Difference between revisions of "NanoPi Duo"
(→快速入门) |
|||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
::For more details refer to the document [http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/index.php/File:Dimension_NanoPi_Duo_v1.0_1706-PCB.rar NanoPi_Duo_v1.0_1706 pcb file in dxf format] | ::For more details refer to the document [http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/index.php/File:Dimension_NanoPi_Duo_v1.0_1706-PCB.rar NanoPi_Duo_v1.0_1706 pcb file in dxf format] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Get Started== |
| − | === | + | ===Essentials You Need=== |
| − | + | Before starting to use your NanoPi Duo get the following items ready | |
| − | * NanoPi | + | * NanoPi Duo |
| − | * | + | * microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC |
| − | * | + | * microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must |
| − | * | + | * A Host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system |
| − | * | + | * a serial communication board |
| − | === | + | ===TF Cards We Tested=== |
| − | + | To make your NanoPi Duo boot and run fast we highly recommend you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here: | |
| − | * | + | * SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD TF card: |
[[File:SanDisk MicroSD.png|frameless|100px|SanDisk MicroSD 8G]] | [[File:SanDisk MicroSD.png|frameless|100px|SanDisk MicroSD 8G]] | ||
| − | * | + | * SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S: |
[[File:SanDisk MicroSD-01.png|frameless|100px|SanDisk MicroSD 128G]] | [[File:SanDisk MicroSD-01.png|frameless|100px|SanDisk MicroSD 128G]] | ||
| − | *川宇 | + | * 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card: |
[[File:SanDisk MicroSD-02.png|frameless|100px|chuanyu MicroSD 8G]] | [[File:SanDisk MicroSD-02.png|frameless|100px|chuanyu MicroSD 8G]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Make an Installation TF Card=== |
| − | ==== | + | ====Download Image Files==== |
| − | + | Get the following files from here [https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pLLmV27 download link] to download image files (under the official-ROMs directory) and the flashing utility(under the tools directory):<br /> | |
| − | + | ||
::{| class="wikitable" | ::{| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan=2| | + | |colspan=2|Image Files: |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |nanopi-duo_ubuntu-core-xenial_4.x.y_YYYYMMDD.img.zip || Ubuntu-Core with Qt- | + | |nanopi-duo_ubuntu-core-xenial_4.x.y_YYYYMMDD.img.zip || Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded Image File, kernel:Linux-4.x.y |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan=2| | + | |colspan=2|Flash Utility: |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |win32diskimager.rar || | + | |win32diskimager.rar || Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd" |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 06:09, 18 July 2017
Contents
1 Introduction
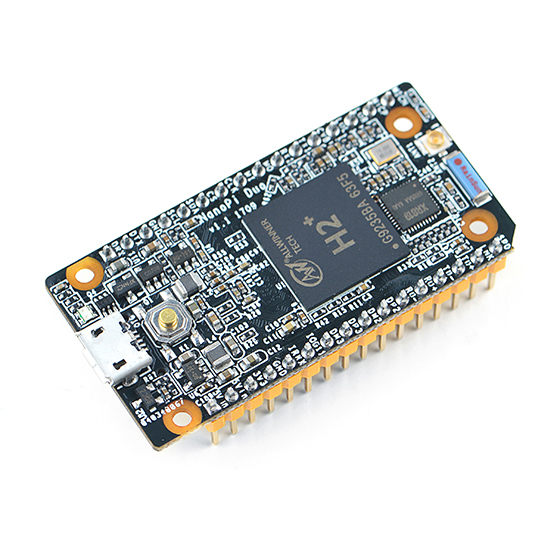
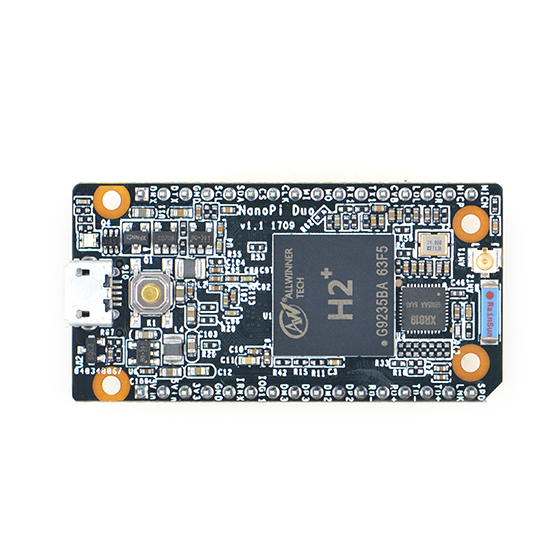
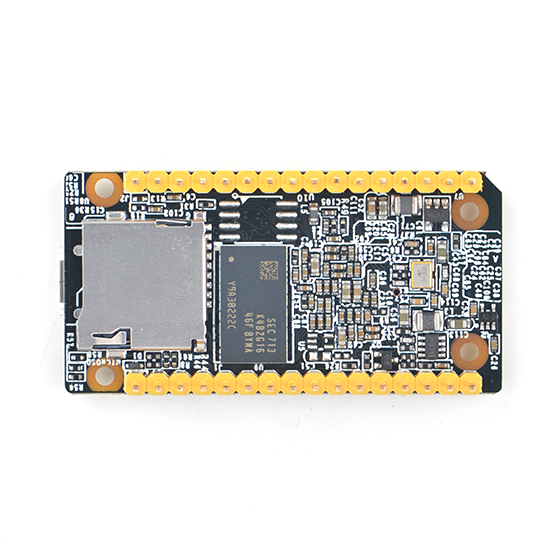
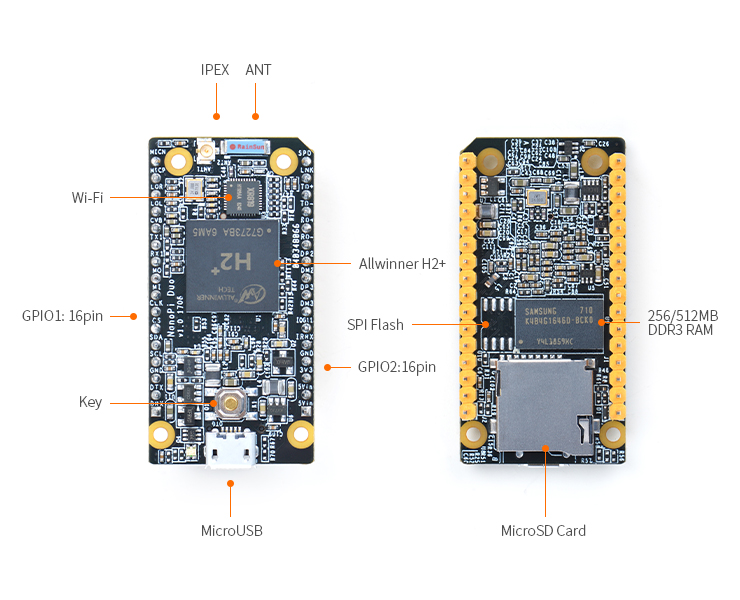
- The NanoPi Duo(abbreviated as Duo) is designed and developed by FriendlyElec for makers, hobbyists and fans. It is open source. It uses Allwinner's Coretex-A7 H2+ with internal Mali400MP2 GPU. It has 256MB/512MB DDR3 RAM.
- The NanoPi Duo's dimension is 25.4 x 50mm. It exposes interfaces such as Ethernet, two USB ports and audio. It can boot from a MicroSD card.
2 Hardware Spec
- CPU: Allwinner H2+, Quad-core Cortex-A7
- DDR3 RAM: 256MB/512MB
- Connectivity: 10/100M Ethernet
- Wifi:XR819
- USB Host: 2.54mm pin x2
- MicroSD Slot x 1
- MicroUSB: OTG and power input
- Debug Serial Port:2.54mm pitch pin header
- Audio input/output Port: 2.54mm pitch pin header
- GPIO: 2.54mm spacing 12pin x2, It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc
- PC Size: 25.4 x 50mm
- Power Supply: DC 5V/2A
- Working Temperature: -40℃ to 80℃
- OS/Software: U-boot,Ubuntu-Core
- Weight: xxg(With Pin-headers)
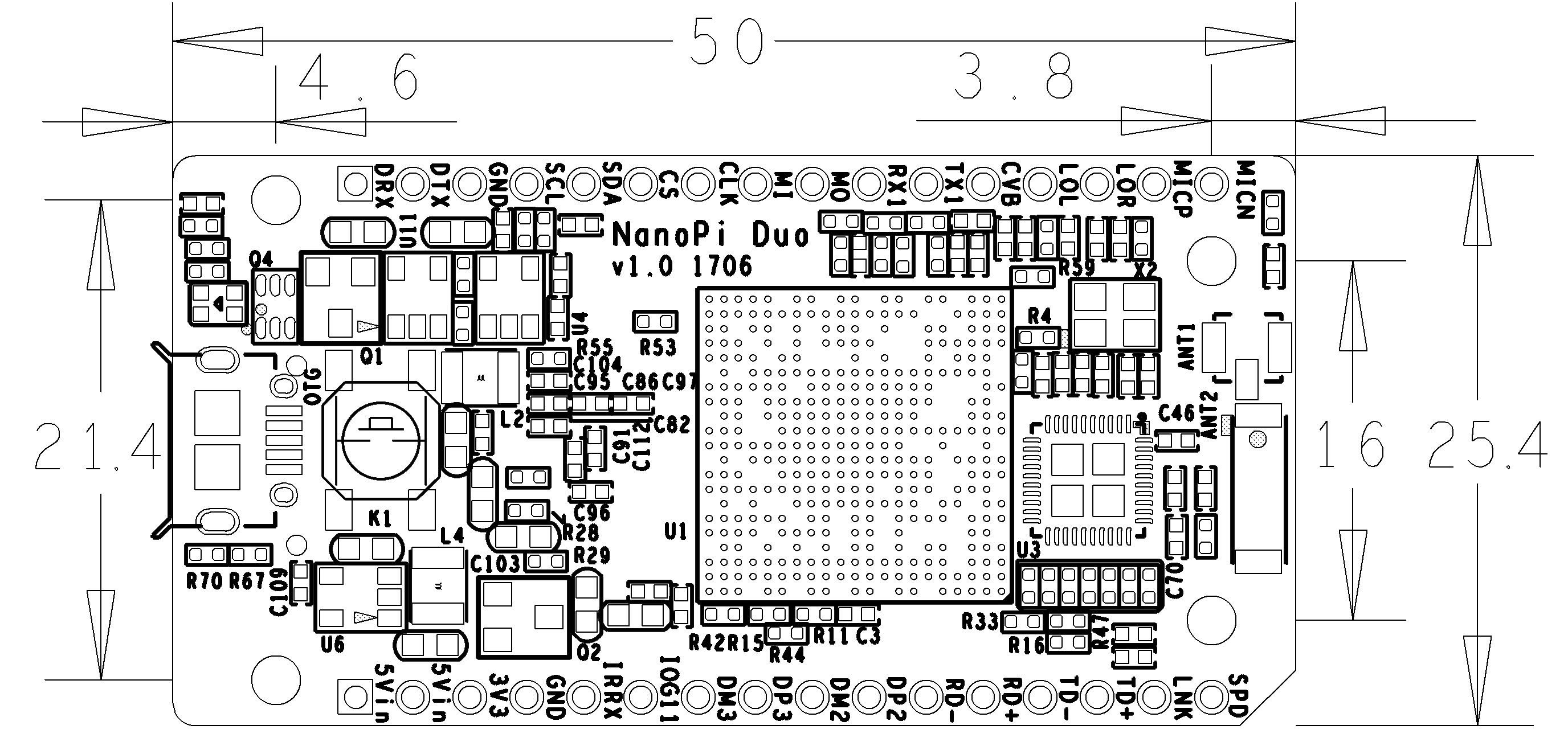
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
3.1 Layout
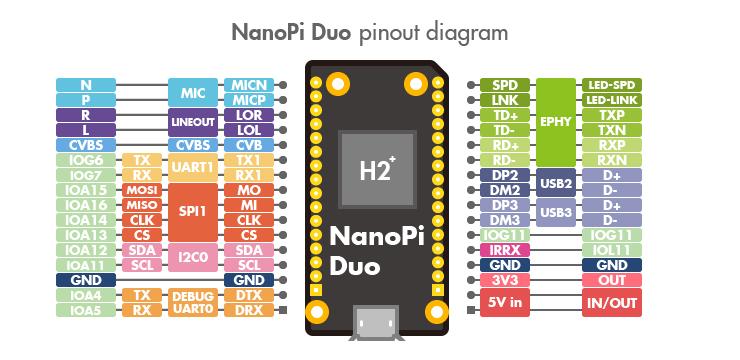
- GPIO Pin Description
Pin silk screen Name Linux gpio Pin silk screen Name Linux gpio MICN MIC_N SPD EPHY-LED-SPD MICP MIC_P LNK EPHY-LED-LINK LOR LINEOUT_R TD+ EPHY-TXP LOL LINEOUT_L TD- EPHY-TXN CVB CVBS RD+ EPHY-RXP TX1 UART1_TX/GPIOG6 198 RD- EPHY-RXN RX1 UART1_RX/GPIOG7 199 DP2 USB-DP2 MO UART3_RTS/SPI1_MOSI/GPIOA15 15 DM2 USB-DM2 MI UART3_CTS/SPI1_MISO/GPIOA16 16 DP3 USB-DP3 CLK UART3_RX/SPI1_CLK/GPIOA14 14 DM3 USB-DM3 CS UART3_TX/SPI1_CS/GPIOA13 13 IOG11 GPIOG11 203 SDA I2C0_SDA/GPIOA12 12 IRRX GPIOL11/IR-RX 363 SCL I2C0_SCL/GPIOA11 11 GND GND GND GND 3V3 SYS_3.3V DTX DEBUG_TX(UART_TXD0)/GPIOA4 4 5Vin VDD_5V DRX DEBUG_RX(UART_RXD0)/GPIOA5/PWM0 5 5Vin VDD_5V
- Note:
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. When the external device’s voltage is greater than the MicroUSB's voltage the external device is charging the board otherwise the board powers the external device. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.6V
- All pins are 3.3V, output current is 5mA
- For more details refer to the document NanoPi Duo Schematic
3.2 Dimensional Diagram
- For more details refer to the document NanoPi_Duo_v1.0_1706 pcb file in dxf format
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi Duo get the following items ready
- NanoPi Duo
- microSD Card/TFCard: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- microUSB power. A 5V/2A power is a must
- A Host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
- a serial communication board
4.2 TF Cards We Tested
To make your NanoPi Duo boot and run fast we highly recommend you use a Class10 8GB SDHC TF card or a better one. The following cards are what we used in all our test cases presented here:
- SanDisk TF 8G Class10 Micro/SD TF card:
- SanDisk TF128G MicroSDXC TF 128G Class10 48MB/S:
- 川宇 8G C10 High Speed class10 micro SD card:
4.3 Make an Installation TF Card
4.3.1 Download Image Files
Get the following files from here download link to download image files (under the official-ROMs directory) and the flashing utility(under the tools directory):
Image Files: nanopi-duo_ubuntu-core-xenial_4.x.y_YYYYMMDD.img.zip Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded Image File, kernel:Linux-4.x.y Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
4.3.2 制作Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded系统TF卡
将Ubuntu系统固件和烧写工具win32diskimager.rar分别解压,在Windows下插入TF卡(限4G及以上的卡),以管理员身份运行 win32diskimager 工具,
在win32diskimager工具的界面上,选择你的TF卡盘符,选择系统固件,点击 Write 按钮烧写即可。烧写完成后,将制作好TF卡插入NanoPi Duo,使用USB供电(5V/2A),
NanoPi Duo会上电自动开机,看到板上的蓝色LED闪烁,这说明系统已经开始启动了。
5 Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded系统的使用
5.1 运行Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded系统
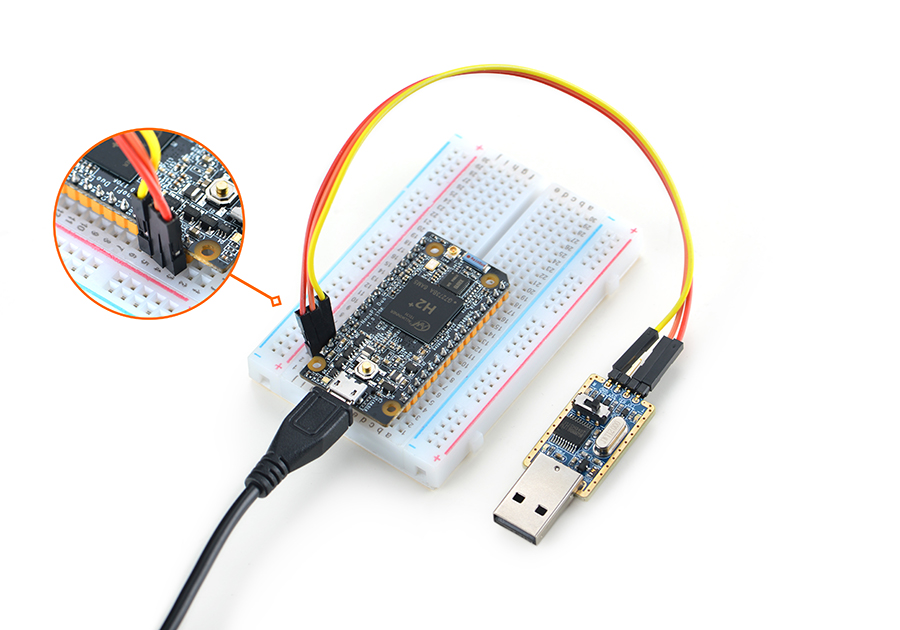
- 如果您需要进行内核开发,你最好选购一个串口配件,连接了串口,则可以通过串口终端对Duo进行操作。以下是串口的接法,接上串口,即可调试。
- 推荐搭配Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo底板使用,Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo底板详细介绍请参考Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo底板介绍,以下是底板的接法。
Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo-Duo
- Ubuntu-Core默认帐户:
普通用户:
用户名: pi 密码: pi
root用户:
用户名: root 密码: fa
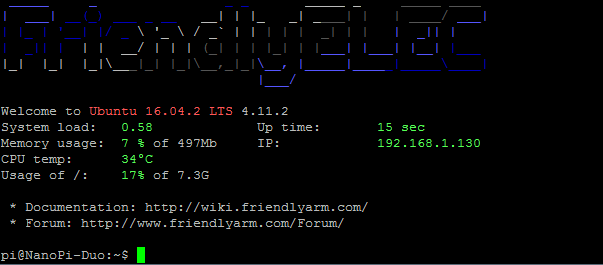
默认会以 pi 用户自动登录,你可以使用 sudo npi-config 命令取消自动登录。
- 更新软件包:
$ sudo apt-get update
5.2 扩展TF卡文件系统
第一次启动系统时,系统会自动扩展文件系统分区,请耐心等待,TF卡的容量越大,需要等待的时间越长,进入系统后执行下列命令查看文件系统分区大小:
$ df -h
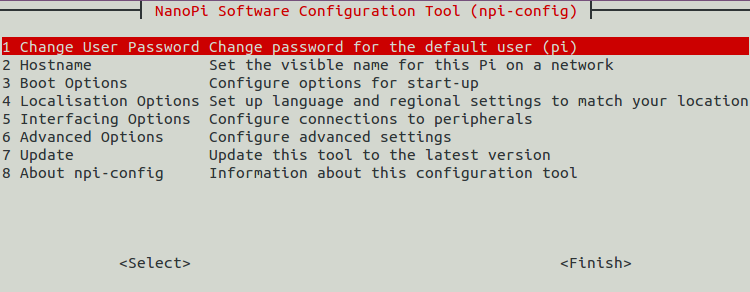
5.3 使用npi-config配置系统
npi-config是一个命令行下的系统配置工具,可以对系统进行一些初始化的配置,可配置的项目包括:用户密码、系统语言、时区、Hostname、SSH开关、自动登录选项、硬件接口(Serial/I2C/SPI/PWM/I2S)使能等,在命令行执行以下命令即可进入:
$ sudo npi-config
5.4 连接有线网络
使用Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo底板能方便的连接有线网络,Duo在加电开机前如果已正确的连接网线,则系统启动时会自动获取IP地址,如果没有连接网线、没有DHCP服务或是其它网络问题,则会导致获取IP地址失败,同时系统启动会因此等待约15~60秒的时间。 手动获取IP地址
$ dhclient eth05.5 连接WiFi
使用以下命令连接Wifi,Duo板子上集成了Wifi天线,为保证数据传输稳定可靠,建议外接扩转天线。
- 查看网络设备列表
$ sudo nmcli dev
注意,如果列出的设备状态是 unmanaged 的,说明网络设备不受NetworkManager管理,你需要清空 /etc/network/interfaces下的网络设置,然后重启.
- 开启WiFi
$ sudo nmcli r wifi on
- 扫描附近的 WiFi 热点
$ sudo nmcli dev wifi
- 连接到指定的 WiFi 热点
$ sudo nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD"
请将 SSID和 PASSWORD 替换成实际的 WiFi名称和密码。
连接成功后,下次开机,WiFi 也会自动连接。
更详细的NetworkManager使用指南可参考这篇维基:Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
搭配Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo底板使用,还可使用USB WiFi。系统默认已经支持市面上众多常见的USB WiFi,想知道你的USB WiFi是否可用只需将其接在Duo上即可,已测试过的USB WiFi型号如下:
序号 型号 1 RTL8188CUS/8188EU 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 小米WiFi mt7601
5.6 SSH登录
Duo没有任何图形界面输出的接口,如果你没有串口模块,可以通过SSH协议登录Duo。假设通过路由器查看到Duo的IP地址为192.168.1.230,你可以在PC机上执行如下命令登录Duo:
$ ssh root@192.168.1.230
密码为fa。
5.7 连接USB摄像头模块(FA-CAM202)使用
搭配Mini Shield for NanoPi Duo底板可连接USB摄像头模块(FA-CAM202)模块。
FA-CAM202是一款200万像素的USB摄像头模块,参考维基Matrix - USB_Camera(FA-CAM202)。
启动系统,连接网络,以root用户登录终端并编译运行mjpg-streamer:
$ su root $ cd /root/mjpg-streamer $ make $ ./start.sh
mjpg-streamer是一个开源的网络视频流服务器,在板子上成功运行mjpg-streamer后会打印下列信息:
i: Using V4L2 device.: /dev/video0 i: Desired Resolution: 1280 x 720 i: Frames Per Second.: 30 i: Format............: YUV i: JPEG Quality......: 90 o: www-folder-path...: ./www/ o: HTTP TCP port.....: 8080 o: username:password.: disabled o: commands..........: enabled
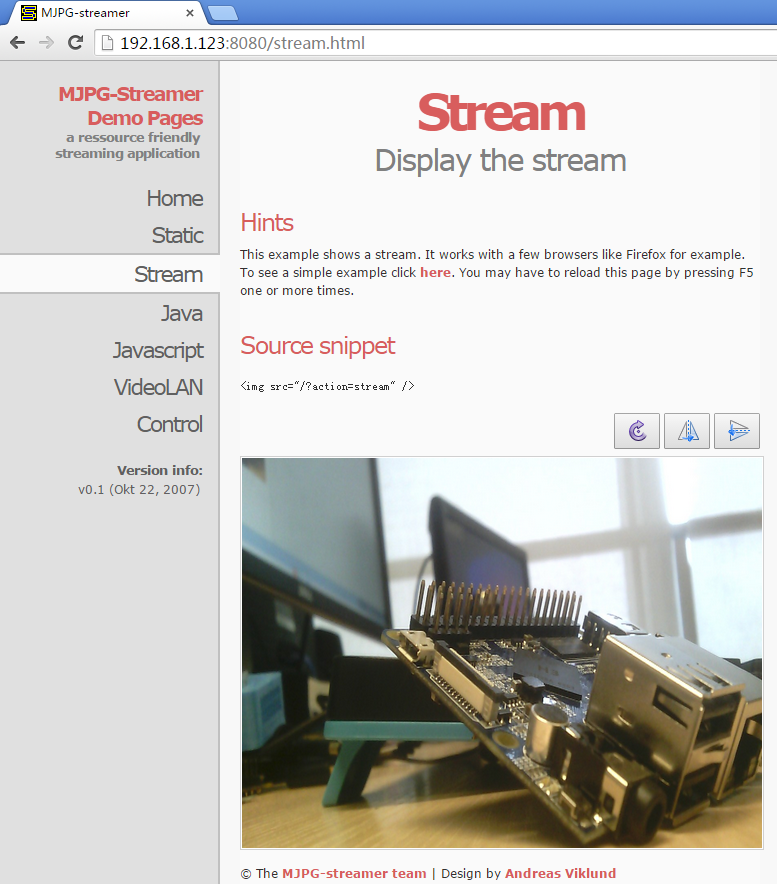
假设Duo的IP地址为192.168.1.123,在PC的浏览器中输入 192.168.1.123:8080 就能浏览摄像头采集的画面了,效果如下:
5.8 命令行查看CPU工作温度
在串口终端执行如下命令,可以快速地获取CPU的当前温度和运行频率等信息:
$ cpu_freq5.9 通过Rpi-Monitor查看系统状态
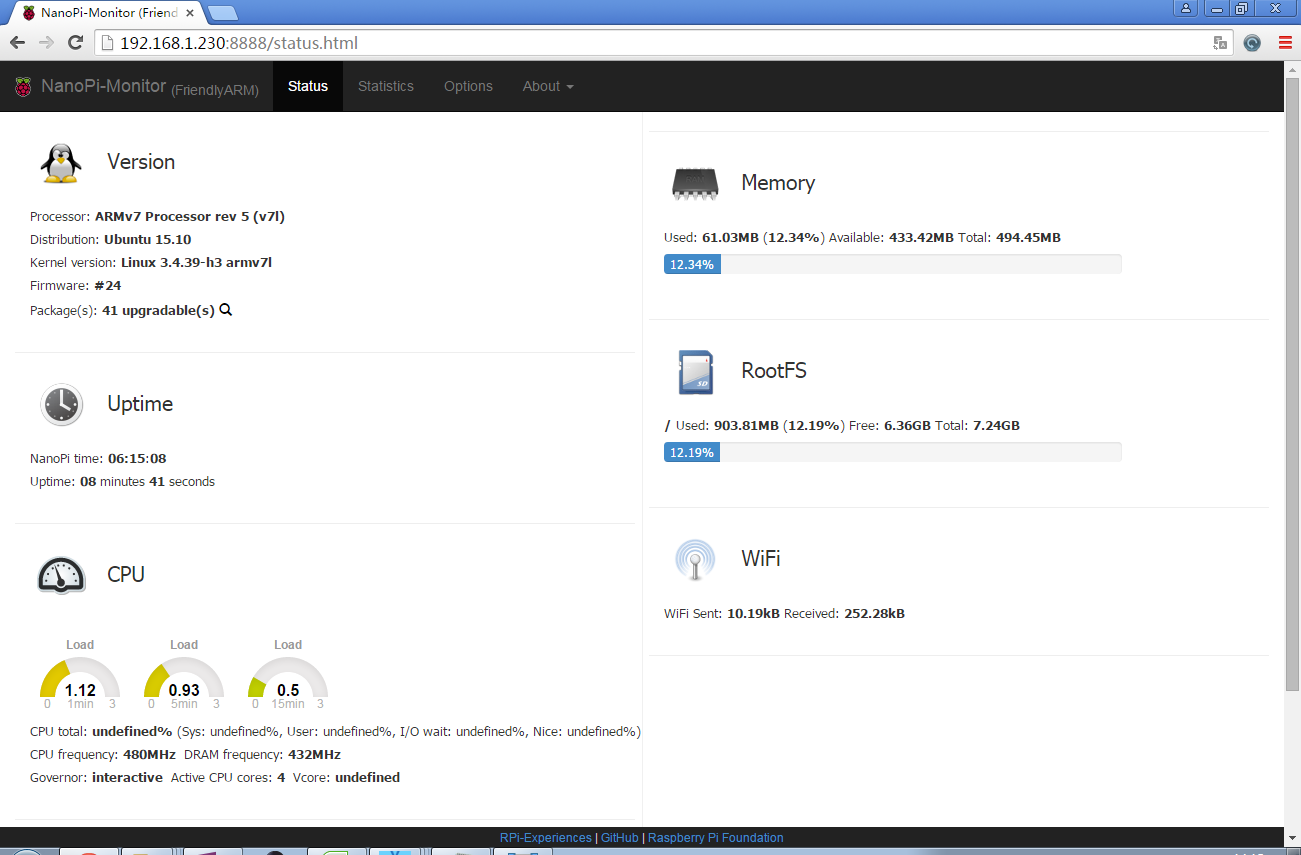
Ubuntu-Core系统里已经集成了Rpi-Monitor,该服务允许用户在通过浏览器查看开发板系统状态。
假设Duo的IP地址为192.168.1.230,在PC的浏览器中输入下述地址:
192.168.1.230:8888用户可以非常方便地查看到系统负载、CPU的频率和温度、可用内存、SD卡容量等信息。
5.10 通过WiringNP测试GPIO
wiringPi库最早是由Gordon Henderson所编写并维护的一个用C语言写成的类库,除了GPIO库,还包括了I2C库、SPI库、UART库和软件PWM库等,由于wiringPi的API函数和arduino非常相似,这也使得它广受欢迎。
wiringPi库除了提供wiringPi类库及其头文件外,还提供了一个命令行工具gpio:可以用来设置和读写GPIO管脚,以方便在Shell脚本中控制GPIO管脚。
我们在Duo系统中集成了这个工具以便客户测试GPIO管脚。详细信息请参看 WiringNP
6 如何编译Ubuntu-Core with Qt-Embedded系统
6.1 使用开源社区主线BSP
Duo现已支持使用Linux-4.x.y内核,并使用Ubuntu Core 16.04,关于H2+芯片系列开发板使用主线U-boot和Linux-4.x.y的方法,请参考维基:Mainline U-boot & Linux
7 使用扩展配件及编程示例
7.1 使用Mini Shield for NanoPi NEO Duo
8 3D 打印外壳
9 资源链接
9.1 手册原理图等开发资料
- 原理图: NanoPi Duo V1.0 1706原理图
- 尺寸图: NanoPi Duo V1.0 1706 PCB尺寸图
- 芯片手册: