Difference between revisions of "NanoPi Zero2"
(→Hardware Spec) |
(→Diagram, Layout and Dimension) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Diagram, Layout and Dimension== | ==Diagram, Layout and Dimension== | ||
===Layout=== | ===Layout=== | ||
| − | [[File:NanoPi_Zero2_Layout.jpg | + | [[File:NanoPi_Zero2_Layout.jpg |300px|NanoPi Zero2 Layout]] |
* '''Debug UART Pin Spec''' | * '''Debug UART Pin Spec''' | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
:'''Notes''' | :'''Notes''' | ||
::#Power Input : 5V/3A, via USB Type-C(USB PD Specification is not supported) | ::#Power Input : 5V/3A, via USB Type-C(USB PD Specification is not supported) | ||
| + | |||
==Get Started== | ==Get Started== | ||
===Essentials You Need=== | ===Essentials You Need=== | ||
Revision as of 06:41, 5 September 2024
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 Hardware Spec
- 3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
- 4 Get Started
- 5 Work with FriendlyCore
- 6 How to Compile
- 7 Using On-Board Hardware Resources
- 8 Backup rootfs and create custom SD image (to burn your application into other boards)
- 9 Unbricking Method
- 10 Link to Rockchip Resources
- 11 Schematic, PCB CAD File
- 12 Update Log
1 Introduction
- The NanoPi-Zero2 is another fun board developed by FriendlyELEC for makers, hobbyists and fans.
2 Hardware Spec
- SoC: Rockchip RK3528A
- CPU: Quad-core ARM Cortex-A53
- GPU: ARM Mali-450 GPU
- VPU: 4K H265/H264 60fps decoding
- RAM: 1GB/2GB LPDDR4/LPDDR4X
- Flash: Supports eMMC Module
- Ethernet: one Native Gigabit Ethernet
- M.2 Key-E 2230 connector with PCIe 2.1
- USB Ports:
- One USB 2.0 Host Type-A port
- One USB 2.0 Device Type-C port for eMMC upgrade
- One microSD Slot
- One 30-pin FPC GPIO connector
- Debug: Debug UART, 3.3V level, 1500000bps
- LEDs: 2 x GPIO Controlled LEDs (SYS & LED1)
- others:
- 2 Pin 1.27/1.25mm battery connector for Low-power RTC
- RESET Button, RECOVERY Button, and MASK Button for eMMC upgrade
- Power supply: DC 5V/2A, via USB-C connector
- PCB Size: 45*45*1.2mm
- Temperature measuring range: 0℃ to 80℃
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
- Debug UART Pin Spec
- 3V level signals, 1500000bps
Pin# Assignment Description 1 GND 0V 2 UART2DBG_TX output 3 UART2DBG_RX intput
- USB Port
- Each USB 3.0 port has 2A overcurrent protection.
- RTC
- RTC backup current is 27uA.
- Connector P/N: Molex 53398-0271
- Notes
- Power Input : 5V/3A, via USB Type-C(USB PD Specification is not supported)
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi-Zero2 get the following items ready
- NanoPi-Zero2
- MicroSD Card/TF Card: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- 5V/3A and above USB Type-C interface power adapter
- If you need to develop and compile,you need a computer that can connect to the Internet. It is recommended to install Ubuntu 20.04 64-bit system and use the following script to initialize the development environment, or use docker container:
4.2 TF Cards We Tested
Refer to: TFCardsWeTested
4.3 Configure parameters for serial port
Use the following serial parameters:
| Baud rate | 1500000 |
| Data bit | 8 |
| Parity check | None |
| Stop bit | 1 |
| Flow control | None |
4.4 Install OS
Template:BurnLinuxToSD-RK3528Router Template:BurnLinuxToEMMC-RK3528Router
5 Work with FriendlyCore
5.1 FriendlyCore User Account
- Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
- Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
5.2 Update Software Packages
$ sudo apt-get update
5.3 Setup Network Configurations
5.3.1 Set static IP address
By default "eth0" is assigned an IP address obtained via dhcp. If you want to change the setting you need to change the following file:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0
For example if you want to assign a static IP to it you can run the following commands:
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.1.231
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.15.3.2 Set a DNS
You also need to modify the following file to add the DNS configuration:
vi /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
For example, set to 192.168.1.1:
[Resolve] DNS=192.168.1.1
Restart the systemd-resolved service with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved.service sudo systemctl enable systemd-resolved.service
5.3.3 Set up to use another network interface
To change the setting of "eth1" you can add a new file similar to eth0's configuration file under the /etc/network/interfaces.d/ directory.
5.4 Setup Wi-Fi
First, use the following command to check if Network-Manager is installed on your system:
which nmcliIf you have installed it, refer to this link to connect to WiFi: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings, If you do not have Network-Manager installed on your system, please refer to the following method to configure WiFi,
By default the WiFi device is "wlan0". You need to create a configuration file under "/etc/network/interfaces.d/" for WiFi:
vi /etc/network/interfaces.d/wlan0
Here is a sample wlan0 file:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet dhcp
wpa-driver wext
wpa-ssid YourWiFiESSID
wpa-ap-scan 1
wpa-proto RSN
wpa-pairwise CCMP
wpa-group CCMP
wpa-key-mgmt WPA-PSK
wpa-psk YourWiFiPasswordPlease replace "YourWiFiESSID" and "YourWiFiPassword" with your WiFiESSID and password. After save and close the file you can connect to your WiFi source by running the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart networking
After you power on your board it will automatically connect to your WiFi source.
Please note that if you use one TF card to boot multiple boards the WiFi device name will likely be named to "wlan1", "wlan2" and etc. You can reset it to "wlan0" by deleting the contents of the following file and reboot your board:
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
5.5 Install the kernel-header package
sudo dpkg -i /opt/archives/linux-headers-*.deb
6 How to Compile
6.1 Setup Development Environment
6.1.1 Method 1: Using docker to cross-compile
Please refre to docker-cross-compiler-novnc
6.1.2 Method 2: Setup build environment on the host machine
6.1.2.1 Install required packages
Install and run requirements ubuntu 20.04, install required packages using the following commands:
sudo apt-get -y update sudo apt-get install -y sudo curl sudo bash -c \ "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/build-env-on-ubuntu-bionic/master/install.sh)"
The following cross-compilers will be installed:
| Version | Architecture | Compiler path | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.9.3 | armhf | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 | Can be used to build 32-bit ARM applications |
| 6.4 | aarch64 | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/6.4-aarch64 | Can be used to build kernel 4.4 |
| 11.3 | aarch64 | /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64 | Can be used to build kernel 4.19 or higher and U-Boot |
6.1.2.2 Setting the compiler path
Based on the table in the previous section, select the appropriate version of the compiler and add the compiler's path to PATH. For example, if you want to use the 11.3 cross-compiler, edit ~/.bashrc using vi and add the following content to the end:
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
Run the ~/.bashrc script to make it effective in the current commandline. Note: there is a space after ".":
. ~/.bashrcTo verify if the installation was successful:
$ aarch64-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=aarch64-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/libexec/gcc/aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu/11.3.0/lto-wrapper Target: aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu Configured with: /home/cross/arm64/src/gcc/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64 --exec_prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu/sysroot --enable-languages=c,c++ --enable-fix-cortex-a53-843419 --with-arch=armv8-a+crypto+crc --with-cpu=cortex-a53 --with-pkgversion=ctng-1.25.0-119g-FA --with-bugurl=http://www.friendlyelec.com/ --enable-objc-gc --enable-__cxa_atexit --disable-libmudflap --disable-libgomp --disable-libssp --disable-libquadmath --disable-libquadmath-support --disable-libsanitizer --disable-libmpx --with-gmp=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --with-mpfr=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --with-mpc=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --with-isl=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --enable-lto --enable-threads=posix --disable-libstdcxx-pch --enable-clocale=gnu --enable-libstdcxx-time=yes --with-default-libstdcxx-abi=new --enable-gnu-indirect-function --enable-gnu-unique-object --enable-default-pie --enable-linker-build-id --with-linker-hash-style=gnu --enable-plugin --enable-gold --with-libintl-prefix=/home/cross/arm64/buildtools --disable-multilib --with-local-prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/aarch64-cortexa53-linux-gnu/sysroot --enable-long-long --enable-checking=release --enable-link-serialization=2 Thread model: posix Supported LTO compression algorithms: zlib gcc version 11.3.0 (ctng-1.25.0-119g-FA)
6.2 Build Openwrt/Friendlywrt
6.2.1 Download Code
Two versions are available, please choose as required:
6.2.1.1 FriendlyWrt 24.10
mkdir friendlywrt24-rk3528 cd friendlywrt24-rk3528 git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --depth 1 tools tools/repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/friendlywrt_manifests -b master-v24.10 \ -m rk3528.xml --repo-url=https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --no-clone-bundle tools/repo sync -c --no-clone-bundle
6.2.1.2 FriendlyWrt 23.05
mkdir friendlywrt23-rk3528 cd friendlywrt23-rk3528 git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --depth 1 tools tools/repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/friendlywrt_manifests -b master-v23.05 \ -m rk3528.xml --repo-url=https://github.com/friendlyarm/repo --no-clone-bundle tools/repo sync -c --no-clone-bundle
6.2.2 First compilation step
./build.sh rk3528.mk # or rk3528-docker.mk
All the components (including u-boot, kernel, and friendlywrt) are compiled and the sd card image will be generated, then execute the following command to generate the image file for installing the system into the emmc:
./build.sh emmc-imgAfter making changes to the project, the sd card image needs to be repackaged by running the following command:
./build.sh sd-img6.2.3 Secondary compilation steps
cd friendlywrt make menuconfig rm -rf ./tmp make -j${nproc} cd ../ ./build.sh sd-img ./build.sh emmc-img
6.2.4 Build u-boot only
./build.sh uboot6.2.5 Build kernel only
./build.sh kernel6.2.6 Build friendlywrt only
./build.sh friendlywrtOr go to the friendlywrt directory and follow the standard openwrt commands. If you get an error with the above command, try using the following command to compile in a single thread:
cd friendlywrt make -j1 V=s
6.3 Build Other Linux
6.3.1 Kernel and u-boot versions
| Operating System | Kernel Version | U-boot version | Cross-compiler | Partition type | Packaging Tool | Kernel branch | Kernel configuration | U-boot branch | U-boot configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| openmediavault-arm64 | linux v6.1.y | u-boot v2017.09 |
11.3-aarch64 | GPT | sd-fuse |
nanopi6-v6.1.y | nanopi5_linux_defconfig | nanopi5-v2017.09 | nanopi5_defconfig |
| ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 | GPT | ||||||||
| debian-bookworm-core-arm64 | |||||||||
| friendlywrt21 | nanopi5_linux_defconfig +friendlywrt.config | ||||||||
| friendlywrt21-docker | |||||||||
| friendlywrt23 | |||||||||
| friendlywrt23-docker |
- Kernel git repo:https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip
- U-boot git repo:https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip
- The cross-compile toolchain is located in the path: /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/
- The SD-Fuse is a helper script to make bootable SD card image.
6.3.2 Build kernel linux-v6.1.y
This section applies to the following operating systems:
| friendlywrt21 | friendlywrt21-docker | friendlywrt23 | friendlywrt23-docker | ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 | openmediavault-arm64 | debian-bookworm-core-arm64 |
Clone the repository to your local drive then build:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi6-v6.1.y kernel-rockchip cd kernel-rockchip export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH touch .scmversion # Configuring the Kernel # Load default configuration make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 nanopi5_linux_defconfig # Optionally, load configuration for FriendlyWrt # make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 nanopi5_linux_defconfig friendlywrt.config # Optionally, if you want to change the default kernel config # make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 menuconfig # Start building kernel make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 -j$(nproc) # Start building kernel modules mkdir -p out-modules && rm -rf out-modules/* make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules -j$(nproc) make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH="$PWD/out-modules" modules_install KERNEL_VER=$(make CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- ARCH=arm64 kernelrelease) [ ! -f "$PWD/out-modules/lib/modules/${KERNEL_VER}/modules.dep" ] && depmod -b $PWD/out-modules -E Module.symvers -F System.map -w ${KERNEL_VER} (cd $PWD/out-modules && find . -name \*.ko | xargs aarch64-linux-strip --strip-unneeded)
Pack the kernel.img and resource.img:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3528/kernel-6.1.y/tools/mkkrnlimg && chmod 755 mkkrnlimg wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3528/kernel-6.1.y/tools/resource_tool && chmod 755 resource_tool wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3528/kernel-6.1.y/prebuilt/boot/logo.bmp wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3528/kernel-6.1.y/prebuilt/boot/logo_kernel.bmp ./mkkrnlimg arch/arm64/boot/Image kernel.img ./resource_tool --dtbname arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3528-nanopi*-rev*.dtb logo.bmp logo_kernel.bmp
After the compilation, the following files will be generated:
| kernel.img | resource.img | The kernel modules are located in the out-modules directory |
Run your build:
Please refre to #Running the build
6.3.3 Build u-boot v2017.09
This section applies to the following operating systems:
| friendlywrt21 | friendlywrt21-docker | friendlywrt23 | friendlywrt23-docker | ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 | openmediavault-arm64 | debian-bookworm-core-arm64 |
Clone the repository to your local drive then build:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/rkbin --single-branch --depth 1 -b friendlyelec git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip --single-branch --depth 1 -b nanopi5-v2017.09 export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/11.3-aarch64/bin/:$PATH cd uboot-rockchip/ ./make.sh nanopi_r3
After the compilation, the following files will be generated:
| uboot.img | trust.img | rk356x_spl_loader_vX.YY.ZZZ.bin (aka MiniLoaderAll.bin) |
Run your build:
Please refre to #Running the build
6.3.4 Running the build
6.3.4.1 Install to target board
This section applies to the following operating systems:
| friendlywrt21 | friendlywrt21-docker | friendlywrt23 | friendlywrt23-docker | ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 | openmediavault-arm64 | debian-bookworm-core-arm64 |
RK3528 uses GPT partitions by default, you can use the dd command, but be careful to choose the right output device:
- The SD/TF Card device node: /dev/mmcblk0
- The eMMC device node: /dev/mmcblk2
The following is an example of how to update the kernel to eMMC:
Use the 'parted' command to view the partition layout:
parted /dev/mmcblk2 print
Sample outputs:
Model: MMC BJTD4R (sd/mmc) Disk /dev/mmcblk2: 31.3GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 8389kB 12.6MB 4194kB uboot 2 12.6MB 16.8MB 4194kB trust 3 16.8MB 21.0MB 4194kB misc 4 21.0MB 25.2MB 4194kB dtbo 5 25.2MB 41.9MB 16.8MB resource 6 41.9MB 83.9MB 41.9MB kernel 7 83.9MB 134MB 50.3MB boot 8 134MB 2500MB 2366MB ext4 rootfs 9 2500MB 31.3GB 28.8GB ext4 userdata
as shown above, the resource partition is located at 5 and the kernel partition is located at 6. Use the dd command to write the resource.img and kernel.img files to these partitions, the commands are as follows:
dd if=resource.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p5 bs=1M dd if=kernel.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p6 bs=1M
If you want to update u-boot:
dd if=uboot.img of=/dev/mmcblk2p1 bs=1M
To update new driver modules, copy the newly compiled driver modules to the appropriate directory under /lib/modules.
6.3.4.2 Packaging and creating an SD image
To create a new OS image file, you need to use the "sd-fuse" packaging tool.
"sd-fuse" is a collection of scripts that can be used to create bootable SD card images for FriendlyElec boards. Its main features include:
- Creation of root filesystem images from a directory
- Building of bootable SD card images
- Simple compilation of kernel, U-Boot, and third-party drivers
Please click on the following link to find out more:
| Kernel version | Packaging Tool |
|---|---|
| linux v6.1.y | sd-fuse_rk3528/kernel-6.1.y |
6.3.4.3 USB flashing
6.3.4.3.1 Linux
Reboot the board and enter loader mode with the following command:
sudo reboot loaderTo flash U-Boot and kernel using the "upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux" tool, please use the following command:
sudo upgrade_tool di -k kernel.img sudo upgrade_tool di -re resource.img sudo upgrade_tool di -u uboot.img sudo upgrade_tool RD
Note: "upgrade_tool" is a command-line tool provided by Rockchip for Linux operating systems (Linux_Upgrade_Tool).
6.4 Build the code using scripts
6.4.1 Download scripts and image files
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3528.git -b kernel-6.1.y cd sd-fuse_rk3528 wget http://112.124.9.243/dvdfiles/rk3528/images-for-eflasher/ubuntu-noble-core-arm64-images.tgz tar xvzf ubuntu-noble-core-arm64-images.tgz
6.4.2 Compile the kernel
Download the kernel source code and compile it. the relevant image files in the ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 directory will be automatically updated, including the kernel modules in the file system:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --depth 1 -b nanopi6-v6.1.y kernel-rk3528 KERNEL_SRC=$PWD/kernel-rk3528 ./build-kernel.sh ubuntu-noble-core-arm64
6.4.3 Compile the kernel headers
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/kernel-rockchip --depth 1 -b nanopi6-v6.1.y kernel-rk3528 MK_HEADERS_DEB=1 BUILD_THIRD_PARTY_DRIVER=0 KERNEL_SRC=$PWD/kernel-rk3528 ./build-kernel.sh ubuntu-noble-core-arm64
6.4.4 Compile the uboot
Download the uboot source code and compile it. the relevant image files in the ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 directory will be automatically updated:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot-rockchip --depth 1 -b nanopi5-v2017.09 UBOOT_SRC=$PWD/uboot-rockchip ./build-uboot.sh ubuntu-noble-core-arm64
6.4.5 Generate new image
Repackage the image file in the ubuntu-noble-core-arm64 directory into sd card image:
./mk-sd-image.sh ubuntu-noble-core-arm64After the command is completed, the image is in the out directory.
7 Using On-Board Hardware Resources
7.1 Using VPU
Please refer to NPU
7.2 Using NPU
Please refer to NPU
7.3 DTS files
Please refer to DTS files
8 Backup rootfs and create custom SD image (to burn your application into other boards)
8.1 Backup rootfs
Run the following commands on your target board. These commands will back up the entire root partition:
sudo passwd root su root cd / tar --warning=no-file-changed -cvpzf /rootfs.tar.gz \ --exclude=/rootfs.tar.gz --exclude=/var/lib/docker/runtimes \ --exclude=/etc/firstuser --exclude=/etc/friendlyelec-release \ --exclude=/usr/local/first_boot_flag --one-file-system /
Note: if there is a mounted directory on the system, an error message will appear at the end, which can be ignored.
8.2 Making a bootable SD card from a root filesystem
Only support RK3328/RK3399/RK3568/RK3566/RK3588
9 Unbricking Method
If the ROM is not installed correctly, causing the development board to become bricked, and you might not have the opportunity to reinstall the ROM via an SD card, you need to enter Maskrom mode to unbrick it by erasing the storage device.
9.1 Windows Users
9.1.1 Download Required Files
- Get the necessary tools: Visit here, find RKDevTool_v3.19_for_window.zip and DriverAssitant_v5.12.zip in the 05_Tools directory, and download them to your local machine.
- Install Rockchip USB driver and RKDevTool: Extract DriverAssitant_v5.12.zip to install the Rockchip USB driver, and extract RKDevTool_v3.19_for_window.zip to obtain the Rockchip flashing tool RKDevTool.
- Get the loader: Visit here, enter the tools directory corresponding to your CPU model, and download MiniLoaderAll.bin.
9.1.2 Enter Maskrom Mode to Erase the Storage Device
- Remove the SD card, USB device, and other peripherals from the development board
- Start RKDevTool on your computer.
- Press and hold the “Mask” key, Use a USB cable, connect NanoPi-Zero2 to a PC,After the status LED has been on for at least 3 seconds, release the Mask key
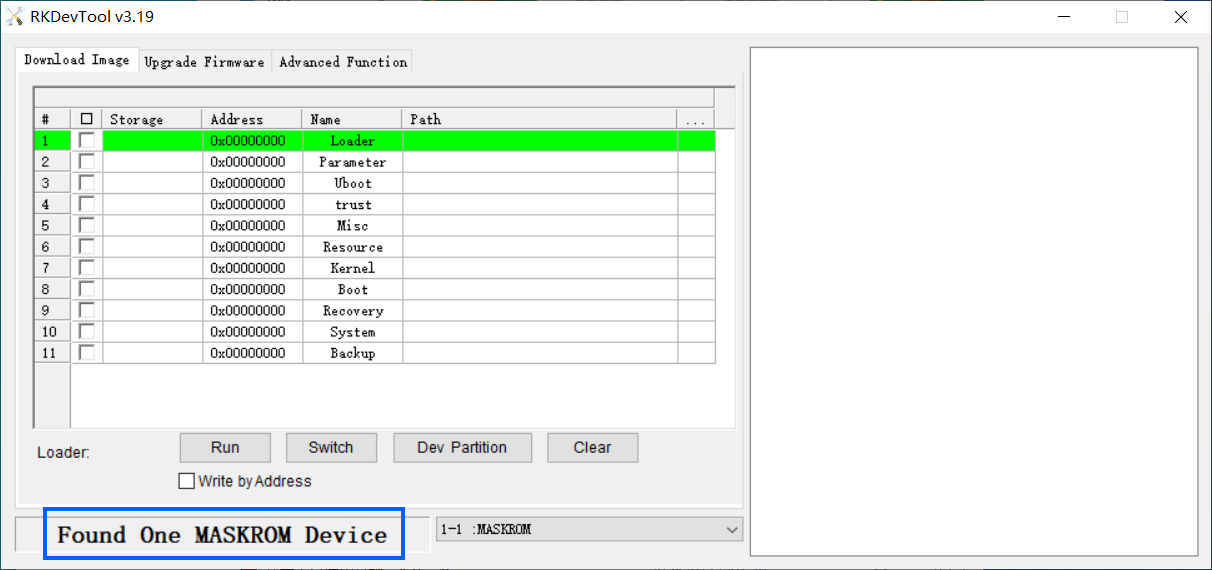
- You will see Found One MASKROM Device displayed at the bottom of the RKDevTool interface, as shown below:
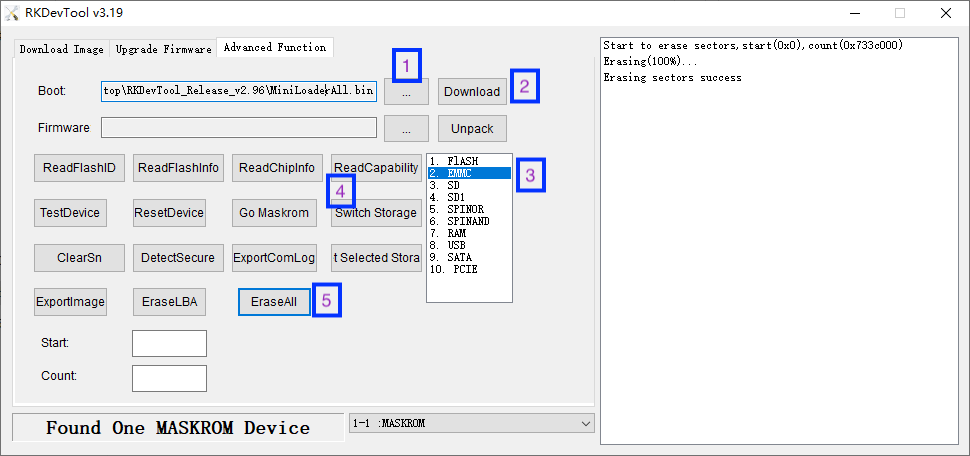
- Click the Advanced Function tab in the RKDevTool interface.
- In the Boot text box, select MiniLoaderAll.bin, then click the Download button.
- Select EMMC, click Switch Storage, then click the EraseAll button to erase the eMMC.
- At this point, NanoPi-Zero2 is restored to its initial state and can be normally booted via SD card or eMMC.
9.2 Linux Users
9.2.1 Download the Required Files
- Get the necessary tools: Visit here and find upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux.tgz in the 05_Tools directory and download it locally.
- Get the loader: Visit here, enter the tools directory corresponding to your CPU model, and download MiniLoaderAll.bin.
9.2.2 Installation for upgrade_tool
Using the following commands:
tar xzf upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux.tgz cd upgrade_tool_v2.30_for_linux sudo cp upgrade_tool /usr/local/sbin/ sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/sbin/upgrade_tool
9.2.3 Enter Maskrom Mode to Erase the Storage Device
- Connect NanoPi-Zero2 to the computer using a USB data cable.
- Disconnect the power from NanoPi-Zero2, hold down the MASK button, connect the power, and release the button after 4 seconds.
- Check the connection with the following command:
upgrade_tool LD
A result similar to "DevNo=1 Vid=0x2207,Pid=0x350b,LocationID=13 Mode=Maskrom SerialNo=" indicates that the device has been detected.
- Erase the eMMC with the following command:
upgrade_tool EF MiniLoaderAll.bin
- At this point, NanoPi-Zero2 has been restored to its initial state and can boot the system normally via SD card or eMMC.
9.3 Mac Users
Our tests found that upgrade_tool_v2.25 does not work properly on macOS. Therefore, we recommend using Windows or Linux unless an updated version of upgrade_tool becomes available.
10 Link to Rockchip Resources
11 Schematic, PCB CAD File
- Schematic: TODO
- PCB CAD File:TODO
12 Update Log
12.1 2025-02-11
- Synchronized upstream kernel update to version 6.1.99
- Integrated hardware acceleration packages such as mpp, gstreamer, rknn, and libmali into the Core system
12.2 2024-11-12
- Improved ramdisk and eflasher for more flexibility and reliability when installing the system on external storage
12.3 2024-10-16
- KVM is enabled by default in the kernel
- Optimized standby power consumption
- Added Proxmox VE system
- Updated FriendlyWrt to version openwrt-23.05.05
12.4 2024-09-04
Initial Release