Difference between revisions of "Template:FriendlyCoreGeneral"
(→HDMI或者3.5mm音频设备输出声音) |
(updated by API) |
||
| (68 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Work with FriendlyCore== | ==Work with FriendlyCore== | ||
| − | === | + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} |
| − | + | | NanoPC-T4 = | |
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399Introduce}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399Introduce}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4V2 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399Introduce}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4B = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399Introduce}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO4 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399Introduce}} | ||
| + | | SOM-RK3399 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399Introduce}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3328Introduce}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo2 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-K1-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M1 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M1-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO2 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO2-Black | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Air | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Core | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Core2 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H3 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H5 | ||
| + | | ZeroPi = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreAllwinnerIntroduce}} | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreGeneralIntroduce}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ===System Login=== | |
| − | + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | |
| − | + | | SOM-4418 = | |
| − | + | | #default = | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | |
* If your board is connected to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and keyboard. | * If your board is connected to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and keyboard. | ||
| − | * If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will | + | * If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will |
| + | }} | ||
{{#switch: {{{1}}} | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| − | | NanoPi-NEO2 = [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | | NanoPC-T4 = |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO = | + | | NanoPi-M4 = |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 = [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO-Plus2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | | NanoPi-M4V2 = |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO-Core = | + | | NanoPi-M4B = |
| − | | NanoPi-M1 = [[File:PSU-ONECOM-M1.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | | NanoPi-NEO4 = |
| − | | NanoPi-M1-Plus = [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NanoPi-M1-Plus.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | | SOM-RK3399 = |
| − | | NanoPi-A64 = [[File:PSU-ONECOM-A64.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | | NanoPi-NEO2 = |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO-Air = | + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: |
| − | | #default = For example, NanoPi-M1:<br>[[File:PSU-ONECOM-M1.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> |
| + | | NanoPi-NEO = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO-Plus2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Core = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO-Core.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M1 = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-M1.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M1-Plus = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NanoPi-M1-Plus.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-A64 = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-A64.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Air = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-AIR.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1 = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-R1.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H3 = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-R1S.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H5 = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-R1S.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO2-Black = | ||
| + | allow you to operate the board via a serial terminal.Here is a setup where we connect a board to a PC via the PSU-ONECOM and you can power on your board from either the PSU-ONECOM or its MicroUSB: | ||
| + | [[File:PSU-ONECOM-NEO2-Black.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo2 = | ||
| + | <!-- Duox not support ONECOM --> | ||
| + | | SOM-4418 = | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | For example, NanoPi-M1:<br>[[File:PSU-ONECOM-M1.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| + | | SOM-RK3399 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial on {{{1}}}:<br>[[File:somrk3399usb2serialport.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T4 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial on {{{1}}}:<br>[[File:T4usb2serialport.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial on {{{1}}}:<br>[[File:m4usb2serialport.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4V2 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial on {{{1}}}:<br>[[File:m4usb2serialport.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4B = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial on {{{1}}}:<br>[[File:m4usb2serialport.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO4 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial on {{{1}}}:<br>[[File:neo4usb2serialport.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO2 = | ||
You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| − | + | [[File:USB2UART-NEO2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO2 = [[File: | + | | NanoPi-NEO2-Black = |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO-Core = | + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> |
| − | | NanoPi-Duo = [[File:USB2UART-Duo.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 = [[File:USB2UART-NEO-Plus2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_nanopi_NEO2-Black.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO = [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | + | | NanoPi-NEO-Core = |
| − | | #default = For example, NanoPi- | + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> |
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:USB2UART-NEO-Core.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M1 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:USB2UART-M1.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M1-Plus = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:USB2UART-M1-Plus.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:USB2UART-Duo.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo2 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:USB2UART-Duo2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:USB2UART-NEO-Plus2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_nanopi_NEO.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Air = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_NEO_Air.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_nanopi_R1.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H3 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_nanopi_R1S-H3.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H5 = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Matrix-USB2UART_nanopi_R1S-H3.jpg|frameless|500px]]<br> | ||
| + | | SOM-4418 = | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too. <br> | ||
| + | Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:<br> | ||
| + | For example, NanoPi-NEO2:<br>[[File:USB2UART-NEO2.jpg|frameless|400px]]<br> | ||
}} | }} | ||
* FriendlyCore User Accounts: | * FriendlyCore User Accounts: | ||
| Line 58: | Line 190: | ||
[[File:npi-config.jpg|frameless|500px|npi-config]]<br /> | [[File:npi-config.jpg|frameless|500px|npi-config]]<br /> | ||
| + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T4 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399QtDev}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399QtDev}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4V2 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399QtDev}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4B = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399QtDev}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO4 = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3399QtDev}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
| + | {{FriendlyCoreRK3328QtDev}} | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
===Develop Qt Application=== | ===Develop Qt Application=== | ||
| − | Please refer to: [[How to | + | Please refer to: [[How to Build and Install Qt Application for FriendlyELEC Boards]] |
| + | }} | ||
===Setup Program to AutoRun=== | ===Setup Program to AutoRun=== | ||
| Line 75: | Line 225: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | === | + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} |
| − | + | | NanoPi-NEO | |
| − | + | | NanoPi-DUO | |
| + | | NanoPi-M1 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Core | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO2 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO-Core2 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO2-Black | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H3 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H5 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C | ||
| + | | ZeroPi = | ||
| + | <!-- 这些板子不带蓝牙功能 --> | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | ===Transfer files using Bluetooth=== | ||
| + | Take the example of transferring files to the mobile phone. First, set your mobile phone Bluetooth to detectable status, then execute the following command to start Bluetooth search.:<br /> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | hcitool scan | |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | + | Search results look like:<br /> | |
| − | + | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | Scanning ... | |
| + | 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 HTC6525LVW | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | This means that a mobile phone named HTC6525LVW is searched. We write down the MAC address in front of the phone name, and then use the sdptool command to view the Bluetooth service supported by the phone:<br /> | |
| − | + | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | sdptool browser 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 | |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Note: Please replace the MAC address in the above command with the actual Bluetooth MAC address of the mobile phone.<br /> | |
| − | + | This command will detail the protocols supported by Bluetooth for mobile phones. What we need to care about is a file transfer service called OBEX Object Push. Take the HTC6525LVW mobile phone as an example. The results are as follows:<br /> | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | Service Name: OBEX Object Push | |
| + | Service RecHandle: 0x1000b | ||
| + | Service Class ID List: | ||
| + | "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) | ||
| + | Protocol Descriptor List: | ||
| + | "L2CAP" (0x0100) | ||
| + | "RFCOMM" (0x0003) | ||
| + | Channel: 12 | ||
| + | "OBEX" (0x0008) | ||
| + | Profile Descriptor List: | ||
| + | "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) | ||
| + | Version: 0x0100 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | As can be seen from the above information, the channel used by the OBEX Object Push service of this mobile phone is 12, we need to pass it to the obexftp command, and finally the command to initiate the file transfer request is as follows: | |
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |
| + | obexftp --nopath --noconn --uuid none --bluetooth -b 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 -B 12 -put example.jpg | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | Note: Please replace the MAC address, channel and file name in the above command with the actual one.<br /><br /> | ||
| + | After executing the above commands, please pay attention to the screen of the mobile phone. The mobile phone will pop up a prompt for pairing and receiving files. After confirming, the file transfer will start.<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | Bluetooth FAQ:<br /> | |
| + | 1) Bluetooth device not found on the development board, try to open Bluetooth with the following command:<br /> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | rfkill unblock 0 | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | 2) Prompt can not find the relevant command, you can try to install related software with the following command:<br /> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | apt-get install bluetooth bluez obexftp openobex-apps python-gobject ussp-push | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ===WiFi=== | |
| − | + | {{Linux-WiFi}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | <!--带WiFi和BT的APXX芯片的板子--> | ||
{{#switch: {{{1}}} | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| − | | NanoPi-M1-Plus | + | | NanoPi-M1-Plus |
| − | | NanoPi-NEO-Air = {{Allwinner-APmode}} | + | | NanoPi-NEO-Air |
| − | | | + | | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 |
| − | | | + | | NanoPi-Duo2 = |
| − | | NanoPC-T3 = {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | + | {{Allwinner-APmode}} |
| − | | NanoPC-T3-Plus = {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} |
| − | | NanoPi2 = {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | + | | NanoPC-T2 = |
| − | | NanoPi_K2 = {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} |
| − | | NanoPi_M3 = {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} |
| + | | SOM-4418 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | ||
| + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T3 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | ||
| + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T3-Plus = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | ||
| + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi2 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | ||
| + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi_K2 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | ||
| + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi_M3 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18-APmode}} | ||
| + | {{Linux-Bluetooth}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 134: | Line 328: | ||
If a board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP with DHCP activated after it is powered up. If you want to set up a static IP refer to: [[Use NetworkManager to configure network settings]]。 | If a board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP with DHCP activated after it is powered up. If you want to set up a static IP refer to: [[Use NetworkManager to configure network settings]]。 | ||
| − | === | + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} |
| − | + | | NanoPC-T4 | NanoPi-M4 | NanoPi-NEO4 = | |
| − | + | ===WiringPi and Python Wrapper=== | |
| − | + | *[[WiringPi for RK3399|WiringPi for RK3399]] | |
| − | + | *[[WiringPi-Python for RK3399|WiringPi-Python for RK3399]] | |
| − | + | | NanoPi-Duo | NanoPi-M1-Plus | NanoPi-M1 | NanoPi-NEO-Air | NanoPi-NEO-Core | NanoPi-NEO-Core2 | NanoPi-NEO-Plus2 | NanoPi-NEO | NanoPi-Duo2 | NanoPi-NEO2 | NanoPi-K1-Plus = | |
| + | ===WiringPi and Python Wrapper=== | ||
| + | *[[WiringNP: NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with C]] | ||
| + | *[[RPi.GPIO : NanoPi NEO/NEO2/Air GPIO Programming with Python]] | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Custom welcome message=== |
| − | + | The welcome message is printed from the script in this directory: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | /etc/update-motd.d/ | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | For example, to change the FriendlyELEC LOGO, you can change the file /etc/update-motd.d/10-header. For example, to change the LOGO to HELLO, you can change the following line: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | $ | + | TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal $BOARD_VENDOR |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | To: | |
| − | + | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal HELLO | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | ===Modify timezone=== | |
| + | For exampe, change to Shanghai timezone: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| − | + | sudo rm /etc/localtime | |
| − | + | sudo ln -ls /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T4 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4V2 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4B = | ||
| + | {{RK3399SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO4 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | SOM-RK3399 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T2 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | SOM-4418 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T3 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T3-Plus = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi2 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Fire2A = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M2A = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-S2 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | Smart4418 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | Smart6818 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Fire3 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M3 = | ||
| + | {{S5Pxx18SelectALSAAudioDevice}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo2 = | ||
| + | {{SelectAudio |NanoPi-Duo2 }} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H3 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H5 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | {{SelectAudio}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#switch: {{{1}}} | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T4 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399FanControl}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399FanControl}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4V2 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399FanControl}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4B = | ||
| + | {{RK3399FanControl}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M4B = | ||
| + | {{RK3399FanControl}} | ||
| + | | SOM-RK3399 = | ||
| + | {{RK3399FanControl}} | ||
| + | | NanoPi-NEO4 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T2 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | SOM-4418 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T3 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPC-T3-Plus = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi2 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Fire2A = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M2A = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-S2 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | Smart4418 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | Smart6818 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Fire3 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-M3 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-Duo2 = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H3 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R1S-H5 | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2S-Plus | ||
| + | | NanoPi-R2C = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | | #default = | ||
| + | <!-- do nothing --> | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:53, 4 December 2023
Contents
1 Work with FriendlyCore
1.1 Introduction
FriendlyCore is a light Linux system without X-windows, based on ubuntu core, It uses the Qt-Embedded's GUI and is popular in industrial and enterprise applications.
Besides the regular Ubuntu core's features our FriendlyCore has the following additional features:
- it supports our LCDs with both capacitive touch and resistive touch(S700, X710, HD702, S430, HD101 and S70)
- it supports WiFi
- it supports Ethernet
- it supports Bluetooth and has been installed with bluez utilities
- it supports audio playing
- it supports Qt 5.10.0 EGLES and OpenGL ES1.1/2.0 (Only for S5P4418/S5P6818)
1.2 System Login
- If your board is connected to an HDMI monitor you need to use a USB mouse and keyboard.
- If you want to do kernel development you need to use a serial communication board, ie a PSU-ONECOM board, which will
For example, NanoPi-M1: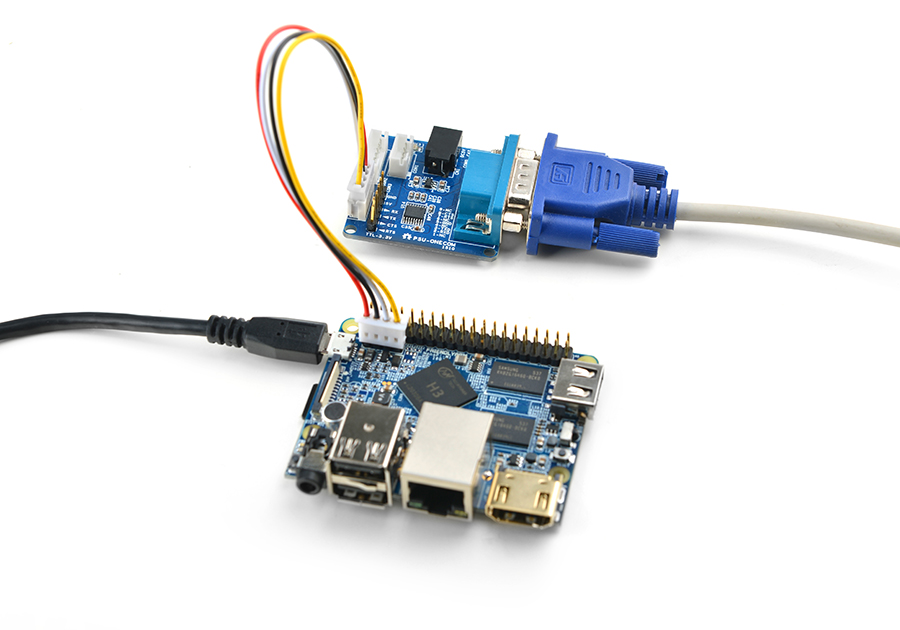
You can use a USB to Serial conversion board too.
Make sure you use a 5V/2A power to power your board from its MicroUSB port:
For example, NanoPi-NEO2: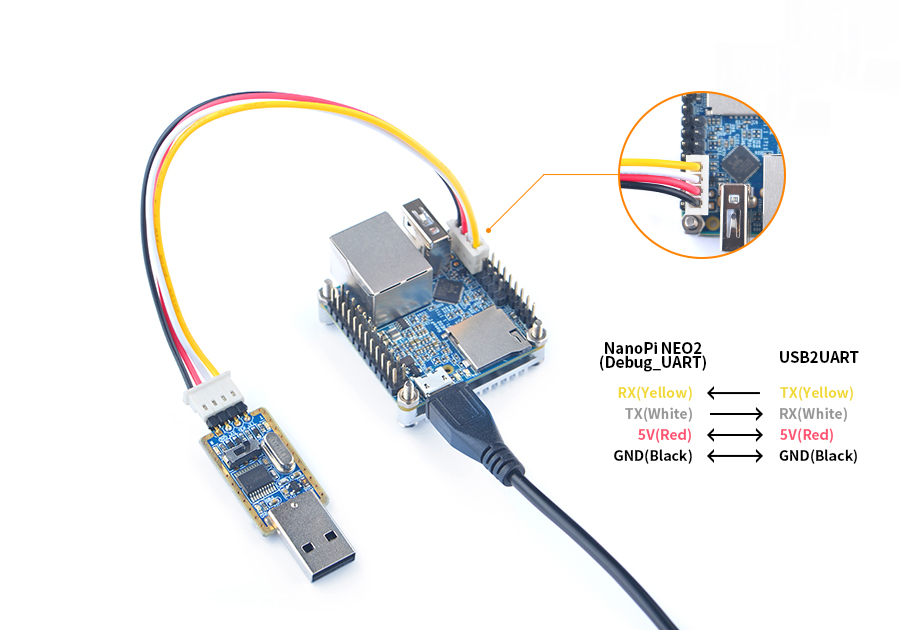
- FriendlyCore User Accounts:
Non-root User:
User Name: pi Password: pi
Root:
User Name: root Password: fa
The system is automatically logged in as "pi". You can do "sudo npi-config" to disable auto login.
- Update packages
$ sudo apt-get update
1.3 Configure System with npi-config
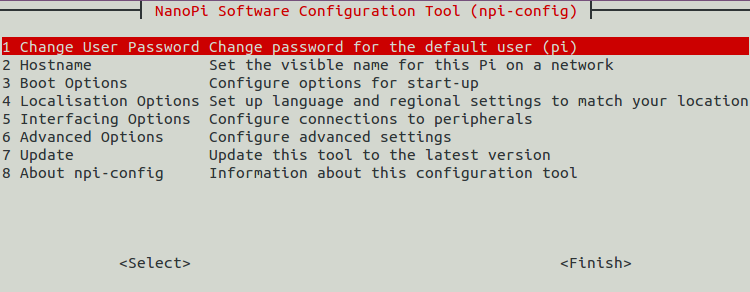
The npi-config is a commandline utility which can be used to initialize system configurations such as user password, system language, time zone, Hostname, SSH switch , Auto login and etc. Type the following command to run this utility.
$ sudo npi-config
Here is how npi-config's GUI looks like:
1.4 Develop Qt Application
Please refer to: How to Build and Install Qt Application for FriendlyELEC Boards
1.5 Setup Program to AutoRun
You can setup a program to autorun on system boot with npi-config:
sudo npi-configGo to Boot Options -> Autologin -> Qt/Embedded, select Enable and reboot.
1.6 Extend TF Card's Section
When FriendlyCore is loaded the TF card's section will be automatically extended.You can check the section's size by running the following command:
$ df -h
1.7 Transfer files using Bluetooth
Take the example of transferring files to the mobile phone. First, set your mobile phone Bluetooth to detectable status, then execute the following command to start Bluetooth search.:
hcitool scan
Search results look like:
Scanning ...
2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 HTC6525LVWThis means that a mobile phone named HTC6525LVW is searched. We write down the MAC address in front of the phone name, and then use the sdptool command to view the Bluetooth service supported by the phone:
sdptool browser 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02
Note: Please replace the MAC address in the above command with the actual Bluetooth MAC address of the mobile phone.
This command will detail the protocols supported by Bluetooth for mobile phones. What we need to care about is a file transfer service called OBEX Object Push. Take the HTC6525LVW mobile phone as an example. The results are as follows:
Service Name: OBEX Object Push Service RecHandle: 0x1000b Service Class ID List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Protocol Descriptor List: "L2CAP" (0x0100) "RFCOMM" (0x0003) Channel: 12 "OBEX" (0x0008) Profile Descriptor List: "OBEX Object Push" (0x1105) Version: 0x0100
As can be seen from the above information, the channel used by the OBEX Object Push service of this mobile phone is 12, we need to pass it to the obexftp command, and finally the command to initiate the file transfer request is as follows:
obexftp --nopath --noconn --uuid none --bluetooth -b 2C:8A:72:1D:46:02 -B 12 -put example.jpg
Note: Please replace the MAC address, channel and file name in the above command with the actual one.
After executing the above commands, please pay attention to the screen of the mobile phone. The mobile phone will pop up a prompt for pairing and receiving files. After confirming, the file transfer will start.
Bluetooth FAQ:
1) Bluetooth device not found on the development board, try to open Bluetooth with the following command:
rfkill unblock 02) Prompt can not find the relevant command, you can try to install related software with the following command:
apt-get install bluetooth bluez obexftp openobex-apps python-gobject ussp-push1.8 WiFi
For either an SD WiFi or a USB WiFi you can connect it to your board in the same way. The APXX series WiFi chips are SD WiFi chips. By default FriendlyElec's system supports most popular USB WiFi modules. Here is a list of the USB WiFi modules we tested:
Index Model 1 RTL8188CUS/8188EU 802.11n WLAN Adapter 2 RT2070 Wireless Adapter 3 RT2870/RT3070 Wireless Adapter 4 RTL8192CU Wireless Adapter 5 mi WiFi mt7601 6 5G USB WiFi RTL8821CU 7 5G USB WiFi RTL8812AU
You can use the NetworkManager utility to manage network. You can run "nmcli" in the commandline utility to start it. Here are the commands to start a WiFi connection:
- Change to root
$ su root
- Check device list
$ nmcli devNote: if the status of a device is "unmanaged" it means that device cannot be accessed by NetworkManager. To make it accessed you need to clear the settings under "/etc/network/interfaces" and reboot your system.
- Start WiFi
$ nmcli r wifi on- Scan Surrounding WiFi Sources
$ nmcli dev wifi- Connect to a WiFi Source
$ nmcli dev wifi connect "SSID" password "PASSWORD" ifname wlan0
The "SSID" and "PASSWORD" need to be replaced with your actual SSID and password.If you have multiple WiFi devices you need to specify the one you want to connect to a WiFi source with iface
If a connection succeeds it will be automatically setup on next system reboot.
For more details about NetworkManager refer to this link: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings
If your USB WiFi module doesn't work most likely your system doesn't have its driver. For a Debian system you can get a driver from Debian-WiFi and install it on your system. For a Ubuntu system you can install a driver by running the following commands:
$ apt-get install linux-firmware
In general all WiFi drivers are located at the "/lib/firmware" directory.
1.9 Ethernet Connection
If a board is connected to a network via Ethernet before it is powered on it will automatically obtain an IP with DHCP activated after it is powered up. If you want to set up a static IP refer to: Use NetworkManager to configure network settings。
1.10 Custom welcome message
The welcome message is printed from the script in this directory:
/etc/update-motd.d/
For example, to change the FriendlyELEC LOGO, you can change the file /etc/update-motd.d/10-header. For example, to change the LOGO to HELLO, you can change the following line:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal $BOARD_VENDOR
To:
TERM=linux toilet -f standard -F metal HELLO
1.11 Modify timezone
For exampe, change to Shanghai timezone:
sudo rm /etc/localtime sudo ln -ls /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
1.12 Set Audio Device
If your system has multiple audio devices such as HDMI-Audio, 3.5mm audio jack and I2S-Codec you can set system's default audio device by running the following commands.
- After your board is booted run the following commands to install alsa packages:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libasound2 $ apt-get install alsa-base $ apt-get install alsa-utils
- After installation is done you can list all the audio devices by running the following command. Here is a similar list you may see after you run the command:
$ aplay -l card 0: HDMI card 1: 3.5mm codec card 2: I2S codec
"card 0" is HDMI-Audio, "card 1" is 3.5mm audio jack and "card 2" is I2S-Codec. You can set default audio device to HDMI-Audio by changing the "/etc/asound.conf" file as follows:
pcm.!default { type hw card 0 device 0 } ctl.!default { type hw card 0 }
If you change "card 0" to "card 1" the 3.5mm audio jack will be set to the default device.
Copy a .wav file to your board and test it by running the following command:
$ aplay /root/Music/test.wav
You will hear sounds from system's default audio device.
If you are using H3/H5/H2+ series board with mainline kernel, the easier way is using npi-config。