Difference between revisions of "NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box"
(→Introduction) |
(updated by API) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
*It has an onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module SIM800C. | *It has an onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module SIM800C. | ||
*It has 2.0mm I2C interface, UART interface, audio interface and CVBS interface etc and can work with various external modules. | *It has 2.0mm I2C interface, UART interface, audio interface and CVBS interface etc and can work with various external modules. | ||
| − | * | + | *Its MicroUSB port is only used as power input. And a power switch is added too. |
| − | * | + | *It has one power LED and one GPIO accessed LED. |
| − | * | + | *It populates the two USB ports of the NanoPi Duo2. |
| − | * | + | *It populates the serial ports and Ethernet port of the NanoPi Duo2. |
| − | * | + | *It has an IPX to SMA antenna converter for WiFi antennas. |
| − | == | + | ==Hardware Spec== |
| − | * | + | * Onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module |
| − | * | + | * 2 x USB Host |
| − | * | + | * Serial port and Ethernet port |
| − | * | + | * Audio input and output |
| − | * | + | * MicroUSB power input and a power switch |
| − | * | + | * IPX to SMA WiFi converter |
| − | * | + | * PCB dimension (mm): 85x56 |
[[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_PCB.png | frameless|600px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_PCB]] | [[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_PCB.png | frameless|600px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_PCB]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Layout=== |
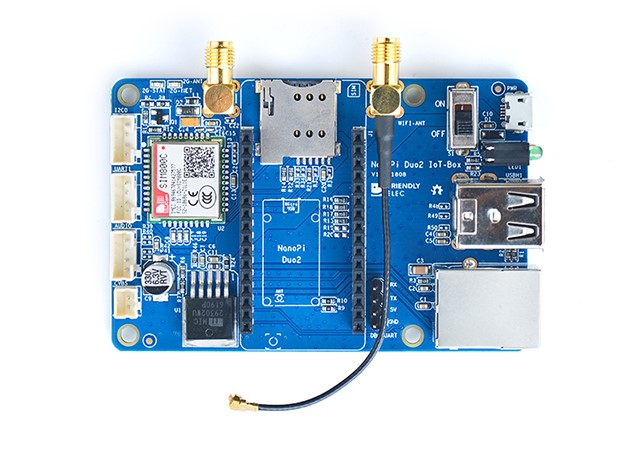
| − | [[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box-layout.jpg |thumb|550px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT- | + | [[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box-layout.jpg |thumb|550px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box Layout]] |
| − | NanoPi Duo2 IoT- | + | Here is the NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box's layout. Its pins' remarks are printed on the board.<br> |
| − | * '''NanoPi Duo | + | * '''NanoPi Duo header Pin Spec ''' |
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Number# || Name | + | | Number# || Name|| Number# || Name |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1 || VDD_5V | + | | 1 || VDD_5V || 17 || DEBUG_RX(UART_RXD0)/GPIOA5/PWM0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2 || VDD_5V | + | | 2 || VDD_5V || 18 || DEBUG_TX(UART_TXD0)/GPIOA4 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 3 || SYS_3.3V | + | | 3 || SYS_3.3V || 19 || GND |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 4 ||GND || | + | | 4 ||GND || 20 || I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 5 || GPIOL11/IR-RX | + | | 5 || GPIOL11/IR-RX || 21 || I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |6 || GPIOG11 | + | |6 || GPIOG11 || 22 || UART3_TX/SPI1_CS/GPIOA13 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 7||USB-DM3 | + | | 7||USB-DM3 || 23 || UART3_RX/SPI1_CLK/GPIOA14 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |8 || USB-DP3 | + | |8 || USB-DP3 || 24 || UART3_CTS/SPI1_MISO/GPIOA16 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 9 ||USB-DM2 | + | | 9 ||USB-DM2 ||25 || UART3_RTS/SPI1_MOSI/GPIOA15 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 10|| USB-DP2 | + | | 10|| USB-DP2 || 26 || UART1_RX/GPIOG7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |11 ||EPHY-RXN | + | |11 ||EPHY-RXN || 27 || UART1_TX/GPIOG6 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 12 || EPHY-RXP | + | | 12 || EPHY-RXP || 28 || CVBS |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |13 || EPHY-TXN | + | |13 || EPHY-TXN || 29 || LINEOUT_L |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |14 ||EPHY-TXP | + | |14 ||EPHY-TXP || 30 || LINEOUT_R |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 15 || EPHY-LED-LINK | + | | 15 || EPHY-LED-LINK || 31 || MIC_P |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 16 || EPHY-LED-SPD | + | | 16 || EPHY-LED-SPD || 32 || MIC_N |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Hardware Setup== |
| − | NanoPi | + | The NanoPi Duo2 can be mounted on the NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box carrier board. You can refer to the following setup to assemble them:<br> |
[[File:NanoPi_Duo2_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box.jpg|frameless|600px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_NanoPi_Duo2]] | [[File:NanoPi_Duo2_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box.jpg|frameless|600px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_NanoPi_Duo2]] | ||
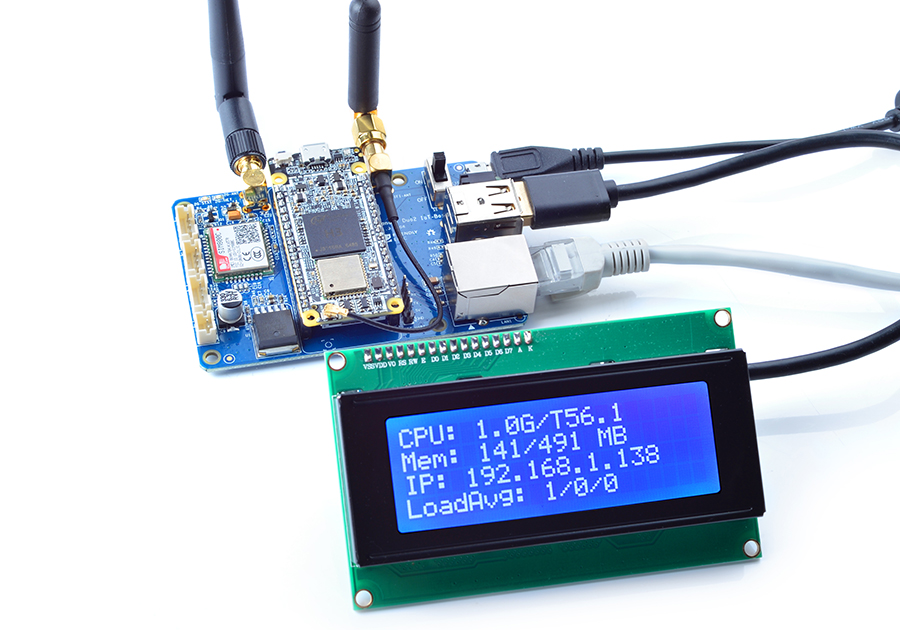
| − | + | You can connect your NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box board to a network and external modules such as USB devices<br> | |
[[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_USB2LCD.jpg|frameless|450px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box]]<br> | [[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box_USB2LCD.jpg|frameless|450px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box]]<br> | ||
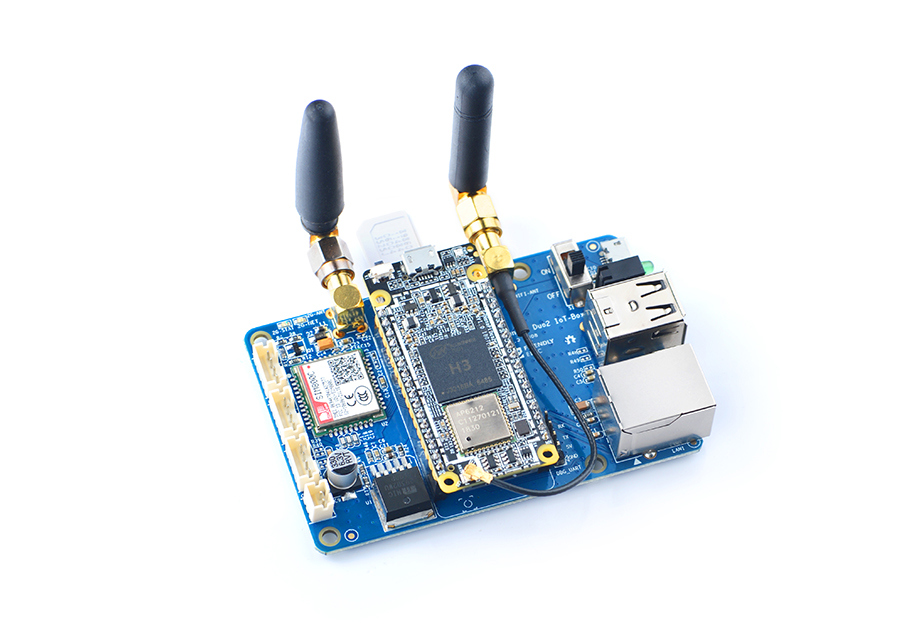
| − | + | When you use the onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module you should use an appropriate antenna and this antenna's band is different from an WiFi antenna's band. You can refer to the following setup:<br> | |
| − | [[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box-ant.jpg|frameless|600px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box | + | [[File:NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box-ant.jpg|frameless|600px|NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box Assemble an antenna]] |
| − | == | + | ==Applications== |
| − | === | + | ===Work with GSM/GPRS Module=== |
| − | + | {{Linux-SIM800C}} | |
| − | === | + | ===Work with USB Host=== |
| − | NanoPi Duo2 IoT- | + | You can connect a USB device e.g. Matrix - LCD2USB to the NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box board as follows:<br /> |
[[File:Matrix-LCD2USB_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box.jpg|frameless|600px|连接Matrix - LCD2USB]] | [[File:Matrix-LCD2USB_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box.jpg|frameless|600px|连接Matrix - LCD2USB]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Work with Audio Input & Output=== |
| − | + | 1. Run the following command to record voices: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
arecord -D hw:0,0 -f cd test.wav | arecord -D hw:0,0 -f cd test.wav | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Here is what you expect to observe:<br> | |
| − | [[File:audio_in.jpg|frameless|600px| | + | [[File:audio_in.jpg|frameless|600px|Voice Recording]]<br> |
| − | + | 2. Run the following command to play audio e.g. the /root/Music/test.wav file | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
aplay /root/Music/test.wav | aplay /root/Music/test.wav | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Here is what you expect to observe:<br> | |
| − | [[File:audio_out.jpg|frameless|600px| | + | [[File:audio_out.jpg|frameless|600px|Audio Play]]<br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | You can use the alsamixer utility to adjust the volume. | |
| − | == | + | ==Resources== |
| − | *[Schematic]([http://wiki. | + | *[Schematic]([http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/d/d5/Schematic_NanoPi_Duo2_IoT_Box-1808.pdf Schematic_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box.pdf]) |
| − | *[Dimension]([http://wiki. | + | *[Dimension]([http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/index.php/File:Dimension_NanoPi_Duo2_IoT_Box_pcb-1808.rar Dimension_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box(dxf)]) |
| − | *[Manual]([http://wiki. | + | *[Manual]([http://wiki.friendlyelec.com/wiki/images/7/76/SIM800_Series_AT_Command_Manual_V1.10.pdf SIM800_Series_AT_Command_Manual_V1.10.pdf]) |
| + | |||
| + | ==Update Log== | ||
| + | ===Oct-10-2018=== | ||
| + | * Released English Version | ||
Latest revision as of 07:19, 21 February 2022
Contents
1 Introduction
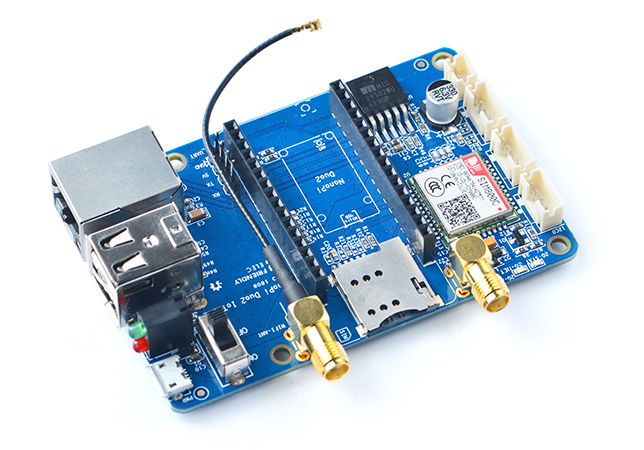
- The NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box is a dedicated carrier board for the NanoPi Duo2. It populates Ethernet port, serial port, audio and USB etc.
- It has an onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module SIM800C.
- It has 2.0mm I2C interface, UART interface, audio interface and CVBS interface etc and can work with various external modules.
- Its MicroUSB port is only used as power input. And a power switch is added too.
- It has one power LED and one GPIO accessed LED.
- It populates the two USB ports of the NanoPi Duo2.
- It populates the serial ports and Ethernet port of the NanoPi Duo2.
- It has an IPX to SMA antenna converter for WiFi antennas.
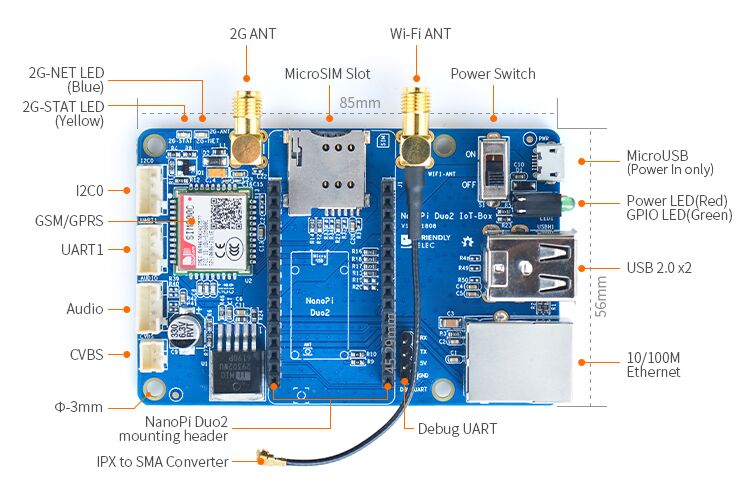
2 Hardware Spec
- Onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module
- 2 x USB Host
- Serial port and Ethernet port
- Audio input and output
- MicroUSB power input and a power switch
- IPX to SMA WiFi converter
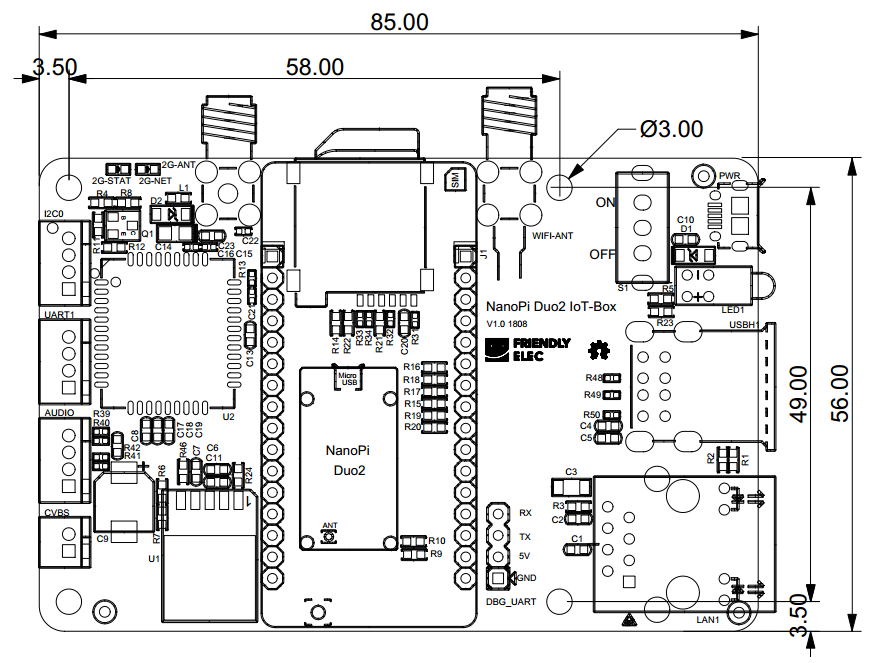
- PCB dimension (mm): 85x56
2.1 Layout
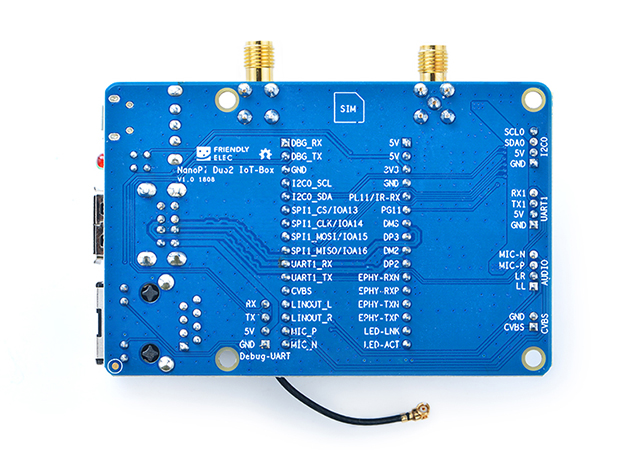
Here is the NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box's layout. Its pins' remarks are printed on the board.
- NanoPi Duo header Pin Spec
Number# Name Number# Name 1 VDD_5V 17 DEBUG_RX(UART_RXD0)/GPIOA5/PWM0 2 VDD_5V 18 DEBUG_TX(UART_TXD0)/GPIOA4 3 SYS_3.3V 19 GND 4 GND 20 I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 5 GPIOL11/IR-RX 21 I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 6 GPIOG11 22 UART3_TX/SPI1_CS/GPIOA13 7 USB-DM3 23 UART3_RX/SPI1_CLK/GPIOA14 8 USB-DP3 24 UART3_CTS/SPI1_MISO/GPIOA16 9 USB-DM2 25 UART3_RTS/SPI1_MOSI/GPIOA15 10 USB-DP2 26 UART1_RX/GPIOG7 11 EPHY-RXN 27 UART1_TX/GPIOG6 12 EPHY-RXP 28 CVBS 13 EPHY-TXN 29 LINEOUT_L 14 EPHY-TXP 30 LINEOUT_R 15 EPHY-LED-LINK 31 MIC_P 16 EPHY-LED-SPD 32 MIC_N
3 Hardware Setup
The NanoPi Duo2 can be mounted on the NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box carrier board. You can refer to the following setup to assemble them:

You can connect your NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box board to a network and external modules such as USB devices

When you use the onboard quad-band GSM/GPRS module you should use an appropriate antenna and this antenna's band is different from an WiFi antenna's band. You can refer to the following setup:
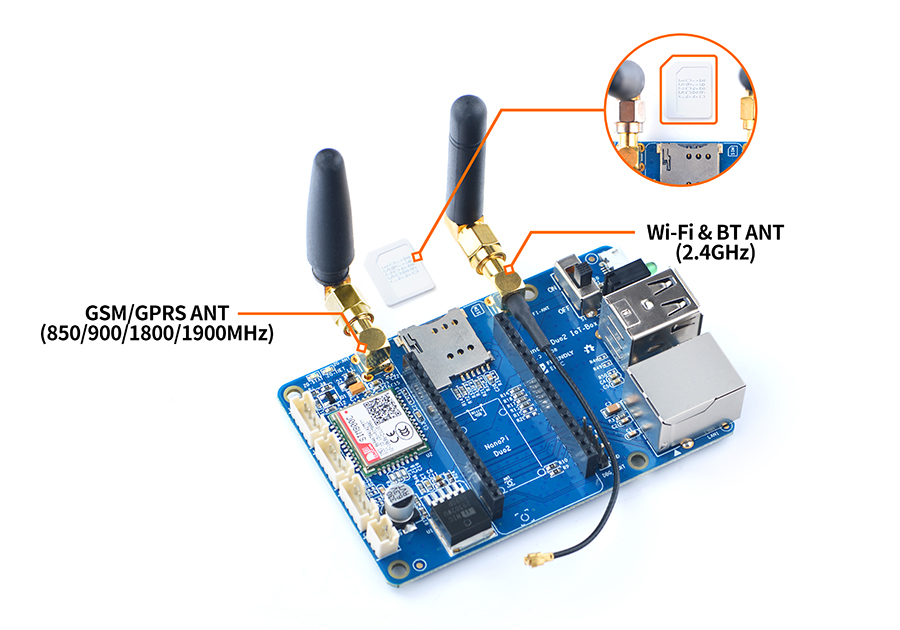
4 Applications
4.1 Work with GSM/GPRS Module
To test SIM800C you need to insert a SIM card and install a GSM/GPRS antenna.
By default the FriendlyCore system FriendlyElec provides has a Python demo for testing SIM800C. Run the following commands to test it:
$ cd /root/Python/GSM-GPRS/sim800-test $ apt-get install python-pip $ pip install --upgrade pip $ pip install pyserial $ ./sim800c-test.py -h # Check help information ./sim800c-test.py -p <phone_number> -o <operator, cmcc> -w <website> $ ./sim800c-test.py -p 136xxxxxxxx -o cmcc -w www.baidu.com # Visit baidu.com
Option Comment -p specifies a telephone number for sim card. -o specifies a telecom operator. For example "cmcc" stands for China Mobile Communication Corporation. -w specifies a website to visit
By default this demo will load 1K bytes' data from the specified website and it takes a while. If it is successful you will see the following information:
4.2 Work with USB Host
You can connect a USB device e.g. Matrix - LCD2USB to the NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box board as follows:
连接Matrix - LCD2USB
4.3 Work with Audio Input & Output
1. Run the following command to record voices:
arecord -D hw:0,0 -f cd test.wav
Here is what you expect to observe:
![]()
2. Run the following command to play audio e.g. the /root/Music/test.wav file
aplay /root/Music/test.wav
Here is what you expect to observe:
You can use the alsamixer utility to adjust the volume.
5 Resources
- [Schematic](Schematic_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box.pdf)
- [Dimension](Dimension_NanoPi Duo2 IoT-Box(dxf))
- [Manual](SIM800_Series_AT_Command_Manual_V1.10.pdf)
6 Update Log
6.1 Oct-10-2018
- Released English Version