Difference between revisions of "Template:FriendlyWrt21"
(updated by API) |
(updated by API) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Work with FriendlyWrt== | ==Work with FriendlyWrt== | ||
===Introduction to FriendlyWrt=== | ===Introduction to FriendlyWrt=== | ||
| − | FriendlyWrt is a customized system made by FriendlyElec based on an OpenWrt distribution. It is open source and well suitable for developing IoT applications, NAS applications | + | FriendlyWrt is a customized system made by FriendlyElec based on an OpenWrt distribution. It is open source and well suitable for developing IoT applications, NAS applications etc.<br /> |
| − | + | ||
===First boot=== | ===First boot=== | ||
For the first boot, the system needs to do the following initialization work: <br /> | For the first boot, the system needs to do the following initialization work: <br /> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
root@FriendlyWrt | root@FriendlyWrt | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
===Account & Password=== | ===Account & Password=== | ||
The default password is password (empty password in some versions). Please set or change a safer password for web login and ssh login. It is recommended to complete this setting before connecting {{{1}}} to the Internet. | The default password is password (empty password in some versions). Please set or change a safer password for web login and ssh login. It is recommended to complete this setting before connecting {{{1}}} to the Internet. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Login FriendlyWrt=== | ===Login FriendlyWrt=== | ||
Connect the PC to the LAN port of {{{1}}}. If your PC without a built-in ethernet port, connect the LAN port of the wireless AP to the LAN port of {{{1}}}, and then connect your PC to the wireless AP via WiFi , Enter the following URL on your PC's browser to access the admin page: <br /> | Connect the PC to the LAN port of {{{1}}}. If your PC without a built-in ethernet port, connect the LAN port of the wireless AP to the LAN port of {{{1}}}, and then connect your PC to the wireless AP via WiFi , Enter the following URL on your PC's browser to access the admin page: <br /> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 18: | ||
* http://[fd00:ab:cd::1] | * http://[fd00:ab:cd::1] | ||
The above is the LAN port address of {{{1}}}. The IP address of the WAN port will be dynamically obtained from your main router through DHCP.<br /> | The above is the LAN port address of {{{1}}}. The IP address of the WAN port will be dynamically obtained from your main router through DHCP.<br /> | ||
| − | |||
===Recommended security settings=== | ===Recommended security settings=== | ||
The following settings are highly recommended to complete before connecting {{{1}}} to the Internet。 | The following settings are highly recommended to complete before connecting {{{1}}} to the Internet。 | ||
* Set a secure password | * Set a secure password | ||
* Only allow access to ssh from lan, change the port | * Only allow access to ssh from lan, change the port | ||
| − | * | + | * Check the firewall settings |
| − | Edit | + | Set up as you wish. |
| − | < | + | ===Change LAN IP in LuCI=== |
| − | + | 1) Click on Network → Interfaces, then click on the Edit button of the LAN Network; <br /> | |
| − | + | 2) In General Setup tab, input new IP address (for example: 192.168.11.1), click "Save" and then click "Save & Apply"; <br /> | |
| − | + | 3) On the pop-up window with the title “Connectivity change“, click "Apply and revert on connectivity loss"; <br /> | |
| − | + | 4) Wait a moment, enter the new address in your computer's browser and login to FriendlyWrt; <br /> | |
| − | + | ===Safe shutdown operation=== | |
| − | + | Enter the "Services" -> "Terminal", enter the "poweroff" command and hit enter, wait until the led light is off, and then unplug the power supply. | |
| − | + | ===Soft Factory Reset=== | |
| + | Enter "System"->"Backup/Flash firmware",Click “Perform reset“ Button, Your device's settings will be reset to defaults like when FriendlyWrt was first installed.<br> | ||
| + | You can also do this in the terminal: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | firstboot && reboot | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | ===Install Software Packages=== | |
| + | ====Set up openwrt official opkg source==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
| − | / | + | sed -i -e 's/mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/downloads.openwrt.org/g' /etc/opkg/distfeeds.conf |
| + | opkg update | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====Update Package List==== | ====Update Package List==== | ||
Before install software packages update the package list: | Before install software packages update the package list: | ||
| Line 63: | Line 48: | ||
$ opkg update | $ opkg update | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
====List Available Packages==== | ====List Available Packages==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
$ opkg list | $ opkg list | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
====List Installed Packages==== | ====List Installed Packages==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
$ opkg list-installed | $ opkg list-installed | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
====Install Packages==== | ====Install Packages==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
$ opkg install <package names> | $ opkg install <package names> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
====Remove Packages==== | ====Remove Packages==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
$ opkg remove <package names> | $ opkg remove <package names> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
===Disable IPv6=== | ===Disable IPv6=== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
| Line 100: | Line 80: | ||
You can change its behavior by changing the configuration file above. | You can change its behavior by changing the configuration file above. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | ===Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking=== | ||
| + | * Go to "Network" -> "Interfaces" | ||
| + | * Click "Delete" next to "WAN6", then click "Save & Apply" | ||
| + | * Click "Edit" next to "WAN", in the "Device" drop-down menu, select "Ethernet Adapter: wwan0", in the "Protocol" drop-down menu, select "QMI Cellular" and click "Switch Protocol" | ||
| + | * Click the "Modem Device" drop-down menu, select "/dev/cdc-wdm0", fill in the APN information (e.g. for China Mobile, enter "cmnet") | ||
| + | * Click "Save" to close the dialog, Finally, click "Save & Apply" at the bottom of the page to initiate the dial-up process | ||
| + | * Devices connected to LAN will have access to the Internet, If your device has a WiFi module, you can enable wireless AP functionality on the "Wireless" page and connect to the Internet via devices connected wirelessly | ||
===Some common issues of FriendlyWrt=== | ===Some common issues of FriendlyWrt=== | ||
* Unable to dial up | * Unable to dial up | ||
** Go to "Network" -> "Firewall" and set "Inbound Data", "Outbound Data" and "Forwarding" in "WAN Zone" to "Accept"; | ** Go to "Network" -> "Firewall" and set "Inbound Data", "Outbound Data" and "Forwarding" in "WAN Zone" to "Accept"; | ||
** If you still cannot access the Internet, you can try to turn off IPV6; | ** If you still cannot access the Internet, you can try to turn off IPV6; | ||
| + | * Dial-up successful, but no outgoing traffic | ||
| + | ** Go to "Services" -> "Terminal" and type "fw4 reload" to try to reload the firewall settings again; | ||
* Unable to power on | * Unable to power on | ||
** Try to replace the power adapter and cable. It is recommended to use a power supply with specifications above 5V/2A; | ** Try to replace the power adapter and cable. It is recommended to use a power supply with specifications above 5V/2A; | ||
| Line 110: | Line 99: | ||
** If your main network is IPv4, and {{{1}}} works in IPv6, the computer may not be able to connect to the Internet. It is recommended to turn off IPv6 (the method is described later in this WiKi), or switch the main route to IPv6; | ** If your main network is IPv4, and {{{1}}} works in IPv6, the computer may not be able to connect to the Internet. It is recommended to turn off IPv6 (the method is described later in this WiKi), or switch the main route to IPv6; | ||
* If you have questions or have better suggestions, please send an email to techsupport@friendlyarm.com; | * If you have questions or have better suggestions, please send an email to techsupport@friendlyarm.com; | ||
| − | |||
===Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature=== | ===Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature=== | ||
Plug the USB2LCD module to the USB interface of{{{1}}} and power on, the IP address and CPU temperature will be displayed on the LCD:<br /> | Plug the USB2LCD module to the USB interface of{{{1}}} and power on, the IP address and CPU temperature will be displayed on the LCD:<br /> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 104: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2S-usb2lcd-01.jpg|frameless|600px]]<br /> | [[File:R2S-usb2lcd-01.jpg|frameless|600px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 122: | Line 111: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{#switch: {{{1}}} | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| − | | NanoPi-R4S = | + | | NanoPi-R4S |
| + | | NanoPi-R4SE = | ||
===How to Control Fan Speed for Cooling=== | ===How to Control Fan Speed for Cooling=== | ||
(Note: The contents of this section are based on firmware released after 2021/08/31, kernel version kernel 5.10.xyz) | (Note: The contents of this section are based on firmware released after 2021/08/31, kernel version kernel 5.10.xyz) | ||
| Line 146: | Line 136: | ||
| #default = | | #default = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | === | + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} |
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus = | ||
| + | ===How to use SDIO WiFi=== | ||
| + | ====AP Mode==== | ||
| + | * FriendlyWrt's wireless function is disabled by default, to enable WiFi, you can click "Network > Wireless", and then click the "Enable" button.<br /> | ||
| + | * Search for a WiFi hotspot with a name like FriendlyWrt-xx:yy:zz on your phone, enter the default password "password" to connect.<br /> | ||
| + | * SDIO WiFi models supported: rtl8822cs<br /> | ||
| + | ====Wireless Repeater Mode==== | ||
| + | [[File:R2S-Plus-RepeaterMode.jpg|frameless|600px]] | ||
| + | * Connect to the wireless router | ||
| + | Click "Network" -> "Wireless", Click the "Scan" button next to "Generic MAC80211 802.11ac/b/g/n" to scan for networks, select the router you want to connect and then click the "Join Network" button, <br /> | ||
| + | In the network joining configuration page, turn on "Replace wireless configuration", enter the key in the "WPA passphrase" field, keep other configurations as default, click "Submit", <br /> | ||
| + | Click "Advanced Settings", input "wlan0" in "Interface Name" field, and then click "Save", <br /> | ||
| + | Finally, click "Save and Apply", if normal, you can see the IP address on the FriendlyWrt homepage. | ||
| + | * Create wireless hotspot | ||
| + | Click "Network" -> "Wireless", Click the "Add" button next to "Generic MAC80211 802.11ac/b/g/n",the "Edit wireless network" page will pop up,<br /> | ||
| + | Set the wireless channel in the "Operating frequency" field (e.g., "40 (5200 MHz)"),<br /> | ||
| + | In the "ESSID" field, input the hotspot name, <br /> | ||
| + | In the "Network" field, select "lan", <br /> | ||
| + | Click on "Wireless Security", set the encryption type, <br /> | ||
| + | Click "Advanced Settings", input "wlan1" in "Interface Name" field, then click "Save" and "Save and Apply", <br /> | ||
| + | It requires a reboot to take effect, click on "System" menu, then select "Reboot". <br /> | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T6 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R5C = | ||
| + | ===How to use M.2 WiFi=== | ||
| + | * M.2 WiFi models supported: rtl8822ce | ||
| + | ====AP Mode==== | ||
| + | * FriendlyWrt's wireless function is disabled by default, to enable WiFi, you can click "Network > Wireless", and then click the "Enable" button.<br /> | ||
| + | * Search for a WiFi hotspot with a name like FriendlyWrt-xx:yy:zz on your phone, enter the default password "password" to connect.<br /> | ||
| + | ====Wireless Repeater Mode==== | ||
| + | [[File:NanoPiAPMode.jpg|frameless|600px]] | ||
| + | * Connect to the wireless router | ||
| + | Click "Network" -> "Wireless", Click the "Scan" button next to "Generic MAC80211 802.11ac/b/g/n" to scan for networks, select the router you want to connect and then click the "Join Network" button, <br /> | ||
| + | In the network joining configuration page, turn on "Replace wireless configuration", enter the key in the "WPA passphrase" field, keep other configurations as default, click "Submit", <br /> | ||
| + | Click "Advanced Settings", input "wlan0" in "Interface Name" field, and then click "Save", <br /> | ||
| + | Finally, click "Save and Apply", if normal, you can see the IP address on the FriendlyWrt homepage. | ||
| + | * Create wireless hotspot | ||
| + | Click "Network" -> "Wireless", Click the "Add" button next to "Generic MAC80211 802.11ac/b/g/n",the "Edit wireless network" page will pop up,<br /> | ||
| + | Set the wireless channel in the "Operating frequency" field (e.g., "40 (5200 MHz)"),<br /> | ||
| + | In the "ESSID" field, input the hotspot name, <br /> | ||
| + | In the "Network" field, select "lan", <br /> | ||
| + | Click on "Wireless Security", set the encryption type, <br /> | ||
| + | Click "Advanced Settings", input "wlan1" in "Interface Name" field, then click "Save" and "Save and Apply", <br /> | ||
| + | It requires a reboot to take effect, click on "System" menu, then select "Reboot". <br /> | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ===How to use USB WiFi=== | ||
====Check USB WiFi Device with Command Line Utility==== | ====Check USB WiFi Device with Command Line Utility==== | ||
(1) Click on "services>ttyd" to start the command line utility<br /> | (1) Click on "services>ttyd" to start the command line utility<br /> | ||
| Line 152: | Line 191: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2s-wrt-jellyfin-002.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2s-wrt-jellyfin-002.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 163: | Line 203: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-09.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-09.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| #default = | | #default = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
(3) Connect a USB WiFi device to the board and run the command again<br /> | (3) Connect a USB WiFi device to the board and run the command again<br /> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| Line 176: | Line 216: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-10.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-10.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| #default = | | #default = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
(4) Type your device's ID (in our case it was "0BDA:C811" or "VID_0BDA&PID_C811") in a search engine and you may find a device that matches the ID. In our case the device we got was Realtek 8811CU. | (4) Type your device's ID (in our case it was "0BDA:C811" or "VID_0BDA&PID_C811") in a search engine and you may find a device that matches the ID. In our case the device we got was Realtek 8811CU. | ||
| − | |||
====Configure a USB WiFi Device as AP==== | ====Configure a USB WiFi Device as AP==== | ||
(1) Connect a USB WiFi device to the {{{1}}}. We recommend you to use the following devices:<br /> | (1) Connect a USB WiFi device to the {{{1}}}. We recommend you to use the following devices:<br /> | ||
| Line 191: | Line 230: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-01.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-01.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 201: | Line 241: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-03.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-03.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 209: | Line 250: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-04.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-04.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 217: | Line 259: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-05.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-05.jpg|frameless|800px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 227: | Line 270: | ||
| NanoPi-R2S | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| NanoPi-R2C-Plus | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| NanoPi-R2C = | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
[[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-07.png|frameless|277px]]<br /> | [[File:R2swrt+usbwifi-07.png|frameless|277px]]<br /> | ||
| #default = | | #default = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
====Common USB WiFi issues==== | ====Common USB WiFi issues==== | ||
1) It is recommended to plug in the usb wifi in the off state, then power it on, FriendlyWrt will automatically generate the configuration file /etc/config/wireless, if not, see if there is wlan0 by ifconfig -a, if there is no wlan0, usually there is no driver. <br /> | 1) It is recommended to plug in the usb wifi in the off state, then power it on, FriendlyWrt will automatically generate the configuration file /etc/config/wireless, if not, see if there is wlan0 by ifconfig -a, if there is no wlan0, usually there is no driver. <br /> | ||
2) If ifconfig -a sees wlan0, but the hotspot is not working properly, try changing the channel and country code, an inappropriate country code can also cause the WiFi to not work. <br /> | 2) If ifconfig -a sees wlan0, but the hotspot is not working properly, try changing the channel and country code, an inappropriate country code can also cause the WiFi to not work. <br /> | ||
3) Some USB WiFis (e.g. MTK MT7662) work in CD-ROM mode by default and need to be switched by usb_modeswitch, you can try to add usb_modeswitch configuration to the following directory: /etc/usb_modeswitch.d.<br /> | 3) Some USB WiFis (e.g. MTK MT7662) work in CD-ROM mode by default and need to be switched by usb_modeswitch, you can try to add usb_modeswitch configuration to the following directory: /etc/usb_modeswitch.d.<br /> | ||
| − | |||
====Change the default WiFi hotspot configuration==== | ====Change the default WiFi hotspot configuration==== | ||
FriendlyWrt sets the country, hotspot name and other parameters for USB WiFi by default, with the aim of being as plug-and-play as possible, but this does not guarantee that all modules will be compatible with this setting, you can change these behaviors by modifying the following file: | FriendlyWrt sets the country, hotspot name and other parameters for USB WiFi by default, with the aim of being as plug-and-play as possible, but this does not guarantee that all modules will be compatible with this setting, you can change these behaviors by modifying the following file: | ||
| Line 242: | Line 284: | ||
/lib/wifi/mac80211.sh | /lib/wifi/mac80211.sh | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
===Work with Docker Applications=== | ===Work with Docker Applications=== | ||
====Work with Docker: Install JellyFin==== | ====Work with Docker: Install JellyFin==== | ||
| Line 252: | Line 293: | ||
After installation, visit port 8096 and here is what you would find:<br /> | After installation, visit port 8096 and here is what you would find:<br /> | ||
[[File:FriendlyWrt+JerryFin.jpg | frameless|600px|FriendlyWrt+JerryFin]] | [[File:FriendlyWrt+JerryFin.jpg | frameless|600px|FriendlyWrt+JerryFin]] | ||
| − | |||
====Work with Docker: Install Personal Nextcloud==== | ====Work with Docker: Install Personal Nextcloud==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| Line 259: | Line 299: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
After installtion, visit port 8888. | After installtion, visit port 8888. | ||
| − | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
===Enable Swap Partition=== | ===Enable Swap Partition=== | ||
| Line 268: | Line 307: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
--> | --> | ||
| − | + | ====Expand Docker Storage==== | |
| + | * Stop docker service first: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | /etc/init.d/dockerd stop | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | * Rename the original /opt directory, create an empty /opt directory: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | mv /opt /opt-old && mkdir /opt | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | * Format your drive as ext4, and mount it to the /opt directory: | ||
| + | [[File:Friendlywrt mount nvme opt-en.jpg|frameless|500px]] | ||
| + | * Enter the command "mount | grep /opt" to check the mount status: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | root@FriendlyWrt:~# mount | grep /opt | ||
| + | /dev/nvme0n1p1 on /opt type ext4 (rw,relatime) | ||
| + | root@FriendlyWrt:~# | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | * Copy the files from the original /opt directory to the new /opt directory: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | cp -af /opt-old/* /opt/ && rm -rf /opt-old | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | * Reboot the device | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | reboot | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | * After reboot, go to the "Docker" -> "Overview" page, check the information in the "Docker Root Dir" line, you can see that the Docker space has been expanded: | ||
| + | [[File:Friendlywrt docker info-en.jpg|frameless|500px]] | ||
| + | ====Docker FAQ and solutions==== | ||
| + | =====Unable to access the network services provided by the Docker container===== | ||
| + | Solution: <br /> | ||
| + | * Go to the "Firewall" settings and set "Forwarding" to "Accept"; | ||
| + | * Turn off "Software Offload"; | ||
===Mount smbfs=== | ===Mount smbfs=== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
mount -t cifs //192.168.1.10/shared /movie -o username=xxx,password=yyy,file_mode=0644 | mount -t cifs //192.168.1.10/shared /movie -o username=xxx,password=yyy,file_mode=0644 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
===Use sdk to compile the package === | ===Use sdk to compile the package === | ||
====Install the compilation environment==== | ====Install the compilation environment==== | ||
Download and run the following script on 64-bit Ubuntu (version 18.04+): | Download and run the following script on 64-bit Ubuntu (version 18.04+): | ||
[https://github.com/friendlyarm/build-env-on-ubuntu-bionic How to setup the Compiling Environment on Ubuntu bionic] | [https://github.com/friendlyarm/build-env-on-ubuntu-bionic How to setup the Compiling Environment on Ubuntu bionic] | ||
| − | |||
====Download and decompress sdk from the network disk==== | ====Download and decompress sdk from the network disk==== | ||
The sdk is located in the toolchain directory of the network disk: | The sdk is located in the toolchain directory of the network disk: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | tar xvf | + | tar xvf openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64.tar.xz |
# If the path is too long, it will cause some package compilation errors, so change the directory name here | # If the path is too long, it will cause some package compilation errors, so change the directory name here | ||
| − | mv openwrt-sdk- | + | mv openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64 sdk |
cd sdk | cd sdk | ||
./scripts/feeds update -a | ./scripts/feeds update -a | ||
./scripts/feeds install -a | ./scripts/feeds install -a | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====Compile the package==== | ====Compile the package==== | ||
download the source code of the example (a total of 3 examples are example1, example2, example3), and copy to the package directory: | download the source code of the example (a total of 3 examples are example1, example2, example3), and copy to the package directory: | ||
| Line 330: | Line 383: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
$ find ./bin -name example*.ipk | $ find ./bin -name example*.ipk | ||
| − | ./bin/packages/ | + | ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk |
| − | ./bin/packages/ | + | ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk |
| − | ./bin/packages/ | + | ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== Install the ipk to NanoPi ==== | ==== Install the ipk to NanoPi ==== | ||
You can use the scp command to upload the ipk file to NanoPi: | You can use the scp command to upload the ipk file to NanoPi: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | cd ./bin/packages/ | + | cd ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/ |
scp example*.ipk root@192.168.2.1:/root/ | scp example*.ipk root@192.168.2.1:/root/ | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 343: | Line 396: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
cd /root/ | cd /root/ | ||
| − | opkg install | + | opkg install example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk |
| − | opkg install | + | opkg install example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk |
| − | opkg install | + | opkg install example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | ===Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions=== | ||
| + | Please refre this link: https://github.com/friendlyarm/Actions-FriendlyWrt | ||
Latest revision as of 09:35, 4 February 2024
Contents
- 1 Work with FriendlyWrt
- 1.1 Introduction to FriendlyWrt
- 1.2 First boot
- 1.3 Account & Password
- 1.4 Login FriendlyWrt
- 1.5 Recommended security settings
- 1.6 Change LAN IP in LuCI
- 1.7 Safe shutdown operation
- 1.8 Soft Factory Reset
- 1.9 Install Software Packages
- 1.10 Disable IPv6
- 1.11 Configure the function of the user button
- 1.12 Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking
- 1.13 Some common issues of FriendlyWrt
- 1.14 Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature
- 1.15 How to use USB WiFi
- 1.16 Work with Docker Applications
- 1.17 Mount smbfs
- 1.18 Use sdk to compile the package
- 1.19 Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions
1 Work with FriendlyWrt
1.1 Introduction to FriendlyWrt
FriendlyWrt is a customized system made by FriendlyElec based on an OpenWrt distribution. It is open source and well suitable for developing IoT applications, NAS applications etc.
1.2 First boot
For the first boot, the system needs to do the following initialization work:
1)Extended root file system
2)Initial setup(will execute /root/setup.sh)
So you need to wait for a while (about 2~3 minutes) to boot up for the first time, and then set FriendlyWrt, you can enter the ttyd terminal on the openwrt webpage, when the prompt is displayed as root@FriendlyWrt, it means the system has been initialized.
root@FriendlyWrt
1.3 Account & Password
The default password is password (empty password in some versions). Please set or change a safer password for web login and ssh login. It is recommended to complete this setting before connecting {{{1}}} to the Internet.
1.4 Login FriendlyWrt
Connect the PC to the LAN port of {{{1}}}. If your PC without a built-in ethernet port, connect the LAN port of the wireless AP to the LAN port of {{{1}}}, and then connect your PC to the wireless AP via WiFi , Enter the following URL on your PC's browser to access the admin page:
- http://friendlywrt/
- http://192.168.2.1/
- http://[fd00:ab:cd::1]
The above is the LAN port address of {{{1}}}. The IP address of the WAN port will be dynamically obtained from your main router through DHCP.
1.5 Recommended security settings
The following settings are highly recommended to complete before connecting {{{1}}} to the Internet。
- Set a secure password
- Only allow access to ssh from lan, change the port
- Check the firewall settings
Set up as you wish.
1.6 Change LAN IP in LuCI
1) Click on Network → Interfaces, then click on the Edit button of the LAN Network;
2) In General Setup tab, input new IP address (for example: 192.168.11.1), click "Save" and then click "Save & Apply";
3) On the pop-up window with the title “Connectivity change“, click "Apply and revert on connectivity loss";
4) Wait a moment, enter the new address in your computer's browser and login to FriendlyWrt;
1.7 Safe shutdown operation
Enter the "Services" -> "Terminal", enter the "poweroff" command and hit enter, wait until the led light is off, and then unplug the power supply.
1.8 Soft Factory Reset
Enter "System"->"Backup/Flash firmware",Click “Perform reset“ Button, Your device's settings will be reset to defaults like when FriendlyWrt was first installed.
You can also do this in the terminal:
firstboot && reboot1.9 Install Software Packages
1.9.1 Set up openwrt official opkg source
sed -i -e 's/mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/downloads.openwrt.org/g' /etc/opkg/distfeeds.conf opkg update
1.9.2 Update Package List
Before install software packages update the package list:
$ opkg update
1.9.3 List Available Packages
$ opkg list
1.9.4 List Installed Packages
$ opkg list-installed
1.9.5 Install Packages
$ opkg install <package names>
1.9.6 Remove Packages
$ opkg remove <package names>
1.10 Disable IPv6
. /root/setup.sh disable_ipv6 reboot
1.11 Configure the function of the user button
By default, the user button is configured to reboot the device, as shown below:
echo 'BTN_1 1 /sbin/reboot' >> /etc/triggerhappy/triggers.d/example.conf
You can change its behavior by changing the configuration file above.
1.12 Configuring Quectel EC20 (4G module) dial-up networking
- Go to "Network" -> "Interfaces"
- Click "Delete" next to "WAN6", then click "Save & Apply"
- Click "Edit" next to "WAN", in the "Device" drop-down menu, select "Ethernet Adapter: wwan0", in the "Protocol" drop-down menu, select "QMI Cellular" and click "Switch Protocol"
- Click the "Modem Device" drop-down menu, select "/dev/cdc-wdm0", fill in the APN information (e.g. for China Mobile, enter "cmnet")
- Click "Save" to close the dialog, Finally, click "Save & Apply" at the bottom of the page to initiate the dial-up process
- Devices connected to LAN will have access to the Internet, If your device has a WiFi module, you can enable wireless AP functionality on the "Wireless" page and connect to the Internet via devices connected wirelessly
1.13 Some common issues of FriendlyWrt
- Unable to dial up
- Go to "Network" -> "Firewall" and set "Inbound Data", "Outbound Data" and "Forwarding" in "WAN Zone" to "Accept";
- If you still cannot access the Internet, you can try to turn off IPV6;
- Dial-up successful, but no outgoing traffic
- Go to "Services" -> "Terminal" and type "fw4 reload" to try to reload the firewall settings again;
- Unable to power on
- Try to replace the power adapter and cable. It is recommended to use a power supply with specifications above 5V/2A;
- Note that some fast chargers with Type-C interface will have a delay, it may take a few seconds to start providing power;
- When doing secondary routing, the computer cannot connect to the Internet
- If your main network is IPv4, and {{{1}}} works in IPv6, the computer may not be able to connect to the Internet. It is recommended to turn off IPv6 (the method is described later in this WiKi), or switch the main route to IPv6;
- If you have questions or have better suggestions, please send an email to techsupport@friendlyarm.com;
1.14 Use USB2LCD to view IP and temperature
Plug the USB2LCD module to the USB interface of{{{1}}} and power on, the IP address and CPU temperature will be displayed on the LCD:

1.15 How to use USB WiFi
1.15.1 Check USB WiFi Device with Command Line Utility
(1) Click on "services>ttyd" to start the command line utility
(2) Make sure no USB devices are connected to your board and run the following command to check if any USB devices are connected or not
lsusb
(3) Connect a USB WiFi device to the board and run the command again
lsusb
You will see a new device is detected. In our test the device's ID was 0BDA:C811
(4) Type your device's ID (in our case it was "0BDA:C811" or "VID_0BDA&PID_C811") in a search engine and you may find a device that matches the ID. In our case the device we got was Realtek 8811CU.
1.15.2 Configure a USB WiFi Device as AP
(1) Connect a USB WiFi device to the {{{1}}}. We recommend you to use the following devices:
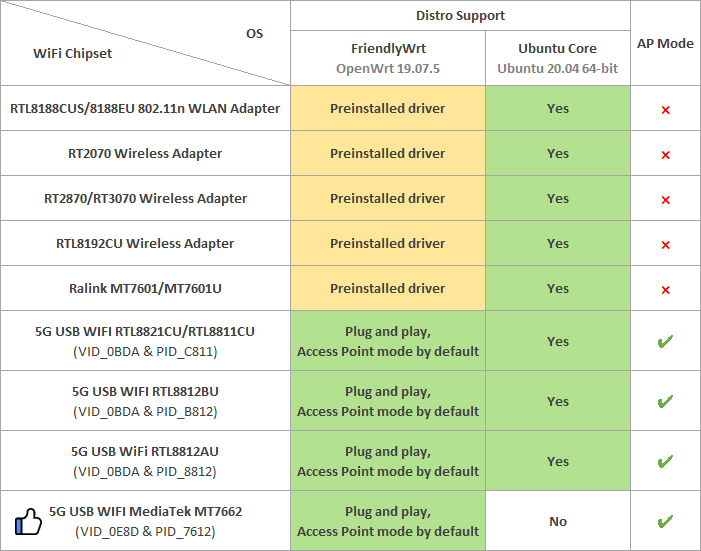
Note: devices that match these VID&PIDs would most likely work.
(2) Click on "System>Reboot" and reboot your {{{1}}}
(3) Click on "Network>Wireless" to enter the WiFi configuration page
(4) Click on "Edit" to edit the configuration
(5) On the "Interface Configuration" page you can set the WiFi mode and SSID, and then go to "Wireless Security" to change the password. By default the password is "password". After you make your changes click on "Save" to save
(6) After you change the settings you can use a smartphone or PC to search for WiFi
1.15.3 Common USB WiFi issues
1) It is recommended to plug in the usb wifi in the off state, then power it on, FriendlyWrt will automatically generate the configuration file /etc/config/wireless, if not, see if there is wlan0 by ifconfig -a, if there is no wlan0, usually there is no driver.
2) If ifconfig -a sees wlan0, but the hotspot is not working properly, try changing the channel and country code, an inappropriate country code can also cause the WiFi to not work.
3) Some USB WiFis (e.g. MTK MT7662) work in CD-ROM mode by default and need to be switched by usb_modeswitch, you can try to add usb_modeswitch configuration to the following directory: /etc/usb_modeswitch.d.
1.15.4 Change the default WiFi hotspot configuration
FriendlyWrt sets the country, hotspot name and other parameters for USB WiFi by default, with the aim of being as plug-and-play as possible, but this does not guarantee that all modules will be compatible with this setting, you can change these behaviors by modifying the following file:
/lib/wifi/mac80211.sh
1.16 Work with Docker Applications
1.16.1 Work with Docker: Install JellyFin
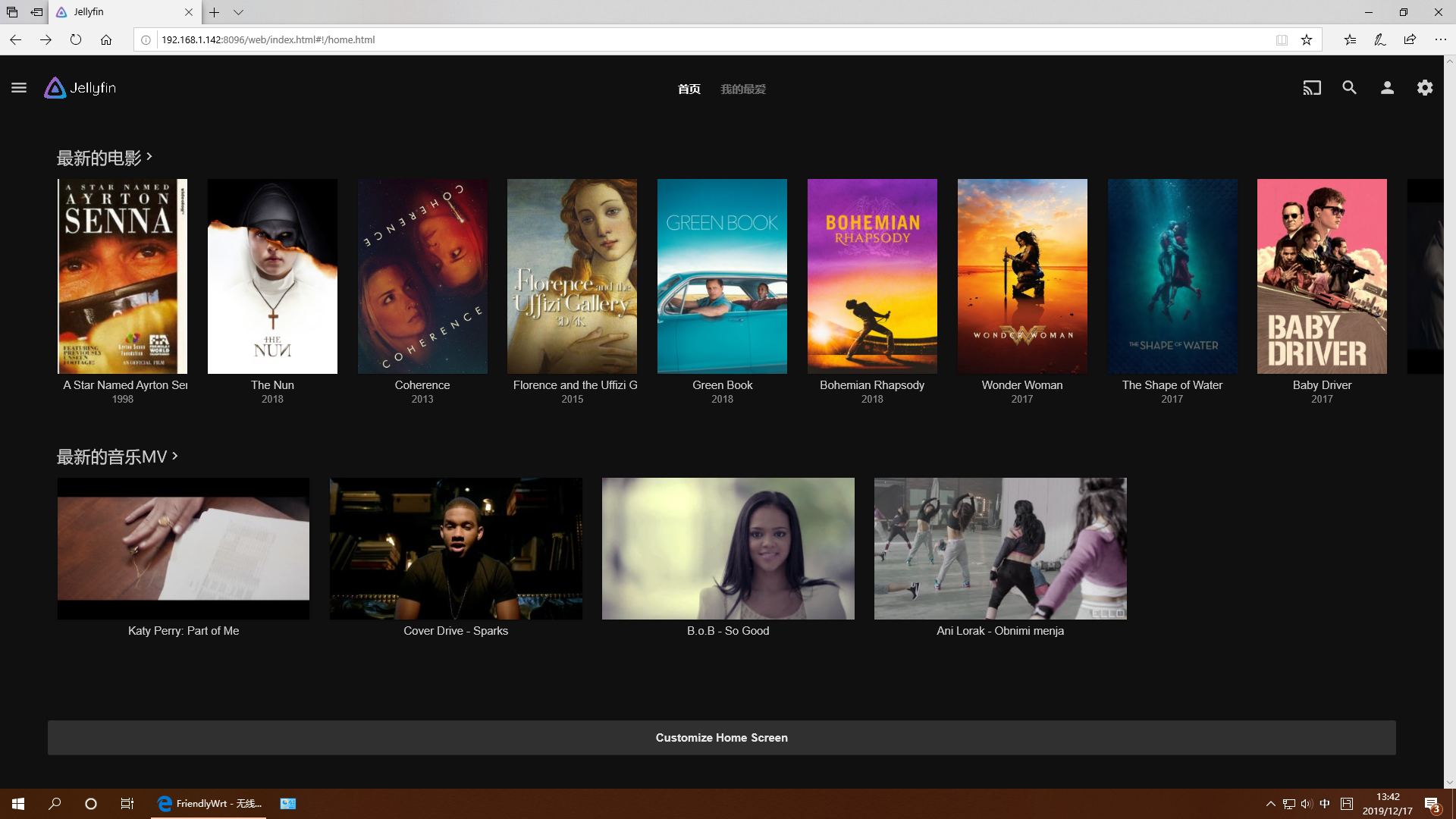
mkdir -p /jellyfin/config mkdir -p /jellyfin/videos docker run --restart=always -d -p 8096:8096 -v /jellyfin/config:/config -v /jellyfin/videos:/videos jellyfin/jellyfin:10.1.0-arm64 -name myjellyfin
After installation, visit port 8096 and here is what you would find:
1.16.2 Work with Docker: Install Personal Nextcloud
mkdir /nextcloud -p docker run -d -p 8888:80 --name nextcloud -v /nextcloud/:/var/www/html/ --restart=always --privileged=true arm64v8/nextcloud
After installtion, visit port 8888.
1.16.3 Expand Docker Storage
- Stop docker service first:
/etc/init.d/dockerd stop
- Rename the original /opt directory, create an empty /opt directory:
mv /opt /opt-old && mkdir /opt
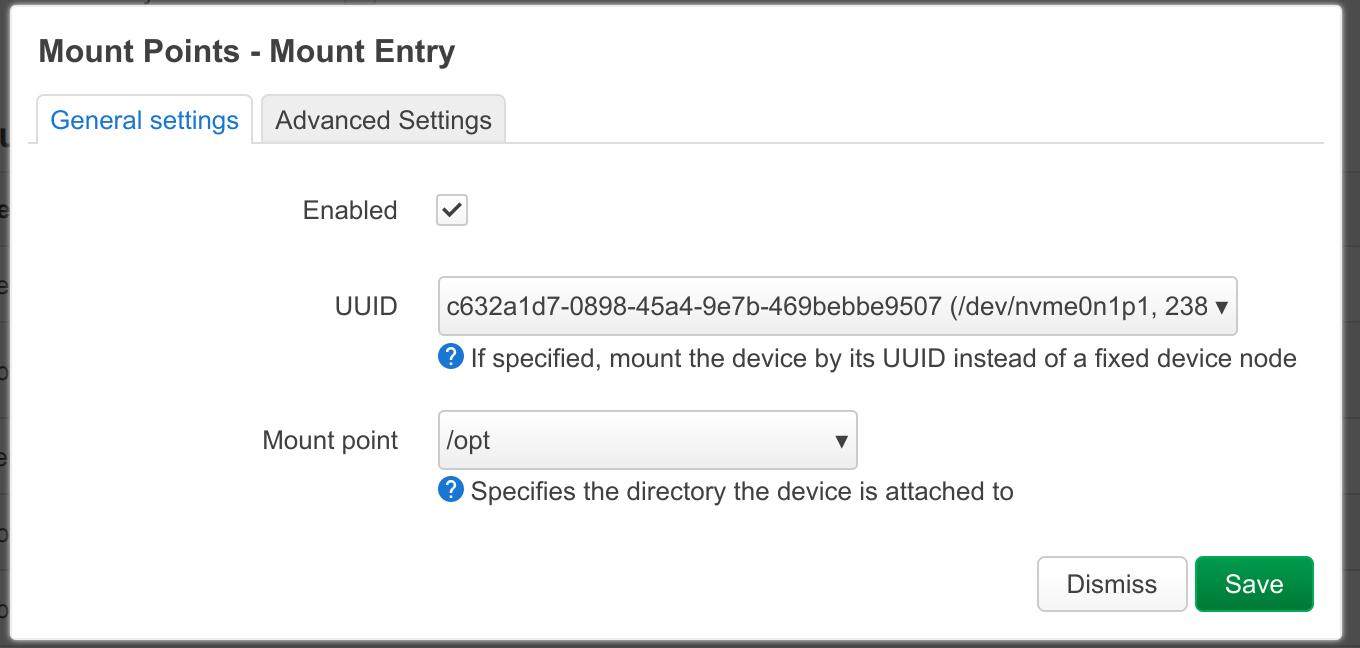
- Format your drive as ext4, and mount it to the /opt directory:
- Enter the command "mount | grep /opt" to check the mount status:
root@FriendlyWrt:~# mount | grep /opt /dev/nvme0n1p1 on /opt type ext4 (rw,relatime) root@FriendlyWrt:~#
- Copy the files from the original /opt directory to the new /opt directory:
cp -af /opt-old/* /opt/ && rm -rf /opt-old
- Reboot the device
reboot
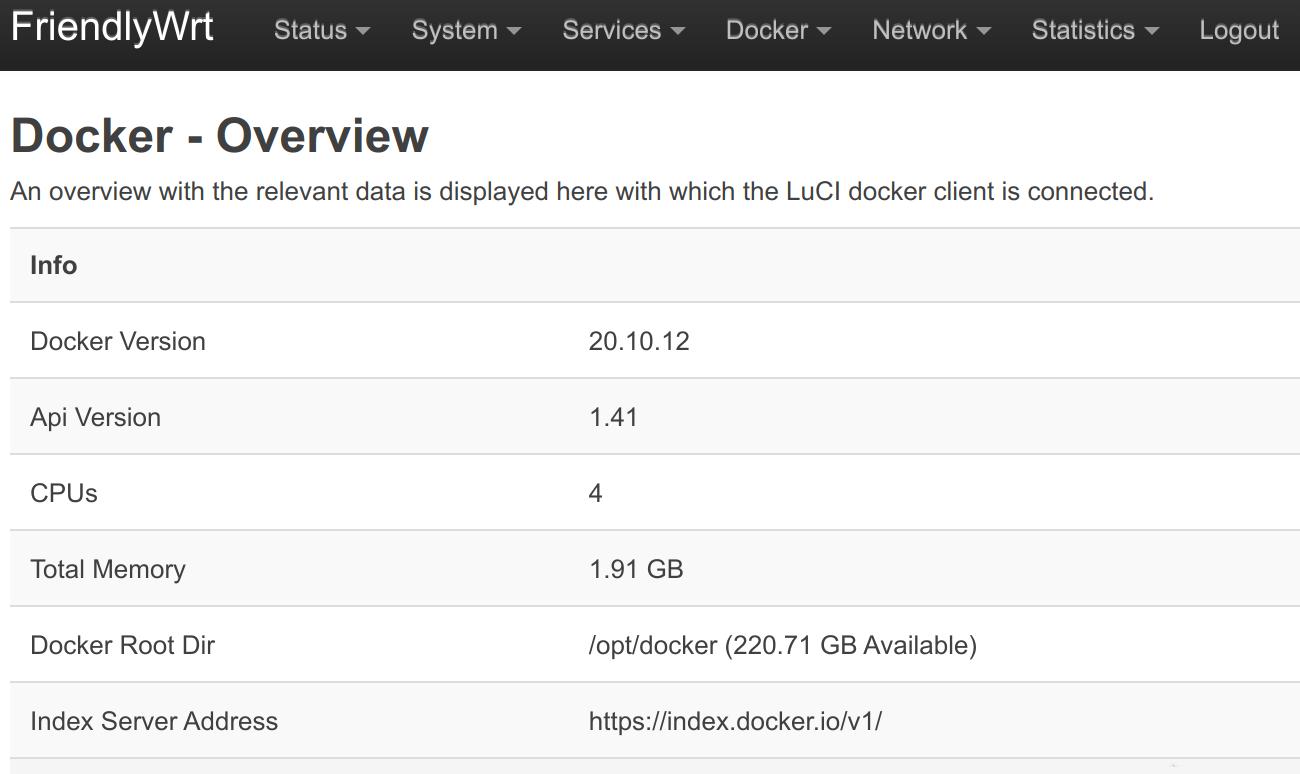
- After reboot, go to the "Docker" -> "Overview" page, check the information in the "Docker Root Dir" line, you can see that the Docker space has been expanded:
1.16.4 Docker FAQ and solutions
1.16.4.1 Unable to access the network services provided by the Docker container
Solution:
- Go to the "Firewall" settings and set "Forwarding" to "Accept";
- Turn off "Software Offload";
1.17 Mount smbfs
mount -t cifs //192.168.1.10/shared /movie -o username=xxx,password=yyy,file_mode=0644
1.18 Use sdk to compile the package
1.18.1 Install the compilation environment
Download and run the following script on 64-bit Ubuntu (version 18.04+): How to setup the Compiling Environment on Ubuntu bionic
1.18.2 Download and decompress sdk from the network disk
The sdk is located in the toolchain directory of the network disk:
tar xvf openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64.tar.xz # If the path is too long, it will cause some package compilation errors, so change the directory name here mv openwrt-sdk-*-rockchip-armv8_gcc-11.2.0_musl.Linux-x86_64 sdk cd sdk ./scripts/feeds update -a ./scripts/feeds install -a
1.18.3 Compile the package
download the source code of the example (a total of 3 examples are example1, example2, example3), and copy to the package directory:
git clone https://github.com/mwarning/openwrt-examples.git cp -rf openwrt-examples/example* package/ rm -rf openwrt-examples/
Then enter the configuration menu through the following command:
make menuconfigIn the menu, select the following packages we want to compile (actually selected by default):
"Utilities" => "example1" "Utilities" => "example3" "Network" => "VPN" => "example2"
execute the following commands to compile the three software packages:
make package/example1/compile V=99 make package/example2/compile V=99 make package/example3/compile V=99
After the compilation is successful, you can find the ipk file in the bin directory, as shown below:
$ find ./bin -name example*.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk
1.18.4 Install the ipk to NanoPi
You can use the scp command to upload the ipk file to NanoPi:
cd ./bin/packages/aarch64_generic/base/ scp example*.ipk root@192.168.2.1:/root/
Then use the opkg command to install them:
cd /root/ opkg install example3_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk opkg install example1_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk opkg install example2_1.0.0-220420.38257_aarch64_generic.ipk
1.19 Build FriendlyWrt using GitHub Actions
Please refre this link: https://github.com/friendlyarm/Actions-FriendlyWrt