Difference between revisions of "Use NetworkManager to configure network settings"
(→配置静态IP地址) |
|||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
[[File:NetworkManangerMenu.png|frameless|400px|NetworkManangerMenu]]<br /> | [[File:NetworkManangerMenu.png|frameless|400px|NetworkManangerMenu]]<br /> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Setup Static IP== |
| − | === | + | ===1: Setup Static IP Manually=== |
| − | + | You can setup a static IP manually without using the NetworkManager: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
sudo vi /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf | sudo vi /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Edit NetworkManger.conf and set the value of "managed" under "ifupdown" to false: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
[ifupdown] | [ifupdown] | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Add network setting to /etc/network/interfaces: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces | $ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | /etc/network/ | + | Here is is sample of /etc/network/interfaces: |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
# The loopback network interface | # The loopback network interface | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | === | + | ===2: Setup Static IP with NetworkManager=== |
| − | + | Here is an example demonstrating how to setup a static IP with NetworkManager in a wired network<br /> | |
| − | + | Check netowrk connection: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
pi@Smart4418SDK:~$ sudo nmcli connection show | pi@Smart4418SDK:~$ sudo nmcli connection show | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | The above messages show that there is a wired connection named "Wired connection 1". You can set a static IP for "Wired connection 1" by running the following commands: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
sudo nmcli connection modify 'Wired connection 1' connection.autoconnect yes ipv4.method manual ipv4.address 192.168.2.199/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.2.1 ipv4.dns 192.168.2.1 | sudo nmcli connection modify 'Wired connection 1' connection.autoconnect yes ipv4.method manual ipv4.address 192.168.2.199/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.2.1 ipv4.dns 192.168.2.1 | ||
sudo reboot | sudo reboot | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | If this is successful the connection will be assigned a static IP with IP address to be 192.168.2.199 and both gateway and DNS to be 192.168.2.1 | |
== NetworkManager的卸载== | == NetworkManager的卸载== | ||
Revision as of 08:36, 19 June 2017
Contents
[hide]1 Introduction to NetworkManager
The NetworkManager is a utility to check network status and manage network connectivity. It can be used to manage both wireless and wired network.
The NetworkManager has a commandline utility nmcli, a commandline based GUI nmtui, and an X-Windows based GUI nm-connection-editor.
2 Images with NetworkManager
All the image files of Linux variants(Debian and Ubuntu) developed by FriendlyElec have this utility. This utility works with the following FriendlyElec boards:
2.1 Board Model
S5P4418 Based Boards:
NanoPi2 / NanoPC-T2 / NanoPi-S2 / Smart4418 / NanoPi2-Fire / NanoPi-M2 / NanoPi-M2A
S5P6818 Based Boards:
NanoPC-T3 / NanoPC-T3T / NanoPi-M3
Allwinner SoC Based Boards:
NanoPi-M1 /NanoPi-NEO /NanoPi-NEO-Air / NanoPi-M1-Plus / NanoPi-NEO2 / NanoPi-M1-Plus2 / NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 / NanoPi-NEO-Core / NanoPi-Duo
2.2 Applicable OS
Debian 8.x jessie (for S5P4418 and S5P6818 only)
Ubuntu core xenial 16.04.x (for all FriendlyElec's nano boards)
These OS images include those based on armhf and aarch64.
3 Setup WiFi Connection with NetworkManager
3.1 Commandline Utility (nmcli)
Command to Check WiFi:
- Check Device List
$ sudo nmcli dev
Note: if a device's status is unmanaged it means this device is not accessed by the NetworkManager and you need to clear the settings under /etc/network/interfaces and reboot.
- Start WiFi
$ sudo nmcli r wifi on
- Scan Surrounding WiFi Hotspots
$ sudo nmcli dev wifi
- Connect to WiFi Hotspot
$ sudo nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD"
The "SSID" and "Password" need to be replaced with your actual WiFi's SSID and password.
If a connection is successfully established your board will be automatically connected to your specified WiFi on system reboot.
- If there are mutiple active WiFi devices you can specify your expected WiFi device by using the ifname option in the following command. For example if you want to operate wlan1 you can do it this way:
sudo nmcli device wifi connect "ssid" password "password" ifname wlan1
3.2 Commandline Based GUI(nmtui)
nmtui is a curses based GUI. You can start it by running the following command:
$ sudo nmtui
For more details refer to "man nmtui".
3.3 Operations with Windows Utility
Under Debian there are two options to start a Windows utility:
Option 1: you can click on the network icon on the bottom right of the task bar. After you click on it a NetworkManger menu will pop up and all the available networks will be listed. If there is an active wireless network you will see something similar to the following screenshot:
You can click on a WiFI AP and connect your board to it.
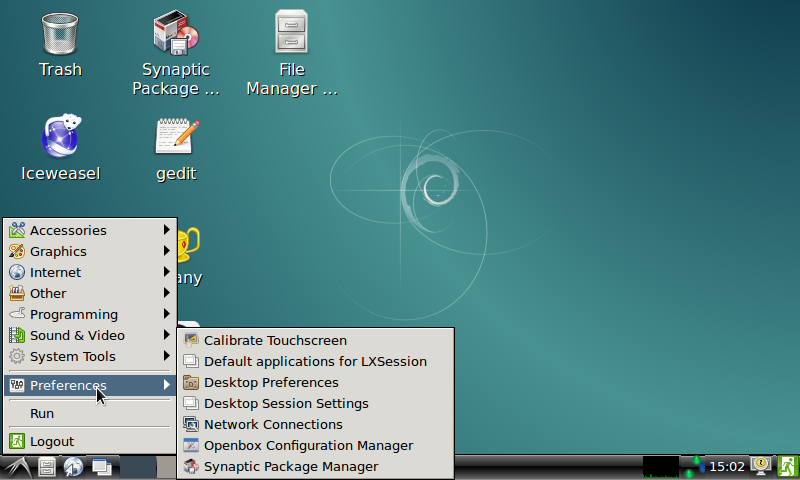
Option 2: you can go to Preferences -> Network Connections and enter the following window:
4 Setup Static IP
4.1 1: Setup Static IP Manually
You can setup a static IP manually without using the NetworkManager:
sudo vi /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf
Edit NetworkManger.conf and set the value of "managed" under "ifupdown" to false:
[ifupdown] managed=false
Add network setting to /etc/network/interfaces:
$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
Here is is sample of /etc/network/interfaces:
# The loopback network interface auto lo iface lo inet loopback # network interface not managed by Network Manager allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.2.199 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.2.1 dns-nameservers 192.168.2.1
4.2 2: Setup Static IP with NetworkManager
Here is an example demonstrating how to setup a static IP with NetworkManager in a wired network
Check netowrk connection:
pi@Smart4418SDK:~$ sudo nmcli connection show NAME UUID TYPE DEVICE Wired connection 1 cffa785e-0425-3777-b670-092c79328a1f 802-3-ethernet eth0
The above messages show that there is a wired connection named "Wired connection 1". You can set a static IP for "Wired connection 1" by running the following commands:
sudo nmcli connection modify 'Wired connection 1' connection.autoconnect yes ipv4.method manual ipv4.address 192.168.2.199/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.2.1 ipv4.dns 192.168.2.1 sudo reboot
If this is successful the connection will be assigned a static IP with IP address to be 192.168.2.199 and both gateway and DNS to be 192.168.2.1
5 NetworkManager的卸载
NetworkManager虽然方便,但如果你还是觉得传统的 wpa_supplicant 网络管理方式更顺手,你可以通过以下方式卸载NetworkManager:
创建一个脚本文件例如 rmnm.sh:
$vi rmnm.sh
脚本内容如下:
#!/bin/bash apt-get --yes --force-yes remove --auto-remove --purge network-manager apt autoremove -y cat >/etc/network/interfaces <<INTERFACEEOL source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d auto lo iface lo inet loopback allow-hotplug wlan0 iface wlan0 inet dhcp wpa-conf /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf INTERFACEEOL cat >/etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0 <<ETH0EOLB auto eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp hwaddress 76:92:d4:85:f3:0f ETH0EOLB
然后执行脚本:
$chmod 755 rmnm.sh $ sudo ./rmnm.sh
完成后重启即可。
6 其他参考资料
更详细的NetworkManager使用指南可参考这篇文章: NetworkManager