Difference between revisions of "Matrix - IR Receiver"
(Created page with "English ==介绍== IR Receiver IR Receiver IR Receiver Matrix-IR Receiver是38KHz红外...") |
(→Update Log) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Matrix - | + | [[Matrix - IR Receiver/zh|查看中文]] |
| − | == | + | ==Introduction== |
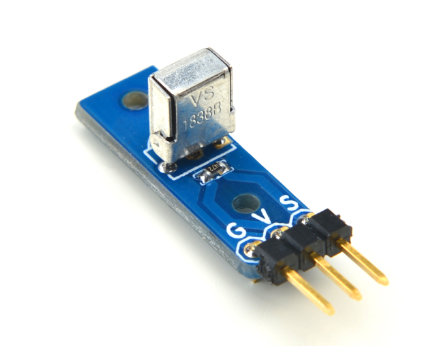
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:IR Receiver01.png|thumb|IR Receiver]] |
| − | + | * The Matrix-IR receiver is a 38KHz infrared receiver that receives 38KHz signals from an infrared remote control, amplifies and filers them to other devices. Its signal decoding is implemented by programming MCU. | |
| − | + | * Transmission distance: 12 ~ 13 meters. | |
| − | Matrix-IR | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ==Features== |
| − | * | + | * GPIO control, 3.3/5V |
| − | * | + | * Small |
| − | * 2. | + | * 2.54mm spacing pin header |
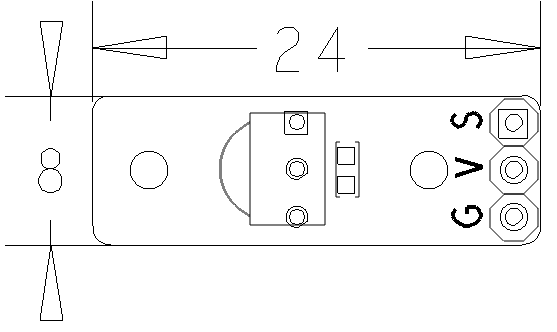
| − | * | + | * PCB Dimension(mm): 8 x 24 |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:IR Receiver.png | frameless|400px|IR Receiver.PCB]] |
| − | * | + | * Pin Description: |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Pin || Description |
|- | |- | ||
|S || GPIO | |S || GPIO | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |V || | + | |V || Supply Voltage 5V |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |G || | + | |G || Ground |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Basic Device Operation== | ||
| + | *The IR receiver contains a photo diode, amplifier, band pass filter, integrator, hysteresis comparator and etc. When the IR receiver detects infrared signals it sends them to the preamplifier and band pass filter. After the signals are processed by the band pass filter (30KHz ~ 60KHz) they will be further processed by the integrator and comparator and finally be output as High or Low. | ||
| + | *Note: the output signal is the reversal of the input signal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Applications== | ||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi M1=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_m1.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_m1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-IR_Receiver || NanoPi M1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |S || Pin7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |G || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi 2=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-IR_Receiver || NanoPi 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |S || Pin7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |G || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_m2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_m2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-IR_Receiver || NanoPi M2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |S || Pin7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |G || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Connect to NanoPC-T2=== | ||
| + | Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-IR_Receiver_NanoPC-T2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-IR_Receiver_NanoPC-T2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-IR_Receiver || NanoPC-T2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |S || Pin15 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |V || Pin29 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |G || Pin30 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Compile & Run Test Program== | ||
| + | Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ apt-get update && apt-get install git | ||
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compile and install Matrix: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd matrix | ||
| + | $ make && make install | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Run test program: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ matrix-ir_receiver | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Note: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.<br> | ||
| + | Here is what you should observe:<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | Press the IR remoter | ||
| + | 0: Type=4, Code=4, Value=3b0d | ||
| + | 1: Type=0, Code=0, Value=0 | ||
| + | 2: Type=4, Code=4, Value=3b12 | ||
| + | 3: Type=0, Code=0, Value=0 | ||
| + | 4: Type=4, Code=4, Value=3b15 | ||
| + | 5: Type=0, Code=0, Value=0 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | When you point our RC-100 controller to it and press any key on the controller an event will be detected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Code Sample== | ||
| + | This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-ir_receiver". Here is its source code: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
| + | int main(int argc, char ** argv) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int board, i, j; | ||
| + | int retSize = -1; | ||
| + | char *devName = GPIO_IR_DEV; | ||
| + | int pin = GPIO_PIN(7); | ||
| + | char modStr[BUF_SIZE]; | ||
| + | struct input_event evKey; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to init board\n"); | ||
| + | return -1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | if (board == BOARD_NANOPI_T2) | ||
| + | pin = GPIO_PIN(15); | ||
| + | |||
| + | sprintf(modStr, "modprobe %s gpio=%d", DRIVER_MODULE, pintoGPIO(pin)); | ||
| + | system(modStr); | ||
| + | signal(SIGINT, IRIntHandler); | ||
| + | sleep(1); | ||
| + | irFD = openHW(devName, O_RDWR); | ||
| + | if (irFD < 0) { | ||
| + | printf("Fail to open GPIO IR device\n"); | ||
| + | goto err; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | printf("Press the IR remoter\n"); | ||
| + | for (i=0; i<IR_EVENT_TIMES; i++) { | ||
| + | if (selectHW(irFD, 0, 0) == 1) { | ||
| + | retSize = readHW(irFD, &evKey, sizeof(struct input_event)); | ||
| + | for (j=0; j<(int) retSize / sizeof(struct input_event); j++) | ||
| + | printf("%2d: Type=%d, Code=%d, Value=%x\n", i, evKey.type, evKey.code, evKey.value); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | closeHW(irFD); | ||
| + | err: | ||
| + | system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to [[Matrix API reference manual]] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!--- | ||
| + | ==Download Matrix Source Code== | ||
| + | |||
| + | All the matrix modules' code samples are open source. They are maintained on GitHub: https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git <br> | ||
| + | Each branch in this hub contains the matrix modules' code samples for a board that the matrix modules can work with.<br> | ||
| + | * The matrix-nanopi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi | ||
| + | * The matrix-nanopi2 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the NanoPi 2 | ||
| + | * The matrix-tiny4412 branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the Tiny4412; | ||
| + | * The matrix-raspberrypi branch contains the matrix modules' code samples for the RaspberryPi; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Please follow the steps below to get the source code:<br> | ||
| + | Install the git utility on a PC running Ubuntu14.04 | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ sudo apt-get install git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Clone the matrix code from GitHub | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | If this is successful a "matrix" directory will be generated, which will contain all the matrix modules' code samples. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Connect to NanoPi 2== | ||
| + | ===Hardware Connection=== | ||
| + | Please refer to the following connection diagram to connect the Matrix-IR_Receiver to the NanoPi 2:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_2.jpg|frameless|600px|Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connection Details: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Matrix-IR_Receiver || NanoPi 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |S || Pin7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |V || Pin4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |G || Pin6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Compile Test Program=== | ||
| + | Please login the matrix hub and enter the nanopi2 branch | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd matrix | ||
| + | $ git checkout nanopi2 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compile the Matrix code | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean | ||
| + | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- | ||
| + | $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Note: please make sure to install the cross compiler "arm-linux-gcc-4.9.3" on your PC, which is used to compile files for the NanoPi 2.<br> | ||
| + | Generated library files are under the "install/lib" directory. The test program is under the "install/usr/bin" directory. <br> | ||
| + | The modules are under the "modules" directory. The driver's source code is in github: https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Run Test Program=== | ||
| + | Please insert a TF card which is flashed with Debian to a Linux host and mount its boot and rootfs sections.<br> | ||
| + | We assume the rootfs is mounted to /media/rootfs then please run the following commands to copy the module, library and test program to the card<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cp modules /media/rootfs/ -r | ||
| + | $ cp install/lib/* /media/rootfs/lib/ -d | ||
| + | $ cp install/usr/bin/* /media/rootfs/usr/bin/ | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Insert this TF card to your NanoPi 2, power on and run the following commands to load the driver<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ cd /modules | ||
| + | $ insmod matrix_ir_recv.ko | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | If the driver is successfully loaded a device node will be generated under /dev/input/. In our test case the node was event1.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is an open source utility "input-utils" which can be used to read the event device's data. Here is how it works:<br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ apt-get install input-utils | ||
| + | $ input-events 1 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 1 stands for device node "event1"<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can use a regular remote control to send signals to it. Here is what you expect to observe:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:matrix-ir_receiver_result.png|frameless|600px|matrix-ir_receiver_result]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Connect to NanoPi== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Connect to Tiny4412== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Connect to RaspberryPi== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Connect to Arduino== | ||
| + | ---> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Resources== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Update Log== | ||
| + | ===Feb-24-2016=== | ||
| + | * Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===June-21-2016=== | ||
| + | * Re-organized and simplified wiki | ||
Latest revision as of 01:31, 21 June 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
- The Matrix-IR receiver is a 38KHz infrared receiver that receives 38KHz signals from an infrared remote control, amplifies and filers them to other devices. Its signal decoding is implemented by programming MCU.
- Transmission distance: 12 ~ 13 meters.
2 Features
- GPIO control, 3.3/5V
- Small
- 2.54mm spacing pin header
- PCB Dimension(mm): 8 x 24
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| S | GPIO |
| V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| G | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
- The IR receiver contains a photo diode, amplifier, band pass filter, integrator, hysteresis comparator and etc. When the IR receiver detects infrared signals it sends them to the preamplifier and band pass filter. After the signals are processed by the band pass filter (30KHz ~ 60KHz) they will be further processed by the integrator and comparator and finally be output as High or Low.
- Note: the output signal is the reversal of the input signal.
4 Applications
4.1 Connect to NanoPi M1
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M1:
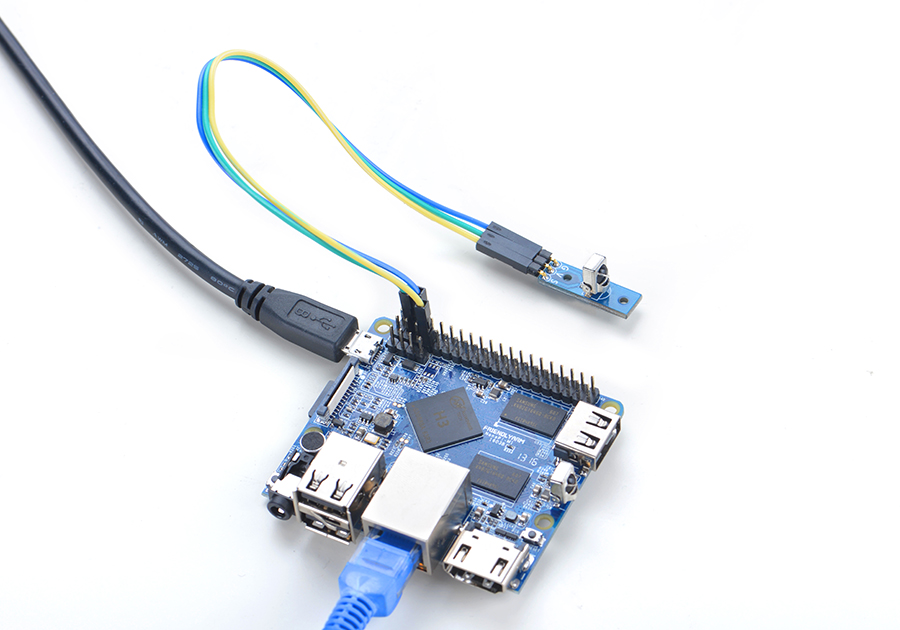
Connection Details:
| Matrix-IR_Receiver | NanoPi M1 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.2 Connect to NanoPi 2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi 2:
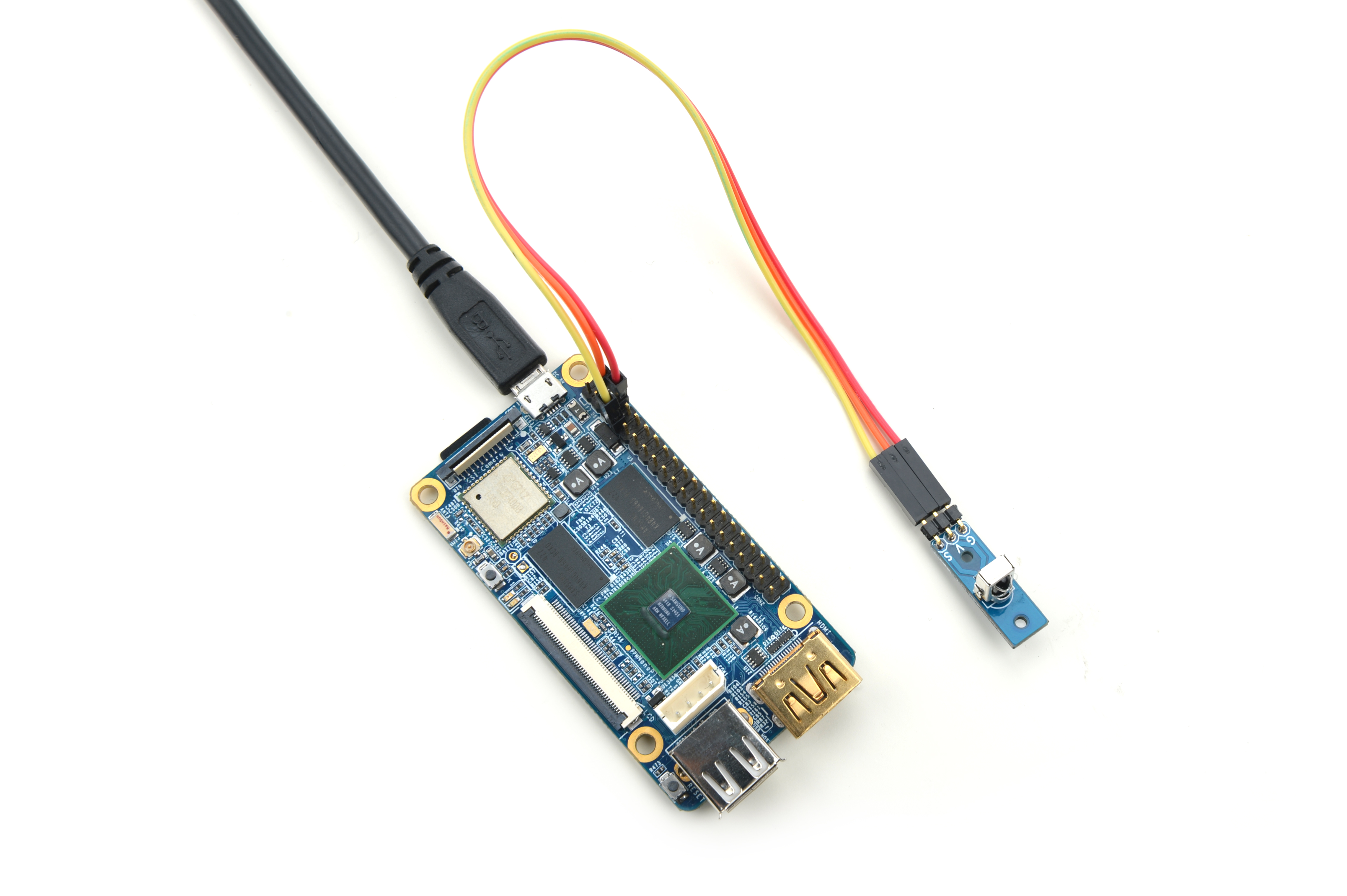

Connection Details
| Matrix-IR_Receiver | NanoPi 2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.3 Connect to NanoPi M2 / NanoPi 2 Fire
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPi M2/ NanoPi 2 Fire:
Matrix-IR_Receiver_nanopi_m2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-IR_Receiver | NanoPi M2 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
4.4 Connect to NanoPC-T2
Refer to the following connection diagram to connect the module to the NanoPC-T2:
Matrix-IR_Receiver_NanoPC-T2
Connection Details:
| Matrix-IR_Receiver | NanoPC-T2 |
| S | Pin15 |
| V | Pin29 |
| G | Pin30 |
5 Compile & Run Test Program
Boot your ARM board with Debian and copy the matrix code:
$ apt-get update && apt-get install git $ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
If your cloning is done successfully a "matrix" directory will be generated.
Compile and install Matrix:
$ cd matrix $ make && make install
Run test program:
$ matrix-ir_receiverNote: this module is not plug and play therefore before running the module please make sure it is connected to an ARM board.
Here is what you should observe:
Press the IR remoter 0: Type=4, Code=4, Value=3b0d 1: Type=0, Code=0, Value=0 2: Type=4, Code=4, Value=3b12 3: Type=0, Code=0, Value=0 4: Type=4, Code=4, Value=3b15 5: Type=0, Code=0, Value=0
When you point our RC-100 controller to it and press any key on the controller an event will be detected.
6 Code Sample
This Matrix code sample can work with all the ARM boards mentioned in this module's wiki. The name of this code sample is "matrix-ir_receiver". Here is its source code:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int board, i, j; int retSize = -1; char *devName = GPIO_IR_DEV; int pin = GPIO_PIN(7); char modStr[BUF_SIZE]; struct input_event evKey; if ((board = boardInit()) < 0) { printf("Fail to init board\n"); return -1; } if (board == BOARD_NANOPI_T2) pin = GPIO_PIN(15); sprintf(modStr, "modprobe %s gpio=%d", DRIVER_MODULE, pintoGPIO(pin)); system(modStr); signal(SIGINT, IRIntHandler); sleep(1); irFD = openHW(devName, O_RDWR); if (irFD < 0) { printf("Fail to open GPIO IR device\n"); goto err; } printf("Press the IR remoter\n"); for (i=0; i<IR_EVENT_TIMES; i++) { if (selectHW(irFD, 0, 0) == 1) { retSize = readHW(irFD, &evKey, sizeof(struct input_event)); for (j=0; j<(int) retSize / sizeof(struct input_event); j++) printf("%2d: Type=%d, Code=%d, Value=%x\n", i, evKey.type, evKey.code, evKey.value); } } closeHW(irFD); err: system("rmmod "DRIVER_MODULE); return 0; }
For more details about this APIs called in this code sample refer to Matrix API reference manual
7 Resources
8 Update Log
8.1 Feb-24-2016
- Added the driver's source code location in Section 5.2
8.2 June-21-2016
- Re-organized and simplified wiki