|
|
| (253 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | [[NanoPC-T3/zh|查看中文]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==Introduction==
| + | {{RockchipUnbrick|NanoPC-T4}} |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T3-01B.jpg|thumb|Overview]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T3-A01.jpg|thumb|Front]]
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T3-B01.jpg|thumb|Back]]
| + | |
| − | * The NanoPC-T3 octa-core single board computer is designed and developed by FriendlyARM for professional and enterprise users. It uses the Samsung Octa-Core Cortex-A53 S5P6818 SoC. Compared to the FriendlyARM NanoPC-T2 the NanoPC-T3 not only has all the T2’s interfaces and ports but also has a more powerful SoC. Its dynamic frequency scales from 400M up to 1.4GHz. The NanoPC-T3 has 8G eMMC onboard, audio jack, video input/output interfaces, built-in WiFi, Bluetooth and Gbps Ethernet port. In addition the NanoPC-T3 has power management, on board porcelain antenna and serial debug port. To avoid overheat issues the NanoPC-T3 has a heat sink with mounting holes.
| + | |
| − | * The NanoPC-T3 has two camera interfaces: a DVP camera interface and a MIPI-CSI interface, and four video interfaces: HDMI 1.4A, LVDS, parallel RGB-LCD interface and MIPI-DSI interface. It supports RTC and has RTC interface pins. It has four USB ports with two being type A ports and two being 2.54mm pitch pin-headers.
| + | |
| − | * The NanoPC-T3 supports muitple OS systems e.g. Android5.1, Debian and UbuntoCore+Qt. It is an open source project with rich interfaces and ports. It is born a choice for professional and enterprise users.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Hardware Spec==
| + | |
| − | * SoC: Samsung S5P6818 Octa-Core Cortex-A53, 400M Hz - 1.4G Hz
| + | |
| − | * Power Management Unit: AXP228 PMU, it supports software power-off and wake-up.
| + | |
| − | * System Memory: 1GB/2GB 32bit DDR3 RAM
| + | |
| − | * Storage: 1 x SD Card Socket
| + | |
| − | * Ethernet: Gbit Ethernet(RTL8211E)
| + | |
| − | * WiFi: 802.11b/g/n
| + | |
| − | * Bluetooth: 4.0 dual mode
| + | |
| − | * Antenna: Porcelain Antenna IPX Interface
| + | |
| − | * eMMC: 8GB
| + | |
| − | * Video Input: DVP Camera/MIPI-CSI (two camera interfaces)
| + | |
| − | * Video Output: HDMI Type-A / LVDS / Parallel RGB-LCD / MIPI-DSI (four video output interfaces)
| + | |
| − | * Audio: 3.5 mm audio jack / via HDMI
| + | |
| − | * Microphone: onboard Microphone
| + | |
| − | * USB Host: 4 x USB 2.0 Host, two type A ports and two 2.54 mm pitch pin-headers
| + | |
| − | * MicroUSB: 1 x MicroUSB 2.0 Client, Type A
| + | |
| − | * LCD Interface: 0.5mm pitch 45 pin FPC seat, full color RGB 8-8-8
| + | |
| − | * HDMI: 1.4A Type A, 1080P
| + | |
| − | * DVP Camera: 0.5mm pitch 24 pin FPC seat
| + | |
| − | * GPIO: 2.54 mm pitch 30 pin-header
| + | |
| − | * Serial Debug Port: 2.54mm pitch 4-pin-header
| + | |
| − | * User Key: K1 (power), Reset
| + | |
| − | * LED: 1 x power LED and 2 x GPIO LED
| + | |
| − | * Other Resources: CPU’s internal TMU
| + | |
| − | * RTC Battery: RTC Battery Seat
| + | |
| − | * Heat Sink: 1 x Heat Sink with mounting holes
| + | |
| − | * Power: DC 5V/2A
| + | |
| − | * PCB: Six Layer
| + | |
| − | * Dimension: 100 mm x 60 mm
| + | |
| − | * Working Temperature: -40℃ to 80℃
| + | |
| − | * OS/Software: uboot, Android and Debian
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Software Features==
| + | |
| − | ===UbuntuCore===
| + | |
| − | <!---
| + | |
| − | * mainline kernel: Linux-4.11.2
| + | |
| − | * rpi-monitor: check system status and information
| + | |
| − | --->
| + | |
| − | * npi-config: system configuration utility for setting passwords, language, timezone, hostname, SSH and auto-login,and enabling/disabling i2c, spi, serial and PWM
| + | |
| − | <!---
| + | |
| − | * software utility: wiringNP to access GPIO pins
| + | |
| − | * software utility: RPi.GPIO_NP to access GPIO pins
| + | |
| − | --->
| + | |
| − | * networkmanager: manage network
| + | |
| − | * system log output from serial port
| + | |
| − | <!---
| + | |
| − | * nano editor
| + | |
| − | --->
| + | |
| − | * welcome window with basic system information and status
| + | |
| − | * auto-login with user account "pi" with access to npi-config
| + | |
| − | * UART2 enabled
| + | |
| − | * supports CAM500B
| + | |
| − | <!---
| + | |
| − | * sudoers include "fa"
| + | |
| − | * on first system boot file system will be automatically extended.
| + | |
| − | * supports file system auto check and repair on system boot.
| + | |
| − | * supports FriendlyElec's [http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/index.php/NanoHat_PCM5102A NanoHat-PCM5102A]
| + | |
| − | * supports USB WiFi module: refer to [[#Connect USB WiFi to NEO]]
| + | |
| − | * supports audio recording and playing with 3.5mm audio jack
| + | |
| − | * supports USB Host and 100M Ethernet
| + | |
| − | * supports FriendlyElec BakeBit modules
| + | |
| − | * supports dynamic frequency scaling and voltage regulation
| + | |
| − | * relieves overheat compared to kernel Linux-3.4
| + | |
| − | * fixed MAC address
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Ubuntu OLED===
| + | |
| − | * mainline kernel: Linux-4.11.2
| + | |
| − | * supports FriendlyElec's OLED module
| + | |
| − | --->
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Debian===
| + | |
| − | * supports CAM500B
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | <!---
| + | |
| − | ===Debian for NAS Dock===
| + | |
| − | * mainline kernel: Linux-4.11.2
| + | |
| − | * supports FriendlyElec's NAS Dock
| + | |
| − | * optimized OpenMediaVault configuration options
| + | |
| − | * allocated swap section
| + | |
| − | --->
| + | |
| − | ===Android===
| + | |
| − | * supports setting up static IP
| + | |
| − | * supports accessing hardware with FriendlyElec's libfriendlyarm-hardware.so
| + | |
| − | * integrated iTest utility for testing hardware
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Diagram, Layout and Dimension==
| + | |
| − | ===Layout===
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T3-1512B-IF-01.png |thumb|600px|NanoPC-T3 Layout]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''30Pin GPIO Pin Spec'''
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Pin# || Name ||Pin# || Name
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1 || SYS_3.3V ||2 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3 || UART2_TX/GPIOD20 ||4 || UART2_RX/GPIOD16
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || I2C0_SCL ||6 || I2C0_SDA
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7 || SPI0_MOSI/GPIOC31 ||8 || SPI0_MISO/GPIOD0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |9 || SPI0_CLK/GPIOC29 ||10 || SPI0_CS/GPIOC30
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || UART3_TX/GPIOD21 ||12 || UART3_RX/GPIOD17
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |13 || UART4_TX/GPIOB29 ||14 || UART4_RX/GPIOB28
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |15 || UART5_TX/GPIOB31 ||16 || UART5_RX/GPIOB30
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |17 || GPIOC4 ||18 || GPIOC7
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 || GPIOC8 ||20 || GPIOC24
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |21 || GPIOC28 ||22 || GPIOB26
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |23 || GPIOD1/PWM0 ||24 || GPIOD8/PPM
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |25 || GPIOC13/PWM1 ||26 || AliveGPIO3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |27 || GPIOC14/PWM2 ||28 || AliveGPIO5
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |29 || VDD_5V ||30 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''20Pin LVDS Interface Pin Spec'''
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Pin# || Name ||Pin# || Name
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1 || SYS_3.3V ||2 || SYS_3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3 ||GPIOC16 ||4 || GPIOB18
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || DGND ||6 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7 || LVDS_D0- ||8 || LVDS_D0+
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |9 || LVDS_D1- ||10 || LVDS_D1+
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || LVDS_D2- ||12 || LVDS_D2+
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |13 || DGND ||14 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |15 || LVDS_CLK- ||16 || LVDS_CLK+
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |17 || LVDS_D3- ||18 || LVDS_D3+
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 ||I2C2_SCL ||20 || I2C2_SDA
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''DVP Camera Interface Pin Spec'''
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Pin# || Name
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1, 2 || SYS_3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7,9,13,15,24 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3 || I2C0_SCL
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |4 || I2C0_SDA
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || GPIOB14
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |6 || GPIOB16
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |8,10 || NC
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || VSYNC
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12 || HREF
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |14 || PCLK
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |16-23 || Data bit7-0
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''RGB LCD Interface Pin Spec'''
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Pin# || Name || Description
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1, 2 || VDD_5V || 5V Output, it can be used to power LCD modules
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11,20,29, 37,38,39,40, 45|| DGND || Ground
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3-10 || Blue LSB to MSB || RGB blue
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12-19 || Green LSB to MSB || RGB green
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |21-28 || Red LSB to MSB || RGB red
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |30 || GPIOB25 || available for users
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |31 || GPIOC15 || occupied by FriendlyARM one wire technology to recognize LCD models and control backlight and implement resistive touch, not applicable for users
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |32 || XnRSTOUT Form CPU || low when system is reset
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |33 || VDEN || signal the external LCD that data is valid on the data bus
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |34 || VSYNC || vertical synchronization
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |35 || HSYNC || horizontal synchronization
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |36 || LCDCLK || LCD clock, Pixel frequency
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |41 || I2C2_SCL || I2C2 clock signal, for capacitive touch data transmission
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |42 || I2C2_SDA || I2C2 data signal, for capacitive touch data transmission
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |43 || GPIOC16 || interrupt pin for capacitive touch, used with I2C2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |44 || NC || Not connected
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''MIPI-DSI Interface Pin Spec'''
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Pin# || Name
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1, 2, 3 || VDD_5V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |4|| DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || I2C2_SDA
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |6 || I2C2_SCL
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |8 || GPIOC0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |9 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |10 || GPIOC1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12 || GPIOA28
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |13 || nRESETOUT
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |14, 15 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |16 || MIPIDSI_DN3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |17 || MIPIDSI_DP3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |18 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 || MIPIDSI_DN2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |20 || MIPIDSI_DP2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |21 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |22 || MIPIDSI_DN1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |23 || MIPIDSI_DP1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |24 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |25 || MIPIDSI_DN0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |26 || MIPIDSI_DP0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |27 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |28 || MIPIDSI_DNCLK
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |29 || MIPIDSI_DPCLK
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |30 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | * '''MIPI-CSI Interface Pin Spec'''
| + | |
| − | ::{| class="wikitable"
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |Pin# || Name
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |1, 2 || SYS_3.3V
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |3|| DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |4 || I2C0_SDA
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |5 || I2C0_SCL
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |6 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |7 || SPI2_MOSI/GPIOC12
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |8 || SPI2_MISO/GPIOC11
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |9 || SPI2_CS/GPIOC10
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |10 || SPI2_CLK/GPIOC9
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |11 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |12 || GPIOB9
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |13 || GPIOC2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |14, 15 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |16 || MIPICSI_DN3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |17 || MIPICSI_DP3
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |18 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |19 || MIPICSI_DN2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |20 || MIPICSI_DP2
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |21 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |22 || MIPICSI_DN1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |23 || MIPICSI_DP1
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |24 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |25 || MIPICSI_DN0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |26 || MIPICSI_DP0
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |27 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |28 || MIPICSI_DNCLK
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |29 || MIPICSI_DPCLK
| + | |
| − | |-
| + | |
| − | |30 || DGND
| + | |
| − | |}
| + | |
| − | :'''Notes'''
| + | |
| − | ::#SYS_3.3V: 3.3V power output
| + | |
| − | ::#VDD_5V: 5V power output
| + | |
| − | ::#For more details refer to the document: [http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/images/d/d5/NanoPC-T2-T3-1603-Schematic.pdf NanoPC-T3 Schematic]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ===Board Dimension===
| + | |
| − | [[File:NanoPC-T2-T3-1603-Dimensions.png|frameless|800px|NanoPC-T3 Dimensions]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ::For more details refer to the document: [http://wiki.friendlyarm.com/wiki/images/2/24/NanoPC-T2-T3-1603-Dimensions%28dxf%29.zip NanoPC-T3-Dimensions(dxf)]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | *'''Power Jack'''
| + | |
| − | ::*DC 4.7~5.6V IN, 4.0*1.7mm Power Jack
| + | |
| − | ::[[File:DC-023.png]]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Notes in Hardware Design==
| + | |
| − | ===EEPROM===
| + | |
| − | * The board has an EEPROM(model: 24AA025E48T-I/OT) with a unique MAC. This EEPROM is connected to I2C0 and its address is 0x51 therefore some EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0 which will cause conflicts of addresses.
| + | |
| − | * In our tests these EEPROM chips cannot be connected to I2C0: 24C04, 24C08 and 24C16. There chips which we tested can be connected to I2C0: 24C01, 24C02 and 24C256
| + | |
| − | * For more details about EEPROM address issues refer to http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/CAT24C01-D.PDF
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | ==Get Started==
| + | |
| − | ===Essentials You Need===
| + | |
| − | Before starting to use your NanoPi-T3 get the following items ready
| + | |
| − | * NanoPi-T3
| + | |
| − | * SD Card: Class 10 or Above
| + | |
| − | * A DC 5V/2A power is a must
| + | |
| − | * HDMI monitor or LCD
| + | |
| − | * USB keyboard, mouse and possible a USB hub(or a TTL to serial board)
| + | |
| − | * A host computer running Ubuntu 16.04 64 bit system
| + | |
| − | {{S5P6818BootFromSDCard|NanoPC-T3}}
| + | |
| − | {{BurnOSToEMMC|NanoPC-T3|s5p6818-eflasher}}
| + | |
| − | {{S5PXX18MakeSDCardViaSDFusing|NanoPC-T3|sd-fuse_s5p6818}}
| + | |
| − | {{ResizeTFCardFS|NanoPC-T3}}
| + | |
| − | {{S5Pxx18HDMI|NanoPC-T3|arch/arm/plat-s5p6818/nanopi3/lcds.c}}
| + | |
| − | {{S5Pxx18MofidyKernelCommandLineOnHostPC|NanoPC-T3|sd-fuse_s5p6818}}
| + | |
| − | {{S5P6818Software|NanoPi-T3}}
| + | |
| − | {{S5P6818ChangeLog}}
| + | |
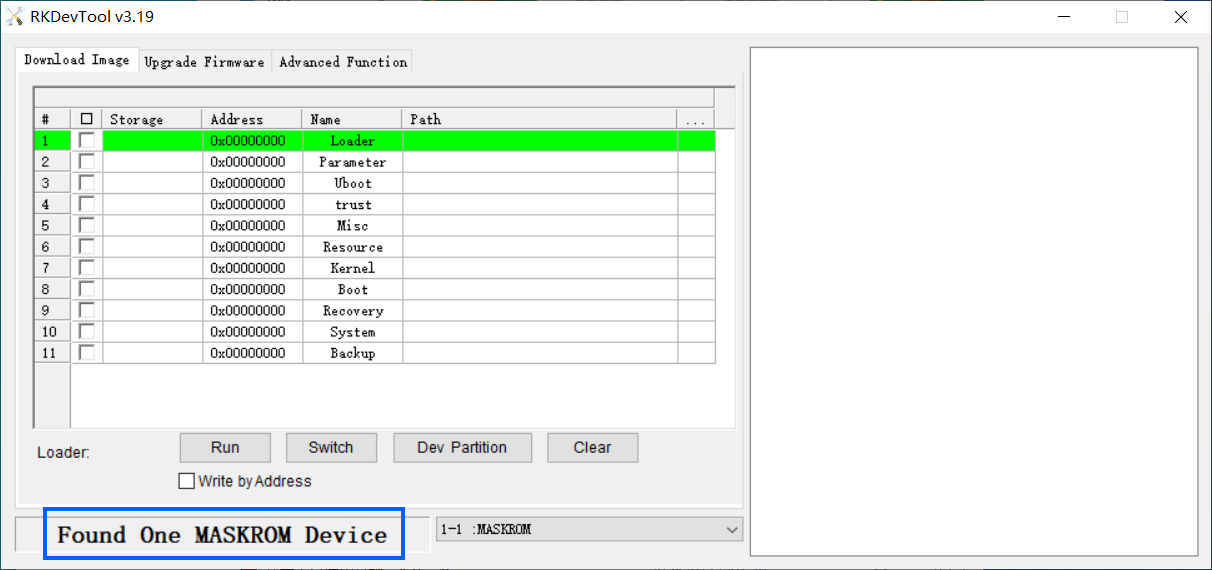
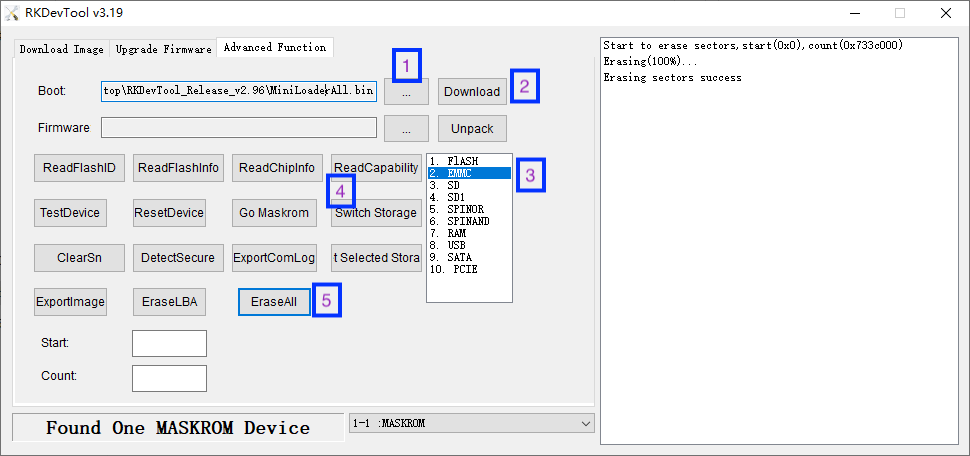
If the ROM is not installed correctly, causing the development board to become bricked, and you might not have the opportunity to reinstall the ROM via an SD card, you need to enter Maskrom mode to unbrick it by erasing the storage device.
The following commands are for Linux, with only slight differences in file and directory names for Mac users:
A result similar to "DevNo=1 Vid=0x2207,Pid=0x350b,LocationID=13 Mode=Maskrom SerialNo=" indicates that the device has been detected.