Difference between revisions of "NanoPi M1"
(→More OS Support) |
(→Under Windows) |
||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
===Make an Installation MicroSD Card=== | ===Make an Installation MicroSD Card=== | ||
====Under Windows==== | ====Under Windows==== | ||
| − | Get the following files from here:[http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/ | + | Get the following files from here:[http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/nanopim1/download/ to download image files.<br /> |
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 03:03, 31 March 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
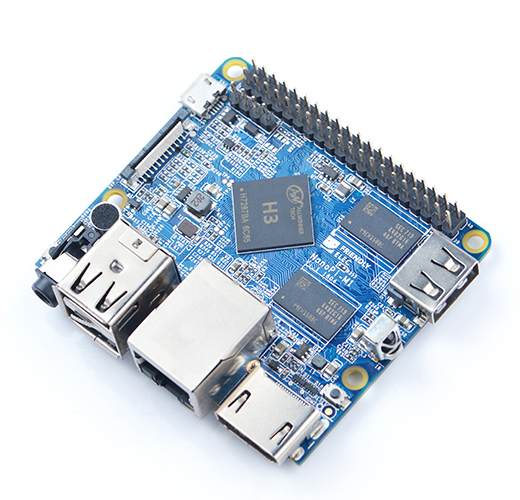
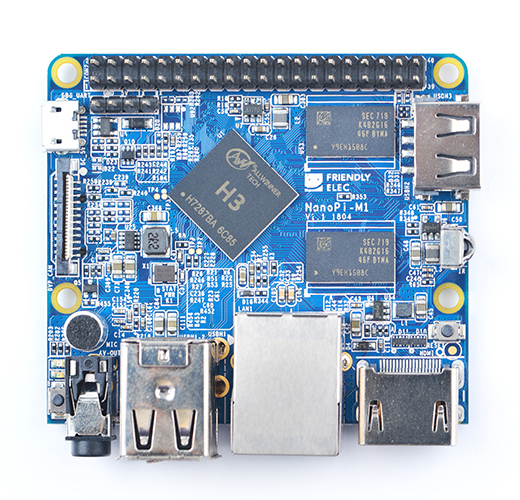
- The NanoPi M1 is an Allwinner H3 based ARM board designed and released by FriendlyARM for hobbyists, makers and electronic fans. It is only two thirds the size of the Raspberry Pi. It is open source. It works with Ubuntu MATE, Debian and etc.
- The NanoPi M1 uses the Allwinner H3 Soc. It integrates Ethernet, IR receiver, video/audio output and supports HDMI and AVOUT. It can be powered via the MicroUSB port
- In such a small board it still integrates rich interfaces and ports. Besides the popular HDMI, Ethernet, USB-Host, USB-OTG, DVP camera interface and AVOUT (audio and video) it has an onboard Microphone, IR receiver, a serial debug port and a Raspberry Pi compatible 40 pin GPIO pin header.
2 Features
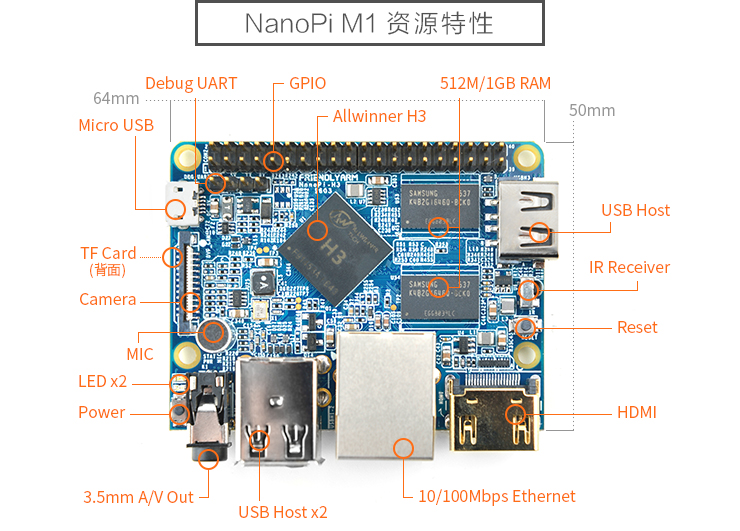
- CPU: Allwinner H3, Quad-core Cortex-A7@1.2GHz
- GPU: Mali400MP2@600MHz,Supports OpenGL ES2.0
- DDR3 RAM: 512MB
- Connectivity: 10/100M Ethernet
- Audio: 3.5mm audio jack/Via HDMI
- Microphone: Onboard microphone
- IR Receiver: Onboard IR receiver
- USB Host:Type A, USB 2.0 x 3
- MicroSD Slot x 1
- MicroUSB: for data transmission and power input, OTG
- Video Output: HDMI 1.4 1080P, CVBS
- DVP Camera Interface: 24pin, 0.5mm pitch FPC seat
- Debug Serial Port: 4Pin, 2.54mm pitch pin header
- GPIO: 2.54mm spacing 40pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi's GPIO. It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc
- User Key: Power LED x 1, Reset x 1
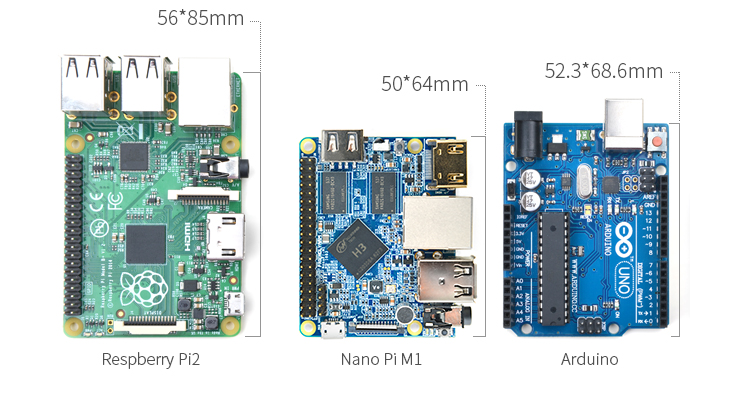
- PC Size: 64 x 50mm
- Power Supply: DC 5V/2A
- OS/Software: u-boot,Ubuntu MATE,Debian
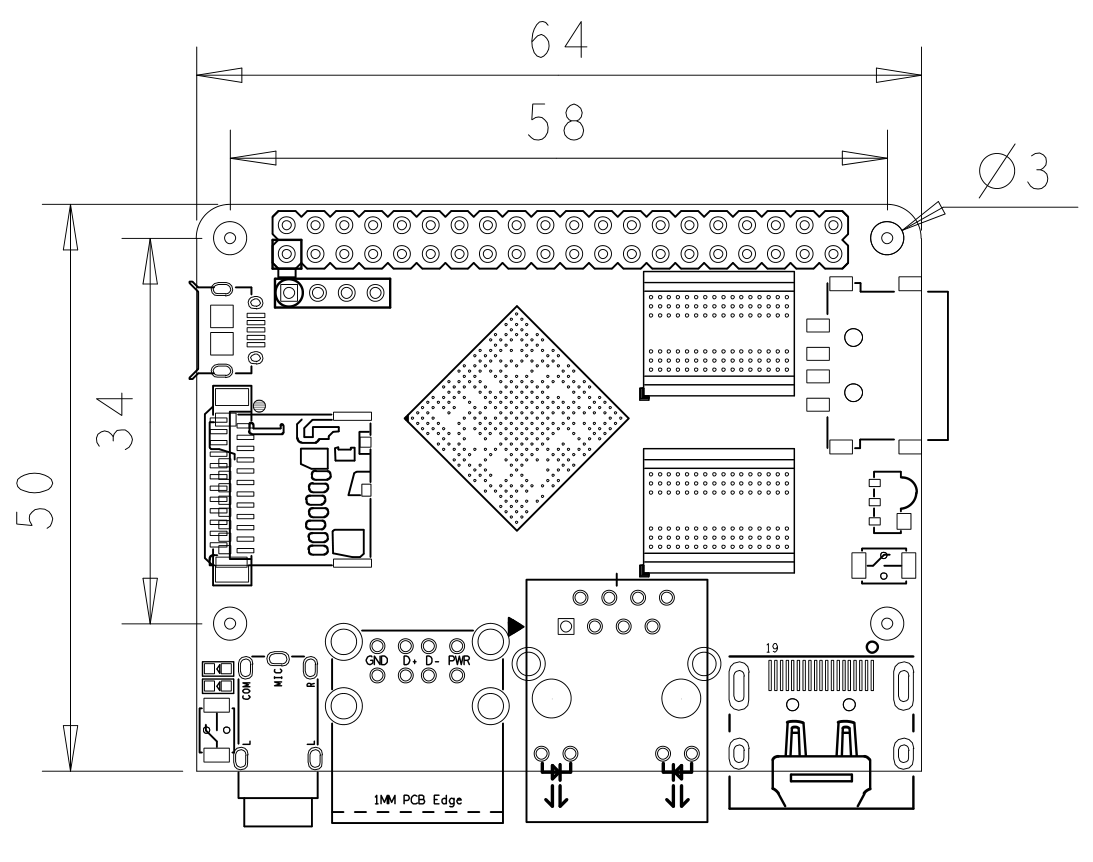
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
- GPIO Pin Spec
Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 SYS_3.3V 2 VDD_5V 3 I2C0_SDA 4 VDD_5V 5 I2C0_SCL 6 GND 7 GPIOG11 8 UART1_TX/GPIOG6 9 GND 10 UART1_RX/GPIOG7 11 UART2_TX/GPIOA0 12 PWM1/GPIOA6 13 UART2_RTS/GPIOA2 14 GND 15 UART2_CTS/GPIOA3 16 UART1_RTS/GPIOG8 17 SYS_3.3V 18 UART1_CTS/GPIOG9 19 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC0 20 GND 21 SIP0_MISO/GPIOC1 22 UART2_RX/GPIOA1 23 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC29 24 SPI0_CS/GPIOC3 25 GND 26 SPDIF-OUT/GPIOA17 27 I2C1_SDA/GPIOA19 28 I2C1_SCL/GPIOA18 29 GPIOA20 30 GND 31 GGPIOA21 32 GPIOA7 33 GPIOA8 34 GND 35 UART3_CTS/SPI1_MISO/GPIOA16 36 UART3_TX/SPI1_CS/GPIOA13 37 GPIOA9 38 UART3_RTS/SPI1_MOSI/GPIOA15 39 GND 40 UART3_RX/SPI1_CLK/GPIOA14
- Debug Port(UART0)
Pin# Name 1 GND 2 VDD_5V 3 UART_TXD0 4 UART_RXD0
- DVP Camera IF Pin Spec
Pin# Name Description 1, 2 SYS_3.3V 3.3V power output, to camera modules 7,9,13,15,24 GND Gound, 0V 3 I2C2_SCL I2C Clock Signal 4 I2C2_SDA I2C Data Signal 5 GPIOE15 Regular GPIO, control signals output to camera modules 6 GPIOE14 Regular GPIO, control signals output to camera modules 8 MCLK Clock signals output to camera modules 10 NC Not Connected 11 VSYNC vertical synchronization to CPU from camera modules 12 HREF/HSYNC HREF/HSYNC signal to CPU from camera modules 14 PCLK PCLK signal to CPU from camera modules 16-23 Data bit7-0 data signals
- Note:
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. When the external device’s power is greater than the MicroUSB’s the external device is charging the board otherwise the board powers the external device. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.6V
- All pins are 3.3V and output current is 5mA. It can drive small loads. No IO pins can drive a load.
- For more details refer to the document: NanoPi-M1-1603-Schematic.pdf
3.2 Board Dimension
- For more details please refer to: pcb file in dxf
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi M1 get the following items ready
- NanoPi M1
- microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must
- HDMI monitor
- USB keyboard and mouse
- A host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
4.2 TF Cards We Tested
To make your NanoPi M1 boot and run fast we highly recommand you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
4.3 Make an Installation MicroSD Card
4.3.1 Under Windows
Get the following files from here:[http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/nanopim1/download/ to download image files.
Image Files nanopi-m1-debian-sd4g.img.zip Debian Image Files Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
- Uncompress these files. Insert an SD card(at least 4G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Insert this card into your NanoPi M1 and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the green LED is on and the blue LED is blinking this indicates your NanoPi M1 has successfully booted.
5 Working with Debian
5.1 Ethernet Connection
If the NanoPi M1 is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP after it is powered up. If it is not connected via Ethernet or its DHCP is not activated obtaining an IP will fail and system will hang on for about 15 to 60 seconds
- 1) Setup MAC Address
The NanoPi M1 by default doesn't have a valid MAC address. If the board connects a network successfully it will automatically generates a random MAC in "/etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0". Users can change it to a self-defined valid one:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0
Here is the content of a sample configuration file:
auto eth0 allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp hwaddress 76:92:d4:85:f3:0f
The "hwaddress" specifies the MAC address. Here the "76:92:d4:85:f3:0f" is a random MAC. We suggest users change it to a valid one.
Note: when you reset the MAC please make sure your MAC meets IEEE's definition otherwise it will cause unexpected issues.
After you make your change, save, exit and reboot your board or run the following commands to restart the network:
systemctl restart networking
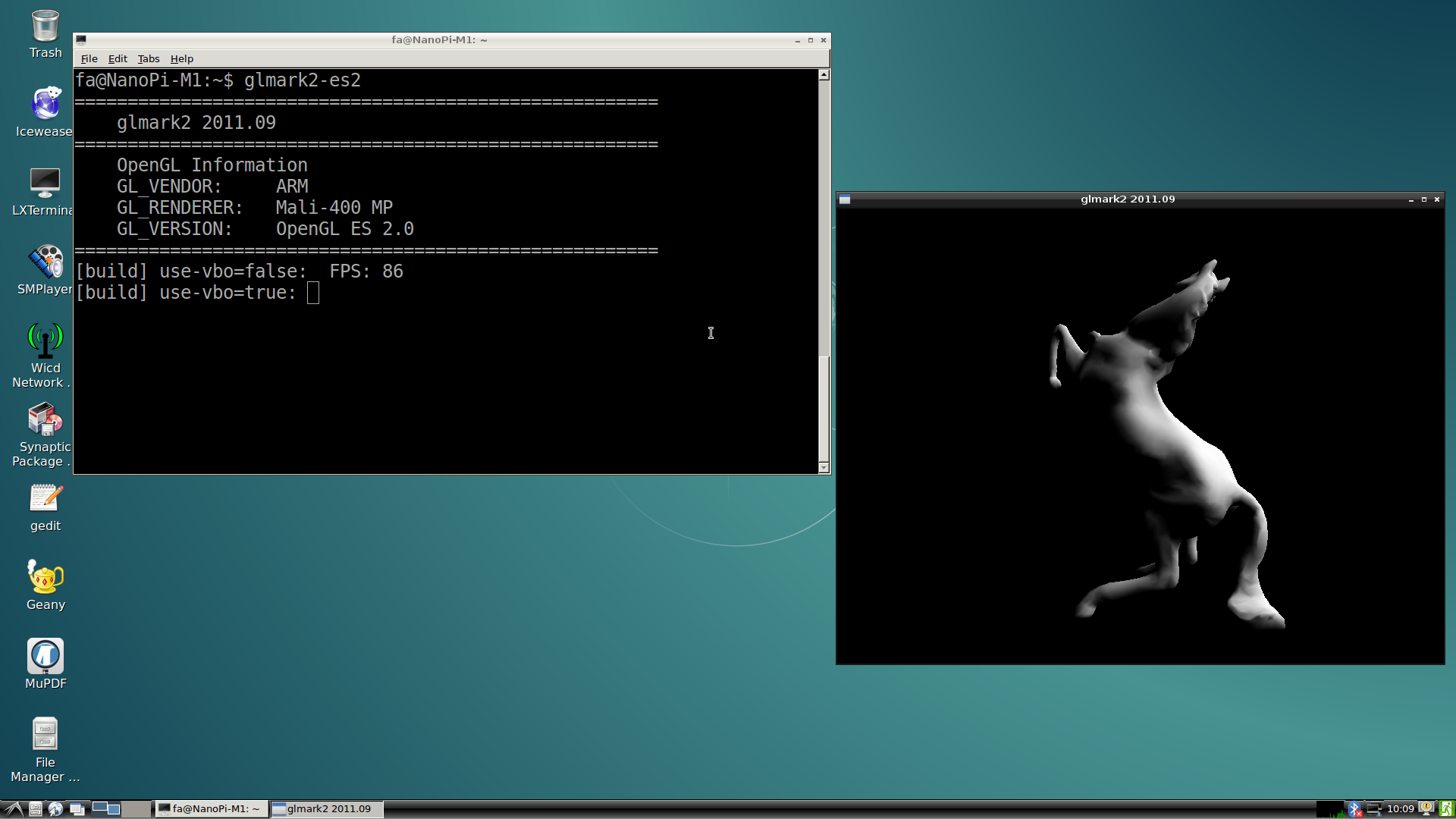
5.2 Test GPU
After Debian loads please login from a terminal and run "glmark2-es2":
glmark2-es2
5.3 Test VPU
Visit this link download link to download files
After Debian is loaded login from a terminal and run "mplayer":
mplayer -vo vdpau -vc ffmpeg12vdpau,ffh264vdpau, ./big_buck_bunny_1080p_H264_AAC_25fps_7200K.MP4
In our test it could play 1080P video fluently.
6 Make Your Own Debian
Go to the lichee directory to get the source code:
cd lichee6.1 Compile Source Code
Compile the whole source code packages including U-boot, Linux Kernel and Modules:
./build.sh -p sun8iw7p1 -b nanopi-h3 ./gen_script.sh
The gen_script.sh script contains all the necessary files to compile all of these files. After it is executed multiple script.bin files will be generated for different display resolutions. A script.bin file is a configuration file made by Allwinnner for its CPU series. For more details refer to script.bin
6.2 Flash Image to TF Card
Run the following command to flash U-boot, Linux Kernel and script.bin to your TF card:
./burn_into_sd.sh /dev/sdx
Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system. This script flashes U-Boot to your TF card and copies uImage and script.bin to your TF card's boot section.
6.3 Compile U-boot
./build.sh -p sun8iw7p1 -b nanopi-h3 -m uboot
After a u-boot executable is generated some extra patches need to be patched to it. Run "./gen_script.sh" to patch this executable.
If you want to manually patch the executable refer to H3_Manual_build_howto
6.4 Compile Linux Kernel
./build.sh -p sun8iw7p1 -b nanopi-h3 -m kernel
After the compilation is done a uImage and its kernel modules will be generated under "linux-3.4/output".
6.5 Clean Source Code
./build.sh -p sun8iw7p1 -b nanopi-h3 -m clean
7 Make Your Own Android
8 More OS Support
8.1 Ubuntu-Core
Ubuntu-Core is a basic verson which has support for Ethernet and SSH.
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it.
- Go to this link download link to download the image files
- Uncompress it and flash the image file to a TF card with win32diskimager under Windows
- After it is done you can boot your NanoPi M1 with this card
- Login name: "root" or "fa", Password: fa
8.2 Ubuntu-MATE
Ubuntu-Mate is a Ubuntu variant and its GUI is Mate-desktop. You can login via SSH when you connect a NanoPi M1 to an HDMI
FriendlyARM doesn't provide technical support for it
- Go to this link download link to download the image files
- Uncompress it and flash the image file to a TF card with win32diskimager under Windows
- After it is done you can boot your NanoPi M1 with this card
- Login name: "root" or "fa", Password: fa
9 Resources
- Schematic NanoPi-M1-1603-Schematic.pdf
- Dimensional Diagram pcb file in dxf
- Allwinner H3 datasheet Allwinner_H3_Datasheet_V1.2.pdf
10 Update Log
10.1 March-22-2016
- Released English Version
10.2 March-29-2016
- Corrected expression errors