Difference between revisions of "NanoPi M3"
(→Boot NanoPi M3 from SD Card) |
(→在Linux Desktop下通过脚本制作) |
||
| Line 211: | Line 211: | ||
* Insert this card into your NanoPi M3's boot slot, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and LED1 is blinking and LED2 is off this indicates your NanoPC-T3 has successfully booted.<br /> | * Insert this card into your NanoPi M3's boot slot, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and LED1 is blinking and LED2 is off this indicates your NanoPC-T3 has successfully booted.<br /> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ====Under Linux Desktop==== |
| − | * 1) | + | * 1) Insert your microSD card into your host running Ubuntu and check your SD card's device name |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
dmesg | tail | dmesg | tail | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card is recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions" | |
| − | *2) | + | * 2) Download Flashing Script |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_nanopi3.git | git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_nanopi3.git | ||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | *3) | + | * 3) Flash Android Firmware to MicroSD Card |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
su | su | ||
./fusing.sh /dev/sdx | ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ( | + | (Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system) <br /> |
| − | + | When you do “git clone” you have to hit “Y” within 10 seconds after it prompts you to download image files otherwise you will miss the download. | |
| − | *4) | + | * 4) Flash Debian Firmware to MicroSD Card |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
./fusing.sh /dev/sdx debian | ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx debian | ||
Revision as of 02:53, 20 May 2016
Contents
1 Introduction
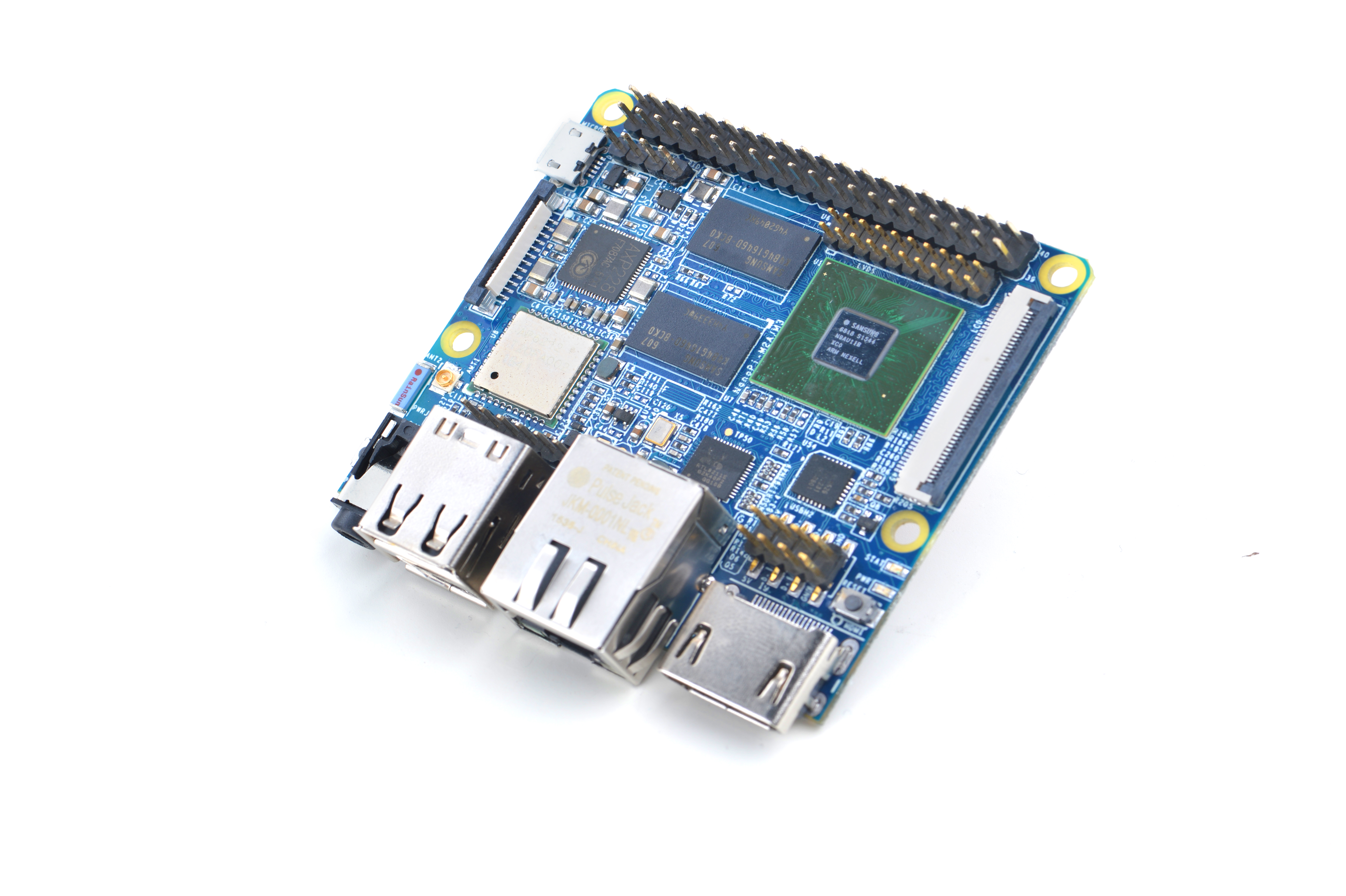
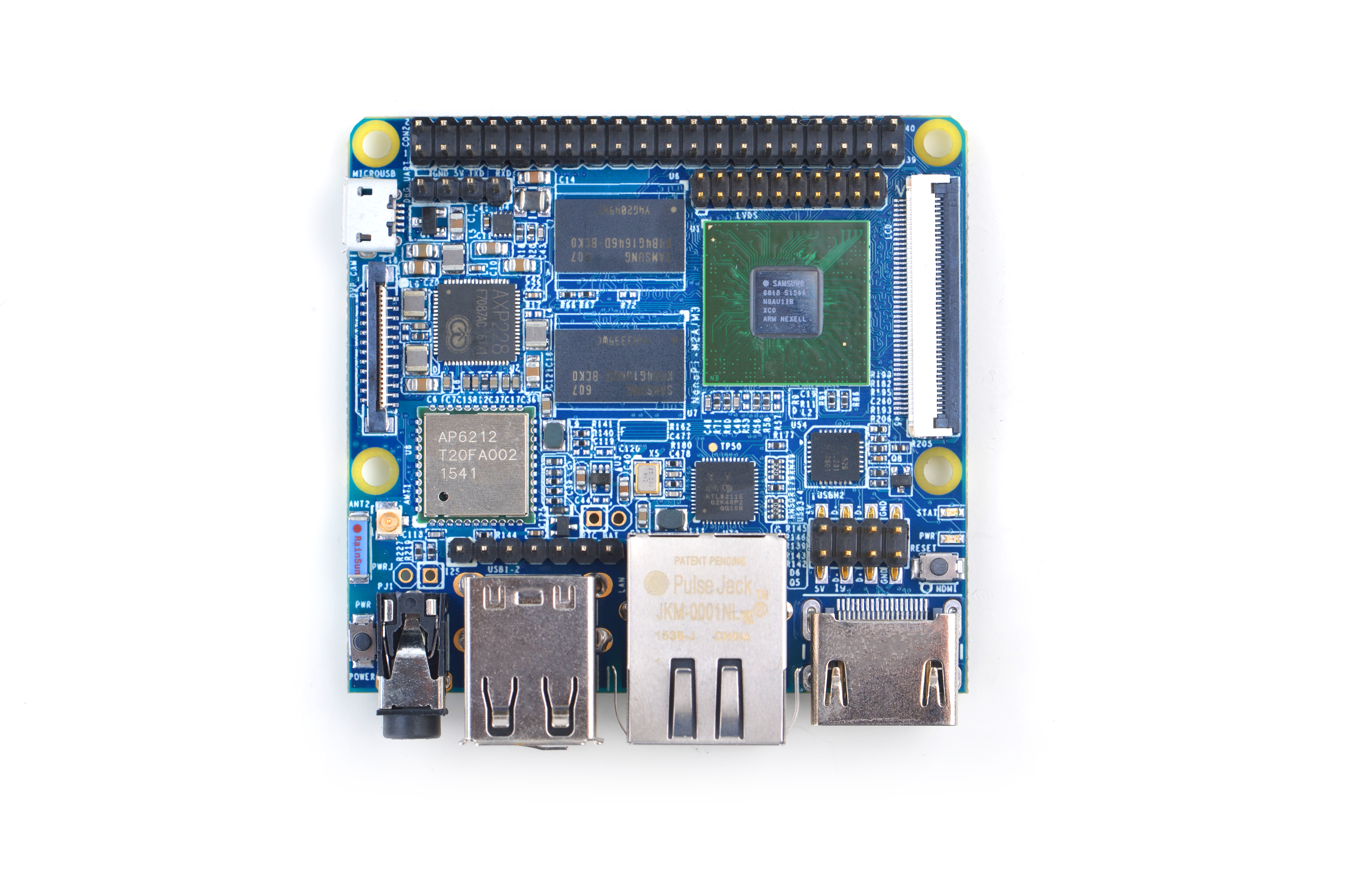
- The NanoPi M3 is another ARM board developed by FriendlyARM for makers, hobbyists and hackers. With this new friend we wish you could get not only tech skills but also unique experiences in various applications and hacking. It is small, elegant but has rich ports and interfaces. Playing with it and working with it the M3 will not only inspire your ideas but also turn them into realities.
- The NanoPi M3 uses the Samsung Octa-Core Cortex-A53 S5P6818 SoC. Its dynamic frequency scales from 400M up to 1.4GHz. It has Gbps Ethernet port, built-in WiFi and Bluetooth. Its AXP228 PMU supports software power-off, sleep and wakeup functions. In addition the NanoPi M3 has MicroUSB port for power supply and on-board porcelain antenna.
- On this tiny board various ports and interfaces are integrated. It has DVP Camera/LVDS/HDMI/LCD interfaces, Gbps Ethernet, I2S, 3.5mm audio jack, four USB ports and a serial debug port.
2 Features
- SoC: Samsung S5P6818 Octa-Core Cortex-A53, 400M Hz - 1.4G Hz
- Power Management Unit: AXP228 PMU, it supports software power-off and wake-up.
- System Memory: 1GB 32bit DDR3 RAM
- Storage: 1 x MicroSD Card Socket
- Ethernet: Gbit Ethernet(RTL8211E)
- WiFi: 802.11b/g/n
- Bluetooth: 4.0 dual mode
- Antenna: Porcelain Antenna IPX Interface
- Audio: 3.5 mm audio jack / via HDMI
- I2S: 7pin, 2.54mm pitch pin-header
- Microphone: onboard Microphone
- USB Host: 4 x USB 2.0 Host, two type A ports and two 2.54 mm pitch pin-headers
- MicroUSB: 1 x MicroUSB 2.0 Client, Type A
- LCD Interface: 0.5mm pitch 45 pin FPC seat, full color RGB 8-8-8
- HDMI: 1.4A Type A, 1080P
- LVDS: 20pin 2.00mm pitch pin-header
- DVP Camera: 0.5mm pitch 24 pin FPC seat
- GPIO: 2.54 mm pitch 40 pin-header
- Serial Debug Port: 2.54mm pitch 4pin-header
- User Key: K1 (power), Reset
- LED: 1 x power LED and 1 x status LED
- RTC Battery: RTC Battery Seat
- Heat Sink: 1 x Heat Sink with mounting holes
- Power: DC 5V/2A
- PCB: Six Layer, ENIG
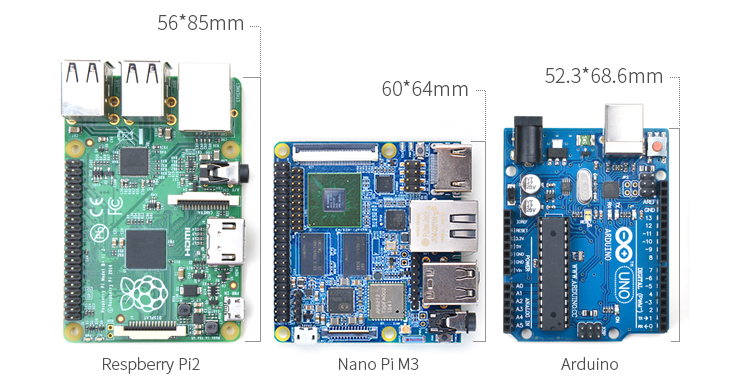
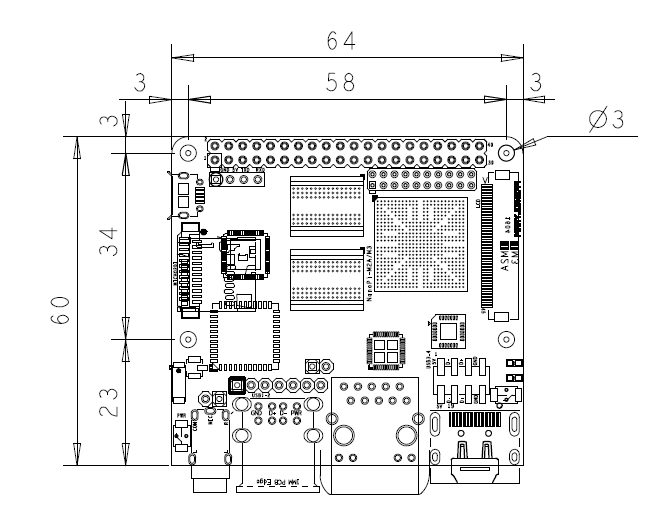
- Dimension: 64 mm x 60 mm
- OS/Software: uboot, Android and Debian
3 Diagram, Layout and Dimension
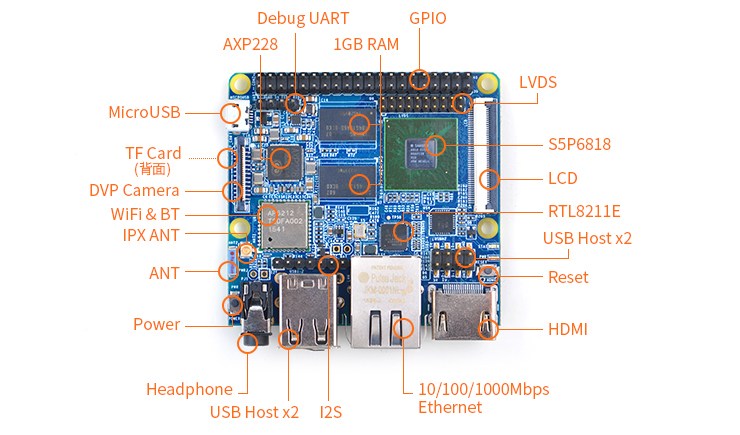
3.1 Layout
- GPIO Pin Spec
Pin# Name Pin# Name 1 SYS_3.3V 2 VDD_5V 3 I2C0_SDA 4 VDD_5V 5 I2C0_SCL 6 DGND 7 GPIOD8/PPM 8 UART3_TXD/GPIOD21 9 DGND 10 UART3_RXD/GPIOD17 11 UART4_TX/GPIOB29 12 GPIOD1/PWM0 13 GPIOB30 14 DGND 15 GPIOB31 16 GPIOC14/PWM2 17 SYS_3.3V 18 GPIOB27 19 SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC31 20 DGND 21 SPI0_MISO/GPIOD0 22 UART4_RX/GPIOB28 23 SPI0_CLK/GPIOC29 24 SPI0_CS/GPIOC30 25 DGND 26 GPIOB26 27 I2C1_SDA 28 I2C1_SCL 29 GPIOC8 30 DGND 31 GPIOC7 32 GPIOC28 33 GPIOC13/PWM1 34 DGND 35 SPI2_MISO/GPIOC11 36 SPI2_CS/GPIOC10 37 AliveGPIO3 38 SPI2_MOSI/GPIOC12 39 DGND 40 SPI2_CLK/GPIOC9
The M3's GPIO pin spec is slightly different from the NanoPi 2's. Here is a comparison table:40 pins GPIO comparison table
- Debug Port(UART0)
Pin# Name 1 DGND 2 VDD_5V 3 UART_TXD0 4 UART_RXD0
- DVP Camera Interface Pin Spec
Pin# Name 1, 2 SYS_3.3V 7,9,13,15,24 DGND 3 I2C0_SCL 4 I2C0_SDA 5 GPIOB14 6 GPIOB16 8,10 NC 11 VSYNC 12 HREF 14 PCLK 16-23 Data bit7-0
- RGB LCD Interface Pin Spec
Pin# Name Description 1, 2 VDD_5V 5V Output, it can be used to power LCD modules 11,20,29, 37,38,39,40, 45 DGND Ground 3-10 Blue LSB to MSB RGB blue 12-19 Green LSB to MSB RGB green 21-28 Red LSB to MSB RGB red 30 GPIOB25 available for users 31 GPIOC15 occupied by FriendlyARM one wire technology to recognize LCD models and control backlight and implement resistive touch, not applicable for users. 32 XnRSTOUT Form CPU low when system is reset 33 VDEN signal the external LCD that data is valid on the data bus 34 VSYNC vertical synchronization 35 HSYNC horizontal synchronization 36 LCDCLK LCD clock, Pixel frequency 41 I2C2_SCL I2C2 clock signal, for capacitive touch data transmission 42 I2C2_SDA I2C2 data signal, for capacitive touch data transmission 43 GPIOC16 interrupt pin for capacitive touch, used with I2C2 44 NC Not connected
- Notes
- SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
- VDD_5V: 5V power input/output. The input range is 4.7V ~ 5.6V
- All pins are 3.3V, output current is 5mA
- For more details refer to the document: NanoPi-M2A-M3-1604-Schematic.pdf
3.2 Board Dimension
- For more details refer to the document:PCB dxf file
4 Get Started
4.1 Essentials You Need
Before starting to use your NanoPi M3 get the following items ready
- NanoPi M3
- SD Card: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
- A DC 5V/2A power is a must
- HDMI monitor or LCD
- USB keyboard, mouse and possible a USB hub(or a TTL to serial board)
- A host computer running Ubuntu 14.04 64 bit system
4.2 Make an Installation SD Card
4.2.1 Boot NanoPi M3 from SD Card
Get the following files from the download link to download necessary files:
- Get a 4G SDHC card and backup its data if necessary.
For LCD or HDMI output use the following files: s5p6818-debian-sd4g-20160426.img Debian image files s5p6818-android-sd4g-20160426.img Android image files s5p6818-core-qte-sd4g-20160426.img Ubuntu Core + QT image files Flash Utility: win32diskimager.rar Windows utility. Under Linux users can use "dd"
- Uncompress these files. Insert an SD card(at least 4G) into a Windows PC and run the win32diskimager utility as administrator. On the utility's main window select your SD card's drive, the wanted image file and click on "write" to start flashing the SD card.
- Insert this card into your NanoPi M3's boot slot, press and hold the boot key and power on (with a 5V/2A power source). If the PWR LED is on and LED1 is blinking and LED2 is off this indicates your NanoPC-T3 has successfully booted.
4.2.2 Under Linux Desktop
- 1) Insert your microSD card into your host running Ubuntu and check your SD card's device name
dmesg | tail
Search the messages output by "dmesg" for similar words like "sdc: sdc1 sdc2". If you can find them it means your SD card is recognized as "/dev/sdc". Or you can check that by commanding "cat /proc/partitions"
- 2) Download Flashing Script
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_nanopi3.git cd sd-fuse_nanopi3
- 3) Flash Android Firmware to MicroSD Card
su ./fusing.sh /dev/sdx
(Note: you need to replace "/dev/sdx" with the device name in your system)
When you do “git clone” you have to hit “Y” within 10 seconds after it prompts you to download image files otherwise you will miss the download.
- 4) Flash Debian Firmware to MicroSD Card
./fusing.sh /dev/sdx debian
4.2.3 关于LCD/HDMI分辨率
系统启动时uboot会自动识别LCD,成功则会设置为该LCD的显示分辨率,失败则缺省会设置为HDMI 720P模式。
如果要修改LCD的显示分辨率,可以直接修改内核中的文件 arch/arm/plat-s5p6818/nanopi3/lcds.c , 然后重新编译内核并更新即可。
对于HDMI的显示模式,Android则是会通过EDID获得HDMI设备如电视机所支持的显示模式,然后自动选择一个合适的分辨率。如果使用的是Debian,则缺省是720P,可通过修改内核配置来切换为1080P。
4.3 在电脑上修改SD卡上的系统
如果你想在运行系统之前,先对系统做一些修改,可以参看本节内容,否则可以跳过本节。
将制作好SD卡插入一台运行Linux的电脑,可以挂载SD卡上的boot和rootfs等分区,对分区内容进行修改,通过在以下情况下你需要进行这些操作:
1) 你想更改Kernel Command Line参数,则可以通过sd-fuse_nanopi3/tools目录下的fw_setenv工具来操作。
查看当前的Command Line:
cd sd-fuse_nanopi3/tools ./fw_printenv /dev/sdc | grep bootargs
目前的Android 5.1.1_r6启用了SELinux,缺省模式是enforcing,你可以通过Command Line来修改它,例如:
./fw_setenv /dev/sdc bootargs XXX androidboot.selinux=permissive
即可修改为permissive模式,其中上面的XXX需要替换成原来的bootargs值。
2) 更新内核
新版本的uboot在启动时如果识别到LCD,将读取SD卡boot分区的uImage,否则将读取uImage.hdmi。
对于Android来说是同一个文件,因此直接使用新编译的uImage来替换SD卡boot分区下的文件即可。
对于Debian来说,这2个文件是不相同的,使用新编译的支持LCD的uImage直接替换SD卡boot分区的文件,如果是支持HDMI的内核,则替换uImage.hdmi。
4.4 运行Android或Debian
- 将制作好SD卡插入NanoPC M3,连接HDMI,按住靠近网口的boot按键,最后接电源(5V 2A)拨动开关,NanoPC M3会从SD卡启动。你可以看到板上PWR灯常亮,LED1灯闪烁,这说明系统已经开始启动了,同时电视上也将能看到系统启动的画面。
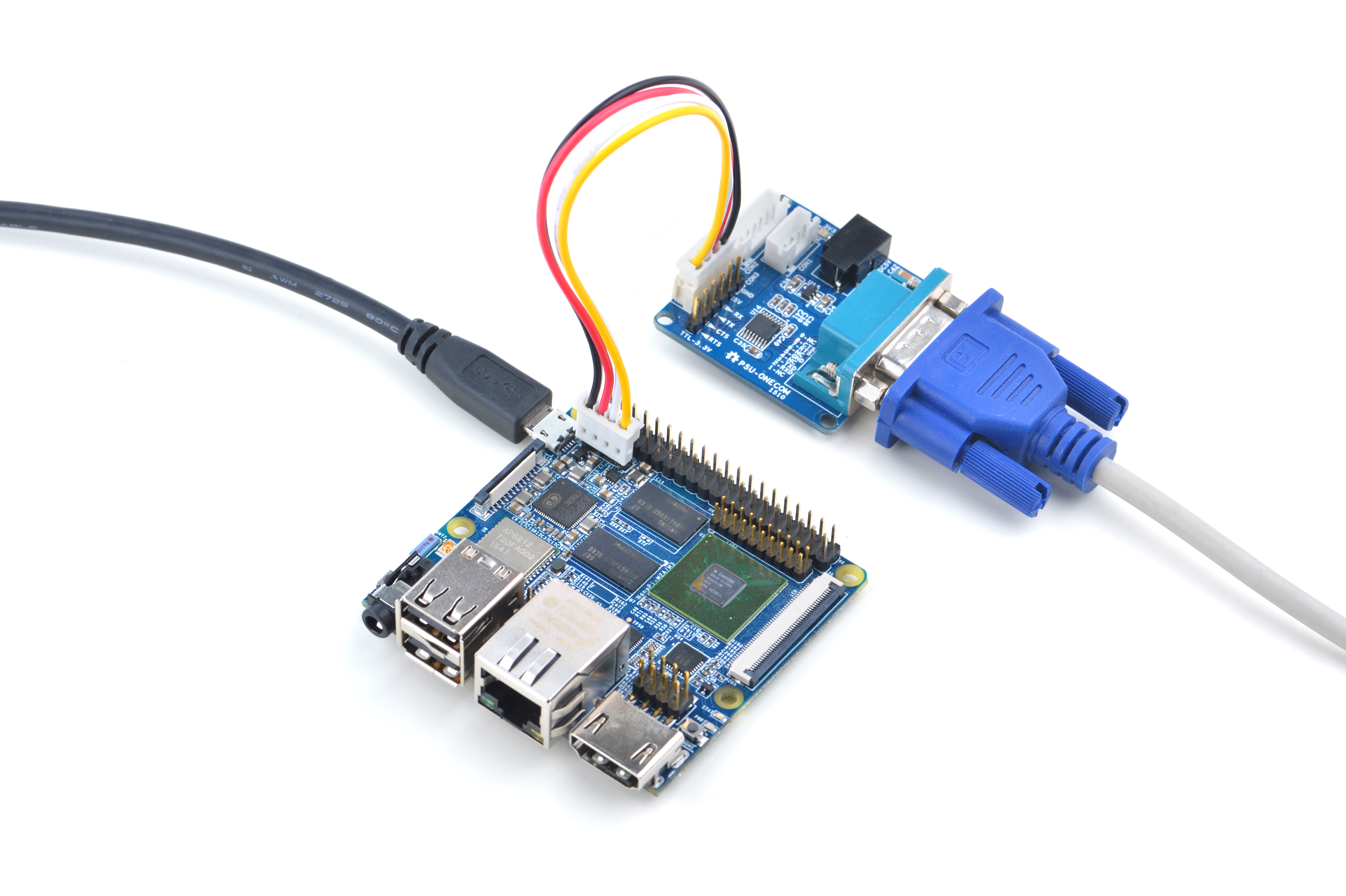
1)要在电视上进行操作,你需要连接USB鼠标和键盘;如果你选购了LCD配件,则可以直接使用LCD上面的触摸屏进行操作。
2)如果您需要进行内核开发,你最好选购一个串口配件,连接了串口,则可以通过终端对NanoPC M3进行操作。
- 以下是串口的接法。接上串口,即可调试:
- 如果提示输入密码,Debian的root用户的默认密码是两个字母fa。
4.5 通过VNC和ssh登录Debian
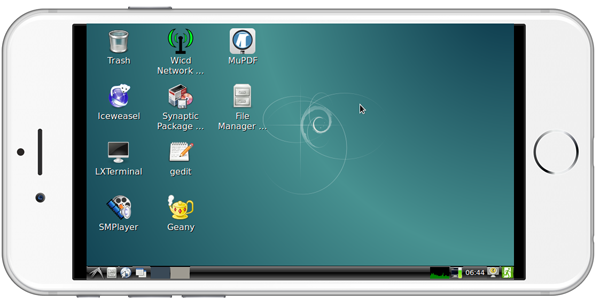
如果你是祼板运行系统(既没有连接LCD也没有连接HDMI),并且烧写了带 -wifiap.img 后辍的固件,你可以使用手机,或者有无线网卡的电脑连接到NanoPC M3开放的 nanopi2-wifiap 无线热点(默认密码是123456789),连接成功后,无论是手机还是电脑,你可以到这里下载并安装一个名为VNC Viewer的软件,用VNC连接到NanoPC M3,NanoPC M3在使用VNC时的连接地址和端口为:192.168.8.1:5901,默认密码为:fa123456,以下是在iPhone上用VNC登录NanoPC-T2的画面:
你也可以通过 ssh -l root 192.168.8.1 命令在终端上登录,默认的root用户密码是 fa。
为了保证ssh的流畅,我们用以下命令关闭wifi的省电模式:
iwconfig wlan0 power off
5 Debian系统的使用
5.1 连接有线网络
- NanoPC M3支持千兆网络,Debian或者Android系统在启动前,只要接上网线,系统启动后则会自动分配IP地址,不需要额外去配置。
5.2 连接无线网络
用vi或在图形界面下用gedit编辑文件 /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf, 在文件末尾填入路由器信息如下所示:
network={ ssid="YourWiFiESSID" psk="YourWiFiPassword" }
其中,YourWiFiESSID和YourWiFiPassword请替换成你要连接的无线AP名称和密码。
保存退出后,执行以下命令即可连接WiFi:
ifdown wlan0 ifup wlan0
如果你的WiFi密码中有特殊字符,或者你不希望明文存放密码,你可以使用wpa_passphrase命令为WiFi密码生成一个密钥(psk),用密钥来代替密码 ,在命令行下,可输入以下命令生成密钥:
wpa_passphrase YourWiFiESSID
在提示输入密码时,输入你的WiFi密码,再打开 /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf 文件你会发现密钥已经被更新,你可以删除明文的密码了。
如果你的WiFi当前处于无线热点模式,你需要先退出该模式方可连接到路由器,使用以下命令退出无线热点模式:
su
turn-wifi-into-apmode no5.3 配置Wi-Fi无线热点
可以通过以下命令,将Wi-Fi切换至无线热点模式:
turn-wifi-into-apmode yes按提示重启即可,默认的热点名称为 nanopi2-wifiap,密码为123456789。
现在,你可以在电脑上搜索并连接nanopi2-wifiap这个无线热点,连接成功后,可以通过ssh到192.168.8.1这个地址来登录NanoPC M3:
ssh root@192.168.8.1
在提示输入密码时,输入预设的密码fa,即可登入。
为了保证ssh的流畅,我们用以下命令关闭wifi的省电模式:
iwconfig wlan0 power off
WiFi工作模式可通过以下命令查询:
cat /sys/module/bcmdhd/parameters/op_mode
输出为数字2则表示当前处于无线热点模式,要切换回普通的Station模式,输入如下命令:
turn-wifi-into-apmode no
5.4 使用蓝牙传输
点击右下角的蓝牙图标,会弹出一个操作菜单,其中,
Make discoverable菜单项是打开NanoPC M3蓝牙的可发现属性,这样其他设备(例如手机)就可以搜索到NanoPC M3并进行配对了;
Devices... 菜单项可以打开搜索界面,主动搜索周边的蓝牙设备(注:需要这个设备先打开可发现属性);
Send Files to Device...菜单项则可以通过蓝牙发送文件到已配对的指定设备上。
5.5 安装Debian软件包
我们提供的是标准的Debian jessie系统,你可以使用apt-get等命令来安装软件包,如果板子是首次运行,需要先用以下命令更新软件包列表:
apt-get update然后就可以安装软件包了,例如要安装ftp服务器,使用以下命令:
apt-get install vsftpd如果软件包下载速度不理想,你可以编辑 /etc/apt/sources.list 更换一个更快的源服务器,这个网址[1]有一份完整的源镜像服务器列表,注意要选用一个带armhf架构的。
6 如何编译系统
6.1 安装交叉编译器
首先下载并解压编译器:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/prebuilts.git sudo mkdir -p /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain sudo tar xf prebuilts/gcc-x64/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf-4.9.3.tar.xz -C /opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/
然后将编译器的路径加入到PATH中,用vi编辑vi ~/.bashrc,在末尾加入以下内容:
export PATH=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/bin:$PATH export GCC_COLORS=auto
执行一下~/.bashrc脚本让设置立即在当前shell窗口中生效,注意"."后面有个空格:
. ~/.bashrc这个编译器是64位的,不能在32位的Linux系统上运行,安装完成后,你可以快速的验证是否安装成功:
arm-linux-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=arm-linux-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/libexec/gcc/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/4.9.3/lto-wrapper Target: arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf Configured with: /work/toolchain/build/src/gcc-4.9.3/configure --build=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3 --with-sysroot=/opt/FriendlyARM/toolchain/4.9.3/arm-cortexa9-linux-gnueabihf/sys-root --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-arch=armv7-a --with-tune=cortex-a9 --with-fpu=vfpv3 --with-float=hard ... Thread model: posix gcc version 4.9.3 (ctng-1.21.0-229g-FA)
6.2 编译U-Boot
下载U-Boot源代码并编译,注意分支是nanopi2-lollipop-mr1:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/uboot_nanopi2.git cd uboot_nanopi2 git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1 make s5p6818_nanopi3_config make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
编译成功结束后您将获得u-boot.bin,您可以通过fastboot来更新正在运行的NanoPC M3板上SD的U-Boot,方法如下:
1) 在电脑上先用命令 sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot 安装 fastboot 工具;
2) 用串口配件连接NanoPC M3和电脑,在上电启动的2秒内,在串口终端上按下回车,进入 u-boot 的命令行模式;
3) 在u-boot 命令行模式下输入命令 fastboot 回车,进入 fastboot 模式;
4) 用microUSB线连接NanoPC M3和电脑,在电脑上输入以下命令烧写u-boot.bin:
fastboot flash bootloader u-boot.bin
注意:您不能直接使用dd来更新SD卡,否则有可能会导致无法正常启动。
6.3 准备mkimage
编译内核需要用到U-Boot中的工具mkimage,因此,在编译内核uImage前,您需要保证您的主机环境可以成功运行它。
你可以直接使用命令 sudo apt-get install u-boot-tools 来安装,也可以自己编译并安装:
cd uboot_nanopi2 make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- tools sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/sbin && sudo cp -v tools/mkimage /usr/local/sbin
6.4 编译Linux kernel
6.4.1 编译内核
- 下载内核源代码
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-3.4.y.git cd linux-3.4.y git checkout nanopi2-lollipop-mr1
NanoPC-T2内核所属的分支是nanopi2-lollipop-mr1,在开始编译前先切换分支。
- 编译Android内核
make nanopi3_android_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
- 编译Debian内核
make nanopi3_linux_defconfig touch .scmversion make uImage
编译成功结束后,新生成的内核烧写文件为 arch/arm/boot/uImage,此内核支持HDMI 720p输出,用于替换掉SD卡boot分区下的uImage.hdmi。
如果要支持HDMI 1080p,则需要修改内核配置:
touch .scmversion make nanopi3_linux_defconfig make menuconfig Device Drivers --> Graphics support --> Nexell Graphics --> [ ] LCD [*] HDMI (0) Display In [0=Display 0, 1=Display 1] Resolution (1920 * 1080p) ---> make uImage
启用LCD,同时取消HDMI,然后退出并保存配置,编译后即可获得支持LCD显示的uImage,用于替换SD卡boot分区下的uImage。
6.4.2 如何使用新编译的内核
- 更新SD卡上的内核
如果您是使用SD卡启动Android,则在PC上复制为Android编译的uImage到SD卡的boot分区(即分区1,设备是/dev/sdX1)即可。
如果您是使用SD卡启动Debian系统,则需要编译好用于HDMI的uImage后替换SD卡boot分区下的uImage.hdmi,然后编译用于LCD的uImage并替换SD卡boot分区下的uImage。
- 更新eMMC上Android的内核
如果只想单独更新eMMC上的内核来测试,则需要先正常启动板,然后mount eMMC的boot分区,使用新编译的uImage来替换原有文件,完成后reboot即可。
从eMMC启动时可通过以下方法来更新内核:
1) 启动完成后,需要手动mount eMMC的boot分区(设备是/dev/mmcblk0p1), 可通过串口在板上操作:
su mount -t ext4 /dev/block/mmcblk0p1 /mnt/media_rw/sdcard1/
2) 连接USB,在PC端Ubuntu下使用adb push命令复制新编译的uImage到已mount的boot分区下;
adb push uImage /mnt/media_rw/sdcard1/
3) 也可以将编译好的内核复制到SD卡或U盘,然后在板上复制到boot分区下;
4) 更新完成后,输入 reboot 命令重启即可,注意不要直接断电或按Reset键,否则可能会损坏文件。
- 更新eMMC上Debian的内核
从eMMC启动时可通过以下方法来更新内核:
1) 启动完成后,系统通常会自动mount eMMC的boot分区(设备是/dev/mmcblk0p1), 可输入命令mount来查看;
2) 连接网络,使用scp/ftp等方式复制新编译的uImage并替换boot分区下的文件,如果是用于HDMI的内核,则替换uImage.hdmi;
3) 也可以将编译好的内核复制到SD卡或U盘,然后在板止复制到boot分区下;
4) 更新完成后,输入 reboot 命令重启即可,注意不要直接断电或按Reset键,否则可能会损坏文件.
- 使用新的内核来生成boot.img
如果要生成直接烧写eMMC的文件,则需要使用新编译的内核来生成boot.img,然后复制到烧写用的SD卡即可直接烧写到eMMC.
对于Android,将新的uImage复制Android源码的device/friendly-arm/nanopi3/boot/ 下,然后编译Android即可获得新的boot.img .
对于Debian, 则需要使用按以下方法来生成boot.img :
1) 下载debian_nanopi2
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/debian_nanopi2.git
2) 复制用于HDMI的uImage到debian_nanopi2/boot/uImage.hdmi, 复制用于LCD的 uImage到debian_nanopi2/boot/uImage ;
3) 生成Debian的 boot.img
cd debian_nanopi2 mkdir rootfs ./build.sh
新的 boot.img 在 debian_nanopi2/sd-fuse_nanopi2/debian 下.
其中命令"mkdir rootfs"只是创建一个空的目录使得build.sh可以运行,因此生成的其它文件比如rootfs.img不能使用。
6.4.3 编译内核模块
Android包含内核模块,位于system分区的 /lib/modules/ 下,如果您有新的内核模块或者内核配置有变化,则需要重新编译。
首先编译内核源代码中的模块:
cd linux-3.4.y make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- modules
另外有2个内核模块的源代码位于Android源代码中,可使用以下命令来编译:
cd /opt/FriendlyARM/s5p6818/android ./vendor/friendly-arm/build/common/build-modules.sh
其中 “/opt/FriendlyARM/s5p6818/android” 是指Android源代码的TOP目录,使用参数“-h”可查看帮助。
编译成功结束后,会显示生成的内核模块。
6.5 编译Android
- 搭建编译环境
搭建编译Android的环境建议使用64位的Ubuntu 14.04,安装需要的包即可。
sudo apt-get install bison g++-multilib git gperf libxml2-utils make python-networkx zip sudo apt-get install flex libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk minicom
更多说明可查看 https://source.android.com/source/initializing.html 。
- 下载源代码
Android源代码的下载需要使用repo,其安装和使用请查看 https://source.android.com/source/downloading.html 。
mkdir android && cd android repo init -u https://github.com/friendlyarm/android_manifest.git -b nanopi3-lollipop-mr1 repo sync
其中“android”是指工作目录。
- 编译系统
source build/envsetup.sh lunch aosp_nanopi3-userdebug make -j8
编译成功完成后,目录 out/target/product/nanopi3/ 下包含可用于烧写的image文件。
filename partition Description boot.img boot - cache.img cache - userdata.img userdata - system.img system - partmap.txt - 分区描述文件
- 烧写到SD卡
如果是采用SD卡启动Android,可复制编译生成的image文件到sd-fuse_nanopi3/android/ 下,使用脚本即可烧到到SD卡,具体请查看#在Linux Desktop下通过脚本制作。
- 烧写到eMMC
成功编译Android后,可过2种方式烧写到eMMC,分别如下:
1) fastboot: 板子从eMMC启动后通过串口快速按任意键进入uboot命令行模式,输入命令fastboot即可启动此方式。
连接USB线,然后PC端输入以下命令:
cd out/target/product/nanopi3 sudo fastboot flash boot boot.img sudo fastboot flash cache cache.img sudo fastboot flash userdata userdata.img sudo fastboot flash system system.img sudo fastboot reboot
2) 使用SD卡烧写
复制out/target/product/nanopi3下的boot.img, cache.img, userdata.img, system.img, partmap.txt到烧写用SD卡的images/android下,再次烧写即可。
7 源代码和固件下载链接
8 资源链接
- CPU(SOC)数据手册: S5P6818 Datasheet
- 原理图: NanoPi-M2A-M3-1604-Schematic.pdf
- PCB详细尺寸: PCB DXF文件