|
|
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| | ==介绍== | | ==介绍== |
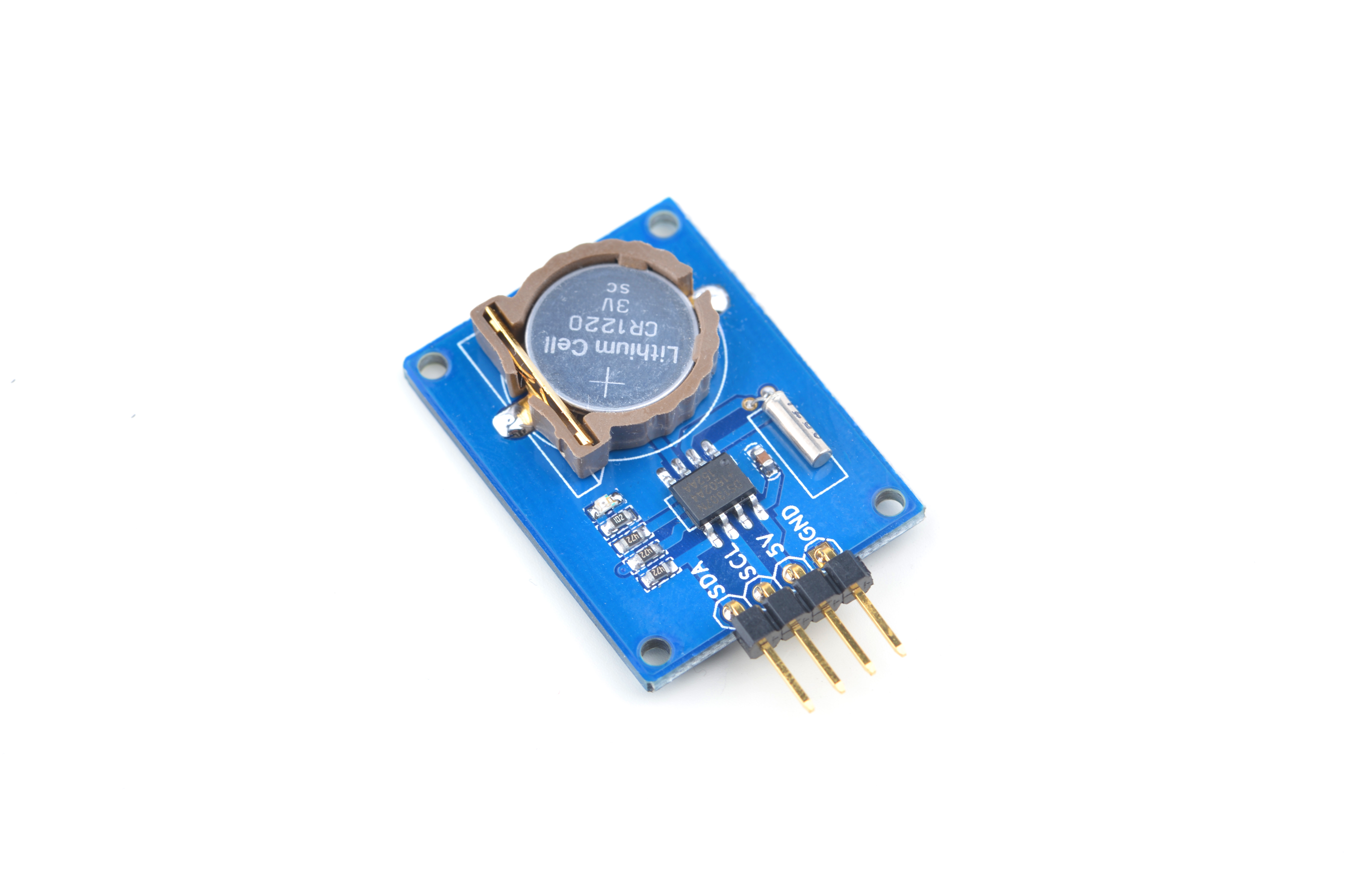
| | [[File:Matrix-RTC.png|thumb|]] | | [[File:Matrix-RTC.png|thumb|]] |
| − | *Matrix - RTC模块是一个实时时钟模块,使用专用低功耗时钟芯片DS1307和32.768KHz晶振。地址和数据通过I2C总线传输,能够提供秒、分、小时、星期、日期、月和年等时钟日历数据。每一个月的天数能自动调整,并且有闰年补偿功能。后备电池确保存储在时钟芯片非易失性RAM的数据在模块断电的时候不丢失。 | + | *DS1307串行实时时钟是一种低功耗,完整的二进制编码的十进制(BCD)时钟/日历加56位字节的NV SRAM。地址和数据通过IIC串行传输,双向总线。 |
| | + | *时钟/日历提供秒、分、时、日、星期、月和年的信息。月的最后一天自动调整月的日数少于31天,包括闰年的修正。时钟运行24小时或者12小时格式与AM/PM指标。 |
| | | | |
| | ==特性== | | ==特性== |
| − | * 低功耗 | + | * I2C串口接口 |
| − | * I2C串行接口 | + | * 56字节、电池支持、通用的RAM和无限写道 |
| − | * 56字节非失性的RAM | + | * 8-Pin DIP和8-Pin SO |
| − | * 自动掉电检测和切换
| + | |
| | * 操作温度在-40度到85度 | | * 操作温度在-40度到85度 |
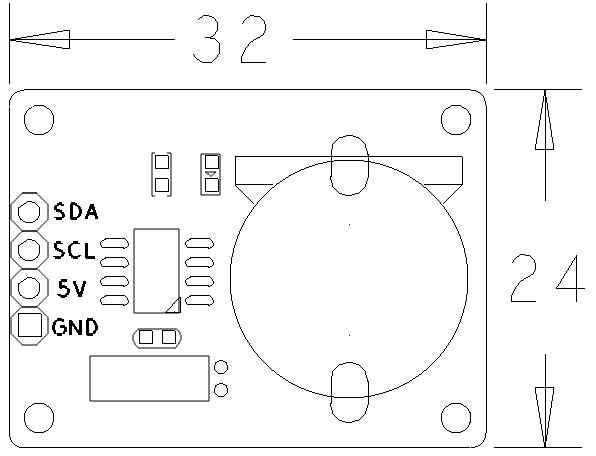
| | * PCB尺寸(mm):24x32 | | * PCB尺寸(mm):24x32 |
| Line 28: |
Line 28: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ==工作原理== | + | ==硬件连接== |
| − | * DS1307是一款专用低功耗,具有56字节非失性RAM的全BCD码时钟日历实时时钟芯片。
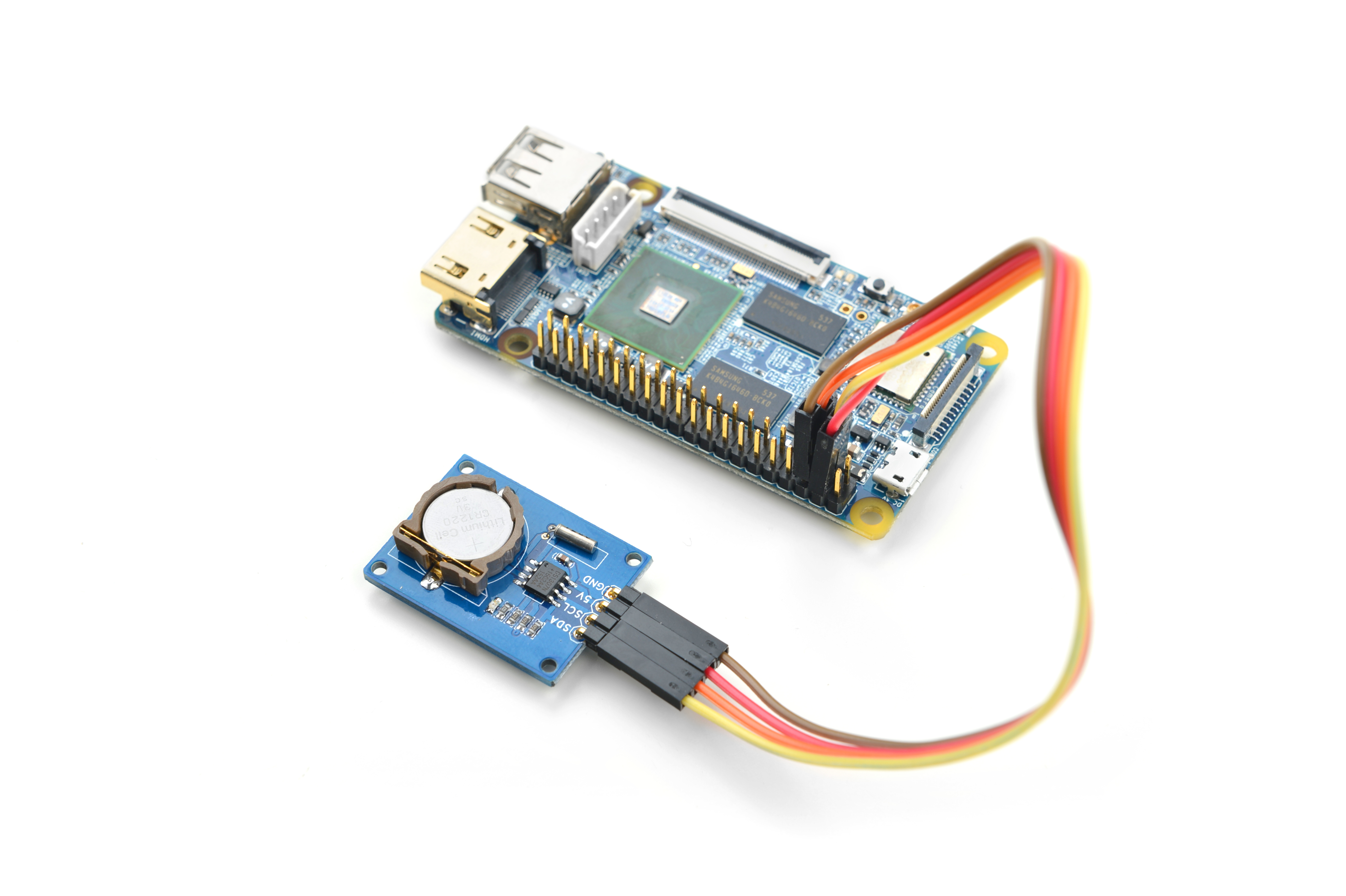
| + | ===连接NanoPi NEO/NanoPi NEO Air=== |
| − | *DS1307的寄存器统一编址,DS1307的各类时间数据均以BCD码的格式存储在相应的时间寄存器中,具体分配为:00H:秒;01H:分;02H:小时;03H:星期;04H:日期;05H:月;06H:年;07H:控制字。
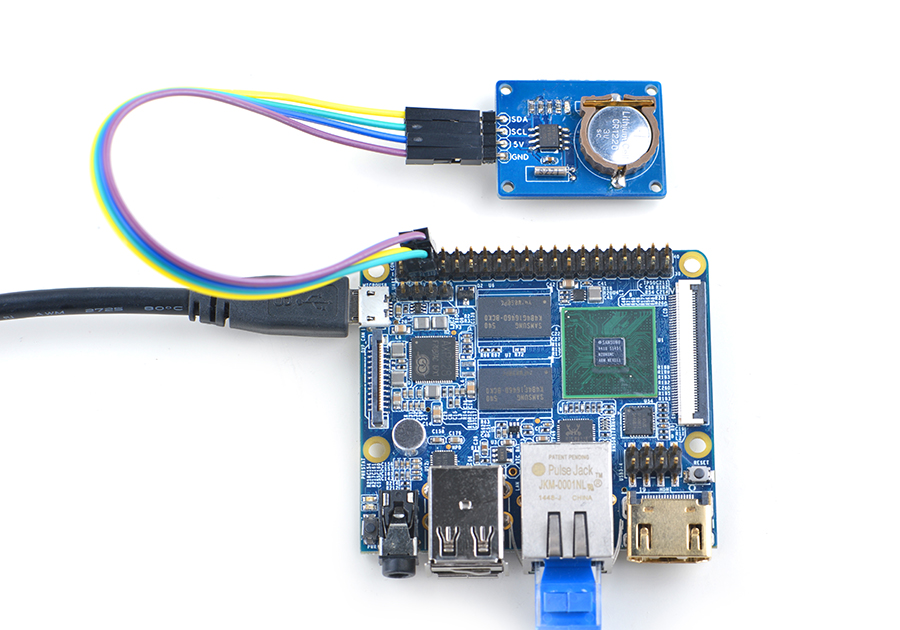
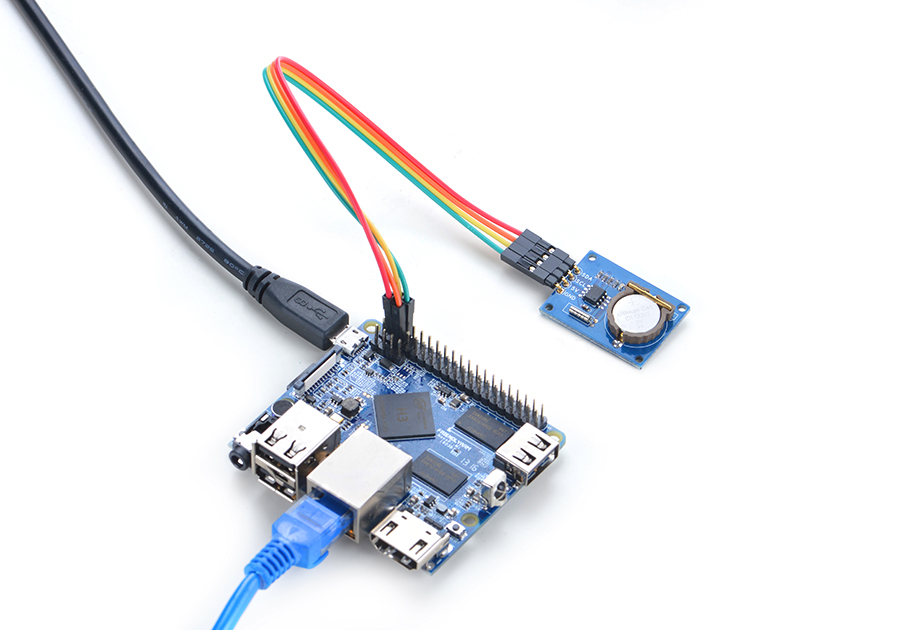
| + | NanoPi M1和NanoPi NEO以及NanoPi NEO Air的前24Pin引脚定义是一模一样的,所以它们操作Matrix配件的步骤是一样的,并且使用同一份代码。<br> |
| − | *具有掉电保护的RAM寄存器的地址编码为08H-3FH。AM/PM 标志位决定时钟工作于24小时或12小时模式。
| + | |
| − | *DS1307在IIC总线上是从器件,地址固定为”11010000”。通过读写对应的寄存器可获取或设置时间和日期信息,星期信息在午夜调整,并且星期信息可以用户自定义(例如1代表星期天,2就代表星期一)
| + | |
| − | *设置不符合规则的时间和日期数据会导致未知的错误。
| + | |
| − | *设置DS1307控制寄存器可用来控制SQW/OWT引脚的输出,从而控制模块上的LED状态。
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ==下载Matrix源码==
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> |
| − | Matrix配件相关的代码是完全开源的,统一由一个仓库进行管理:https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br>
| + | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_NEO]] |
| − | 该仓库里不同的分支代表着Matrix配件所支持的不同开发板。<br>
| + | |
| − | * nanopi分支用于支持NanoPi;
| + | |
| − | * nanopi2分支用于支持NanoPi 2;
| + | |
| − | * tiny4412分支用于支持Tiny4412;
| + | |
| − | * raspberrypi分支用于支持RaspberryPi;
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | 在主机PC上安装git,以Ubuntu14.04为例
| + | 连接说明: |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | $ sudo apt-get install git
| + | |- |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPi NEO |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |SDA || Pin3 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |SCL || Pin5 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |5V || Pin4 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |GND || Pin6 |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | 克隆Matrix配件代码仓库
| + | ===连接NanoPi M1=== |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> |
| − | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
| + | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_m1]] |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 克隆完成后会得到一个名为matrix的目录,里面存放着所有Matrix配件的代码。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==与NanoPi 2连接使用== | + | |
| − | ===硬件连接===
| + | |
| − | 参考下图连接模块Matrix-RTC和NanoPi 2:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_2]] | + | |
| | | | |
| | 连接说明: | | 连接说明: |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPi 2 | + | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPi M1 |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |SDA || Pin3 | | |SDA || Pin3 |
| Line 74: |
Line 67: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ===编译测试程序=== | + | ===连接NanoPi 2=== |
| − | 进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到nanopi2分支
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_2]] |
| − | $ cd matrix
| + | |
| − | $ git checkout nanopi2
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 编译Matrix配件代码
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi 2配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3。<br>
| + | |
| − | 编译成功后库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-RTC对应的测试程序为matrix-rtc。<br>
| + | |
| − | 硬件驱动模块位于modules目录下,对应的驱动源码都包含在在NanoPi 2的Linux内核仓库里:https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git <br>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===运行测试程序===
| + | |
| − | 将带有Debian系统的SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs分区。<br>
| + | |
| − | 假设rootfs分区的挂载路径为/media/rootfs,执行以下命令将Matrix的硬件驱动、库文件和测试程序拷贝到NanoPi 2的文件系统上。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r
| + | |
| − | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d
| + | |
| − | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 将SD卡重新插入NanoPi 2,上电启动,在Debian的shell终端中执行以下命令加载硬件驱动。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ cd /modules
| + | |
| − | $ insmod rtc-ds1307.ko
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 运行模块Matrix-RTC的测试程序。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ matrix-rtc
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br>
| + | |
| − | 运行效果:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:matrix-rtc_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-rtc_result]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 该程序只是读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01":
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ date -s "2016-11-17 17:26:01"
| + | |
| − | $ hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc1
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 设置完成后,就算重启系统,时间仍然是准确的。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===代码展示===
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="c">
| + | |
| − | int main(int argc, char **argv)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | int fd, retval;
| + | |
| − | struct rtc_time rtc_tm;
| + | |
| − | const char *rtc = default_rtc;
| + | |
| − | const char *date_time = default_date_time;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | switch (argc) {
| + | |
| − | case 3:
| + | |
| − | rtc = argv[1];
| + | |
| − | date_time = argv[2];
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | case 1:
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | default:
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "usage: rtctest [rtcdev] [year mon day hour min sec]\n");
| + | |
| − | return 1;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fd = open(rtc, O_RDONLY);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | if (fd == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror(rtc);
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "RTC Driver Test Example.\n");
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | sscanf(date_time, "%d %d %d %d %d %d",
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_year,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mon,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mday,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_hour,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_min,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_year -= 1900;
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon -= 1;
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_SET_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_SET_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Set RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | /* Read the RTC time/date */
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_RD_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_RD_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Read RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Test complete\n");
| + | |
| − | close(fd);
| + | |
| − | return 0;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==与NanoPi M2连接使用==
| + | |
| − | ===硬件连接===
| + | |
| − | 参考下图连接模块Matrix-RTC和NanoPi M2:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_M2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_M2]] | + | |
| | | | |
| | 连接说明: | | 连接说明: |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPi M2 | + | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPi 2 |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |SDA || Pin3 | | |SDA || Pin3 |
| Line 205: |
Line 85: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ===编译测试程序=== | + | ===连接NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire=== |
| − | 进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到nanopi_M2分支
| + | NanoPi M2和NanoPi 2 Fire的40 Pin引脚定义是一模一样的,所以它们操作Matrix配件的步骤是一样的,这里仅以NanoPi M2为例。<br> |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> |
| − | $ cd matrix
| + | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_M2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_M2]] |
| − | $ git checkout nanopi_M2
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 编译Matrix配件代码
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi M2配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3。<br>
| + | |
| − | 编译成功后库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-RTC对应的测试程序为matrix-rtc。<br>
| + | |
| − | 硬件驱动模块位于modules目录下,对应的驱动源码都包含在在NanoPi 2的Linux内核仓库里:https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git <br>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===运行测试程序===
| + | |
| − | 将带有Debian系统的SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs分区。<br>
| + | |
| − | 假设rootfs分区的挂载路径为/media/rootfs,执行以下命令将Matrix的硬件驱动、库文件和测试程序拷贝到NanoPi M2的文件系统上。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r
| + | |
| − | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d
| + | |
| − | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 将SD卡重新插入NanoPi M2,上电启动,在Debian的shell终端中执行以下命令加载硬件驱动。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ cd /modules
| + | |
| − | $ insmod rtc-ds1307.ko
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 运行模块Matrix-RTC的测试程序。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ matrix-rtc
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br>
| + | |
| − | 运行效果:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:matrix-rtc_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-rtc_result]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 该程序只是读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01":
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ date -s "2016-11-17 17:26:01"
| + | |
| − | $ hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc1
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 设置完成后,就算重启系统,时间仍然是准确的。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===代码展示===
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="c">
| + | |
| − | int main(int argc, char **argv)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | int fd, retval;
| + | |
| − | struct rtc_time rtc_tm;
| + | |
| − | const char *rtc = default_rtc;
| + | |
| − | const char *date_time = default_date_time;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | switch (argc) {
| + | |
| − | case 3:
| + | |
| − | rtc = argv[1];
| + | |
| − | date_time = argv[2];
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | case 1:
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | default:
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "usage: rtctest [rtcdev] [year mon day hour min sec]\n");
| + | |
| − | return 1;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fd = open(rtc, O_RDONLY);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | if (fd == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror(rtc);
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "RTC Driver Test Example.\n");
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | sscanf(date_time, "%d %d %d %d %d %d",
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_year,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mon,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mday,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_hour,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_min,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_year -= 1900;
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon -= 1;
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_SET_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_SET_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Set RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | /* Read the RTC time/date */
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_RD_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_RD_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Read RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Test complete\n");
| + | |
| − | close(fd);
| + | |
| − | return 0;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==与NanoPC-T2连接使用==
| + | |
| − | ===硬件连接===
| + | |
| − | 参考下图连接模块Matrix-RTC和NanoPC-T2:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Matrix-RTC_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_NanoPC-T2]] | + | |
| | | | |
| | 连接说明: | | 连接说明: |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPC-T2 | + | | || NanoPi M2 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |SDA || Pin6 | + | |SDA || Pin3 |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |SCL || Pin5 | | |SCL || Pin5 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |5V || Pin29 | + | |5V || Pin4 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |GND || Pin30 | + | |GND || Pin6 |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ===编译测试程序=== | + | ===连接NanoPi M3=== |
| − | 进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到NanoPC-T2分支
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi_M3.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi_M3]] |
| − | $ cd matrix
| + | |
| − | $ git checkout NanoPC-T2
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 编译Matrix配件代码
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
| + | |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi M2配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3。<br>
| + | |
| − | 编译成功后库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-RTC对应的测试程序为matrix-rtc。<br>
| + | |
| − | 硬件驱动模块位于modules目录下,对应的驱动源码都包含在在NanoPC-T2的Linux内核仓库里:https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git <br>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===运行测试程序===
| + | |
| − | 将带有Debian系统的SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs分区。<br>
| + | |
| − | 假设rootfs分区的挂载路径为/media/rootfs,执行以下命令将Matrix的硬件驱动、库文件和测试程序拷贝到NanoPC-T2的文件系统上。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r
| + | |
| − | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d
| + | |
| − | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 将SD卡重新插入NanoPC-T2,上电启动,在Debian的shell终端中执行以下命令加载硬件驱动。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ cd /modules
| + | |
| − | $ insmod rtc-ds1307.ko
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 运行模块Matrix-RTC的测试程序。<br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ matrix-rtc
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br>
| + | |
| − | 运行效果:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:matrix-rtc_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-rtc_result]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 该程序只是读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01":
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ date -s "2016-11-17 17:26:01"
| + | |
| − | $ hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc1
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 设置完成后,就算重启系统,时间仍然是准确的。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===代码展示===
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="c">
| + | |
| − | int main(int argc, char **argv)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | int fd, retval;
| + | |
| − | struct rtc_time rtc_tm;
| + | |
| − | const char *rtc = default_rtc;
| + | |
| − | const char *date_time = default_date_time;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | switch (argc) {
| + | |
| − | case 3:
| + | |
| − | rtc = argv[1];
| + | |
| − | date_time = argv[2];
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | case 1:
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | default:
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "usage: rtctest [rtcdev] [year mon day hour min sec]\n");
| + | |
| − | return 1;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fd = open(rtc, O_RDONLY);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | if (fd == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror(rtc);
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "RTC Driver Test Example.\n");
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | sscanf(date_time, "%d %d %d %d %d %d",
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_year,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mon,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mday,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_hour,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_min,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_year -= 1900;
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon -= 1;
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_SET_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_SET_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Set RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | /* Read the RTC time/date */
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_RD_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_RD_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Read RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Test complete\n");
| + | |
| − | close(fd);
| + | |
| − | return 0;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==与NanoPi连接使用==
| + | |
| − | 在NanoPi上运行Debian系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器,参考wiki: [[NanoPi/zh|NanoPi]] & [[How_to_build_the_Compiling_Environment/zh|How to Build the Compiling Environment]]。<br>
| + | |
| − | 注意: 只有使用nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix分支编译出来的内核才能配合Matrix配件正常工作。<br>
| + | |
| − | 下载NanoPi内核源代码并编译: <br>
| + | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | |
| − | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-4.x.y.git
| + | |
| − | $ cd linux-4.x.y
| + | |
| − | $ git checkout nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix
| + | |
| − | $ make nanopi_defconfig
| + | |
| − | $ touch .scmversion
| + | |
| − | $ make
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| − | 编译好后的zImage位于内核源码arch/arm/boot/目录下,把该zImage替换掉NanoPi烧写文件sd-fuse_nanopi/prebuilt下的zImage,重新制作SD卡即可。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===硬件连接===
| + | |
| − | 参考下图连接模块Matrix-RTC和NanoPi:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Matrix-RTC_nanopi.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_nanopi]] | + | |
| | | | |
| | 连接说明: | | 连接说明: |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPi | + | | || NanoPi M3 |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |SDA || Pin3 | | |SDA || Pin3 |
| Line 480: |
Line 122: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ===编译测试程序=== | + | ===连接NanoPC-T2=== |
| − | 进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到nanopi分支
| + | 参考下图连接模块:<br> |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | + | [[File:Matrix-RTC_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_NanoPC-T2]] |
| − | $ cd matrix
| + | |
| − | $ git checkout nanopi
| + | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | 编译Matrix配件代码
| + | 连接说明: |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
| + | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean
| + | |- |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
| + | |Matrix-RTC || NanoPC-T2 |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
| + | |- |
| − | </syntaxhighlight>
| + | |SDA || Pin6 |
| − | 注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi-Debian配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3。<br>
| + | |- |
| − | 编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-RTC对应的测试程序为matrix-rtc。<br>
| + | |SCL || Pin5 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |5V || Pin29 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |GND || Pin30 |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ===运行测试程序=== | + | ==H3平台== |
| − | 将带有Debian系统的SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs分区。<br>
| + | ===Linux-4.14 / Linux-3.4=== |
| − | 假设rootfs分区的挂载路径为/media/rootfs,执行以下命令将Matrix的硬件驱动、库文件和测试程序拷贝到NanoPi的文件系统上。<br>
| + | ====C程序读写RTC==== |
| | + | 启动开发板,进入系统后克隆Matrix代码仓库: |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r | + | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git |
| − | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git |
| − | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/ | + | |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | + | 克隆完成后会得到一个名为matrix的目录。 |
| | | | |
| − | 将SD卡重新插入NanoPi,上电启动,在Debian的shell终端中执行以下命令加载硬件驱动。<br>
| + | 编译并安装Matrix: |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | $ cd /modules | + | $ cd matrix |
| − | $ insmod rtc-ds1307.ko | + | $ make && make install |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | 运行模块Matrix-RTC的测试程序。<br>
| + | 运行测试程序: |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | $ matrix-rtc | | $ matrix-rtc |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br> | | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br> |
| − | | + | 运行效果如下:<br> |
| − | 运行效果:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:matrix-rtc_nanopi1_shell.png|frameless|400px|matrix-rtc_nanopi1_shell]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 该程序只是简单的读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01":
| + | |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | $ date -s "2016-11-17 17:26:01"
| + | RTC Driver Test Example. |
| − | $ hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc1
| + | Set RTC date/time is 9-15-2015, 01:01:01. |
| | + | Read RTC date/time is 9-15-2015, 01:01:01. |
| | + | Test complete |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | 设置完成后,就算重启系统,时间仍然是准确的。
| + | 该程序只是简单的读写硬件RTC |
| | | | |
| − | ===代码展示=== | + | ====使用hwclock命令读写RTC==== |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | + | * 读取当前时间 |
| − | int main(int argc, char **argv)
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | {
| + | $ sudo modprobe rtc-ds1307 |
| − | int fd, retval;
| + | sudo hwclock -r -f /dev/rtc-ds1307 |
| − | struct rtc_time rtc_tm;
| + | |
| − | const char *rtc = default_rtc;
| + | |
| − | const char *date_time = default_date_time;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | switch (argc) {
| + | |
| − | case 3:
| + | |
| − | rtc = argv[1];
| + | |
| − | date_time = argv[2];
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | case 1:
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | default:
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "usage: rtctest [rtcdev] [year mon day hour min sec]\n");
| + | |
| − | return 1;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fd = open(rtc, O_RDONLY);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | if (fd == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror(rtc);
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "RTC Driver Test Example.\n");
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | sscanf(date_time, "%d %d %d %d %d %d",
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_year,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mon,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mday,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_hour,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_min,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_year -= 1900;
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon -= 1;
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_SET_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_SET_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Set RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | /* Read the RTC time/date */
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_RD_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_RD_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Read RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Test complete\n");
| + | |
| − | close(fd);
| + | |
| − | return 0;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | ==与Tiny4412连接使用==
| + | * 设置时间并保存 |
| − | ===准备工作===
| + | |
| − | 参考Tiny4412光盘里的《友善之臂Ubuntu使用手册》,在Tiny4412上运行UbuntuCore系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。<br>
| + | |
| − | 注意:只能使用Tiny4412SDK-1506的底板。
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===硬件连接===
| + | |
| − | 参考下图连接模块Matrix-RTC和Tiny4412:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:Matrix-RTC_tiny4412.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-RTC_tiny4412]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 连接说明:
| + | |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Matrix-RTC || Tiny4412
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |SDA || CON18 SDA
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |SCL || CON18 SCL
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5V || CON18 5V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |GND || CON18 GND
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===编译测试程序===
| + | |
| − | 进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到tiny4412分支
| + | |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | $ cd matrix
| + | sudo date -s "2019-10-09 17:00:00" |
| − | $ git checkout tiny4412
| + | sudo hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc-ds1307 |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | 编译Matrix配件代码
| + | ==S5P4418/S5P6818平台== |
| | + | 启动开发板,进入系统后克隆Matrix代码仓库: |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean | + | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- | + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git |
| − | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- install
| + | |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | 注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为Tiny4412-UbuntuCore配套的arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-4.7.3。<br>
| + | 克隆完成后会得到一个名为matrix的目录。 |
| − | 编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-RTC对应的测试程序为matrix-rtc。
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | ===运行测试程序===
| + | 编译并安装Matrix: |
| − | 将带有UbuntuCore系统的SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs分区。<br>
| + | |
| − | 假设rootfs分区的挂载路径为/media/rootfs,执行以下命令可将Matrix的所有库文件和测试程序拷贝到Tiny4412的文件系统上。<br>
| + | |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/ | + | $ cd matrix |
| − | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d | + | $ make && make install |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | 将SD卡重新插入Tiny4412,上电启动,在UbuntuCore的shell终端中执行以下命令运行模块Matrix-RTC的测试程序。<br>
| + | 运行测试程序: |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | $ matrix-rtc | | $ matrix-rtc |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。 | + | 注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件连接正确。<br> |
| − | | + | 运行效果如下:<br> |
| − | 运行效果:<br>
| + | |
| − | [[File:matrix-rtc_tiny4412_shell.png|frameless|400px|matrix-rtc_tiny4412_shell]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | 该程序只是简单的读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01":
| + | |
| | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | + | RTC Driver Test Example. |
| | + | Set RTC date/time is 9-15-2015, 01:01:01. |
| | + | Read RTC date/time is 9-15-2015, 01:01:01. |
| | + | Test complete |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | + | 该程序只是简单的读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间并将其保持在Matrix-RTC模块里,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01": |
| | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| | + | $ modprobe rtc-ds1307 |
| | $ date -s "2016-11-17 17:26:01" | | $ date -s "2016-11-17 17:26:01" |
| − | $ hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc1 | + | $ hwclock -w -f /dev/rtc-ds1307 |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − | 设置完成后,就算重启系统,时间仍然是准确的。
| + | 然后修改/etc/modprobe.d/matrix-blacklist.conf,在"blacklist rtc_ds1307"前加上一个#,表示注释该行,这样下次开机就会自动加载驱动了。<br> |
| − | | + | 重启系统,可以看到时间仍然是准确的: |
| − | ===代码展示===
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="c">
| + | $ hwclock -r -f /dev/rtc-ds1307 |
| − | static const char default_rtc[] = "/dev/rtc0";
| + | 2016年11月18日 星期五 08时29分48秒 -0.492649 seconds |
| − | static const char default_date_time[] = "2015 9 15 1 1 1";
| + | |
| − | int main(int argc, char **argv)
| + | |
| − | {
| + | |
| − | int fd, retval;
| + | |
| − | struct rtc_time rtc_tm;
| + | |
| − | const char *rtc = default_rtc;
| + | |
| − | const char *date_time = default_date_time;
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | switch (argc) {
| + | |
| − | case 3:
| + | |
| − | rtc = argv[1];
| + | |
| − | date_time = argv[2];
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | case 1:
| + | |
| − | break;
| + | |
| − | default:
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "usage: rtctest [rtcdev] [year mon day hour min sec]\n");
| + | |
| − | return 1;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fd = open(rtc, O_RDONLY);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | if (fd == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror(rtc);
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "RTC Driver Test Example.\n");
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | sscanf(date_time, "%d %d %d %d %d %d",
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_year,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mon,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_mday,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_hour,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_min,
| + | |
| − | &rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_year -= 1900;
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon -= 1;
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_SET_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_SET_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Set RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | /* Read the RTC time/date */
| + | |
| − | retval = ioctl(fd, RTC_RD_TIME, &rtc_tm);
| + | |
| − | if (retval == -1) {
| + | |
| − | perror("RTC_RD_TIME ioctl");
| + | |
| − | exit(errno);
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Read RTC date/time is %d-%d-%d, %02d:%02d:%02d.\n",
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_mon + 1, rtc_tm.tm_mday, rtc_tm.tm_year + 1900,
| + | |
| − | rtc_tm.tm_hour, rtc_tm.tm_min, rtc_tm.tm_sec);
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | fprintf(stderr, "Test complete\n");
| + | |
| − | close(fd);
| + | |
| − | return 0;
| + | |
| − | }
| + | |
| | </syntaxhighlight> | | </syntaxhighlight> |
| − |
| |
| − | ==与RaspberryPi连接使用==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==与Arduino连接使用==
| |
| | | | |
| | ==相关资料== | | ==相关资料== |
| | [http://datasheets.maximintegrated.com/en/ds/DS1307.pdf DS1307.pdf] | | [http://datasheets.maximintegrated.com/en/ds/DS1307.pdf DS1307.pdf] |
NanoPi M1和NanoPi NEO以及NanoPi NEO Air的前24Pin引脚定义是一模一样的,所以它们操作Matrix配件的步骤是一样的,并且使用同一份代码。
该程序只是简单的读写硬件RTC,如果想设置Debian的系统时间并将其保持在Matrix-RTC模块里,可执行以下命令,假设当前时间为"2016-11-17 17:26:01":
然后修改/etc/modprobe.d/matrix-blacklist.conf,在"blacklist rtc_ds1307"前加上一个#,表示注释该行,这样下次开机就会自动加载驱动了。
重启系统,可以看到时间仍然是准确的: