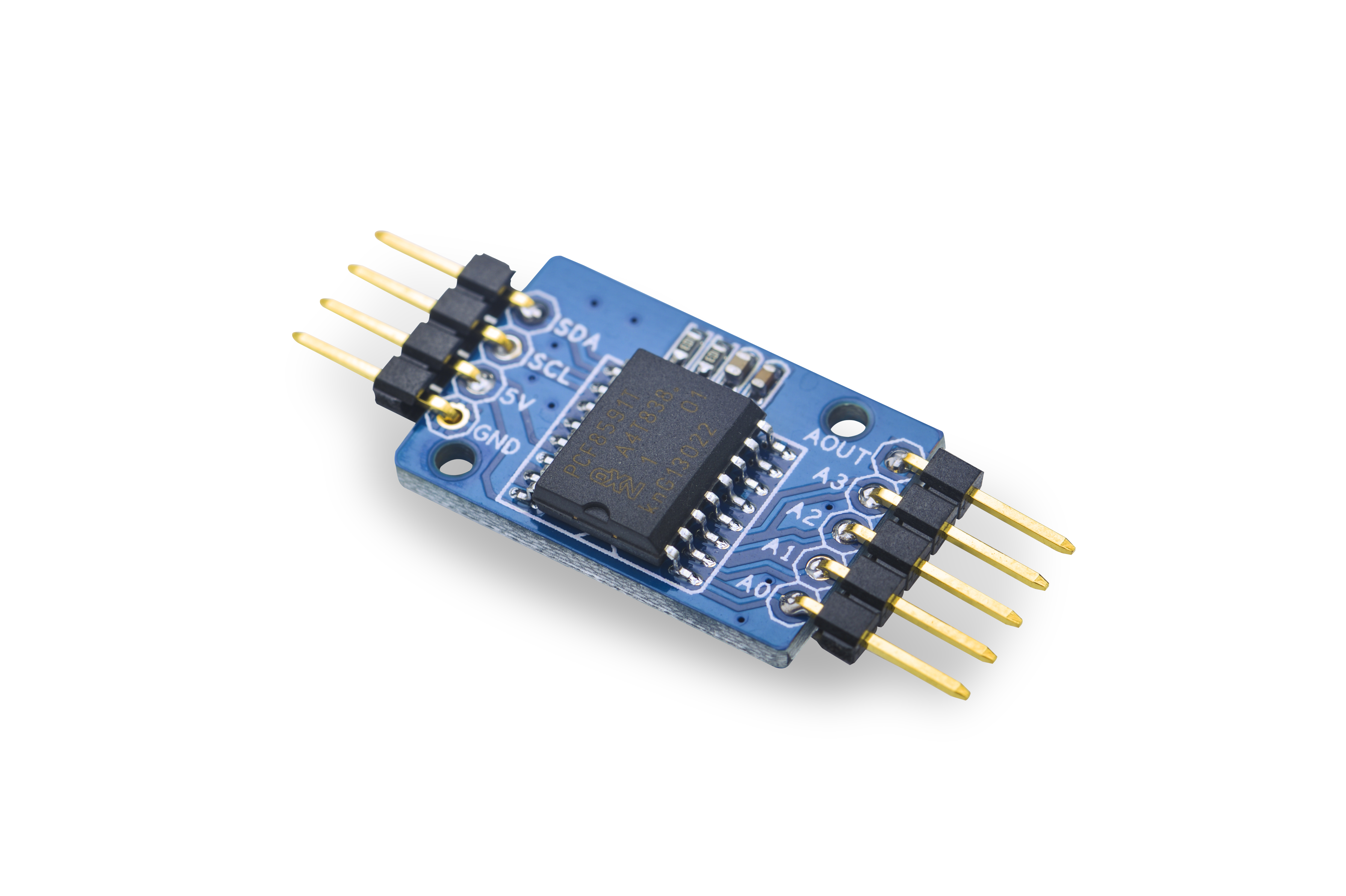
Matrix - Analog to Digital Converter
Contents
1 Introduction
- The Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter is a single-chip, single-supply low-power 8-bit CMOS data acquisition device.
- It utilizes the PCF8591 chip with four analog inputs, one analog output and a serial I2C-bus interface. Three address pins A0, A1 and A2 are used for programming the hardware address, allowing
the use of up to eight devices connected to the I2C-bus without additional hardware. Address, control and data to and from the device are transferred serially via the two-line bidirectional I2C-bus. The maximum conversion rate is given by the maximum speed of the I2C-bus.
- The I2C hardware address is configured to 1001000x
- The operating supply voltage is from 2.5V to 6.0V,Among the 2.54 mm spacing pin header the 5V pin is the supply voltage. If you need 0 - 3.3V analog signals and keep the acquisition resolution you can connect it to a 3.3V supply voltage.
2 Features
- Wide range supply voltage: 2.5V - 6.0V
- I2C interface: 3.3V/5V
- 8-bit A/D x 4
- 8-bit D/A x 1
- Small and easy to be used in various situations
- 2.54 mm spacing pin
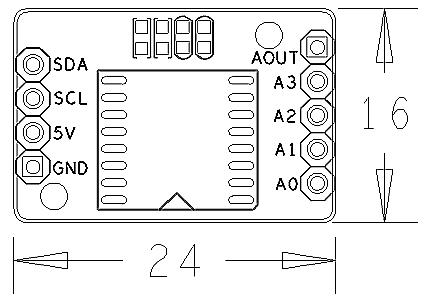
- PCB dimension (mm): 16 x 24
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| SDA | I2C SDA |
| SCL | I2C SCL |
| 5V | Supply Voltage 5V |
| GND | Ground |
| AOUT | Analog Output |
| A3 | Analog Input3 |
| A2 | Analog Input2 |
| A1 | Analog Input1 |
| A0 | Analog Input0 |
3 Basic Device Operation
The PCF8591's I2C-bus is for bidirectional, two-line communication between different ICs or modules. The two lines are a Serial DAta line (SDA) and a Serial CLock line (SCL). Both lines must
be connected to a positive supply via a pull-up resistor. Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy. The AINT0 - AINT4 pins are analog inputs which can be programmed to single-ended or differential inputs. The supply voltage is 0 - VDD.
1. After a START condition, the I2C slave address has to be sent to the PCF8591 device. Bit 1 to bit 3 of the slave address are defined by connecting the input pins A0 to A2 to either VSS (logic 0) or VDD (logic 1). The least significant bit of the slave address byte is bit R/W.
2、发送到PCF8591 的第二个字节将被存储在控制寄存器,用于控制器件功能。控制寄存器的高半字节用于允许模拟输出,和将模拟输入编程为单端或差分输入。低半字节选择一个由高半字节定义的模拟输入通道。
3、在A/D 转换周期将临时使用片上D/A 转换器和高增益比较器。一个A/D 转换周期总是开始于发送一个有效读模式地址给PCF8591 之后。A/D 转换周期在应答时钟脉冲的后沿被触发,并在传输前一次转换结果时执行A/D转换器采用。
4 下载Matrix源码
Matrix配件相关的代码是完全开源的,统一由一个仓库进行管理:git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
该仓库里不同的分支代表着Matrix配件所支持的不同开发板。
- nanopi分支包含了Matrix对NanoPi的支持;
- tiny4412分支包含了Matrix对Tiny4412的支持;
- raspberrypi分支包含了Matrix对RaspberryPi的支持;
在主机PC上安装git,以Ubuntu14.04为例
$ sudo apt-get install git
克隆Matrix配件代码仓库
$ git clone git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
克隆完成后会得到一个matrix目录,里面存放着所有Matrix配件的代码。
5 与NanoPi连接使用
5.1 准备工作
在NanoPi上运行Debian系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。参考wiki:NanoPi
注意:必须使用nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix分支编译出来的内核。
下载NanoPi内核源代码并编译
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-4.x.y.git $ cd linux-4.x.y $ git checkout nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix $ make nanopi_defconfig $ touch .scmversion $ make
5.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter和NanoPi
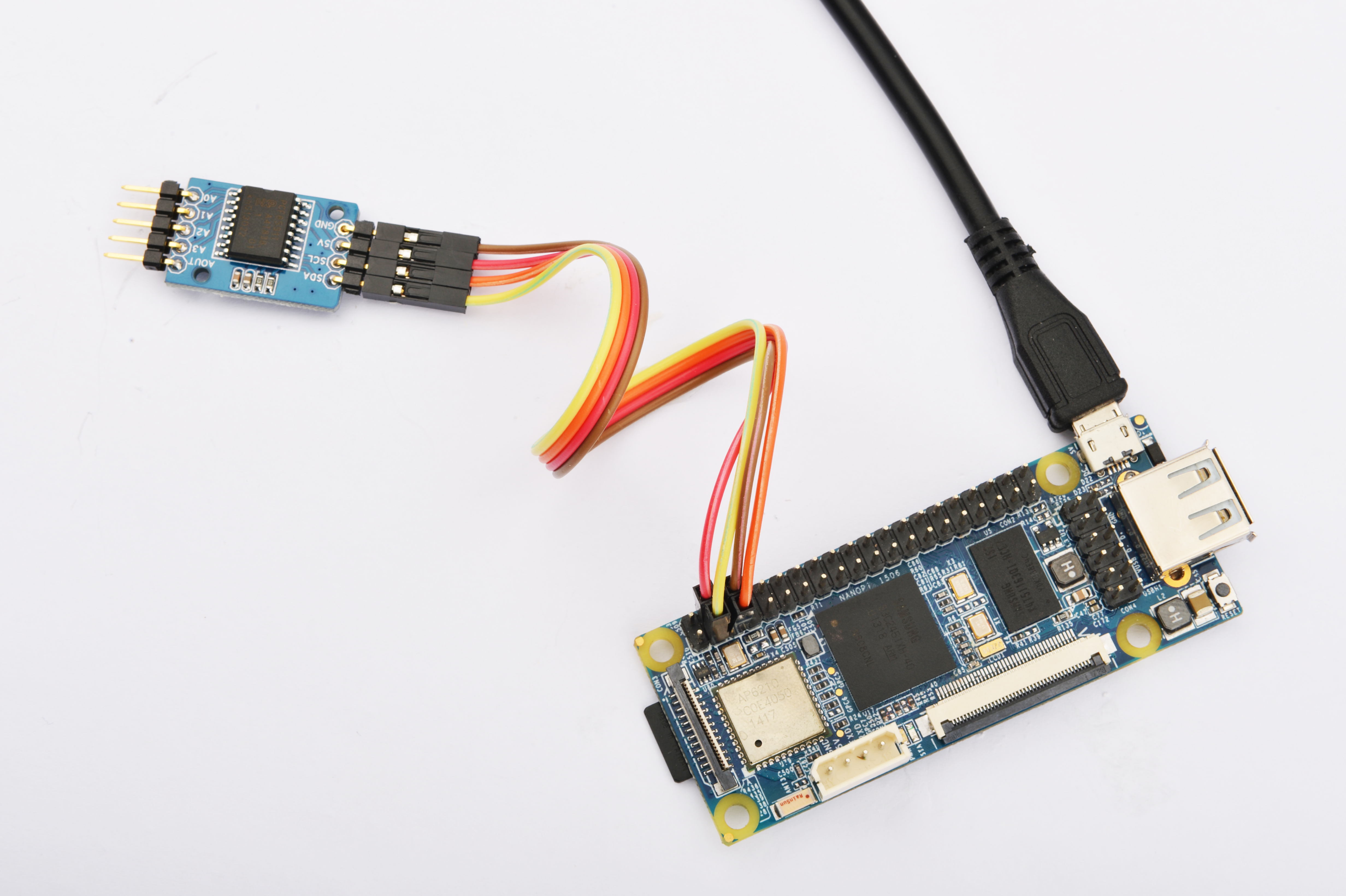
连接说明:
| Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter | NanoPi |
| SDA | Pin3 |
| SCL | Pin5 |
| 5V | Pin4 |
| GND | Pin6 |
5.3 编译测试程序
进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到nanopi分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout nanopi
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi-Debian配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter对应的测试程序为matrix-analog_to_digital_converter。
5.4 运行测试程序
拷贝库文件和测试程序到NanoPi的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* nanopi_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* nanopi_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动NanoPi,在Debian的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter的测试程序
注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件正常连接。
$ matrix-analog_to_digital_converter5.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int devFD; int data, channel, mode; if ((devFD = pcf8591Init()) == -1) { printf("Fail to init pcf8591\n"); return -1; } if (pcf8591SetCtrl(devFD, PCF8591_INIT_AD_CONTROL) == -1) { printf("Fail to Set pcf8591 control AD\n"); pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return -1; } mode = 0; printf("pcf8591 working as AD in mode%d\n",mode); for (channel = PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL0; channel <= PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL3; channel++) { data = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, channel); printf("Channel%d's value: %d\n",channel,data); } pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return 0; }
6 与Tiny4412连接使用
6.1 准备工作
参考Tiny4412光盘里的《友善之臂Ubuntu使用手册》,在Tiny4412上运行UbuntuCore系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。
注意:只能使用Tiny4412SDK-1506的底板。
6.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter和Tiny4412
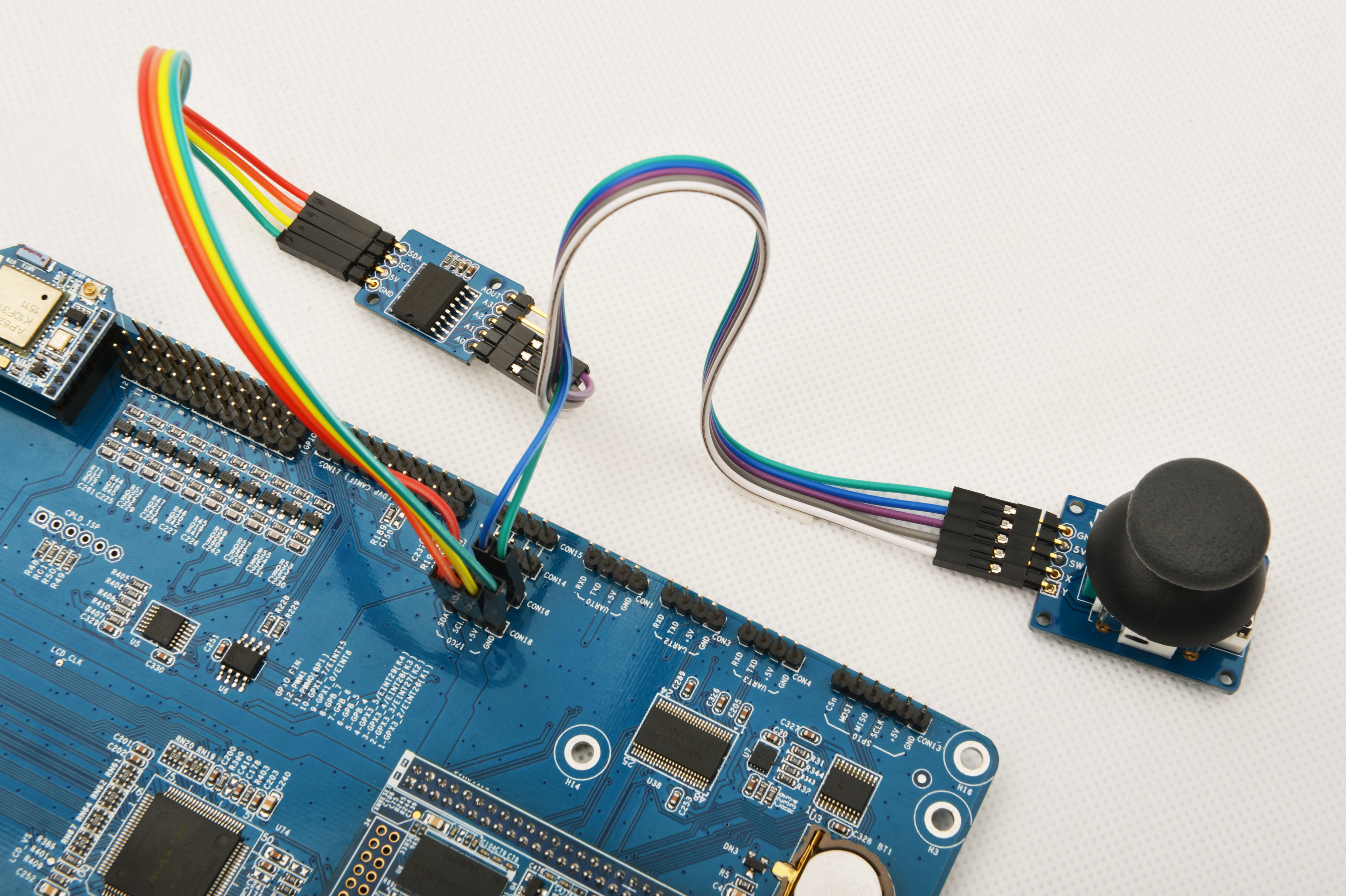
连接说明:
| Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter | NanoPi |
| SDA | CON18 SDA |
| SCL | CON18 SCL |
| 5V | CON18 5V |
| GND | CON18 GND |
6.3 编译测试程序
进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到tiny4412分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout tiny4412
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为Tiny4412-UbuntuCore配套的arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-4.7.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter对应的测试程序为matrix-analog_to_digital_converter。
6.4 运行测试程序
拷贝库文件和测试程序到Tiny4412的UbuntuCore的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* tiny4412_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* tiny4412_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动Tiny4412,在UbuntuCore的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-Analog_to_Digital_Converter的测试程序
$ matrix-analog_to_digital_converter6.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int devFD; int data, channel, mode; if ((devFD = pcf8591Init()) == -1) { printf("Fail to init pcf8591\n"); return -1; } if (pcf8591SetCtrl(devFD, PCF8591_INIT_AD_CONTROL) == -1) { printf("Fail to Set pcf8591 control AD\n"); pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return -1; } mode = 0; printf("pcf8591 working as AD in mode%d\n",mode); for (channel = PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL0; channel <= PCF8591_AIN_CHANNEL3; channel++) { data = pcf8591Read(devFD, mode, channel); printf("Channel%d's value: %d\n",channel,data); } pcf8591DeInit(devFD); return 0; }
7 与RaspberryPi连接使用
8 与Arduino连接使用
9 相关资料