Difference between revisions of "NanoPi 2 Fire"
(→Play with Debian) |
(→Compile U-Boot) |
||
| Line 347: | Line 347: | ||
After your compilation succeeds a u-boot.bin will be generated. If you want to test it please flash it to your installation MicroSD card via fastboot. Here is how you can do it:<br /> | After your compilation succeeds a u-boot.bin will be generated. If you want to test it please flash it to your installation MicroSD card via fastboot. Here is how you can do it:<br /> | ||
1) On your PC host please run "sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot" to install the fastboot utility<br /> | 1) On your PC host please run "sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot" to install the fastboot utility<br /> | ||
| − | 2) Connect your | + | 2) Connect your NanoPi 2 Fire to your PC host via a serial cable (e.g. PSU-ONECOME). Press the enter key within two seconds right after you power on your NanoPi 2 Fire and you will enter uboot's command line mode:<br /> |
3) After type "fastboot" and press "enter" you will enter the fastboot mode:<br /> | 3) After type "fastboot" and press "enter" you will enter the fastboot mode:<br /> | ||
| − | 4) Connect your | + | 4) Connect your NanoPi 2 Fire to this PC host via a microUSB cable and type the following command to flash the u-boot.bin:<br /> |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
fastboot flash bootloader u-boot.bin | fastboot flash bootloader u-boot.bin | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | Warning: you cannot update this MicroSD card by commanding "dd". This command which will cause trouble when booting the | + | Warning: you cannot update this MicroSD card by commanding "dd". This command which will cause trouble when booting the NanoPi 2 Fire.<br /> |
===Prepare mkimage=== | ===Prepare mkimage=== | ||
Revision as of 11:29, 22 January 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
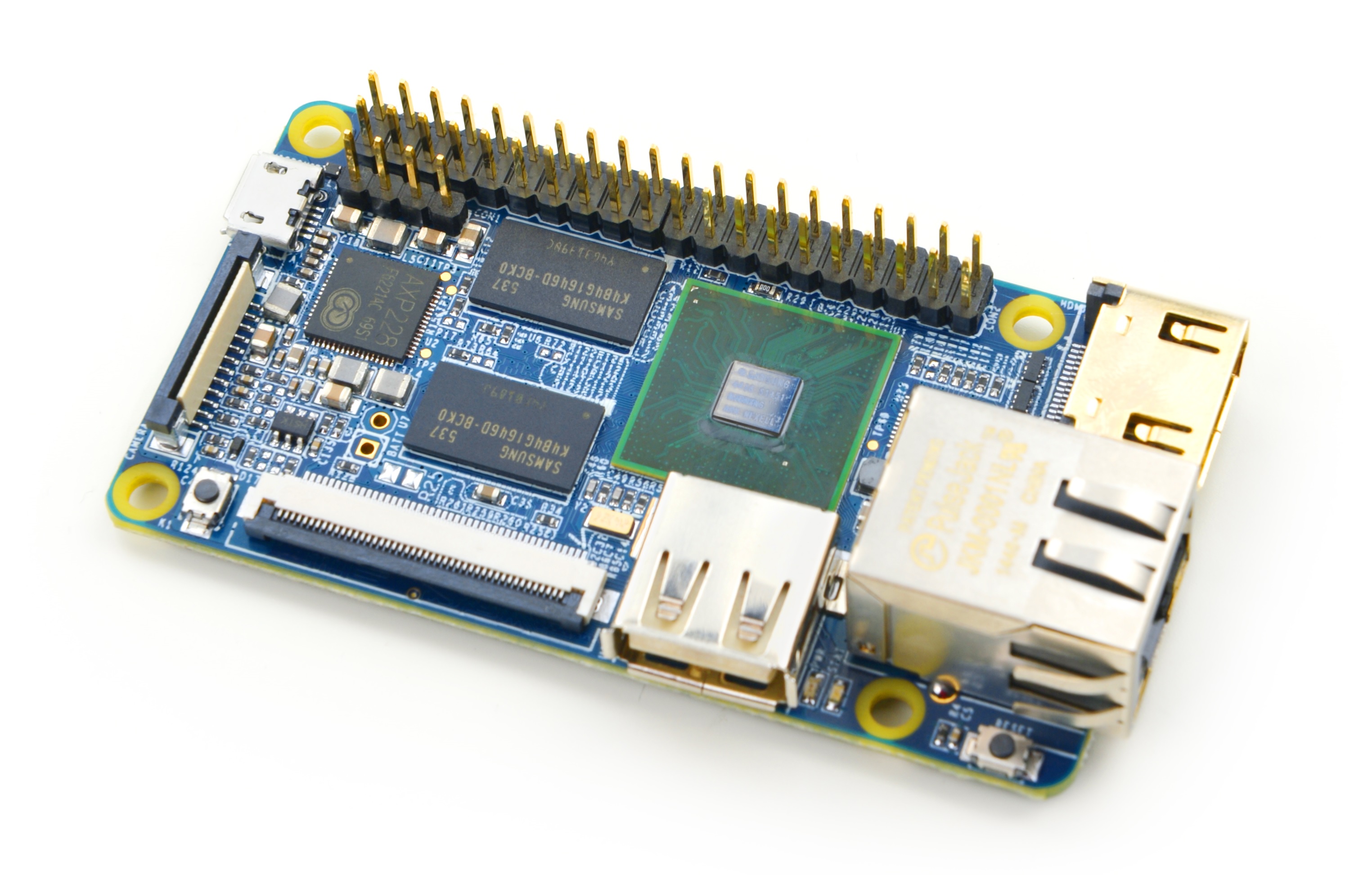
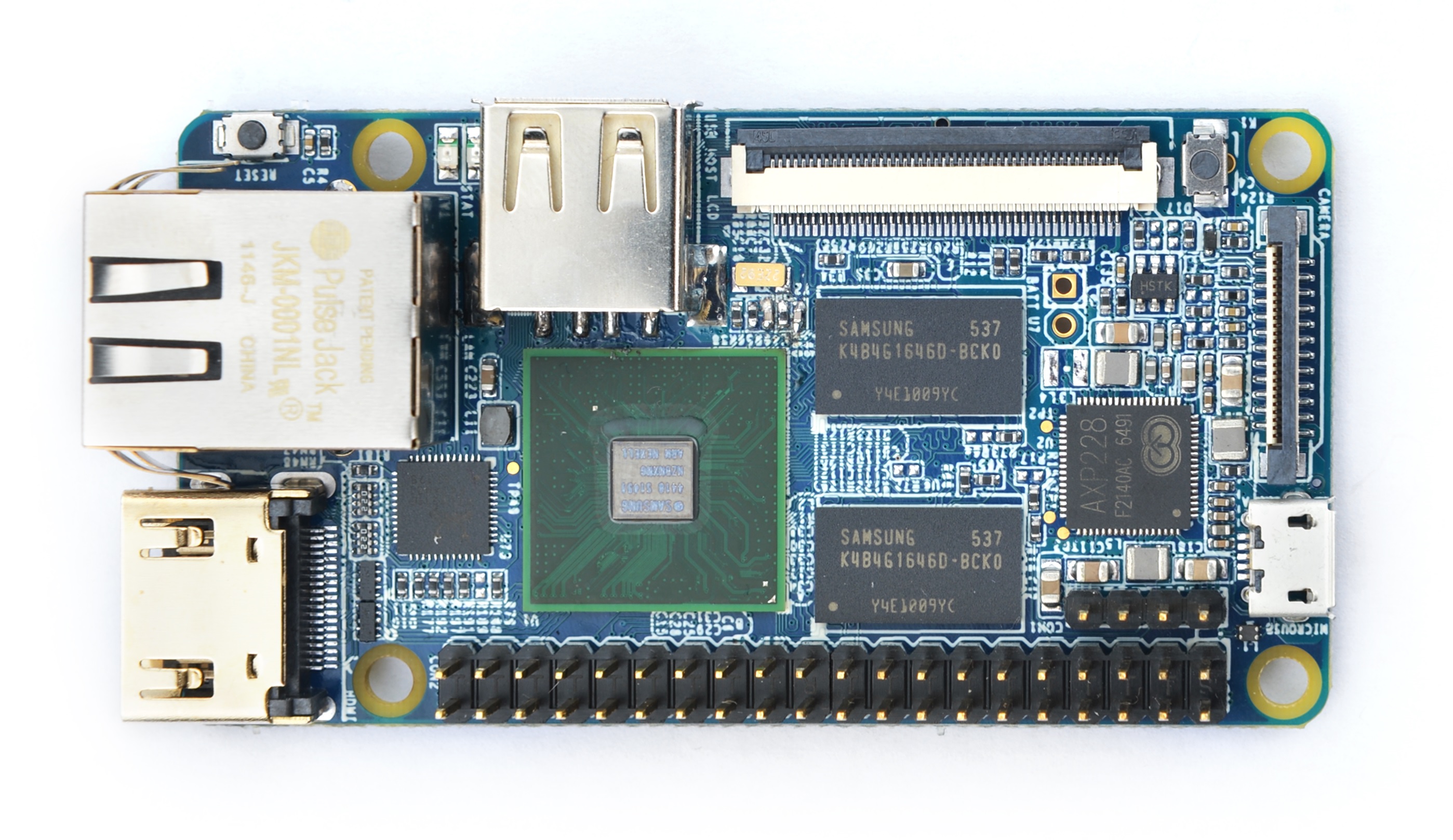
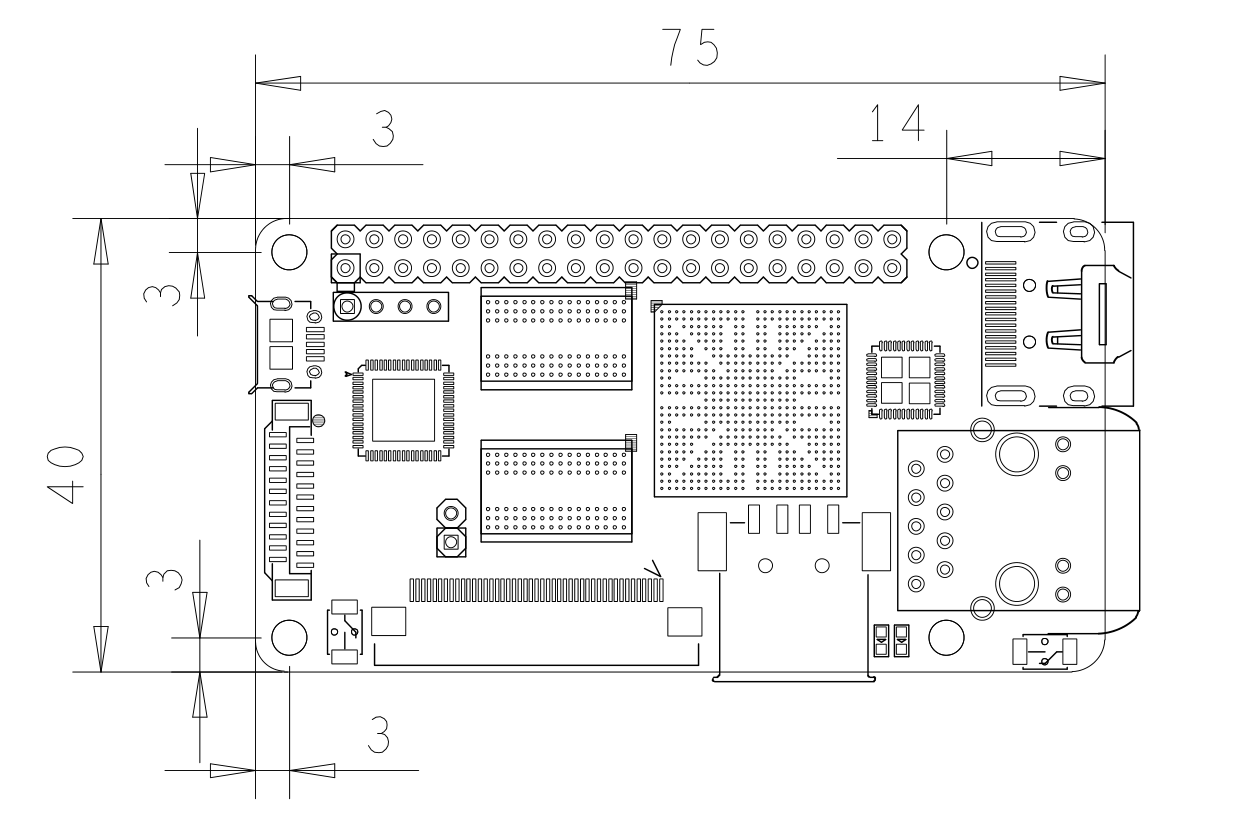
- The NanoPi2 Fire is a high performance ARM Board developed by FriendlyARM for Hobbysts, Makers and Hackers for IOT projects. It features Samsung’s Cortex-A9 Quad Core S5P4418@1.4GHz SoC and 1G 32bit DDR3 RAM. It has a Gbps Ethernet port. It boots Android and Debian from a TF card. It integrates an HDMI and LCD interface. Its adoption of the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pin header makes it compatible with both Raspberry Pi’s external GPIO modules and Arduino’s shield boards. Its PCB dimension is 75 x 40 mm.
2 Features
- CPU: S5P4418, 1.4GHz
- RAM: 1GB DDR3
- Connectivity: Gbps Ethernet port
- PMU Power Management: AXP228, support software power-off, sleep and wakeup functions
- USB 2.0 Type A x 1
- Debug Serial Port/UART0 x 1
- microSD Slot x 1
- microUSB x 1: for data transmission and power input
- LCD Interface: 0.5 mm pitch SMT FPC seat, for full-color LCD (RGB: 8-8-8)
- HDMI: HDMI 1.4A, Type-A, 1080P60
- DVP Camera Interface: 0.5mm spacing FPC socket. It includes ITU-R BT 601/656 8-bit, I2C and IO
- GPIO: 2.54mm spacing 40pin, compatible with Raspberry Pi's GPIO. It includes UART, SPI, I2C, PWM, IO etc
- Button: Power Button x 1, Reset Button x 1
- LED: LED for Power Indication x 1, System LED x 1
- PCB Dimension: 75 x 40mm
- Power: DC 5V/2A
- OS: Android, Debian
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
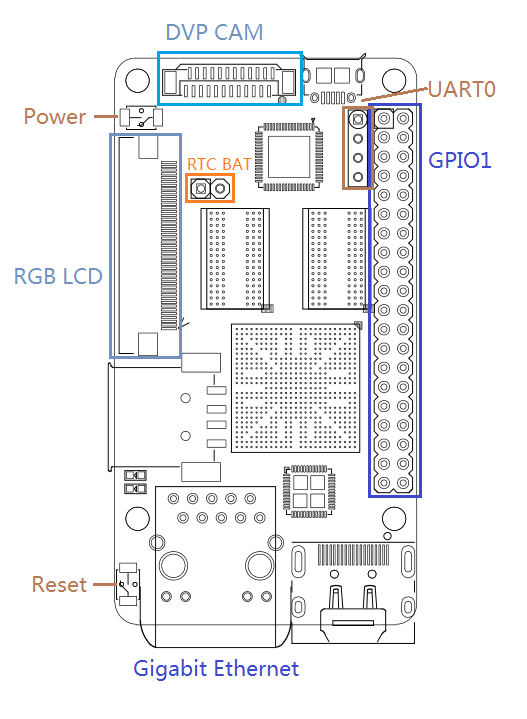
3.1 Layout
- GPIO Pin Spec
Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 SYS_3.3V 2 VDD_5V 3 I2C0_SDA 4 VDD_5V 5 I2C0_SCL 6 DGND 7 GPIOD8/PPM 8 UART3_TXD/GPIOD21 9 DGND 10 UART3_RXD/GPIOD17 11 UART4_TX/GPIOB29 12 GPIOD1/PWM0 13 GPIOB30 14 DGND 15 GPIOB31 16 GPIOC14/PWM2 17 SYS_3.3V 18 GPIOB27 19 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC31 20 DGND 21 SPI0_MISO/GPIOD0 22 UART4_RX/GPIOB28 23 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC29 24 SPI0_CS/GPIOC30 25 DGND 26 GPIOB26 27 I2C1_SDA 28 I2C1_SCL 29 GPIOC8 30 DGND 31 GPIOC8 32 GPIOC28 33 GPIOC13/PWM1 34 DGND 35 SPI2_MISO/GPIOC11 36 SPI2_CS/GPIOC10 37 AliveGPIO3 38 SPI2_MOSI/GPIOC12 39 DGND 40 SPI2_CLK/GPIOC9
- Debug Port(UART0)
Pin# Name 1 DGND 2 VDD_5V 3 UART_TXD0 4 UART_RXD0
- DVP Camera Interface Pin Spec
Pin# Name 1, 2 SYS_3.3V 7,9,13,15,24 DGND 3 I2C0_SCL 4 I2C0_SDA 5 GPIOB14 6 GPIOB16 8,10 NC 11 VSYNC 12 HREF 14 PCLK 16-23 Data bit7-0
- RGB LCD Interface Pin Spec
Pin# Name Description 1, 2 VDD_5V 5V output, LCD power 11,20,29, 37,38,39,40, 45 DGND ground 3-10 Blue LSB to MSB RGB Blue 12-19 Green LSB to MSB RGB Green 21-28 Red LSB to MSB RGB Red 30 GPIOB25 available for users 31 GPIOC15 occupied by FriendlyARM one wire technology to recognize LCD models and control backlight and implement resistive touch, not applicable for users 32 XnRSTOUT Form CPU low when system is reset 33 VDEN signal the external LCD that data is valid on the data bus 34 VSYNC vertical synchronization 35 HSYNC horizontal synchronization 36 LCDCLK LCD clock, Pixel frequency 41 I2C2_SCL I2C2 clock signal, for capacitive touch's data transmission 42 I2C2_SDA I2C2 data signal, for capacitive touch's data transmission 43 GPIOC16 interrupt pin for capacitive touch, used with I2C2 44 NC not connected
- Note
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. When the external device’s power is greater than the MicroUSB’s the external device is charging the board otherwise the board powers the external device. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.6V
- For more details please refer to the document:NanoPi2_Fire_1512B_Schematic.pdf
3.2 Board Dimension
- For more details please refer to the document:NanoPi2_Fire_1512B_Dimensions(dxf).zip
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
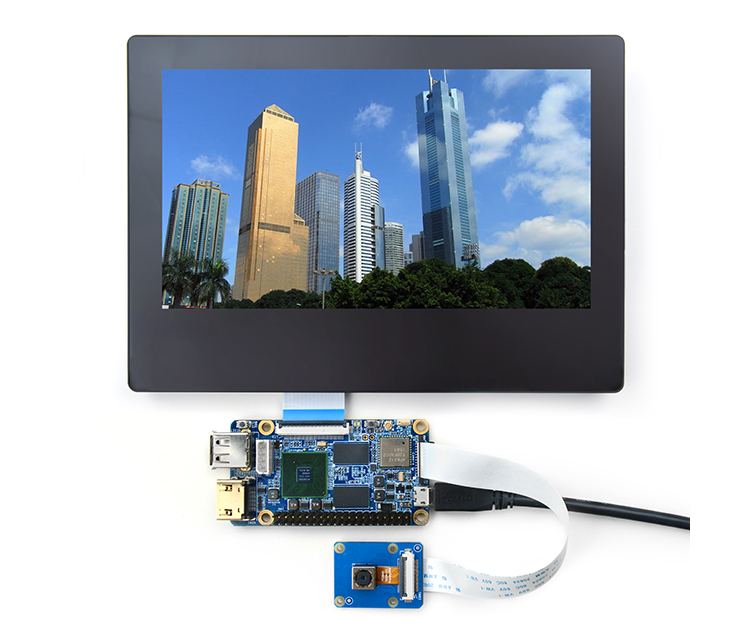
Before play with your NanoPi 2 Fire please get the following items ready
- NanoPi 2 Fire
- microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must
- HDMI monitor or LCD
- USB keyboard and mouse
- A Host running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
4.2 TF Card We Tested
To make your NanoPi 2 Fire boot and run fast we highly recommand you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
4.3 Make an Installation MicroSD Card
4.3.1 Under Windows
Please get the following files from here:download link to download image files:
For LCD or HDMI output please use the following files: nanopi2-debian-sd4g.img.zip Debian image files nanopi2-android-sd4g.img.zip Android image files Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
- Please uncompress these files. Insert an SD card(at least 4G) to a Windows PC, run the win32diskimager utility as administrator,On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive and the image files and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Please insert this card to your NanoPi 2 Fire and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the blue LED and green LED are blinking this indicates your NanoPi 2 Fire is successfully booted.
4.3.2 Under Linux Desktop
- 1) Insert your microSD card to your host running Ubuntu and check your SD card's device name
dmesg | tail
Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card is recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions".
- 2) Download Firmware Package
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_nanopi2.git cd sd-fuse_nanopi2
- 3) Flash Android Firmware to MicroSD Card
su ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system) When you do “git clone” you have to hit “Y” within 10 seconds after it prompts you to download image files otherwise you will miss the download.
- 4) Flash Debian Firmware to MicroSD Card
./fusing.sh /dev/sdx debian
4.4 Update Image Files in MicroSD Card From PC Host
If you want to make some changes to the image files in your MicroSD card please follow steps below otherwise you can skip this section.
Please insert your MicroSD card to a PC host running LINUX, mount the boot and rootfs sections of the SD card and follow the steps below:
1) If you want to change your kernel command line parameters you can do it via the fw_setevn utility under "sd-fuse_nanopi2/tools"
Check the current Command Line:
cd sd-fuse_nanopi2/tools ./fw_printenv /dev/sdc | grep bootargs
Android 5.1.1_r6 starts SELinux. By default it is enforcing. You can change it this way:
./fw_setenv /dev/sdc bootargs XXX androidboot.selinux=permissive
This will set it to "permissive". The "XXX" stands for the original bootargs' value.
2) Update Kernel
Our customized uboot will check the LCD type when it boots.For a non-Android OS If it recognizes an LCD connected to the NanoPi 2 Fire it will load "uImage" from "boot" otherwise it will load "uImage.hdmi"
However for Android these two files don't make any differences for whatever display device it detects. You can use your generated uImage to replace the existing one under "boot".
For Debian if your generated kernel is for LCD you need to replace the existing uImage or if your kernel is for HDMI you need to replace the existing uImage.hdmi .
4.5 Run Android or Debian
Insert a MicroSD card with Android image files to your NanoPi 2 Fire, connect the NanoPi 2 Fire to an HDMI monitor and a 5V/2A power source the NanoPi 2 Fire will be automatically powered on. If you can see the blue LED flashing it means your board is working and you will see Android loading on the HDMI monitor. If at the same time you connect your NanoPi 2 Fire to a PC running Ubuntu and Minicom via a serial cable you will see system messages output to the PC’s minicom terminal. Under Debian the password for "root" is "fa".
4.6 Login Debian via VNC or SSH
If your NanoPi 2 Fire is not connected to a display device you can download and install a "VNC Viewer" on your PC or mobile phone and login the NanoPi 2 Fire via VNC. Its default password is "fa123456". Here is a screenshot which shows how it looks like when users login the NanoPi2 from an iPhone via VNC:
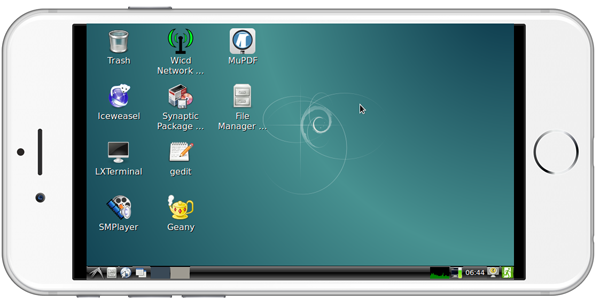
You can login via "SSH -l root 192.168.8.1" too and the default password for "root" is "fa".
5 Play with Debian
5.1 连接有线网络
NanoPi 2 Fire在加电开机前如果已正确的连接网线,则系统启动时会自动获取IP地址,如果没有连接网线、没有DHCP服务或是其它网络问题,则会导致获取IP地址失败,同时系统启动会因此等待约15~60秒的时间。
- 1) 配置MAC地址
板子没有提供有效的Ethernet的MAC地址,系统在连接网络时会自动生成一个随机的MAC地址,您可以修改 /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0 ,配置一个固定的MAC地址:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0
以下是配置文件的具体内容:
auto eth0 allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp hwaddress 76:92:d4:85:f3:0f
其中"hwaddress" 就是用来指定MAC地址,"76:92:d4:85:f3:0f"是一个随机生成的地址,为防止冲突导致网络问题,请修改为一个不同的且有效的地址。
需要注意的一点是,MAC地址必须符合IEEE的规则,请不要随意指定,否则会出现无法获取IP地址、无法上网等问题。
修改完配置文件并保存后,可重启板子或直接下列命令重启网络服务:
systemctl restart networking
5.2 Install Debian Packages
We provide a Debian jessie image. You can install Jessie's packages by commanding "apt-get". If this is your first installation you need to update the package list by running the following command:
apt-get updateYou can install your preferred packages. For example if you want to install an FTP server you can do this:
apt-get install vsftpdNote: you can change your download server by editting "/etc/apt/sources.list". You can get a complete server list from [1]. You need to select the one with "armhf".
6 Make Your Own OS Image
6.1 Setup Development Environment
6.2 Install Cross Compiler
Please download the compiler package:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/prebuilts.git sudo mkdir -p /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain sudo tar xf prebuilts/gcc-x64/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf-4.9.3.tar.xz -C /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/
Then add the compiler's directory to "PATH" by appending the following lines in "~/.bashrc":
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
Execute "~/.bashrc" to make the changes into effect. Please note that there is a space after ".":
. ~/.bashrcThis compiler is a 64-bit one therefore it cannot be run on a 32-bit LINUX. After the compiler is installed you can verify it by running the following commands:
arm-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=arm-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/libexec/gcc/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/4.9.3/lto-wrapper Target: arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf Configured with: /work/toolchain/build/src/gcc-4.9.3/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/sys-root --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-arch=armv7-a --with-tune=cortex-a9 --with-fpu=vfpv3 --with-float=hard ... Thread model: posix gcc version 4.9.3 (ctng-1.21.0-229g-FA)
6.3 Compile U-Boot
Download the U-Boot source code and compile it. Please note the github's branch is nanopi2-lollipop-mr1:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot_nanopi2.git cd uboot_nanopi2 git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 make s5p4418_nanopi2_config make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
After your compilation succeeds a u-boot.bin will be generated. If you want to test it please flash it to your installation MicroSD card via fastboot. Here is how you can do it:
1) On your PC host please run "sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot" to install the fastboot utility
2) Connect your NanoPi 2 Fire to your PC host via a serial cable (e.g. PSU-ONECOME). Press the enter key within two seconds right after you power on your NanoPi 2 Fire and you will enter uboot's command line mode:
3) After type "fastboot" and press "enter" you will enter the fastboot mode:
4) Connect your NanoPi 2 Fire to this PC host via a microUSB cable and type the following command to flash the u-boot.bin:
fastboot flash bootloader u-boot.bin
Warning: you cannot update this MicroSD card by commanding "dd". This command which will cause trouble when booting the NanoPi 2 Fire.
6.4 Prepare mkimage
You need the mkimage utility to compile a U-Boot source code package. Please make sure this utility works well on your host before you start compiling a uImage.
You can install this utility by either commanding "sudo apt-get install u-boot-tools" or following the commands below:
cd uboot_nanopi2 make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- tools sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/sbin && sudo cp -v tools/mkimage /usr/local/sbin
6.5 Compile Linux kernel
6.5.1 Compile Kernel
- Download Kernel Source Code
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git cd linux-3.4.y git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1
The NanoPi2's kernel source code lies in the "nanopi2-lollipop-mr1" branch.
- Compile Android Kernel
make nanopi2_android_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
- Compile Debian Kernel
make nanopi2_linux_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
After your compilation succeeds a uImage will be generated in the "arch/arm/boot/uImage" directory. This kernel is for HDMI. You can use it to replace the existing uImage.hdmi
If you want to generate a kernel for LCD you can do it this way:
touch .scmversion make nanopi2_linux_defconfig make menuconfig Device Drivers --> Graphics support --> Nexell Graphics --> [*] LCD [ ] HDMI make uImage
After your compilation succeeds a uImage will be generated for HDMI. You can use it to replace the existing uImage.
6.5.2 Compile Kernel Modules
Android contains kernel modules which are in the "/lib/modules" directory in the system section. If you want to add your own modules to the kernel or you changed your kernel configurations you need to recompile these new modules.
Compile Original Kernel Modules:
cd linux-3.4.y make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-eabi- modules
Here we have two new modules and we can compile them by following the commands below:
cd /opt/FriendlyARM/s5p4418/android ./vendor/friendly-arm/build/common/build-modules.sh
The "/opt/FriendlyARM/s5p4418/android" directory points to the top directory of Android source code. You can get more details by specifying option "-h".
After your compilation succeeds new modules will be generated
6.6 Compile Android
- Install Cross Compiler
We recommend installing 64 bit Ubuntu 14.04 on your PC host.
sudo apt-get install bison g++-multilib git gperf libxml2-utils make python-networkx zip sudo apt-get install flex libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk minicom
For more details please refer to https://source.android.com/source/initializing.html 。
- Download Source Code
You need to use repo to get the Android source code. Please refer to https://source.android.com/source/downloading.html 。
mkdir android && cd android repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/android_manifest.git -b nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 repo sync
The "android" directory is the working directory.
- Compile System Package
source build/envsetup.sh lunch aosp_nanopi2-userdebug make -j8
After your compilation succeeds an image will be generated in the "out/target/product/nanopi2/" directory.
7 Connect NanoPi 2 to External Modules
7.1 Connect NanoPi 2 to USB Camera(FA-CAM202)
- In this usecase the NanoPi 2 runs Debian. If you connect your NanoPi 2 to our LCD after Debain is fully loaded please click on "other"-->"xawtv9" on the left bottom of the GUI and the USB Camera application will be started. After enter "welcome to xawtv!" please click on "OK" to start exploring.
7.2 Connect NanoPi 2 to CMOS 5M-Pixel Camera
- In this usecase the NanoPi 2 runs Android5.1. If you connect your NanoPi 2 to our LCD after Debain is fully loaded please click on the "Camera" icon the application will be started.
7.3 Use OpenCV to Access USB Camera
- The full name of "OpenCV" is Open Source Computer Vision Library and it is a cross platform vision library.
- When the NanoPi 2 runs Debian users can use OpenCV APIs to access a USB Camera device
Here is a guideline on how to use OpenCV with C++ on the NanoPi 2
1. Preparations
---Firstly you need to make sure your NanoPi 2 is connected to the internet. Login your NanoPi 2 via a serial terminal or SSH. After login please type your username(root) and password(fa): ---Run the following commands:
#apt-get update (The OS images we provide for the NanoPi 2 by default have the vi utility. However we suggest you install the vim utility) #apt-get install vim #apt-get install libcv-dev libopencv-dev
2. Make sure your USB camera works with the NanoPi 2. You can test your camera with NanoPi 2's camera utility.
3. Check your camera device:
#ls /dev/video + "Tab" key (This lists available USB camera devices. In our test case video9 was available and video0 to video8 were occupied)
4. OpenCV's code sample:
#cd /home/fa #vim test.cpp
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp" using namespace cv; int main(int, char**) { VideoCapture cap(0); // open the default camera if(!cap.isOpened()) // check if we succeeded return -1; Mat edges; namedWindow("edges",1); for(;;) { Mat frame; cap >> frame; // get a new frame from camera cvtColor(frame, edges, CV_BGR2GRAY); GaussianBlur(edges, edges, Size(7,7), 1.5, 1.5); Canny(edges, edges, 0, 30, 3); imshow("edges", edges); if(waitKey(30) >= 0) break; } // the camera will be deinitialized automatically in VideoCapture destructor return 0; }
Compile the code sample:
#g++ test.cpp -o test -lopencv_core -lopencv_highgui -lopencv_imgproc
If it is compiled successfully a "test" executable will be generated:
5. Note: the NanoPi 2 has nine video devices. However this OpenCV's code sample defines a maximum of 8 cameras can be accessed therefore one video needs to be removed. Here we removed video0
#rm /dev/video0 #mv /dev/video9 /dev/video0
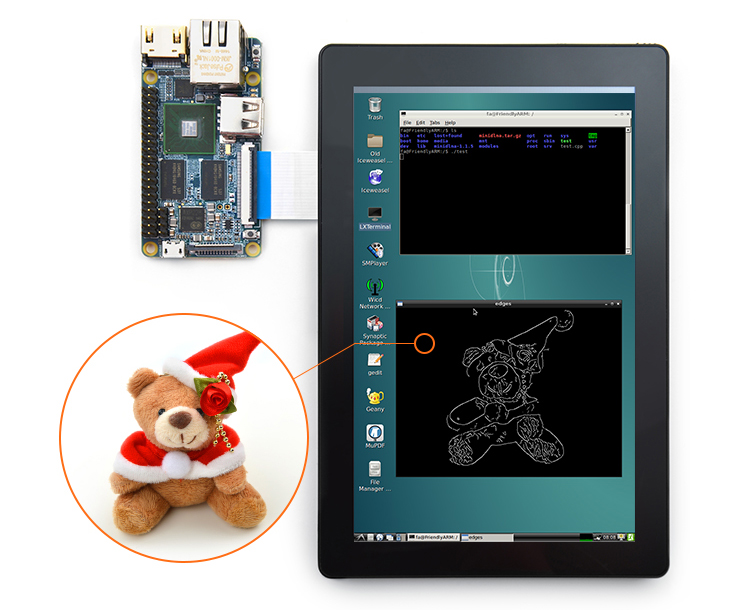
6. Connect NanoPi 2 to USB Keyboard & Run the Following Command:
#./test
This is what you expect to observe:
8 Extend NanoPi 2's TF Card Section
8.1 For Debian
- Please run the following commands on a PC host's terminal:
sudo umount /dev/sdx? sudo parted /dev/sdx unit % resizepart 2 100 unit MB print sudo resize2fs -f /dev/sdx2
8.2 For Android
- Please run the following commands on a PC host's terminal:
sudo umount /dev/sdx? sudo parted /dev/sdx unit % resizepart 4 100 resizepart 7 100 unit MB print sudo resize2fs -f /dev/sdx7
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
9 Resources
- Schematic (NanoPi2_Fire_1512B_Schematic.pdf)
- Dimensions (NanoPi2_Fire_1512B_Dimensions(dxf).zip)
- SOC Datasheet (Pi2_SOC_DS_0.1.pdf)