Difference between revisions of "Matrix - Ball Rolling Switch"
(→Applications) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
*The Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch module is a ball switch. Its electrical characteristics are very similar to a mercury switch's however a mercury switch is easily broken, oxidized, leaking and not environment-friendly. This ball switch prevents all these issues. | *The Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch module is a ball switch. Its electrical characteristics are very similar to a mercury switch's however a mercury switch is easily broken, oxidized, leaking and not environment-friendly. This ball switch prevents all these issues. | ||
*The switch is free to move any angle and if that angle is between 15 degrees and 45 degrees a signal will be generated and used as an input to a Schmitt trigger. | *The switch is free to move any angle and if that angle is between 15 degrees and 45 degrees a signal will be generated and used as an input to a Schmitt trigger. | ||
| − | |||
==Features== | ==Features== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
==Basic Device Operation== | ==Basic Device Operation== | ||
Please connect Pin V to a power supply, Pin G grounded and Pin S to a digital output. When you move the switch pushing the internal metal ball to connect the trigger point a high level signal will be generated and output to a Schmitt trigger which reverses this signal to output a low level signal. When you move the switch pushing the internal metal ball away from the trigger point a low level signal will be generated and output to a Schmitt trigger which reverses this signal to output a high level signal. | Please connect Pin V to a power supply, Pin G grounded and Pin S to a digital output. When you move the switch pushing the internal metal ball to connect the trigger point a high level signal will be generated and output to a Schmitt trigger which reverses this signal to output a low level signal. When you move the switch pushing the internal metal ball away from the trigger point a low level signal will be generated and output to a Schmitt trigger which reverses this signal to output a high level signal. | ||
| − | |||
==Applications== | ==Applications== | ||
===Connect to NanoPi M1=== | ===Connect to NanoPi M1=== | ||
| − | + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:<br> | |
[[File:Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-BAll_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m1]] | [[File:Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-BAll_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m1]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 46: | ||
===Connect to NanoPi 2=== | ===Connect to NanoPi 2=== | ||
| − | + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:<br> | |
[[File:matrix-BAll Rolling Switch_nanopi.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-BAll Rolling Switch_nanopi2]] | [[File:matrix-BAll Rolling Switch_nanopi.jpg|frameless|600px|matrix-BAll Rolling Switch_nanopi2]] | ||
| Line 63: | Line 61: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire=== |
| − | NanoPi | + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire.<br> |
| − | + | ||
[[File:Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m2]] | [[File:Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_nanopi_m2]] | ||
| − | + | Connection Details: | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 80: | Line 77: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Connect to NanoPC-T2=== |
| − | + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:<br> | |
[[File:Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_NanoPC-T2]] | [[File:Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_NanoPC-T2]] | ||
| − | + | Connection Details: | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 96: | Line 93: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Compile & Run Test Program== |
| − | + | Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git | ||
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated. | |
| − | + | Compile and install Matrix: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ cd matrix | $ cd matrix | ||
| Line 110: | Line 107: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Run test program: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ matrix-gpio_int | $ matrix-gpio_int | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Note: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.<br> | |
| − | + | Here is what you should observe:<br> | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
Waiting event... | Waiting event... | ||
Device[0] value is 1 | Device[0] value is 1 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | When you tilt the module, roll the ball and make it touch the trigger point you will see an event is detected. | |
| − | == | + | ==Code Sample== |
| − | + | This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-gpio_int". Here is its source code: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
int main(int argc, char ** argv) | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| Line 161: | Line 158: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to [[Matrix API reference manual]] <br> | |
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
*[Schematic]([http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/images/0/00/TIL-01-1511-Schematic.pdf Matrix - Ball Rolling Switch-Schematic.pdf]) | *[Schematic]([http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/images/0/00/TIL-01-1511-Schematic.pdf Matrix - Ball Rolling Switch-Schematic.pdf]) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!--- | <!--- | ||
| Line 284: | Line 279: | ||
===Feb-24-2016=== | ===Feb-24-2016=== | ||
* Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2 | * Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2 | ||
| + | ===June-17-2016=== | ||
| + | * Re-organized and simplified wiki | ||
Latest revision as of 10:30, 19 June 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
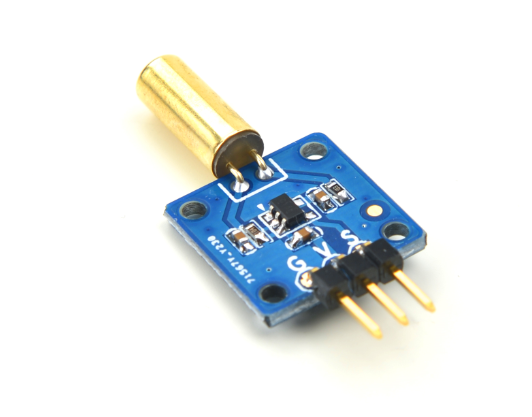
- The Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch module is a ball switch. Its electrical characteristics are very similar to a mercury switch's however a mercury switch is easily broken, oxidized, leaking and not environment-friendly. This ball switch prevents all these issues.
- The switch is free to move any angle and if that angle is between 15 degrees and 45 degrees a signal will be generated and used as an input to a Schmitt trigger.
2 Features
- GPIO
- Small
- 2.54 mm spacing pin header
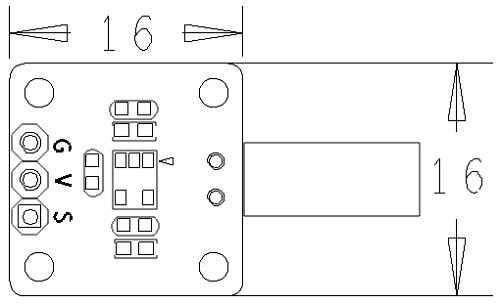
- PCB Dimension(mm):16 x 16
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| S | Digital GPIO |
| V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| G | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
Please connect Pin V to a power supply, Pin G grounded and Pin S to a digital output. When you move the switch pushing the internal metal ball to connect the trigger point a high level signal will be generated and output to a Schmitt trigger which reverses this signal to output a low level signal. When you move the switch pushing the internal metal ball away from the trigger point a low level signal will be generated and output to a Schmitt trigger which reverses this signal to output a high level signal.
4 Applications
4.1 Connect to NanoPi M1
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:
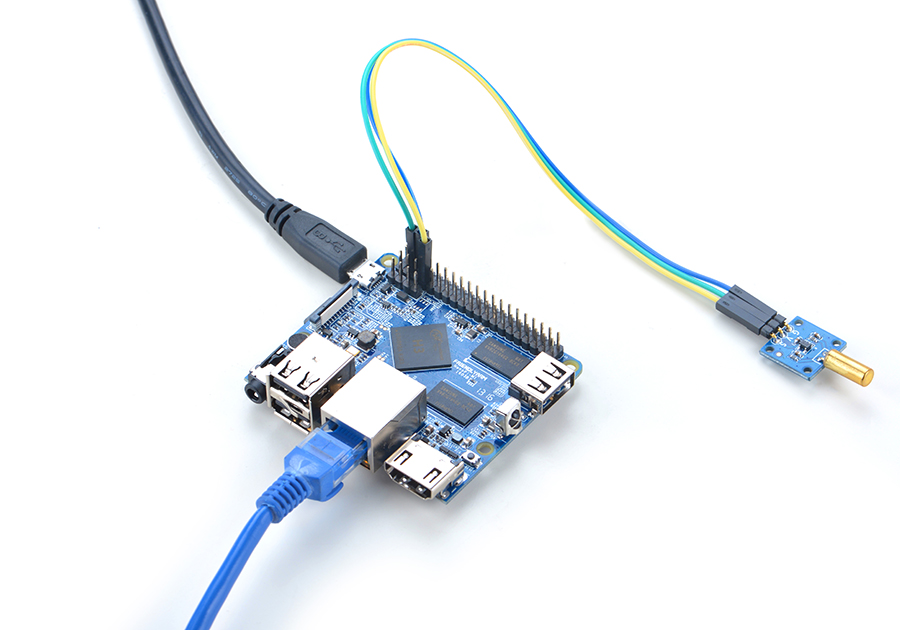
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch | NanoPi M1 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.2 Connect to NanoPi 2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch | NanoPi 2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
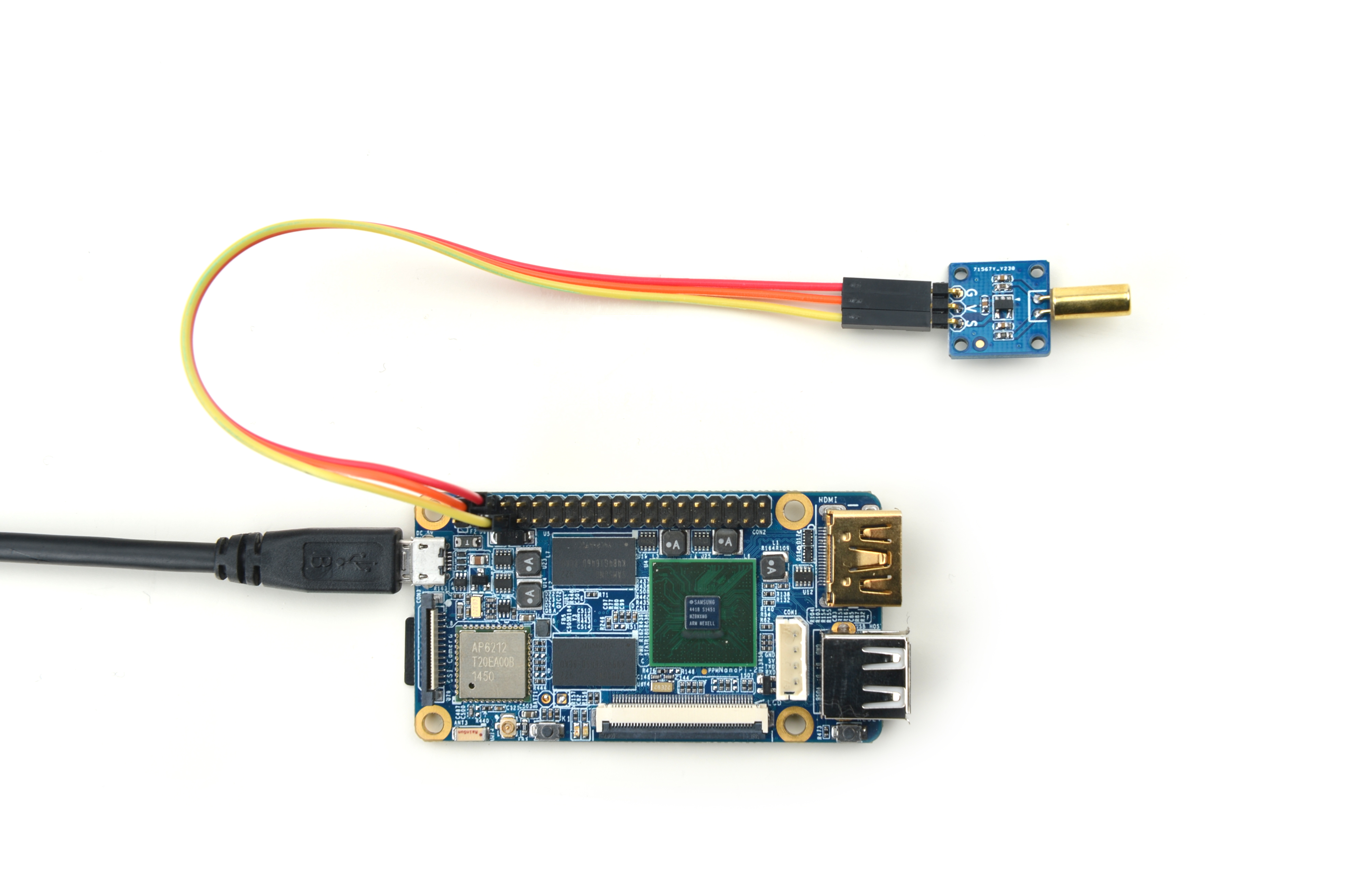
4.3 Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire.
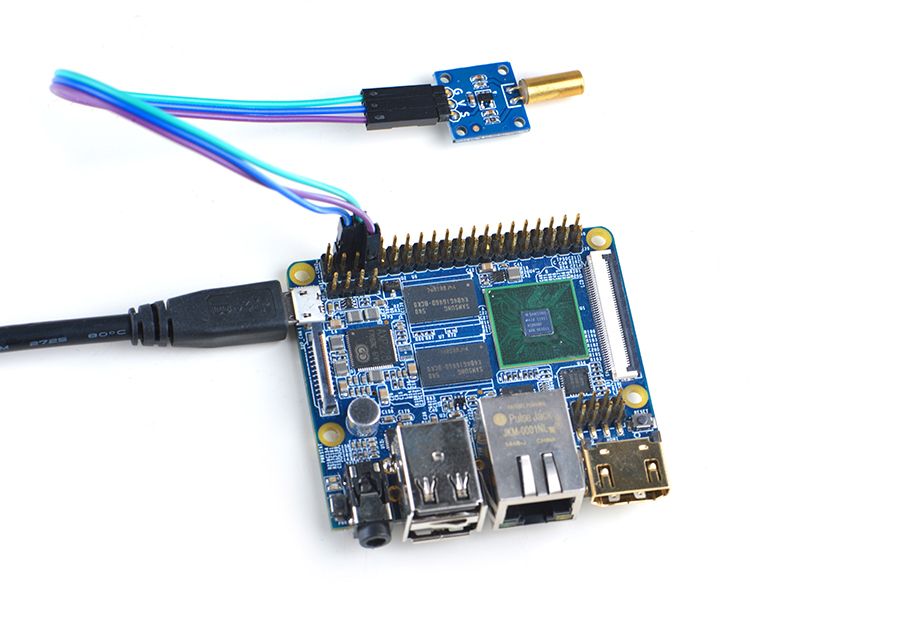
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch | NanoPi M2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.4 Connect to NanoPC-T2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:
Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch_NanoPC-T2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-Ball_Rolling_Switch | NanoPC-T2 |
| S | Pin15 |
| V | Pin29 |
| G | Pin30 |
5 Compile & Run Test Program
Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code:
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated.
Compile and install Matrix:
$ cd matrix $ make && make install
Run test program:
$ matrix-gpio_intNote: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.
Here is what you should observe:
Waiting event... Device[0] value is 1
When you tilt the module, roll the ball and make it touch the trigger point you will see an event is detected.
6 Code Sample
This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-gpio_int". Here is its source code:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int i, board; int retSize = -1; char value[ARRAY_SIZE(dev)]; if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) printf("Fail to init board\n"); if (argc == 2) { dev[0].pin = atoi(argv[1]); } printf("Using GPIO_PIN(%d)\n", dev[0].pin); system("modprobe "DRIVER_MODULE); signal(SIGINT, intHandler); if (board == BOARD_NANOPI_T2) dev[0].pin = GPIO_PIN(15); if ((devFD =sensorInit(dev, ARRAY_SIZE(dev))) == -1) { printf("Fail to init sensor\n"); return -1; } printf("Waiting event...\n"); if ((retSize = sensorRead(devFD, value, ARRAY_SIZE(dev))) == -1) { printf("Fail to read sensors\n"); } if (retSize > 0) { i = 0; for (i=0; i<retSize; i++) { printf("dev[%d] value: %d\n", i, value[i]); } } sensorDeinit(devFD); system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); return 0; }
For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to Matrix API reference manual
7 Resources
- [Schematic](Matrix - Ball Rolling Switch-Schematic.pdf)
8 Update Log
8.1 Feb-24-2016
- Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2
8.2 June-17-2016
- Re-organized and simplified wiki