Debian Bullseye Desktop
Contents
- 1 Work with Debian11 Desktop
- 1.1 Introduction to Debian11 Desktop
- 1.2 Account & Password
- 1.3 View IP address
- 1.4 Connect to Debian via SSH
- 1.5 Update Software Packages
- 1.6 Install x11vnc Server on Debian for Remote Access
- 1.7 Install the kernel-header package
- 1.8 Change time zone
- 1.9 Change startup LOGO and Wallpaper
- 1.10 Soft Factory Reset
- 1.11 Start the program automatically at startup(For example Kodi)
- 1.12 Disable auto-mounting
- 1.13 Setup Chinese language and Input method
- 1.14 Installing Plex Multimedia Server
- 1.15 Install Docker on Debian
- 1.16 How to test NPU
- 1.17 How to test VPU
- 1.18 WiFi Connection
- 1.19 Cancel auto-login
- 1.20 Test OpenGL ES
- 1.21 HDMI/DP LCD Resolution
- 1.22 HiDPI and display scaling
- 1.23 Adjust HDMI overscan
- 1.24 Chromium web browser
- 1.25 Test hardware encoding
- 1.26 How to test HDMI-IN
1 Work with Debian11 Desktop
1.1 Introduction to Debian11 Desktop
Debian11 Desktop is a light-weighted debian desktop system,it has the following features:
- Uses Xfce as default desktop;
- Mali GPU-based OpenGL support;
- Support Rockhip MPP video hard coding and hard decoding;
- Pre-installed mpv and smplayer, both support 4K video hardware decoding;
- Pre-installed Chromium browser, support vpu/gpu hardware acceleration (video hard decoding limited to h264/mp4 format);
- Compatible with Plex Server and Docker;
1.2 Account & Password
Regular Account:
User Name: pi
Password: pi
Root:
the root user account is disabled by default, you may configure the root password through the 'sudo passwd root' command.
1.3 View IP address
Since the Debian Bullseye hostname is the hardware model by default, you can use the ping command to get the IP address:ping NanoPC-T6
1.4 Connect to Debian via SSH
Run the following commandssh pi@NanoPC-T6
The default password is: pi
1.5 Update Software Packages
$ sudo apt-get update
1.6 Install x11vnc Server on Debian for Remote Access
1.6.1 Install x11vnc server
The following command to install x11vnc server:
sudo apt-get install x11vnc
1.6.2 Set your password
sudo x11vnc -storepasswd /etc/x11vnc.pwd
1.6.3 Setup x11vnc server with systemd auto start up
Create service configuration file:
sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/x11vnc.service
Let’s copy and paste the following configuration into our newly create service file:
[Unit] Description=Start x11vnc at startup. Requires=display-manager.service After=syslog.target network-online.target Wants=syslog.target network-online.target [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/bin/x11vnc -display :0 -forever -loop -noxdamage -repeat -rfbauth /etc/x11vnc.pwd -rfbport 5900 -shared -capslock -nomodtweak ExecStop=/usr/bin/x11vnc -R stop Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
The following commands to reload the systmd system and to enable and start the x11vnc service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable x11vnc.service sudo systemctl start x11vnc
1.6.4 Testing remote access
Start the VNC client software, input IP:5900 to connect:
1.7 Install the kernel-header package
sudo dpkg -i /opt/archives/linux-headers-*.deb
try to compile a kernel module:
sudo apt update sudo apt install git gcc make bc git clone https://github.com/RinCat/RTL88x2BU-Linux-Driver.git cd RTL88x2BU-Linux-Driver make -j$(nproc) sudo make install sudo modprobe 88x2bu
1.8 Change time zone
1.8.1 Check the current time zone
timedatectl
1.8.2 List all available time zones
timedatectl list-timezones
1.8.3 Set the time zone (e.g. Shanghai)
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
1.9 Change startup LOGO and Wallpaper
1.9.1 Change startup LOGO
Replace the following two files in the kernel source code directory and recompile the kernel:
kernel/logo.bmp
kernel/logo_kernel.bmp
Or use the script to operate, as shown below:
- Download scripts:
git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/sd-fuse_rk3588.git -b kernel-6.1.y --single-branch cd sd-fuse_rk3588
- Compile kernel and repackage firmware
convert files/logo.jpg -type truecolor /tmp/logo.bmp convert files/logo.jpg -type truecolor /tmp/logo_kernel.bmp sudo LOGO=/tmp/logo.bmp KERNEL_LOGO=/tmp/logo_kernel.bmp ./build-kernel.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 sudo ./mk-sd-image.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64 sudo ./mk-emmc-image.sh debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64
Note: If your system is not debian-bullseye-desktop-arm64, please specify according to the actual situation
1.9.2 Change Wallpaper
Modify the following configuration file:
/home/pi/.config/xfce4/xfconf/xfce-perchannel-xml/xfce4-desktop.xml
1.10 Soft Factory Reset
Execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo firstboot && sudo reboot
1.11 Start the program automatically at startup(For example Kodi)
Put the desktop file in the ~/.config/autostart/ directory, for example:
mkdir ~/.config/autostart/ cp /usr/share/applications/kodi.desktop ~/.config/autostart/
1.12 Disable auto-mounting
sudo systemctl mask udisks2 sudo reboot
1.13 Setup Chinese language and Input method
1.13.1 Setup Chinese language
Enter the following command and select 'zh_CN.UTF-8':
sudo dpkg-reconfigure localesAdd environment variables to .bashrc:
echo "export LC_ALL=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export LANGUAGE=zh_CN.UTF-8" >> ~/.bashrc
Reboot device:
sudo reboot1.13.2 Installing Chinese input method
Enter the following command to install fcitx and Pinyin input method:
sudo apt update sudo apt-get install fcitx fcitx-pinyin sudo apt-get install im-config sudo apt-get install fcitx-table* sudo apt-get install fcitx-ui-classic fcitx-ui-light sudo apt-get install fcitx-frontend-gtk2 fcitx-frontend-gtk3 fcitx-frontend-qt4 sudo apt-get remove --purge scim* ibus* sudo reboot
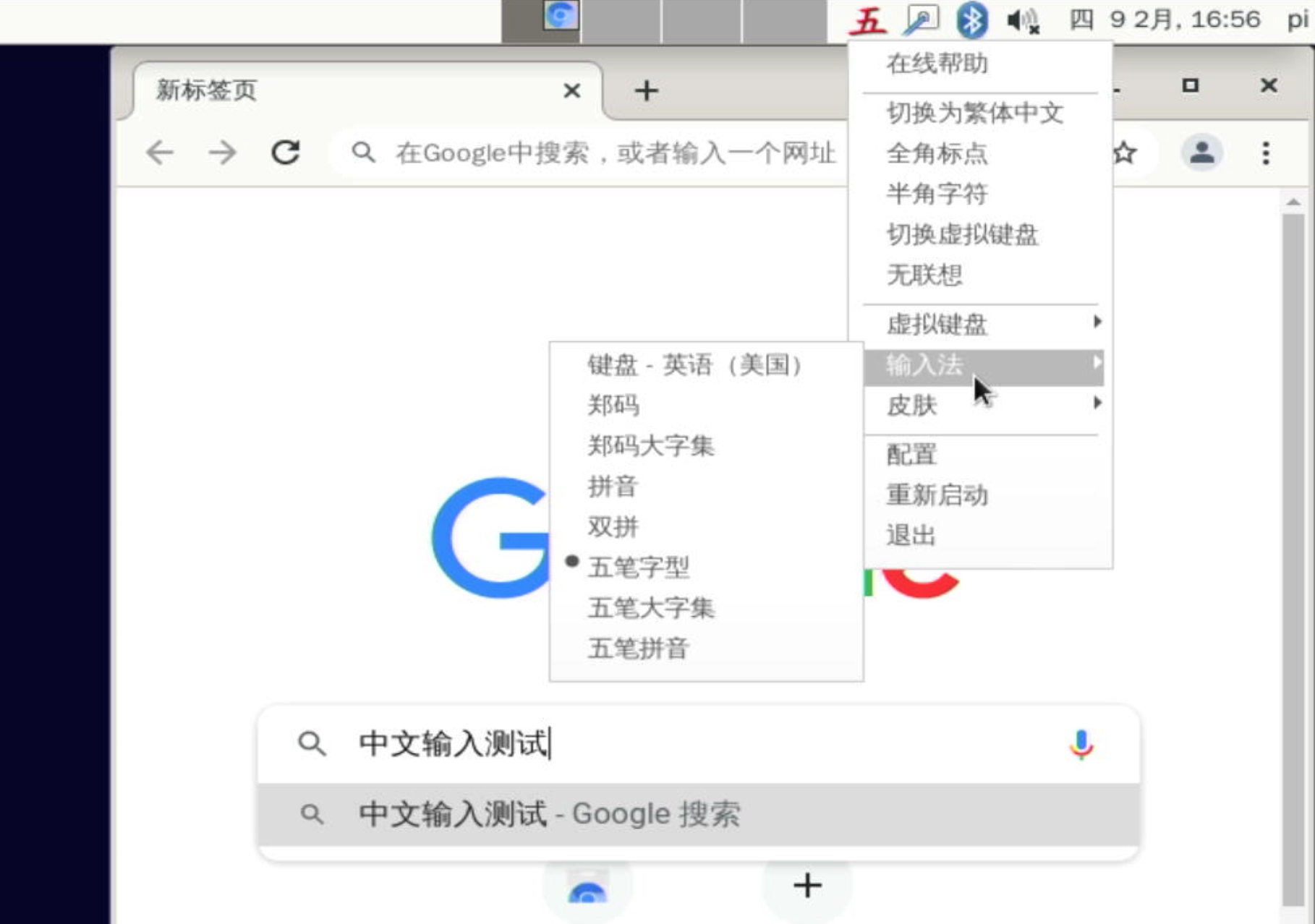
After reboot, press Ctrl+Space to switch between Chinese and English input methods, and the input method icon will appear in the upper right corner, right-click the input method icon in the upper right corner to switch input methods in the pop-up menu, as shown below:
1.14 Installing Plex Multimedia Server
Visit the Plex website: https://www.plex.tv/media-server-downloads/
On the download page, select the category "Plex Media Server", choose "Linux" for the platform and "Ubuntu(16.04+)/Debian(8+) - ARMv8" for the version,
After downloading the deb package, use the dpkg command to install the package:
sudo dpkg -i plexmediaserver_1.31.0.6654-02189b09f_arm64.deb
After installation, login to the Plex server by typing the following URL into your computer browser: http://IP地址:32400/web/
1.15 Install Docker on Debian
Please refer to: How to Install Docker on Debian
1.16 How to test NPU
Please refer to: NPU
1.17 How to test VPU
Please refer to: VPU
1.18 WiFi Connection
1.18.1 Gui
Click on the icon on the top right in the Debian's main window, select your wanted WiFi hotspot and proceed with prompts
1.18.2 Console
Please visit: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
1.19 Cancel auto-login
Edit file:
sudo vim /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf
Comment out the following two lines (insert # in front of them):
autologin-user=pi
autologin-user-timeout=01.20 Test OpenGL ES
You can test it by clicking on the Terminator icon to start a commandline utility in the System Tools and run the following commands:
glmark2-es2
1.21 HDMI/DP LCD Resolution
Open the system's menu and go to Settings -> Display to customize your settings.
1.22 HiDPI and display scaling
Xfce supports HiDPI scaling which can be enabled using the settings manager: Go to Settings Manager > Appearance > Settings > Window Scaling and select 2 as the scaling factor.
Or Edit this file: ~/.config/xfce4/xfconf/xfce-perchannel-xml/xsettings.xml
1.23 Adjust HDMI overscan
Open the command line terminal and enter the command to operate, Note:
1) You need to login to the desktop;
2) If you are using ssh terminal, please use the same username as the desktop login. The default is pi. You cannot use the root user. you also need to assign the DISPLAY variable:
export DISPLAY=:0.0
1.23.1 Query which resolutions the display supports
xrandr -q1.23.2 Set resolution
For example set to 1920X1080@60Hz:
xrandr --output HDMI-1 --mode 1920x1080 --refresh 60
1.23.3 Adjust the HDMI overscan
For example, the transformation scaling horizontal coordinates by 0.8, vertical coordinates by 1.04 and moving the screen by 35 pixels right and 19 pixels down:
xrandr --output HDMI-1 --transform 0.80,0,-35,0,1.04,-19,0,0,1
1.23.4 Automatic adjustment at boot
Edit ~/.config/autostart/lxrandr-autostart.desktop,Write the full xrandr command to the key at the beginning of "Exec= as shown below:
[Desktop Entry] Type=Application Name=LXRandR autostart Comment=Start xrandr with settings done in LXRandR Exec=sh -c 'xrandr --output HDMI-1 --mode 1920x1080 --refresh 50 --transform 1.04,0,-35,0,1.05,-30,0,0,1'
1.24 Chromium web browser
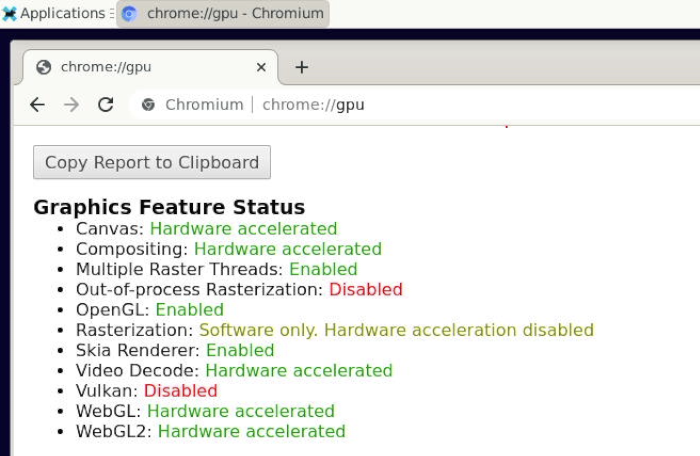
1.24.1 GPU
Chromium web browser has enabled hardware acceleration by default, supports WebGL, and can view hardware acceleration details by entering the URL chrome://gpu, as shown below:
1.24.2 VPU
Play a video in the browser, then use fuser on the command line to view the mpp device node to confirm that the vpu interface is being called:
pi@FriendlyElec:~$ fuser /dev/mpp_service /dev/mpp_service: 3258
If there is no content output from the fuser command, it means software decoding.
1.25 Test hardware encoding
mpi_enc_test -w 1920 -h 1080 -t 7 -f 0 -o test.h264 -n 300 export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/0 ffplay test.h264
1.25.1 Check Supported Hardware Decoding Formats
Enter about://gpu in your browser's address bar and scroll to the bottom of the page to view the "Video Acceleration Information" table.
After playing a video, enter about://media-internals in your browser's address bar to check if hardware decoding was enabled for the most recent playback.
1.26 How to test HDMI-IN
1.26.1 Using script
The debian integrates the hdmirx_preview.sh test script, just run the script directly:
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ hdmirx_preview.shthe script path: /usr/local/bin/hdmirx_preview.sh
Please note that only the NV12 format can achieve optimal performance.
1.26.2 Using V4L2
The node of HDMI-IN device is: /dev/video0, which can be operated by the v4l2-ctl command.
- Obtain device information
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -V -D Driver Info: Driver name : rk_hdmirx Card type : rk_hdmirx Bus info : fdee0000.hdmirx-controller Driver version : 5.10.110 Capabilities : 0x84201000 Video Capture Multiplanar Streaming Extended Pix Format Device Capabilities Device Caps : 0x04201000 Video Capture Multiplanar Streaming Extended Pix Format Format Video Capture Multiplanar: Width/Height : 3840/2160 Pixel Format : 'NV12' (Y/CbCr 4:2:0) Field : None Number of planes : 1 Flags : premultiplied-alpha, 0x000000fe Colorspace : Unknown (0x11507070) Transfer Function : Unknown (0x000000b8) YCbCr/HSV Encoding: Unknown (0x000000ff) Quantization : Default Plane 0 : Bytes per Line : 3840 Size Image : 12441600
- View the resolution and image format of the currently connected device
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --get-fmt-video Format Video Capture Multiplanar: Width/Height : 3840/2160 Pixel Format : 'NV12' (Y/CbCr 4:2:0) Field : None Number of planes : 1 Flags : premultiplied-alpha, 0x000000fe Colorspace : Unknown (0x1193b008) Transfer Function : Unknown (0x000000b8) YCbCr/HSV Encoding: Unknown (0x000000ff) Quantization : Default Plane 0 : Bytes per Line : 3840 Size Image : 12441600
- Capture a frame
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=3840,height=2160,pixelformat='NV12' \ --stream-mmap=4 --stream-skip=10 --stream-to=/home/pi/4k_nv12.yuv --stream-count=1 \ --stream-poll
- Preview
use ffplay:
export DISPLAY=:0.0 ffplay -f rawvideo -video_size 3840x2160 -pixel_format nv12 4k_nv12.yuv
use mpv:
export DISPLAY=:0.0 mpv 4k_nv12.yuv --demuxer=rawvideo --demuxer-rawvideo-w=3840 --demuxer-rawvideo-h=2160 \ --demuxer-rawvideo-mp-format=nv12 --demuxer-rawvideo-fps=60
- View HDMI-IN audio device
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ cat /proc/asound/card* 0 [rockchipdp0 ]: rockchip_dp0 - rockchip,dp0 rockchip,dp0 1 [rockchiphdmi0 ]: rockchip_hdmi0 - rockchip,hdmi0 rockchip,hdmi0 2 [realtekrt5616co]: realtek_rt5616- - realtek,rt5616-codec realtek,rt5616-codec 3 [rockchiphdmi1 ]: rockchip_hdmi1 - rockchip,hdmi1 rockchip,hdmi1 4 [rockchiphdmiin ]: rockchip_hdmiin - rockchip,hdmiin rockchip,hdmiin
As you can see, the sound card number of HDMI-IN is 4.
- Recording audio (recording 10 seconds)
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ arecord -D hw:4,0 -f cd test.wav -d 10
- Playback recorded audio (output to HDMI0)
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ aplay test.wav -D 'hw:rockchiphdmi0'
1.26.3 Using GStreamer
- Live Preview
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ export DISPLAY=:0.0 pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! video/x-raw,format=NV12,width=3840,height=2160,framerate=60/1 \ ! queue ! xvimagesink
- Audio and video recording
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! video/x-raw,format=NV12,width=3840,height=2160,framerate=60/1 \ ! queue ! mpph265enc ! h265parse ! queue ! mux. alsasrc device=hw:CARD=rockchiphdmiin ! audio/x-raw,channels=2 \ ! audioconvert ! voaacenc ! queue ! mux. matroskamux name=mux ! filesink location="4kp60.mkv"
- Live preview + audio and video recording
pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ export DISPLAY=:0.0 pi@NanoPC-T6:~$ gst-launch-1.0 -e v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! 'video/x-raw,format=NV12,width=3840,height=2160' \ ! tee name=t t. ! mpph265enc bps=20000000 bps-max=40000000 rc-mode=vbr ! h265parse ! mp4mux name=mux \ ! filesink location=4k60.mp4 alsasrc device=hw:CARD=rockchiphdmiin ! opusenc ! mux. t. ! queue leaky=1 ! autovideosink sync=false