Template:DebianJessieGeneral
Contents
[hide]1 Working with Debian
1.1 Ethernet Connection
- If the board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on, it will automatically obtain an IP after it is powered up.
1.2 Wireless Connection
Under Debian you can manage your network with NetworkManager.
After Debian boots click on the network icon on the bottom right of the task bar a NetworkManger menu will pop up and all the available networks will be listed. If there is an active wireless network you will see something similar to the following screenshot:
![]()
You can click on a WiFI AP and connect your board to it.
For more details refer to:NetworkManager.
1.3 Bluetooth
Here are the steps to transfer a file from T2 to a mobile phone. Run the following command to search a surrounding Bluetooth device:
hcitool scan
In our example a mobile phone was detected and the following messages were listed:
Scanning ...
38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DD MEIZU MX4
These messages indicated that a MEIZU MX4 mobile phone was detected. We then checked the Bluetooth services this phone supported with its MAC address presented in front of its device name
sdptool browse 38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DDNote: you need to use your device's name and its MAC address when you run these commands.
The command listed all the services the phone supported. We needed the "OBEX Object Push" service which is for file transfers.
Service Name: OBEX Object Push
Service RecHandle: 0x1000b
Service Class ID List:
"OBEX Object Push" (0x1105)
Protocol Descriptor List:
"L2CAP" (0x0100)
"RFCOMM" (0x0003)
Channel: 25
"OBEX" (0x0008)
Profile Descriptor List:
"OBEX Object Push" (0x1105)
Version: 0x0100
From the above messages we could get the channel number 25 for the "OBEX Object Push" service. We input this number to the "ussp-push" by running the following command:
ussp-push 38:BC:1A:B1:7E:DD@25 example.jpg example.jpg
Note: you need to use your device's name, its MAC address and channel number when you run these commands.
Usually after the above commands are run a popup window will show on the phone that communicates with T2 and you can start file transfers.
Common Issues:
1) If T2 cannot find a Bluetooth device you can try this command to restart its Bluetooth:
rfkill unblock 02) If any of these commands is not installed you can try this command to install it:
apt-get install bluetooth bluez obexftp openobex-apps python-gobject ussp-push1.4 Install Debian Packages
We provide a Debian Jessie image. You can install Jessie's packages by commanding "apt-get". If this is your first installation you need to update the package list by running the following command
apt-get updateYou can install your preferred packages. For example if you want to install an FTP server you can do this:
apt-get install vsftpdNote: you can change your download server by editting "/etc/apt/sources.list". You can get a complete server list from [1]. You need to select the one with "armhf".
1.5 Audio via HDMI or 3.5mm Audio Jack
By default our system's audio via either HDMI or 3.5mm audio jack is not enabled because the package for audio is not installed in our system. If you want to enable audio you need to install the alsa packages.
- Firstly make sure your board is installed with our latest Debian image and is connected to the internet;
- After your board is booted run the following commands to install the alsa packages:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libasound2 $ apt-get install alsa-base $ apt-get install alsa-utils
- After installation is done copy an audio file with the extension of ".wav" to your board, connect an earphone to your board's 3.5mm audio jack and play this audio file by running the following command:
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav
- By default system's audio output is set to the board's 3.5mm audio jack. If you want to switch the audio output to HDMI you can run the following command:
Firstly check all the audio devices by running the following command. In our test we got similar result as follows:
$ aplay -l card 0: 3.5mm codec card 1: HDMI
Here "card 0" stands for the 3.5mm audio jack and "card 1" stands for HDMI. You can change the configuration file "/etc/asound.conf" as follows:
pcm.!default { type hw card 1 device 0 } ctl.!default { type hw card 1 }
Reboot your board and your change will be effective.
1.6 Login via VNC and SSH
If your board is not connected to a display device you can login to your board from a mobile phone. You need to download and install a "VNC Viewer" from here on a mobile phone and login to the board via VNC at port 1. Its default password is "fa123456".
Here is a screenshot which shows how it looks like when users login to the board from an iPhone via VNC:
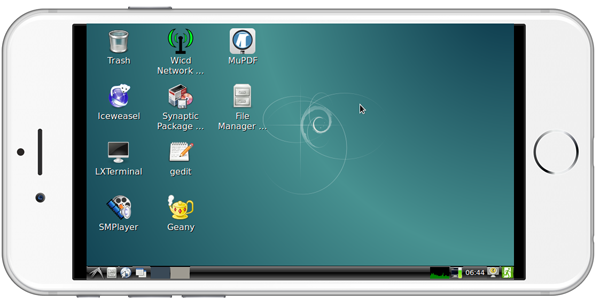
In our case our board's IP address is 192.168.1.230. You can login via SSH by running the following commands:
$ ssh root@192.168.1.230
The password is fa.
1.7 Test USB WiFi
Our OS system has support for popular USB WiFi drivers. Many USB WiFi modules are plug and play with our system. Here is a list of models we tested;
Number Model 1 RTL8188CUS 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 mi WiFi mt7601
- Check device list
$ nmcli dev DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION eth0 ethernet connected Wired connection 1 wlan0 wifi disconnected -- lo loopback unmanaged --
Note: if the status of a device is "unmanaged" it means that device cannot be accessed by NetworkManager. To make is accessed you need to clear the settings under "/etc/network/interfaces" and reboot your system.
- Start WiFi
$ nmcli r wifi on- Scan Surrounding WiFi Sources
$ nmcli dev wifi- Connect to a WiFi Source
$ nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD"
The "SSID" and "PASSWORD" need to be replaced with your actual SSID and password.
If a connection succeeds it will be automatically setup on next system reboot.
For more details about NetworkManager refer to this link:Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
1.8 Connect to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
The FA-CAM202 is a 200M USB camera.
Refer to this link for more details on how to connect to a FA-CAM202:
Connect NanoPi M1 to DVP Camera CAM500B
In Debian, click on "other"-->"xawtv" on the left bottom of the GUI and the USB Camera application will be started. After enter "welcome to xawtv!" click on "OK" to start exploring.
1.9 Use OpenCV to Access Camera
- The full name of "OpenCV" is Open Source Computer Vision Library and it is a cross platform vision library.
- Make sure your board is connected to the internet and an HDMI monitor, Boot Debian and login.
- Install OpenCV libraries:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libcv-dev libopencv-dev
- Refer to the instructions in the previous sections to make sure the camera works
- Compile and run a code sample(Official Code Sample in C++ provided by the OpenCV organization):
$ cd /home/fa/Documents/opencv-demo $ make $ ./demo