If you want to make some changes to the image files in your SD card follow steps below otherwise you can skip this section.
Insert your SD card into a host PC running Linux, mount the boot and rootfs sections of the SD card and follow the steps below:
1) If you want to change your kernel command line parameters you can do it via the fw_setevn utility under "sd-fuse_nanopi2/tools":
Check the current Command Line:
cd sd-fuse_nanopi2/tools ./fw_printenv /dev/sdc | grep bootargs
Android 5.1.1_r6 starts SELinux. By default it is enforcing. You can change it this way:
./fw_setenv /dev/sdc bootargs XXX androidboot.selinux=permissive
This sets it to "permissive". The "XXX" stands for the original bootargs' value.
2) Update Kernel
Our customized uboot will check the LCD type when it boots.
For a non-Android OS If it recognizes an LCD connected to the Smart6818 it will load "uImage" from "boot" otherwise it will load "uImage.hdmi".
For Android it doesn't make any difference what display device is detected. You can use your generated uImage to replace the existing one under "boot".
For Debian if your generated kernel is for an LCD you need to replace the existing uImage or if your kernel is for an HDMI monitor you need to replace the existing uImage.hdmi.
7.4 Run Android or Debian
- Insert an SD card with Android/Debian image file into your Smart6818's carrier board, connect the board to an HDMI monitor, switch S2 to "SDBOOT", power on the board the Smart6818 will be booted from the SD card. If you can see the PWR LED on and the LED1 flashing it means your board is working and you will see Android/Debain being loaded on the HDMI monitor.
1) If you connect the Smart6818 to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and a USB keyboard to operate. If you connect it to an LCD with capacitive touch you can operate directly on the LCD.
2)If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.
- Here is a setup in which we connect the COM0 on the Smart6818's V1606 SDK carrier board to a PC running Ubuntu and Minicom via a serial cable you will see system messages output to the PC’s minicom terminal
- Under Debian the password for "root" is "fa"
7.5 Login Debian via VNC or SSH
If your Smart6818 is not connected to a display device and your board runs the "-wifiap.img" image you can login to your Smart6818's nanopi2-wifiap(the default password is "123456789") via a mobile phone. You can download and install a "VNC Viewer" from here on mobile phone and login to the Smart6818 via VNC. Its default password is "fa123456". Here is a screenshot which shows how it looks like when users login to the Smart6818 from an iPhone via VNC:
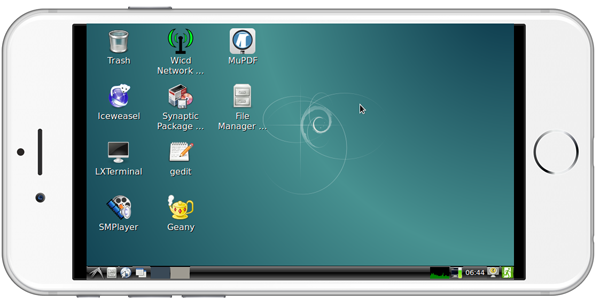
You can login via "SSH -l root 192.168.8.1" too and the default password for "root" is "fa"
To make SSH session run faster turn off the WiFi's power saving mode by using the following command:
iwconfig wlan0 power off
8 Working with Debian
8.1 Ethernet Connection
- If the Smart6818 is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on, it will automatically obtain an IP after it is powered up.
8.2 Wireless Connection
Open the file /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf and append the following lines:
network={ ssid="YourWiFiESSID" psk="YourWiFiPassword" }
The "YourWiFiESSID" and "YourWiFiPassword" need to be replaced with your actual ESSID and password.
Save, exit and run the following commands to connect to a WiFi:
ifdown wlan0 ifup wlan0
If your WiFi password has special characters or you don't want your password saved as plain text you can use "wpa_passphrase" to generate a psk for your WiFi password. Here is how you can do it:
wpa_passphrase YourWiFiESSID
Following the prompt type in your password and open the file /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf you will find that your password has been changed and your can delete your plain text password.
If your AP mode is turned on you need to turn it off. You can do it by using the following commands:
su
turn-wifi-into-apmode no8.3 Setup Wi-Fi AP
You can follow the steps below to setup Wi-Fi AP:
turn-wifi-into-apmode yesReboot the system as prompted. By default the AP's name is "nanopi2-wifiap" and the password is 123456789.
Now you are able to find the "nanopi2-wifiap" from a host PC and connect to it. If the connection is successful you will be able to SSH to this Smart6818 at "192.168.8.1":
ssh root@192.168.8.1
The password for it is "fa".
To make SSH run faster turn off the WiFi's power saving mode by using the following command:
iwconfig wlan0 power off
You can check the WiFi mode via the following command:
cat /sys/module/bcmdhd/parameters/op_mode
If the result is "2" it means it is currently working as a WiFi AP.If you want to switch back to the Station mode you can do it this way:
turn-wifi-into-apmode no
8.4 Bluetooth
Here are the steps to transfer a file from Smart6818 to a mobile phone. Run the following command to search a surrounding Bluetooth device:
hcitool scan
In our example a mobile phone was detected and the following messages were listed:
Scanning ...
38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DD MEIZU MX4
These messages indicated that a MEIZU MX4 mobile phone was detected. We then checked the Bluetooth services this phone supported with its MAC address presented in front of its device name
sdptool browse 38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DDNote: you need to use your device's name and its MAC address when you run these commands.
The command listed all the services the phone supported. We needed the "OBEX Object Push" service which is for file transfers.
Service Name: OBEX Object Push
Service RecHandle: 0x1000b
Service Class ID List:
"OBEX Object Push" (0x1105)
Protocol Descriptor List:
"L2CAP" (0x0100)
"RFCOMM" (0x0003)
Channel: 25
"OBEX" (0x0008)
Profile Descriptor List:
"OBEX Object Push" (0x1105)
Version: 0x0100
From the above messages we could get the channel number 25 for the "OBEX Object Push" service. We input this number to the "ussp-push" by running the following command:
ussp-push 38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DD@25 example.jpg example.jpg
Note: you need to use your device's name, its MAC address and channel number when you run these commands.
Usually after the above commands are run a popup window will show on the phone that communicates with Smart6818 and you can start file transfers.
Common Issues:
1) If Smart6818 cannot find a Bluetooth device you can try this command to restart its Bluetooth:
rfkill unblock 02) If any of these commands is not installed you can try this command to install it:
apt-get install bluetooth bluez obexftp openobex-apps python-gobject ussp-push
8.5 Install Debian Packages
We provide a Debian Jessie image. You can install Jessie's packages by commanding "apt-get". If this is your first installation you need to update the package list by running the following command:
apt-get updateYou can install your preferred packages. For example if you want to install an FTP server you can do this:
apt-get install vsftpdNote: you can change your download server by editting "/etc/apt/sources.list". You can get a complete server list from [1]. You need to select the one with "armhf".
9 Make Your Own OS Image
9.1 Install Cross Compiler
Download the compiler package:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/prebuilts.git sudo mkdir -p /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain sudo tar xf prebuilts/gcc-x64/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf-4.9.3.tar.xz -C /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/
Then add the compiler's directory to "PATH" by appending the following lines in "~/.bashrc":
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
Execute "~/.bashrc" to make the changes into effect. Note that there is a space after the first ".":
. ~/.bashrcThis compiler is a 64-bit one therefore it cannot be run on a 32-bit Linux. After the compiler is installed you can verify it by running the following commands:
arm-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=arm-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/libexec/gcc/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/4.9.3/lto-wrapper Target: arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf Configured with: /work/toolchain/build/src/gcc-4.9.3/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/sys-root --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-arch=armv7-a --with-tune=cortex-a9 --with-fpu=vfpv3 --with-float=hard ... Thread model: posix gcc version 4.9.3 (ctng-1.21.0-229g-FA)
9.2 Compile U-Boot
Download the U-Boot source code and compile it. Note the github's branch is nanopi2-lollipop-mr1:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot_nanopi2.git cd uboot_nanopi2 git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 make s5p4418_nanopi2_config make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
After your compilation succeeds a u-boot.bin will be generated. If you want to test it flash it to your installation SD card via fastboot. Here is how you can do it
1) On your host PC run "sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot" to install the fastboot utility;
2) Connect your Smart6818 to your host PC via a serial cable (e.g. PSU-ONECOME). Press the enter key within two seconds right after you power on your Smart6818 and you will enter uboot's command line mode;
3) After type in "fastboot" and press "enter" you will enter the fastboot mode;
4) Connect your Smart6818 to this host PC via a microUSB cable and type in the following command to flash the u-boot.bin you generated:
fastboot flash bootloader u-boot.bin
Warning: you cannot update this SD card by commanding "dd". This command which will cause trouble when booting the Smart6818.
9.3 Prepare mkimage
You need the mkimage utility to compile a U-Boot source code package. Make sure this utility works well on your host before you start compiling a uImage.
You can install this utility by either commanding "sudo apt-get install u-boot-tools" or following the commands below:
cd uboot_nanopi2 make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- tools sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/sbin && sudo cp -v tools/mkimage /usr/local/sbin
9.4 Compile Linux Kernel
9.4.1 Compile Kernel
- Download Kernel Source Code
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git cd linux-3.4.y git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1
The Smart6818's kernel source code lies in the "nanopi2-lollipop-mr1" branch.
- Compile Android Kernel
make nanopi2_android_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
- Compile Debian Kernel
make nanopi2_linux_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
After your compilation succeeds a uImage will be generated in the "arch/arm/boot/uImage" directory. This kernel is for HDMI 720P. You can use it to replace the existing uImage.hdmi.
If you want to generate a kernel for HDMI 1080P you can do it this way
touch .scmversion make nanopi2_linux_defconfig make menuconfig Device Drivers --> Graphics support --> Nexell Graphics --> [ ] LCD [*] HDMI (0) Display In [0=Display 0, 1=Display 1] Resolution (1920 * 1080p) ---> make uImage
After your compilation succeeds a uImage will be generated for HDMI 1080P. You can use it to replace the existing uImage
9.4.2 Compile Kernel Modules
Android contains kernel modules which are in the "/lib/modules" directory in the system section. If you want to add your own modules to the kernel or you changed your kernel configurations you need to recompile these new modules.
Compile Original Kernel Modules:
cd linux-3.4.y make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules
Here we have two new modules and we can compile them by following the commands below:
cd /opt/FriendlyARM/s5p4418/android ./vendor/friendly-arm/build/common/build-modules.sh
The "/opt/FriendlyARM/s5p4418/android" directory points to the top directory of Android source code. You can get more details by specifying option "-h".
After your compilation succeeds new modules will be generated
9.5 Compile Android
- Install Cross Compiler
Install 64 bit Ubuntu 14.04 on your PC host.
sudo apt-get install bison g++-multilib git gperf libxml2-utils make python-networkx zip sudo apt-get install flex libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk minicom
For more details refer to https://source.android.com/source/initializing.html 。
- Download Source Code(Android 5.1)
You need to use repo to get the Android source code. Refer to https://source.android.com/source/downloading.html 。
mkdir android && cd android repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/android_manifest.git -b nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 repo sync
The "android" directory is the working directory.
If you want to try Android4.4's source code you can run the following commands:
mkdir android && cd android repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/android_manifest.git -b nanopi2-kitkat repo sync
Option "-b" specifies a branch
- Compile System Package
source build/envsetup.sh lunch aosp_nanopi2-userdebug make -j8
After your compilation succeeds the following files will be generated in the "out/target/product/nanopi2/" directory.
filename partition Description boot.img boot - cache.img cache - userdata.img userdata - system.img system - partmap.txt - partition description file
- Flash Image to eMMC
After compiling Android successfully you can flash it to eMMC with either of the following methods
1) fastboot: right after the Smart6818 is booted from eMMC press any key to enter the uboot commandline mode and type in "fastboot"
Connect your board to a host PC running Ubuntu with a USB cable and run the following commands in the PC's terminal:
cd out/target/product/nanopi2 sudo fastboot flash boot boot.img sudo fastboot flash cache cache.img sudo fastboot flash userdata userdata.img sudo fastboot flash system system.img sudo fastboot reboot
2) Use an SD Card
Copy these files: boot.img, cache.img, userdata.img, system.img, partmap.txt from the out/target/product/nanopi2 directory to your installation SD card's images/android directory and you can use this SD card to flash Android to eMMC
10 Connect Smart6818 to External Modules
10.1 Connect Smart6818 to 4G Module
- The Smart6818 can work with some 4G modules under Android 4.4. After you connect a 4G module (e.g. ME909u-521 which supports FDD-LTE) to a Smart6818 power on the board the 4G module will be activated automatically
10.2 Connect Smart6818 to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
- In this use case the Smart6818 runs Debian. If you connect your Smart6818 to our LCD or an HDMI monitor after Debain is fully loaded click on "other"-->"xawtv9" on the left bottom of the GUI and the USB Camera application will be started. After enter "welcome to xawtv!" click on "OK" to start exploring.
10.3 Connect Smart6818 to CMOS 5M-Pixel Camera
For more details about the CAM500A camera refer to [2]
- If your Smart6818 runs Android5.1 and it is connected to our LCD or an HDMI monitor after Android is fully loaded click on the "Camera" icon and the application will be started. You can take pictures or record videos
- Under Debian/Ubuntu a camera utility "nanocams" is available for previewing 40 frames and picture taking. You can try it by following the commands below
sudo nanocams -p 1 -n 40 -c 4 -o IMG001.jpg
For more details about the usage of the nanocams run "nanocams -h". You can get its source code from our git hub:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/nexell_linux_platform.git
10.4 Use OpenCV to Access USB Camera
- The full name of "OpenCV" is Open Source Computer Vision Library and it is a cross platform vision library.
- When the Smart6818 runs Debian users can use OpenCV APIs to access a USB Camera device.
1. Here is a guideline on how to use OpenCV with C++ on the Smart6818:
- Firstly you need to make sure your Smart6818 is connected to the internet. Login to your Smart6818 via a serial terminal or SSH. After login type your username(root) and password(fa):
- Run the following commands:
apt-get update apt-get install libcv-dev libopencv-dev
2. Make sure your USB camera works with the Smart6818. You can test your camera with Smart6818's camera utility.
3. Check your camera device:
ls /dev/video*
- Note:in our test case video0 was the USB camera device
4. OpenCV's code sample(official code in C++) is under /home/fa/Documents/opencv-demo. Compile the code sample with the following commands:
cd /home/fa/Documents/opencv-demo make
After it is compiled successfully a "demo" executable will be generated
6. Connect Smart6818 to USB Keyboard & Run the Following Command
./demoThis is what you expect to observe:
11 More OS Support
11.1 Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded
Ubuntu Core with Qt-Embedded is a light Linux system without X-windows. It uses the Qt-Embedded's GUI and is popular in industrial and enterprise applications.
Besides the regular Ubuntu core's features our Ubuntu-Core has the following additional features:
- it supports our LCDs with both capacitive touch and resistive touch(S700, X710, S70)
- it supports WiFi
- it supports Ethernet
- it supports Bluetooth and has been installed with bluez utilities
- it supports audio playing
For more details refer to Ubuntu Core with Qt-Embedded.
11.1.1 Flash Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded to eMMC
1. Make an installation SD card with the win32 utility;
2. Insert this SD card to a host PC and copy the UbuntuCore image (in our example it was "ubuntu_core.img") and 2nboot file(in our example it was "2ndboot.bin.emmc") to it;
2nboot can be downloaded from: https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_s5p6818/tree/master/prebuilt
3. Run the following commands to flash the image file to your board's eMMC:
dd if=ubuntu_core.img of= /dev/mmcblk1
4. Flash the 2nboo file to the eMMC:
dd if=2ndboot.bin.emmc of=/dev/mmcblk1 bs=512 seek=1
11.2 Ubuntu-Mate
Ubuntu-Mate is a Ubuntu variant and its GUI is Mate-desktop. You can log in via SSH when you connect the Smart6818 to an LCD or HDMI
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it
- Go to this link download link to download the image files
- Uncompress it and flash the image file to a TF card with win32diskimager under Windows
- After it is done you can boot your Smart6818 with this card
- Login name: "root" or "fa", Password: fa
11.3 Kali
- Go to this link [3] to download the image files;
- Prepare an 8G High Speed MicroSD card, insert it to a Linux host and do "sudo fdisk -l" to check its device name, i.e. "/dev/sd*".
- Copy the image files to the card by running the following commands as root:
xzcat kali-2.0-nanopi2.img.xz | dd of=<YOURDEVICE> bs=1m
- After it is done you can boot your Smart6818 with this card.
Note: this is offered by Kali and FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
11.4 Deepin15 ARM
- Go to this link [4] to download the image files
- Uncompress the file and you will get a 16g.img file which is the image file for MicroSD card.
tar -xf deepin15_nanopi2_armhf_16g.tar.gz
- Prepare an 16G High Speed SD card, insert it into a Linux host and do "sudo fdisk -l" to check its device name, i.e. "/dev/sd*"
- Flash the image files to the card by running the following command as root(in our case our card was recognized as "/dev/sdc"):
sudo dd if=16g.img of=/dev/sdc
This process takes a while which can be up to one hour
- After it is done you can boot your Smart6818 with this card
Notes:
1. The password for login name "deepin" is "deepin". The password for login name "root" is "admin".
2. The initial booting of Deepin15 takes a relative long time for it generates some configuration files.
3. If WiFi is activated in your system booting might take longer. In this case wait for the sound and wifi icons on the right bottom of the GUI to appear before you start any action.
ARM code: http://packages.deepin.com/armhf/ NanoPC-T2 Image: http://cdimage.deepin.com/armhf/15/beta1.0/ NanoPC-T2 Image Installation Instruction; http://bbs.deepin.org/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=36670 Forum for Migrating Deepin15 to ARM: http://bbs.deepin.org/
Note: this is offered by the Deepin15 team and FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
11.5 Android-Remixos
Go to this link [5] to download the image files;
- Untar the image ball:
tar -xf nanopi2-android-remixos-sd4g.tar
- Use the win32diskimager utility to flash the image to an SD card.
It supports HDMI and LCD output and works with all existing FriendlyARM 4418 boards.
Note: this is offered by Remix team and FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
12 Resources
- 《创客秘籍》Hacker's Book in Chinese by FriendlyARM
- 《创客秘籍-02》Hacker's Book-02 in Chinese by FriendlyARM
- 《创客秘籍-03》Hacker's Book-03 in Chinese by FriendlyARM
13 Update Log
13.1 07-26-2018
- Released English version
14 Introduction
- The Smart6818 CPU board is a quad core Cortex A9 CPU board designed and developed by FriendlyARM for industrial applications. As a successor of the Smart210 CPU board it uses the Samsung Quad Core Cortex-A9 S5P4418 SoC with dynamic frequency scaling up to 1.4GHz. The standard Smart6818 CPU board has 1GB DDR3 RAM and 8GB eMMC. It has the AXP229 PMU enabling software power off/on and wake-up functions. In addition its Gbps Ethernet and audio jack make it suitable for various industrial applications.
- The Smart6818 CPU board has 2.0mm pitch double row pin headers(P1, P2 and P4) containing 174 pins in total. These pins contain most popular interface pins. By default we have P1 and P2 soldered on the board and leave P4 for users' applications. It works with various FriendlyARM LCDs e.g. 3.5"LCD, 4.3"LCD, 5"LCD, 7"LCD and 10.1"LCD.
- In addition we have a Smart4418/6818SDK carrier board which enables the Smart6818 CPU board's Gbps Ethernet.In addition FriendlyARM will soon release a Samsung Octa Core Cortex-A53 S5P6818@1.4GHz based board which is pin to pin compatible to the Smart4418 CPU board.
- For more details about the Smart4418 SDK carrier board V1606 refer to Smart4418SDK 1606.
15 Features
- CPU: Samsung S5P4418 Quad Core Cortex-A9, with dynamic frequency scaling from 400M Hz to 1.4G Hz
- PMU Power Management Unit: AXP228. it supports software power-off and wake-up functions.
- DDR3 RAM: 1GB 32bit DDR3 RAM
- Ethernet: Gbps Ethernet(RTL8211E) with unique MAC
- eMMC: 8GB
- Audio: 1 x audio codec chip, 1 x onboard Microphone and 1 x audio jack
- LED: 1 x Power LED, 2 x GPIO LED
- Others: onboard thermistor
- PCB Dimension: 74 x 55 mm, Six-Layer
- Power: DC 5V, up to 1.2A
- Temperature measuring range: -40℃ to 80℃
- OS/Software: u-boot, Android5.1/4.4, Debian8, ubuntu-core
- 3 x 2.0mm pitch double row pin header, 174 pins in total:
- USB 2.0 - Host x1, OTG x1
- Video output/Display - RGB Parallel I/F (24-bit), LVDS and HDMI 1.4a
- Video input - DVP Camera interface, ITU-R BT 601/656 8-bit and MIPI-CSI
- Audio input - Microphone
- Audio output - Audio jack (with headset detection) and HDMI audio
- Ethernet - 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet x 1
- ADC - CPU internal ADC, 7 channels, 12-bit, range: 0 ~ 1.8V
- External interface - SDIO/MMC x2, SPI x2, I2C x3, UART x5, PWM x3, GPIOs x24
- Others - Power key input, RESET input, RESET output, RTC battery input
16 Pin Spec
P1 P2 Pin# Name Pin# Name Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 VDD_5V 2 DGND 1 UART0_TX 2 UART0_RX 3 RTC_BATT 4 GPIOB8 3 UART1_TX 4 UART1_RX 5 NRESETIN 6 GPIOC17 5 UART2_TX 6 UART2_RX 7 MMC0_CMD 8 MMC1_CMD 7 UART3_TX 8 UART3_RX 9 MMC0_CLK 10 MMC1_CLK 9 UART1_nCTS 10 UART1_nRTS 11 MMC0_D0 12 MMC1_D0 11 CAM0_D0 12 CAM0_D1 13 MMC0_D1 14 MMC1_D1 13 CAM0_D2 14 CAM0_D3 15 MMC0_D2 16 MMC1_D2 15 CAM0_D4 16 CAM0_D5 17 MMC0_D3 18 MMC1_D3 17 CAM0_D6 18 CAM0_D7 19 MMC0_CD 20 GPIOB24 19 CAM0_PCLK 20 CAM0_VSYNC 21 PWRKEY 22 SPI1_CS/GPIOC10 21 CAM0_HYNC 22 GPIOB14 23 GPIOB28/UART4_RX 24 SPI1_MISO/GPIOC11 23 GPIOB16 24 HDMI_TX1P 25 GPIOB29/UART4_TX 26 SPI1_MOSI/GPIOC12 25 HDMI_TX0P 26 HDMI_TX1N 27 GPIOB30 28 SPI1_CLK/GPIOC9 27 HDMI_TX0N 28 HDMI_TXCP 29 GPIOC15 30 GPIOC16 29 HDMI_TX2P 30 HDMI_TXCN 31 GPIOB31 32 GPIOB18 31 HDMI_TX2N 32 HDMI_HPD 33 GPIOD1/PWM0 34 I2C0_SCL 33 I2C1_SDA 34 I2C1_SCL 35 GPIOC13/PWM1 36 I2C0_SDA 35 USB_OTG_ID 36 SPI0_CS 37 USB_HOST_D- 38 I2C2_SCL 37 USB_OTG_D- 38 SPI0_MISO 39 USB_HOST_D+ 40 I2C2_SDA 39 USB_OTG_D+ 40 SPI0_MOSI 41 LCD_B0 42 LCD_B1 41 VBUS_5V 42 SPI0_CL 43 LCD_B2 44 LCD_B3 43 LVDS_CLKP 44 GPIOB25 45 LCD_B4 46 LCD_B5 45 LVDS_CLKM 46 DGND 47 LCD_B6 48 LCD_B7 47 LVDS_Y0P 48 LAN_MDI1_N 49 LCD_G0 50 LCD_G1 49 LVDS_Y0M 50 LAN_MDI1_P 51 LCD_G2 52 LCD_G3 51 LVDS_Y1P 52 LAN_MDI0_N 53 LCD_G4 54 LCD_G5 53 LVDS_Y1M 54 LAN_MDI0_P 55 LCD_G6 56 LCD_G7 55 LVDS_Y2P 56 LINK_LED 57 LCD_R0 58 LCD_R1 57 LVDS_Y2M 58 SPEED_LED 59 LCD_R2 60 LCD_R3 59 LVDS_Y3P 60 DGND 61 LCD_R4 62 LCD_R5 61 LVDS_Y3M 62 HP_DETECT 63 LCD_R6 64 LCD_R7 63 HP-R 64 HP-L 65 LCD_VSYNC 66 LCD_HSYNC 65 LAN_MDI2_P 66 LAN_MDI3_P 67 LCD_CLK 68 LCD_DE 67 LAN_MDI2_N 68 LAN_MDI3_N 69 DGND 70 BOOT_CS 69 Mic-P 70 Mic-N
P4 Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 MIPICSI_DP0 2 GPIOD8/PPM 3 MIPICSI_DN0 4 GPIOC7 5 MIPICSI_DP1 6 GPIOC8 7 MIPICSI_DN1 8 GPIOC24 9 MIPICSI_DP2 10 GPIOC28 11 MIPICSI_DN2 12 GPIOC0 13 MIPICSI_DP3 14 GPIOC1 15 MIPICSI_DN3 16 GPIOC2 17 MIPICSI_DPCLK 18 GPIOC3 19 MIPICSI_DNCLK 20 DGND 21 GPIOB9 22 ADC1 23 GPIOB26 24 ADC3 25 GPIOC4 26 ADC4 27 AliveGPIO3 28 ADC5 29 PWREN_SYS 30 ADC6 31 GPIOC14/PWM2 32 ADC7 33 NRESETOUT 34 DGND
- Note:
- VDD_5V: Supply voltage, range:4.7 ~ 5.6V. We recommend a 5V/1.2A(MAX) power. You can lower the clock to decrease the power consumption. When the clock is lowered by 200MHz the power consumption roughly decreases 0.5W .
- BOOT_CS: Boot chip selection. When it is not connected or pulled up the board boots from eMMC otherwise it boots from SD card
- NRESETIN: Reset input. Activated when it is low. A reset signal is input to CPU from this pin
- NRESETOUT: Reset output. Activated when it is low. CPU's reset signal outputs to this pin.
- RTC_BATT: RTC's input, direct connection to a 3V power source. If the CPU board is powered on the RTC seat is powered by 3.3V external power otherwise when the CPU board is not powered on it is powered by the RTC battery.
- ADC1~7: CPU internal ADC, 12-bit, 7 channels 1~7, range:0 ~ 1.8V
- 10/100M Ethernet mode: LAN_MDI1_N/P=RX-/+, LAN_MDI0_N/P=TX-/+, four pins connected to RJ45
- 10/100/1000M Ethernet mode: LAN_MDI0_N/P~LAN_MDI3N/P, all eight pins connected to RJ45
- For more details refer to our carrier board's design:Smart210/4418 SDK
- For more details about the Smart4418 SDK carrier board V1606 refer to Smart4418SDK 1606.
- Smart6818 Schematic in pdf
17 Board Dimension

- For more details refer to the dxf file:Smart6818-1711-Drawing(dxf).zip
18 Notes in Hardware Design
18.1 EEPROM
- The Smart6818 CPU board has an EEPROM(model: 24AA025E48T-I/OT) with a unique MAC. This EEPROM is connected to I2C0 and its address is 0x51 therefore some EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0 which will cause conflicts of addresses.
- In our tests these EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0: 24C04, 24C08 and 24C16. There chips which we tested can be connected to I2C0: 24C01, 24C02 and 24C256
- For more details about EEPROM address issues refer to http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/CAT24C01-D.PDF
19 Carrier Board
20 Get Started
20.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your Smart6818 get the following items ready
- Smart6818 CPU board and Smart210/4418 SDK carrier board
- Standard SD card: Class10 or above 8GB SDHC card
- A DC 12V/2A power is a must
- HDMI monitor or LCD
- USB keyboard and mouse
- A host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
20.2 Make an Installation SD Card
20.2.1 Boot Smart6818 from SD Card
Get the following files from here download link:
- Get a 8G SDHC card and backup its data if necessary
Image Files s5p4418-debian-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Debian image file with X Window s5p4418-debian-wifiap-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Debian image file with X Window and WiFi configured as AP s5p4418-kitkat-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Android4.4 image file with support for 4G LTE s5p4418-android-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Android5.1 image file s5p4418-core-qte-sd4g-YYYYMMDD.img.zip Ubuntu core with Qt Embedded Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
- Uncompress these files. Insert an SD card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator,On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Insert this card into your Smart6818's boot slot, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 12V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and LED1 is blinking this indicates your Smart6818 has successfully booted.
20.2.2 Flash Image to Smart6818's eMMC
- Download eflasher
Get the eflasher utility s5p4418-eflasher-sd8g-xxx-full.img.7z
This package includes a Ubuntu Core, Debian, Android 5 and Android 4.4 image files;
Get the Windows utility: win32diskimager.rar;
- Flash eflasher Image
Extract the .7z package and you will get .img files.Insert an SD card(at least 8G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
If your PC runs Linux you can use the dd command to flash a .img file to the SD card;
- Flash image to eMMC
Insert this card into your Smart6818 SDK carrier board, connect the board to an HDMI monitor or an LCD, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 12V/2A power source) the board. After your board is powered on you will see multiple OS options and you can select an OS to start installation.
20.2.3 Make Installation Card under Linux Desktop
- 1) Insert your SD card into your host PC running Ubuntu and check your SD card's device name
dmesg | tail
Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card has been recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions"
- 2) Downlaod Linux script
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_nanopi2.git cd sd-fuse_nanopi2
- 3) Make Android SD Card
su ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
When you run the script for the first time it will prompt you to download an image you have to hit “Y” within 10 seconds otherwise you will miss the download
- 4) Here is how to make a Debian SD card
./fusing.sh /dev/sdx debian
20.2.4 Extend Smart6818's SD Card Section
- When Debian/Ubuntu boots it will automatically extend its SD card's section. On its initial booting the system will extend the root file system and other sections.
- Under Android users need to extend the section by using the following commands:
sudo umount /dev/sdx? sudo parted /dev/sdx unit % resizepart 4 100 resizepart 7 100 unit MB print sudo resize2fs -f /dev/sdx7
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
20.2.5 LCD/HDMI Resolution
When system boots our uboot will check whether it is connected to an LCD or an HDMI monitor. If it recognizes an LCD it will configure its resolution. Our uboot defaults to the HDMI 720P configuration.
If you want to modify the LCD resolution you can modify file "arch/arm/plat-s5p4418/nanopi2/lcds.c" in the kernel and recompile it.
If your Smart6818 is connected to an HDMI monitor and it runs Android it will automatically set the resolution to an appropriate HDMI mode by checking the "EDID". If your Smart6818 is connected an HDMI monitor and it runs Debian by default it will set the resolution to HDMI 720P. If you want to modify the HDMI resolution to 1080P modify your kernel's configuration as explained above.
20.3 Update Image Files in SD Card From PC Host
If you want to make some changes to the image files in your SD card follow steps below otherwise you can skip this section.
Insert your SD card into a host PC running Linux, mount the boot and rootfs sections of the SD card and follow the steps below:
1) If you want to change your kernel command line parameters you can do it via the fw_setevn utility under "sd-fuse_nanopi2/tools":
Check the current Command Line:
cd sd-fuse_nanopi2/tools ./fw_printenv /dev/sdc | grep bootargs
Android 5.1.1_r6 starts SELinux. By default it is enforcing. You can change it this way:
./fw_setenv /dev/sdc bootargs XXX androidboot.selinux=permissive
This sets it to "permissive". The "XXX" stands for the original bootargs' value.
2) Update Kernel
Our customized uboot will check the LCD type when it boots.
For a non-Android OS If it recognizes an LCD connected to the Smart6818 it will load "uImage" from "boot" otherwise it will load "uImage.hdmi".
For Android it doesn't make any difference what display device is detected. You can use your generated uImage to replace the existing one under "boot".
For Debian if your generated kernel is for an LCD you need to replace the existing uImage or if your kernel is for an HDMI monitor you need to replace the existing uImage.hdmi.
20.4 Run Android or Debian
- Insert an SD card with Android/Debian image file into your Smart6818's carrier board, connect the board to an HDMI monitor, switch S2 to "SDBOOT", power on the board the Smart6818 will be booted from the SD card. If you can see the PWR LED on and the LED1 flashing it means your board is working and you will see Android/Debain being loaded on the HDMI monitor.
1) If you connect the Smart6818 to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and a USB keyboard to operate. If you connect it to an LCD with capacitive touch you can operate directly on the LCD.
2)If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.
- Here is a setup in which we connect the COM0 on the Smart6818's V1606 SDK carrier board to a PC running Ubuntu and Minicom via a serial cable you will see system messages output to the PC’s minicom terminal
- Under Debian the password for "root" is "fa"
20.5 Login Debian via VNC or SSH
If your Smart6818 is not connected to a display device and your board runs the "-wifiap.img" image you can login to your Smart6818's nanopi2-wifiap(the default password is "123456789") via a mobile phone. You can download and install a "VNC Viewer" from here on mobile phone and login to the Smart6818 via VNC. Its default password is "fa123456". Here is a screenshot which shows how it looks like when users login to the Smart6818 from an iPhone via VNC:

You can login via "SSH -l root 192.168.8.1" too and the default password for "root" is "fa"
To make SSH session run faster turn off the WiFi's power saving mode by using the following command:
iwconfig wlan0 power off
21 Working with Debian
21.1 Ethernet Connection
- If the Smart6818 is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on, it will automatically obtain an IP after it is powered up.
21.2 Wireless Connection
Open the file /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf and append the following lines:
network={ ssid="YourWiFiESSID" psk="YourWiFiPassword" }
The "YourWiFiESSID" and "YourWiFiPassword" need to be replaced with your actual ESSID and password.
Save, exit and run the following commands to connect to a WiFi:
ifdown wlan0 ifup wlan0
If your WiFi password has special characters or you don't want your password saved as plain text you can use "wpa_passphrase" to generate a psk for your WiFi password. Here is how you can do it:
wpa_passphrase YourWiFiESSID
Following the prompt type in your password and open the file /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf you will find that your password has been changed and your can delete your plain text password.
If your AP mode is turned on you need to turn it off. You can do it by using the following commands:
su
turn-wifi-into-apmode no21.3 Setup Wi-Fi AP
You can follow the steps below to setup Wi-Fi AP:
turn-wifi-into-apmode yesReboot the system as prompted. By default the AP's name is "nanopi2-wifiap" and the password is 123456789.
Now you are able to find the "nanopi2-wifiap" from a host PC and connect to it. If the connection is successful you will be able to SSH to this Smart6818 at "192.168.8.1":
ssh root@192.168.8.1
The password for it is "fa".
To make SSH run faster turn off the WiFi's power saving mode by using the following command:
iwconfig wlan0 power off
You can check the WiFi mode via the following command:
cat /sys/module/bcmdhd/parameters/op_mode
If the result is "2" it means it is currently working as a WiFi AP.If you want to switch back to the Station mode you can do it this way:
turn-wifi-into-apmode no
21.4 Bluetooth
Here are the steps to transfer a file from Smart6818 to a mobile phone. Run the following command to search a surrounding Bluetooth device:
hcitool scan
In our example a mobile phone was detected and the following messages were listed:
Scanning ...
38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DD MEIZU MX4
These messages indicated that a MEIZU MX4 mobile phone was detected. We then checked the Bluetooth services this phone supported with its MAC address presented in front of its device name
sdptool browse 38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DDNote: you need to use your device's name and its MAC address when you run these commands.
The command listed all the services the phone supported. We needed the "OBEX Object Push" service which is for file transfers.
Service Name: OBEX Object Push
Service RecHandle: 0x1000b
Service Class ID List:
"OBEX Object Push" (0x1105)
Protocol Descriptor List:
"L2CAP" (0x0100)
"RFCOMM" (0x0003)
Channel: 25
"OBEX" (0x0008)
Profile Descriptor List:
"OBEX Object Push" (0x1105)
Version: 0x0100
From the above messages we could get the channel number 25 for the "OBEX Object Push" service. We input this number to the "ussp-push" by running the following command:
ussp-push 38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DD@25 example.jpg example.jpg
Note: you need to use your device's name, its MAC address and channel number when you run these commands.
Usually after the above commands are run a popup window will show on the phone that communicates with Smart6818 and you can start file transfers.
Common Issues:
1) If Smart6818 cannot find a Bluetooth device you can try this command to restart its Bluetooth:
rfkill unblock 02) If any of these commands is not installed you can try this command to install it:
apt-get install bluetooth bluez obexftp openobex-apps python-gobject ussp-push
21.5 Install Debian Packages
We provide a Debian Jessie image. You can install Jessie's packages by commanding "apt-get". If this is your first installation you need to update the package list by running the following command:
apt-get updateYou can install your preferred packages. For example if you want to install an FTP server you can do this:
apt-get install vsftpdNote: you can change your download server by editting "/etc/apt/sources.list". You can get a complete server list from [6]. You need to select the one with "armhf".
22 Make Your Own OS Image
22.1 Install Cross Compiler
Download the compiler package:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/prebuilts.git sudo mkdir -p /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain sudo tar xf prebuilts/gcc-x64/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf-4.9.3.tar.xz -C /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/
Then add the compiler's directory to "PATH" by appending the following lines in "~/.bashrc":
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
Execute "~/.bashrc" to make the changes into effect. Note that there is a space after the first ".":
. ~/.bashrcThis compiler is a 64-bit one therefore it cannot be run on a 32-bit Linux. After the compiler is installed you can verify it by running the following commands:
arm-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=arm-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/libexec/gcc/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/4.9.3/lto-wrapper Target: arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf Configured with: /work/toolchain/build/src/gcc-4.9.3/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/sys-root --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-arch=armv7-a --with-tune=cortex-a9 --with-fpu=vfpv3 --with-float=hard ... Thread model: posix gcc version 4.9.3 (ctng-1.21.0-229g-FA)
22.2 Compile U-Boot
Download the U-Boot source code and compile it. Note the github's branch is nanopi2-lollipop-mr1:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot_nanopi2.git cd uboot_nanopi2 git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 make s5p4418_nanopi2_config make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
After your compilation succeeds a u-boot.bin will be generated. If you want to test it flash it to your installation SD card via fastboot. Here is how you can do it
1) On your host PC run "sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot" to install the fastboot utility;
2) Connect your Smart6818 to your host PC via a serial cable (e.g. PSU-ONECOME). Press the enter key within two seconds right after you power on your Smart6818 and you will enter uboot's command line mode;
3) After type in "fastboot" and press "enter" you will enter the fastboot mode;
4) Connect your Smart6818 to this host PC via a microUSB cable and type in the following command to flash the u-boot.bin you generated:
fastboot flash bootloader u-boot.bin
Warning: you cannot update this SD card by commanding "dd". This command which will cause trouble when booting the Smart6818.
22.3 Prepare mkimage
You need the mkimage utility to compile a U-Boot source code package. Make sure this utility works well on your host before you start compiling a uImage.
You can install this utility by either commanding "sudo apt-get install u-boot-tools" or following the commands below:
cd uboot_nanopi2 make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- tools sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/sbin && sudo cp -v tools/mkimage /usr/local/sbin
22.4 Compile Linux Kernel
22.4.1 Compile Kernel
- Download Kernel Source Code
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git cd linux-3.4.y git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1
The Smart6818's kernel source code lies in the "nanopi2-lollipop-mr1" branch.
- Compile Android Kernel
make nanopi2_android_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
- Compile Debian Kernel
make nanopi2_linux_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
After your compilation succeeds a uImage will be generated in the "arch/arm/boot/uImage" directory. This kernel is for HDMI 720P. You can use it to replace the existing uImage.hdmi.
If you want to generate a kernel for HDMI 1080P you can do it this way
touch .scmversion make nanopi2_linux_defconfig make menuconfig Device Drivers --> Graphics support --> Nexell Graphics --> [ ] LCD [*] HDMI (0) Display In [0=Display 0, 1=Display 1] Resolution (1920 * 1080p) ---> make uImage
After your compilation succeeds a uImage will be generated for HDMI 1080P. You can use it to replace the existing uImage
22.4.2 Compile Kernel Modules
Android contains kernel modules which are in the "/lib/modules" directory in the system section. If you want to add your own modules to the kernel or you changed your kernel configurations you need to recompile these new modules.
Compile Original Kernel Modules:
cd linux-3.4.y make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules
Here we have two new modules and we can compile them by following the commands below:
cd /opt/FriendlyARM/s5p4418/android ./vendor/friendly-arm/build/common/build-modules.sh
The "/opt/FriendlyARM/s5p4418/android" directory points to the top directory of Android source code. You can get more details by specifying option "-h".
After your compilation succeeds new modules will be generated
22.5 Compile Android
- Install Cross Compiler
Install 64 bit Ubuntu 14.04 on your PC host.
sudo apt-get install bison g++-multilib git gperf libxml2-utils make python-networkx zip sudo apt-get install flex libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk minicom
For more details refer to https://source.android.com/source/initializing.html 。
- Download Source Code(Android 5.1)
You need to use repo to get the Android source code. Refer to https://source.android.com/source/downloading.html 。
mkdir android && cd android repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/android_manifest.git -b nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 repo sync
The "android" directory is the working directory.
If you want to try Android4.4's source code you can run the following commands:
mkdir android && cd android repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/android_manifest.git -b nanopi2-kitkat repo sync
Option "-b" specifies a branch
- Compile System Package
source build/envsetup.sh lunch aosp_nanopi2-userdebug make -j8
After your compilation succeeds the following files will be generated in the "out/target/product/nanopi2/" directory.
filename partition Description boot.img boot - cache.img cache - userdata.img userdata - system.img system - partmap.txt - partition description file
- Flash Image to eMMC
After compiling Android successfully you can flash it to eMMC with either of the following methods
1) fastboot: right after the Smart6818 is booted from eMMC press any key to enter the uboot commandline mode and type in "fastboot"
Connect your board to a host PC running Ubuntu with a USB cable and run the following commands in the PC's terminal:
cd out/target/product/nanopi2 sudo fastboot flash boot boot.img sudo fastboot flash cache cache.img sudo fastboot flash userdata userdata.img sudo fastboot flash system system.img sudo fastboot reboot
2) Use an SD Card
Copy these files: boot.img, cache.img, userdata.img, system.img, partmap.txt from the out/target/product/nanopi2 directory to your installation SD card's images/android directory and you can use this SD card to flash Android to eMMC
23 Connect Smart6818 to External Modules
23.1 Connect Smart6818 to 4G Module
- The Smart6818 can work with some 4G modules under Android 4.4. After you connect a 4G module (e.g. ME909u-521 which supports FDD-LTE) to a Smart6818 power on the board the 4G module will be activated automatically
23.2 Connect Smart6818 to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
- In this use case the Smart6818 runs Debian. If you connect your Smart6818 to our LCD or an HDMI monitor after Debain is fully loaded click on "other"-->"xawtv9" on the left bottom of the GUI and the USB Camera application will be started. After enter "welcome to xawtv!" click on "OK" to start exploring.
23.3 Connect Smart6818 to CMOS 5M-Pixel Camera
For more details about the CAM500A camera refer to [7]
- If your Smart6818 runs Android5.1 and it is connected to our LCD or an HDMI monitor after Android is fully loaded click on the "Camera" icon and the application will be started. You can take pictures or record videos
- Under Debian/Ubuntu a camera utility "nanocams" is available for previewing 40 frames and picture taking. You can try it by following the commands below
sudo nanocams -p 1 -n 40 -c 4 -o IMG001.jpg
For more details about the usage of the nanocams run "nanocams -h". You can get its source code from our git hub:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/nexell_linux_platform.git
23.4 Use OpenCV to Access USB Camera
- The full name of "OpenCV" is Open Source Computer Vision Library and it is a cross platform vision library.
- When the Smart6818 runs Debian users can use OpenCV APIs to access a USB Camera device.
1. Here is a guideline on how to use OpenCV with C++ on the Smart6818:
- Firstly you need to make sure your Smart6818 is connected to the internet. Login to your Smart6818 via a serial terminal or SSH. After login type your username(root) and password(fa):
- Run the following commands:
apt-get update apt-get install libcv-dev libopencv-dev
2. Make sure your USB camera works with the Smart6818. You can test your camera with Smart6818's camera utility.
3. Check your camera device:
ls /dev/video*
- Note:in our test case video0 was the USB camera device
4. OpenCV's code sample(official code in C++) is under /home/fa/Documents/opencv-demo. Compile the code sample with the following commands:
cd /home/fa/Documents/opencv-demo make
After it is compiled successfully a "demo" executable will be generated
6. Connect Smart6818 to USB Keyboard & Run the Following Command
./demoThis is what you expect to observe:
24 More OS Support
24.1 Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded
Ubuntu Core with Qt-Embedded is a light Linux system without X-windows. It uses the Qt-Embedded's GUI and is popular in industrial and enterprise applications.
Besides the regular Ubuntu core's features our Ubuntu-Core has the following additional features:
- it supports our LCDs with both capacitive touch and resistive touch(S700, X710, S70)
- it supports WiFi
- it supports Ethernet
- it supports Bluetooth and has been installed with bluez utilities
- it supports audio playing
For more details refer to Ubuntu Core with Qt-Embedded.
24.1.1 Flash Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded to eMMC
1. Make an installation SD card with the win32 utility;
2. Insert this SD card to a host PC and copy the UbuntuCore image (in our example it was "ubuntu_core.img") and 2nboot file(in our example it was "2ndboot.bin.emmc") to it;
2nboot can be downloaded from: https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_s5p6818/tree/master/prebuilt
3. Run the following commands to flash the image file to your board's eMMC:
dd if=ubuntu_core.img of= /dev/mmcblk1
4. Flash the 2nboo file to the eMMC:
dd if=2ndboot.bin.emmc of=/dev/mmcblk1 bs=512 seek=1
24.2 Ubuntu-Mate
Ubuntu-Mate is a Ubuntu variant and its GUI is Mate-desktop. You can log in via SSH when you connect the Smart6818 to an LCD or HDMI
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it
- Go to this link download link to download the image files
- Uncompress it and flash the image file to a TF card with win32diskimager under Windows
- After it is done you can boot your Smart6818 with this card
- Login name: "root" or "fa", Password: fa
24.3 Kali
- Go to this link [8] to download the image files;
- Prepare an 8G High Speed MicroSD card, insert it to a Linux host and do "sudo fdisk -l" to check its device name, i.e. "/dev/sd*".
- Copy the image files to the card by running the following commands as root:
xzcat kali-2.0-nanopi2.img.xz | dd of=<YOURDEVICE> bs=1m
- After it is done you can boot your Smart6818 with this card.
Note: this is offered by Kali and FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
24.4 Deepin15 ARM
- Go to this link [9] to download the image files
- Uncompress the file and you will get a 16g.img file which is the image file for MicroSD card.
tar -xf deepin15_nanopi2_armhf_16g.tar.gz
- Prepare an 16G High Speed SD card, insert it into a Linux host and do "sudo fdisk -l" to check its device name, i.e. "/dev/sd*"
- Flash the image files to the card by running the following command as root(in our case our card was recognized as "/dev/sdc"):
sudo dd if=16g.img of=/dev/sdc
This process takes a while which can be up to one hour
- After it is done you can boot your Smart6818 with this card
Notes:
1. The password for login name "deepin" is "deepin". The password for login name "root" is "admin".
2. The initial booting of Deepin15 takes a relative long time for it generates some configuration files.
3. If WiFi is activated in your system booting might take longer. In this case wait for the sound and wifi icons on the right bottom of the GUI to appear before you start any action.
ARM code: http://packages.deepin.com/armhf/ NanoPC-T2 Image: http://cdimage.deepin.com/armhf/15/beta1.0/ NanoPC-T2 Image Installation Instruction; http://bbs.deepin.org/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=36670 Forum for Migrating Deepin15 to ARM: http://bbs.deepin.org/
Note: this is offered by the Deepin15 team and FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
24.5 Android-Remixos
Go to this link [10] to download the image files;
- Untar the image ball:
tar -xf nanopi2-android-remixos-sd4g.tar
- Use the win32diskimager utility to flash the image to an SD card.
It supports HDMI and LCD output and works with all existing FriendlyARM 4418 boards.
Note: this is offered by Remix team and FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
25 Resources
- 《创客秘籍》Hacker's Book in Chinese by FriendlyARM
- 《创客秘籍-02》Hacker's Book-02 in Chinese by FriendlyARM
- 《创客秘籍-03》Hacker's Book-03 in Chinese by FriendlyARM
26 Update Log
26.1 07-26-2018
- Released English version