Difference between revisions of "WiringNP: NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with C"
(→May-16-2017) |
(→Nov-14-2018) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[WiringNP: NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with C/zh|查看中文]] |
==Introduction to WiringPi== | ==Introduction to WiringPi== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Here is WiringNP's project page: https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP<br /> | Here is WiringNP's project page: https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP<br /> | ||
| − | ==Install WiringNP on | + | ==Install WiringNP on NEO/NEO2== |
Log into your nano board via SSH, open a terminal and install the WiringNP library by running the following commands:<br /> | Log into your nano board via SSH, open a terminal and install the WiringNP library by running the following commands:<br /> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ==Install WiringNP on | + | ==Install WiringNP on NanoPi M1== |
Log into your nano board via SSH, open a terminal and install the WiringNP library by running the following commands:<br /> | Log into your nano board via SSH, open a terminal and install the WiringNP library by running the following commands:<br /> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP | ||
cd WiringNP/ | cd WiringNP/ | ||
| − | git checkout | + | git checkout nanopi-m1 |
chmod 755 build | chmod 755 build | ||
./build | ./build | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
root@FriendlyARM:~# gpio readall | root@FriendlyARM:~# gpio readall | ||
| − | + | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+-NanoPi NEO/NEO2--+------+----------+-----+-----+ | |
| BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM | | | BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM | | ||
+-----+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+-----+ | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+-----+ | ||
| | | 3.3V | | | 1 || 2 | | | 5V | | | | | | | 3.3V | | | 1 || 2 | | | 5V | | | | ||
| − | | 12 | 8 | GPIOA12 | | + | | 12 | 8 | GPIOA12 | OFF | 0 | 3 || 4 | | | 5V | | | |
| − | | 11 | 9 | GPIOA11 | | + | | 11 | 9 | GPIOA11 | OFF | 0 | 5 || 6 | | | 0v | | | |
| − | | 203 | 7 | GPIOG11 | | + | | 203 | 7 | GPIOG11 | OUT | 1 | 7 || 8 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG6 | 15 | 198 | |
| − | | | | 0v | | | 9 || 10 | 0 | | + | | | | 0v | | | 9 || 10 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG7 | 16 | 199 | |
| 0 | 0 | GPIOA0 | OFF | 0 | 11 || 12 | 0 | OFF | GPIOA6 | 1 | 6 | | | 0 | 0 | GPIOA0 | OFF | 0 | 11 || 12 | 0 | OFF | GPIOA6 | 1 | 6 | | ||
| 2 | 2 | GPIOA2 | OFF | 0 | 13 || 14 | | | 0v | | | | | 2 | 2 | GPIOA2 | OFF | 0 | 13 || 14 | | | 0v | | | | ||
| 3 | 3 | GPIOA3 | OFF | 0 | 15 || 16 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG8 | 4 | 200 | | | 3 | 3 | GPIOA3 | OFF | 0 | 15 || 16 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG8 | 4 | 200 | | ||
| | | 3.3v | | | 17 || 18 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG9 | 5 | 201 | | | | | 3.3v | | | 17 || 18 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG9 | 5 | 201 | | ||
| − | | 64 | 12 | GPIOC0 | | + | | 64 | 12 | GPIOC0 | OFF | 0 | 19 || 20 | | | 0v | | | |
| − | | 65 | 13 | GPIOC1 | | + | | 65 | 13 | GPIOC1 | OFF | 0 | 21 || 22 | 0 | OFF | GPIOA1 | 6 | 1 | |
| − | | 66 | 14 | GPIOC2 | | + | | 66 | 14 | GPIOC2 | OFF | 0 | 23 || 24 | 0 | OFF | GPIOC3 | 10 | 67 | |
+-----+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+-----+ | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+-----+ | ||
| BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM | | | BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM | | ||
| − | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+-NanoPi NEO2--+------+----------+-----+-----+ | + | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+-NanoPi NEO/NEO2--+------+----------+-----+-----+ |
| − | +-----+----NanoPi NEO2 Debug UART-+----+ | + | +-----+----NanoPi NEO/NEO2 Debug UART-+----+ |
| BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Ph | | | BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Ph | | ||
+-----+-----+----------+------+---+----+ | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----+ | ||
| 4 | 17 | GPIOA4 | ALT5 | 0 | 37 | | | 4 | 17 | GPIOA4 | ALT5 | 0 | 37 | | ||
| − | | 5 | 18 | GPIOA5 | | + | | 5 | 18 | GPIOA5 | ALT4 | 0 | 38 | |
+-----+-----+----------+------+---+----+ | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----+ | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
==Code Sample with WiringNP== | ==Code Sample with WiringNP== | ||
| − | Here is a setup to connect a [[Matrix - LED]] module to a NanoPi | + | Here is a setup to connect a [[Matrix - LED]] module to a NanoPi NEO2:<br> |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:WiringNP-LED-Demo.jpg|frameless|300px|WiringNP-LED-Demo]]<br /> |
| − | + | Here is the connection:<br/> | |
| − | Here is the connection: | + | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 114: | Line 113: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
gcc -Wall -o test test.c -lwiringPi -lpthread | gcc -Wall -o test test.c -lwiringPi -lpthread | ||
| − | ./test | + | sudo ./test |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
You can see the LED is blinking. | You can see the LED is blinking. | ||
| − | |||
===PWM Code Sample=== | ===PWM Code Sample=== | ||
| − | Create a source file in C: | + | The PWM pin in NanoPi NEO/NEO2 is multiplexing which can be set to either PWM or SerialPort0. To set this pin to PWM you need to run "sudo npi-config" and enter the "Advanced Options" menu to Enable/Disable PWM. Note: after PWM is enabled SerialPort0 will not be accessed and you need to login your board via SSH.<br /> |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Here is a hardware setup to connect a [[Matrix - Buzzer]] to a NanoPi NEO2:<br /> | ||
| + | [[File:WiringNP-PWM-Demo.jpg|frameless|300px|WiringNP-PWM-Demo]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Create a source file in C:<br/> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
vi pwmtest.c | vi pwmtest.c | ||
| Line 127: | Line 130: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> | ||
#include <wiringPi.h> | #include <wiringPi.h> | ||
| − | |||
#include <stdio.h> | #include <stdio.h> | ||
#include <stdlib.h> | #include <stdlib.h> | ||
#include <stdint.h> | #include <stdint.h> | ||
| − | |||
int main (void) | int main (void) | ||
{ | { | ||
int l ; | int l ; | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
printf ("PWM test program\n") ; | printf ("PWM test program\n") ; | ||
| + | //using wiringPi Pin Number | ||
| + | int pin = 18; | ||
if (wiringPiSetup () == -1) | if (wiringPiSetup () == -1) | ||
| − | exit (1) ; | + | exit (1) ; |
| − | + | ||
| − | pinMode (pin, PWM_OUTPUT) ; | + | /* |
| − | + | //using Physical Pin Number | |
| − | for (;;) { | + | int pin = 38; |
| + | if (wiringPiSetupPhys() == -1) | ||
| + | exit (1) ; | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* | ||
| + | //using BCM Pin Number | ||
| + | int pin = 5; | ||
| + | if (wiringPiSetupGpio() == -1) | ||
| + | exit (1); | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | |||
| + | pinMode (pin, PWM_OUTPUT); | ||
| + | for (;;) { | ||
for (l = 0 ; l < 1024 ; ++l) { | for (l = 0 ; l < 1024 ; ++l) { | ||
| − | pwmWrite (pin, l) ; | + | pwmWrite (pin, l) ; |
| − | delay (1) ; | + | delay (1) ; |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | + | ||
for (l = 1023 ; l >= 0 ; --l) { | for (l = 1023 ; l >= 0 ; --l) { | ||
| − | pwmWrite (pin, l) ; | + | pwmWrite (pin, l) ; |
| − | delay (1) ; | + | delay (1) ; |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | + | ||
return 0 ; | return 0 ; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 184: | Line 196: | ||
Run the script: | Run the script: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | source test.sh | + | sudo source test.sh |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
You can see the LED is blinking. | You can see the LED is blinking. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Regular WiringNP APIs== |
Note:most of the descriptions for the following functions are from http://wiringpi.com/. To get more details refer to http://wiringpi.com/. | Note:most of the descriptions for the following functions are from http://wiringpi.com/. To get more details refer to http://wiringpi.com/. | ||
=== Initialization === | === Initialization === | ||
==== wiringPiSetup (void) ==== | ==== wiringPiSetup (void) ==== | ||
| − | This initializes wiringPi and | + | This function initializes wiringPi and uses the pin specifications defined by wiringPi. To check detailed pin specifications you can command "gpio readall".<br/> |
| − | You | + | You need to call this function as root. |
==== int wiringPiSetupGpio(void) ==== | ==== int wiringPiSetupGpio(void) ==== | ||
| − | This function is | + | This function is similar to the wiringPiSetup function. The only difference is that this function assumes the GPIO's pin specifications are the ones defined by CPU and haven't been redefined.<br/> |
| − | You | + | You need to call this function as root. |
==== int wiringPiSetupPhys (void) ==== | ==== int wiringPiSetupPhys (void) ==== | ||
| − | This function is the | + | This function is similar to the wiringPiSetup function. The only difference is that it only supports P1's interface and doesn't support physical pin specifications.<br/> |
| − | You | + | You need to call this function as root. |
==== int wiringPiSetupSys (void) ==== | ==== int wiringPiSetupSys (void) ==== | ||
| − | This function initializes wiringPi | + | This function initializes wiringPi and access hardware by using "/sys/class/gpio" APIs rather than commanding hardware directly.<br/> |
| − | This can be called | + | This function can be called by any users. The GPIO pin numbers used by this function should be the ones defined by CPU. This is similar to the rules followed by the wiringPiSetupGpio function.<br/> |
| − | + | Before calling this function make sure to call "/sys/class/gpio" APIs to list the pins you want to access.<br/> | |
| − | You can | + | You can list the pins you want to access in a separate shell script. Or you can command GPIO pins by calling "system()". |
=== Core Functions === | === Core Functions === | ||
==== void pinMode (int pin, int mode) ==== | ==== void pinMode (int pin, int mode) ==== | ||
| − | This function sets | + | This function sets a pin to INPUT, OUTPUT, PWM_OUTPUT or GPIO_CLOCK.<br/> |
| − | + | Note: after you call the wiringPiSetupSys function to access a pin calling this function will not make change that pin's mode.<br/> | |
| − | + | You can set a pin's mode in a shell script. | |
==== void pullUpDnControl (int pin, int pud) ==== | ==== void pullUpDnControl (int pin, int pud) ==== | ||
| − | This function sets the pull-up or pull-down resistor mode | + | This function sets a pin to the pull-up or pull-down resistor mode when that pin is set to INPUT.<br /> |
| − | Unlike the Arduino the NanoPi M1 has both pull-up an down | + | Unlike the Arduino the NanoPi M1 has both the pull-up an pull-down resistor modes.<br /> |
| − | The parameter pud | + | The parameter pud can be: PUD_OFF, (no pull up/down), PUD_DOWN (pull to ground) or PUD_UP (pull to 3.3v).<br /> |
The internal pull up/down resistors have a value of approximately 100KΩ on the NanoPi M1.<br /> | The internal pull up/down resistors have a value of approximately 100KΩ on the NanoPi M1.<br /> | ||
| − | + | Note: after you call the wiringPiSetupSys function to access a pin calling this function will not make change that pin's mode.<br /> | |
| − | If you need to activate a pull-up/pull-down you can do it | + | If you need to activate a pull-up/pull-down resistor you can do it by using GPIO commands in a script before you start your program. |
==== void digitalWrite (int pin, int value) ==== | ==== void digitalWrite (int pin, int value) ==== | ||
| − | This function | + | This function writes either HIGH or LOW to a pin. Before you call this function to access a pin make sure you have set that pin to OUTPUT.<br /> |
| − | WiringPi | + | WiringPi treat any non-0 value to HIGH and 0 is the only value that is treated as LOW. |
==== void pwmWrite (int pin, int value) ==== | ==== void pwmWrite (int pin, int value) ==== | ||
| − | This function | + | This function writes a value to a PWM register. The value can be any one in 0~1024. Different PWM devices may take different value ranges.<br /> |
| − | + | Note: after you call the wiringPiSetupSys function to access a pin calling this function will not be able to write a value to that pin.<br /> | |
==== digitalRead(int pin); ==== | ==== digitalRead(int pin); ==== | ||
| − | This function | + | This function reads a pin's value. The value is either HIGH(1) or LOW(0).<br /> |
==== analogRead (int pin) ; ==== | ==== analogRead (int pin) ; ==== | ||
| − | This function returns | + | This function returns a value it reads from an analog pin. To effectively call this function make sure you have connected a working analog device such as Gertboard and quick2Wire to your board.<br /> |
==== analogWrite (int pin, int value) ; ==== | ==== analogWrite (int pin, int value) ; ==== | ||
| − | This function writes a | + | This function writes a value to an analog pin. To effectively call this function make sure you have connected a working analog device such as Gertboard to your board.<br/> |
==Update Log== | ==Update Log== | ||
| Line 249: | Line 261: | ||
* Added section 4 by adding support for H5 based NEO2 | * Added section 4 by adding support for H5 based NEO2 | ||
* Added section 5.2: code sample on how to access a PWM device | * Added section 5.2: code sample on how to access a PWM device | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===May-17-2017=== | ||
| + | * Updated section 4 by adding installation steps for M1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===May-24-2017=== | ||
| + | * Updated section 5.2 by adding a PWM code sample for NEO2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Nov-14-2018=== | ||
| + | * Updated section 6 | ||
Latest revision as of 05:59, 14 November 2018
Contents
1 Introduction to WiringPi
The wiringPi library was initially developed by Gordon Henderson in C. It contains libraries to access GPIO, I2C, SPI, UART, PWM and etc.
The wiringPi library contains various libraries, header files and a commandline utility:gpio. The gpio utility can be used to read and write GPIO pins.
2 Introduction to WiringNP
The wiringPi library was initially developed for BCM2835, and later migrated to Allwinner H3 and renamed as WiringNP. Now the WiringNP works with FriendlyElec's NanoPi M1, NanoPi NEO and NanoPi NEO2. The first version was made by wertyzp. FriendlyElec developed a version for Allwinner H5 based NanoPi NEO2.
Here is WiringNP's project page: https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP
3 Install WiringNP on NEO/NEO2
Log into your nano board via SSH, open a terminal and install the WiringNP library by running the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP cd WiringNP/ chmod 755 build ./build
4 Install WiringNP on NanoPi M1
Log into your nano board via SSH, open a terminal and install the WiringNP library by running the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/WiringNP cd WiringNP/ git checkout nanopi-m1 chmod 755 build ./build
4.1 Verify WiringNP
The WiringNP library contains a set of gpio commands. Users can use them to access the GPIO pins on a nano board. You can verify your WiringNP by running the following command:
gpio readall
If your installation is successful the following messages will show up. Here is the message list for NEO2:
root@FriendlyARM:~# gpio readall +-----+-----+----------+------+---+-NanoPi NEO/NEO2--+------+----------+-----+-----+ | BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+-----+ | | | 3.3V | | | 1 || 2 | | | 5V | | | | 12 | 8 | GPIOA12 | OFF | 0 | 3 || 4 | | | 5V | | | | 11 | 9 | GPIOA11 | OFF | 0 | 5 || 6 | | | 0v | | | | 203 | 7 | GPIOG11 | OUT | 1 | 7 || 8 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG6 | 15 | 198 | | | | 0v | | | 9 || 10 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG7 | 16 | 199 | | 0 | 0 | GPIOA0 | OFF | 0 | 11 || 12 | 0 | OFF | GPIOA6 | 1 | 6 | | 2 | 2 | GPIOA2 | OFF | 0 | 13 || 14 | | | 0v | | | | 3 | 3 | GPIOA3 | OFF | 0 | 15 || 16 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG8 | 4 | 200 | | | | 3.3v | | | 17 || 18 | 0 | OFF | GPIOG9 | 5 | 201 | | 64 | 12 | GPIOC0 | OFF | 0 | 19 || 20 | | | 0v | | | | 65 | 13 | GPIOC1 | OFF | 0 | 21 || 22 | 0 | OFF | GPIOA1 | 6 | 1 | | 66 | 14 | GPIOC2 | OFF | 0 | 23 || 24 | 0 | OFF | GPIOC3 | 10 | 67 | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+-----+ | BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+-NanoPi NEO/NEO2--+------+----------+-----+-----+ +-----+----NanoPi NEO/NEO2 Debug UART-+----+ | BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Ph | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----+ | 4 | 17 | GPIOA4 | ALT5 | 0 | 37 | | 5 | 18 | GPIOA5 | ALT4 | 0 | 38 | +-----+-----+----------+------+---+----+
5 Code Sample with WiringNP
Here is a setup to connect a Matrix - LED module to a NanoPi NEO2:
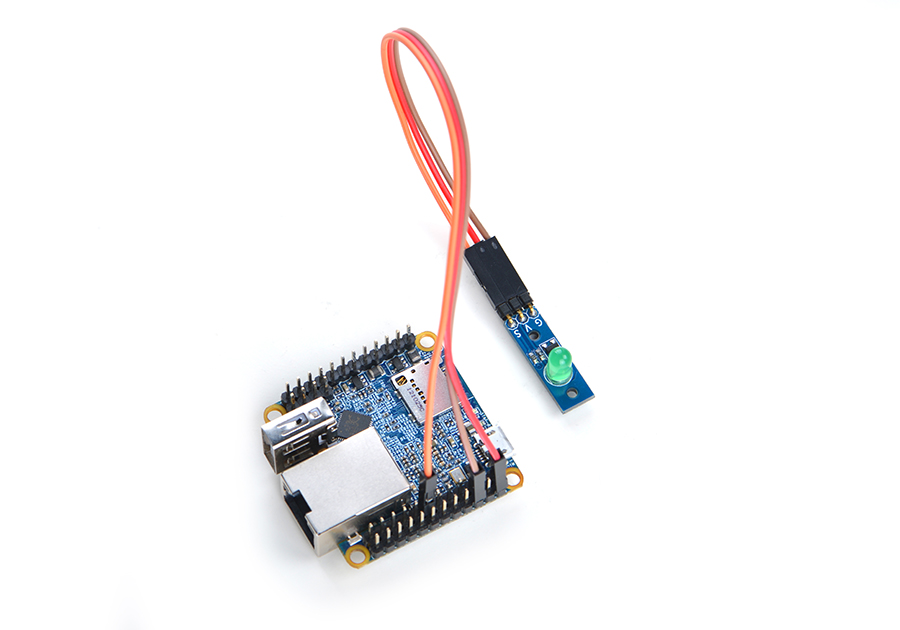
Here is the connection:
| Matrix-LED | NanoPi M1 |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
We will show how to use WiringNP to control a LED module.
In the following code samples index 7 stands for Pin7. We will use "7" to access this physical pin.
5.1 C Source Code
Make a C source file:
vi test.cType the following lines:
#include <wiringPi.h> int main(void) { wiringPiSetup() ; pinMode (7, OUTPUT) ; for(;;) { digitalWrite(7, HIGH) ; delay (500) ; digitalWrite(7, LOW) ; delay (500) ; } }
Compile and run "test.c":
gcc -Wall -o test test.c -lwiringPi -lpthread sudo ./test
You can see the LED is blinking.
5.2 PWM Code Sample
The PWM pin in NanoPi NEO/NEO2 is multiplexing which can be set to either PWM or SerialPort0. To set this pin to PWM you need to run "sudo npi-config" and enter the "Advanced Options" menu to Enable/Disable PWM. Note: after PWM is enabled SerialPort0 will not be accessed and you need to login your board via SSH.
Here is a hardware setup to connect a Matrix - Buzzer to a NanoPi NEO2:
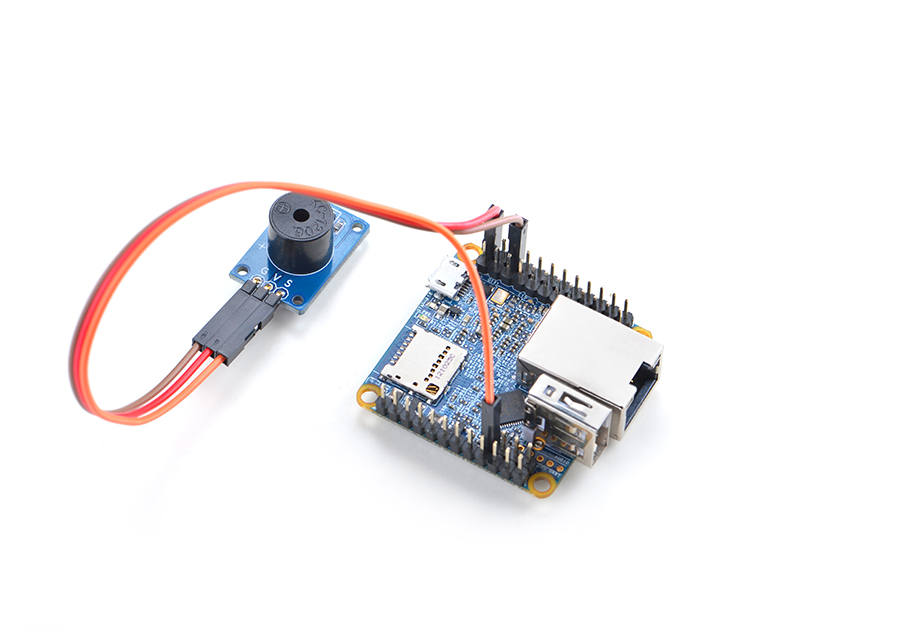
Create a source file in C:
vi pwmtest.cType the following code:
#include <wiringPi.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdint.h> int main (void) { int l ; printf ("PWM test program\n") ; //using wiringPi Pin Number int pin = 18; if (wiringPiSetup () == -1) exit (1) ; /* //using Physical Pin Number int pin = 38; if (wiringPiSetupPhys() == -1) exit (1) ; */ /* //using BCM Pin Number int pin = 5; if (wiringPiSetupGpio() == -1) exit (1); */ pinMode (pin, PWM_OUTPUT); for (;;) { for (l = 0 ; l < 1024 ; ++l) { pwmWrite (pin, l) ; delay (1) ; } for (l = 1023 ; l >= 0 ; --l) { pwmWrite (pin, l) ; delay (1) ; } } return 0 ; }
Compile the pwmtest.c file and run the generated executable:
gcc -Wall -o pwmtest pwmtest.c -lwiringPi -lpthread ./pwmtest
Connect a PWM beeper to a NEO/NEO2 and the beeper will sound.
5.3 Shell Script
Make a shell script:
vi test.shType the following lines:
LED=7 gpio mode $LED out while true; do gpio write $LED 1 sleep 0.5 gpio write $LED 0 sleep 0.5 done
Run the script:
sudo source test.sh
You can see the LED is blinking.
6 Regular WiringNP APIs
Note:most of the descriptions for the following functions are from http://wiringpi.com/. To get more details refer to http://wiringpi.com/.
6.1 Initialization
6.1.1 wiringPiSetup (void)
This function initializes wiringPi and uses the pin specifications defined by wiringPi. To check detailed pin specifications you can command "gpio readall".
You need to call this function as root.
6.1.2 int wiringPiSetupGpio(void)
This function is similar to the wiringPiSetup function. The only difference is that this function assumes the GPIO's pin specifications are the ones defined by CPU and haven't been redefined.
You need to call this function as root.
6.1.3 int wiringPiSetupPhys (void)
This function is similar to the wiringPiSetup function. The only difference is that it only supports P1's interface and doesn't support physical pin specifications.
You need to call this function as root.
6.1.4 int wiringPiSetupSys (void)
This function initializes wiringPi and access hardware by using "/sys/class/gpio" APIs rather than commanding hardware directly.
This function can be called by any users. The GPIO pin numbers used by this function should be the ones defined by CPU. This is similar to the rules followed by the wiringPiSetupGpio function.
Before calling this function make sure to call "/sys/class/gpio" APIs to list the pins you want to access.
You can list the pins you want to access in a separate shell script. Or you can command GPIO pins by calling "system()".
6.2 Core Functions
6.2.1 void pinMode (int pin, int mode)
This function sets a pin to INPUT, OUTPUT, PWM_OUTPUT or GPIO_CLOCK.
Note: after you call the wiringPiSetupSys function to access a pin calling this function will not make change that pin's mode.
You can set a pin's mode in a shell script.
6.2.2 void pullUpDnControl (int pin, int pud)
This function sets a pin to the pull-up or pull-down resistor mode when that pin is set to INPUT.
Unlike the Arduino the NanoPi M1 has both the pull-up an pull-down resistor modes.
The parameter pud can be: PUD_OFF, (no pull up/down), PUD_DOWN (pull to ground) or PUD_UP (pull to 3.3v).
The internal pull up/down resistors have a value of approximately 100KΩ on the NanoPi M1.
Note: after you call the wiringPiSetupSys function to access a pin calling this function will not make change that pin's mode.
If you need to activate a pull-up/pull-down resistor you can do it by using GPIO commands in a script before you start your program.
6.2.3 void digitalWrite (int pin, int value)
This function writes either HIGH or LOW to a pin. Before you call this function to access a pin make sure you have set that pin to OUTPUT.
WiringPi treat any non-0 value to HIGH and 0 is the only value that is treated as LOW.
6.2.4 void pwmWrite (int pin, int value)
This function writes a value to a PWM register. The value can be any one in 0~1024. Different PWM devices may take different value ranges.
Note: after you call the wiringPiSetupSys function to access a pin calling this function will not be able to write a value to that pin.
6.2.5 digitalRead(int pin);
This function reads a pin's value. The value is either HIGH(1) or LOW(0).
6.2.6 analogRead (int pin) ;
This function returns a value it reads from an analog pin. To effectively call this function make sure you have connected a working analog device such as Gertboard and quick2Wire to your board.
6.2.7 analogWrite (int pin, int value) ;
This function writes a value to an analog pin. To effectively call this function make sure you have connected a working analog device such as Gertboard to your board.
7 Update Log
7.1 December-31-2016
- Released English Version
7.2 May-16-2017
- Updated section 2 by adding support for H5 based NEO2
- Added section 4 by adding support for H5 based NEO2
- Added section 5.2: code sample on how to access a PWM device
7.3 May-17-2017
- Updated section 4 by adding installation steps for M1
7.4 May-24-2017
- Updated section 5.2 by adding a PWM code sample for NEO2
7.5 Nov-14-2018
- Updated section 6