Difference between revisions of "Matrix - Ultrasonic Ranger"
(→Basic Device Operation) |
(→Basic Device Operation) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Basic Device Operation== | ==Basic Device Operation== | ||
* The sensor emits a 40kHz, 6 mm sound wave, which bounces off a reflective surface and returns to the sensor. The receiver converts ultrasound waves to electrical signals in mV. | * The sensor emits a 40kHz, 6 mm sound wave, which bounces off a reflective surface and returns to the sensor. The receiver converts ultrasound waves to electrical signals in mV. | ||
| − | * The master sends a signal to the module starting to emit a sound wave. After the module receives the returned signal it will will generate a high level indicating the elapsed time | + | * The master sends a signal to the module starting to emit a sound wave. After the module receives the returned signal it will will generate a high level indicating the elapsed time and the distance will be calculated by distance = (elapsed time * speed of sound)/2. |
[[File:Ultrasonic Ranger.png|thumb|matrix Ultrasonic Ranger]] | [[File:Ultrasonic Ranger.png|thumb|matrix Ultrasonic Ranger]] | ||
Revision as of 10:36, 22 September 2015
Contents
1 Introduction
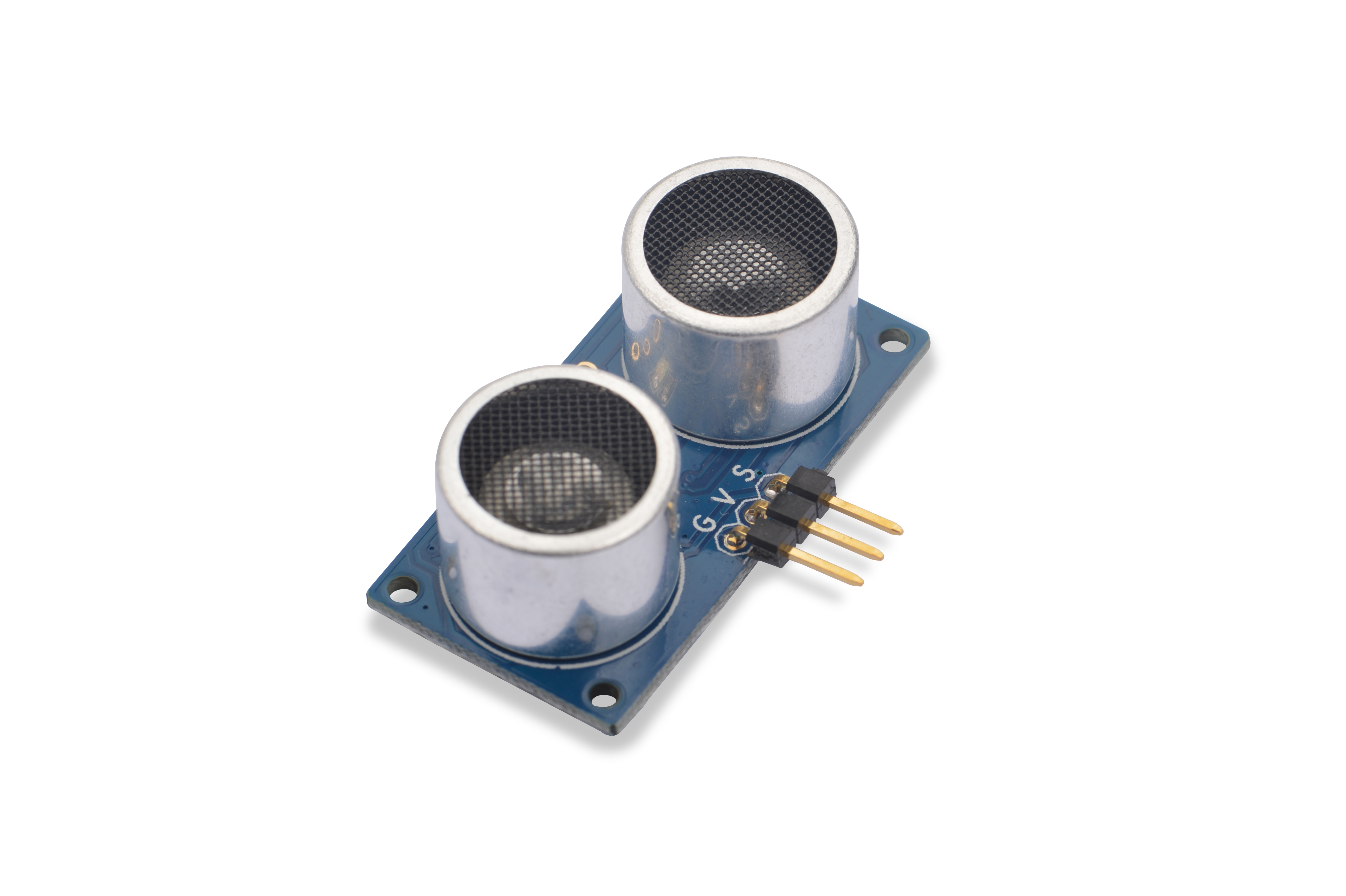
- The Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger is used to measure the distance.
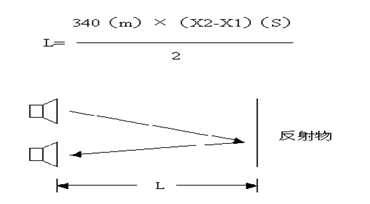
- The module's sensor emits a sound wave, which bounces off a reflective surface and returns to the sensor. Then, using the amount of time it takes for the wave to return to the sensor, the distance to the object can be computed.
2 Features
- 5V Power
- Range: 5 cm - 300 cm,Accuracy: 1 cm
- One wire gpio
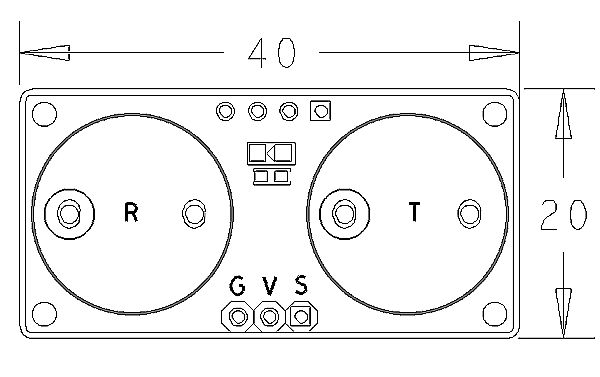
- PCB Dimension (mm): 20 x 40
- Pin Description:
| Pin | Description |
| S | GPIO |
| V | Power 5V |
| G | Ground |
3 Basic Device Operation
- The sensor emits a 40kHz, 6 mm sound wave, which bounces off a reflective surface and returns to the sensor. The receiver converts ultrasound waves to electrical signals in mV.
- The master sends a signal to the module starting to emit a sound wave. After the module receives the returned signal it will will generate a high level indicating the elapsed time and the distance will be calculated by distance = (elapsed time * speed of sound)/2.
4 下载Matrix源码
Matrix配件相关的代码是完全开源的,统一由一个仓库进行管理:git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
该仓库里不同的分支代表着Matrix配件所支持的不同开发板。
- nanopi分支包含了Matrix对NanoPi的支持;
- tiny4412分支包含了Matrix对Tiny4412的支持;
- raspberrypi分支包含了Matrix对RaspberryPi的支持;
在主机PC上安装git,以Ubuntu14.04为例
$ sudo apt-get install git
克隆Matrix配件代码仓库
$ git clone git://github.com/friendlyarm/matrix.git
克隆完成后会得到一个matrix目录,里面存放着所有Matrix配件的代码。
5 与NanoPi连接使用
5.1 准备工作
在NanoPi上运行Debian系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。参考wiki:NanoPi
注意:必须使用nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix分支编译出来的内核。
下载NanoPi内核源代码并编译
$ git clone https://github.com/friendlyarm/linux-4.x.y.git $ cd linux-4.x.y $ git checkout nanopi-v4.1.y-matrix $ make nanopi_defconfig $ touch .scmversion $ make
5.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger和NanoPi
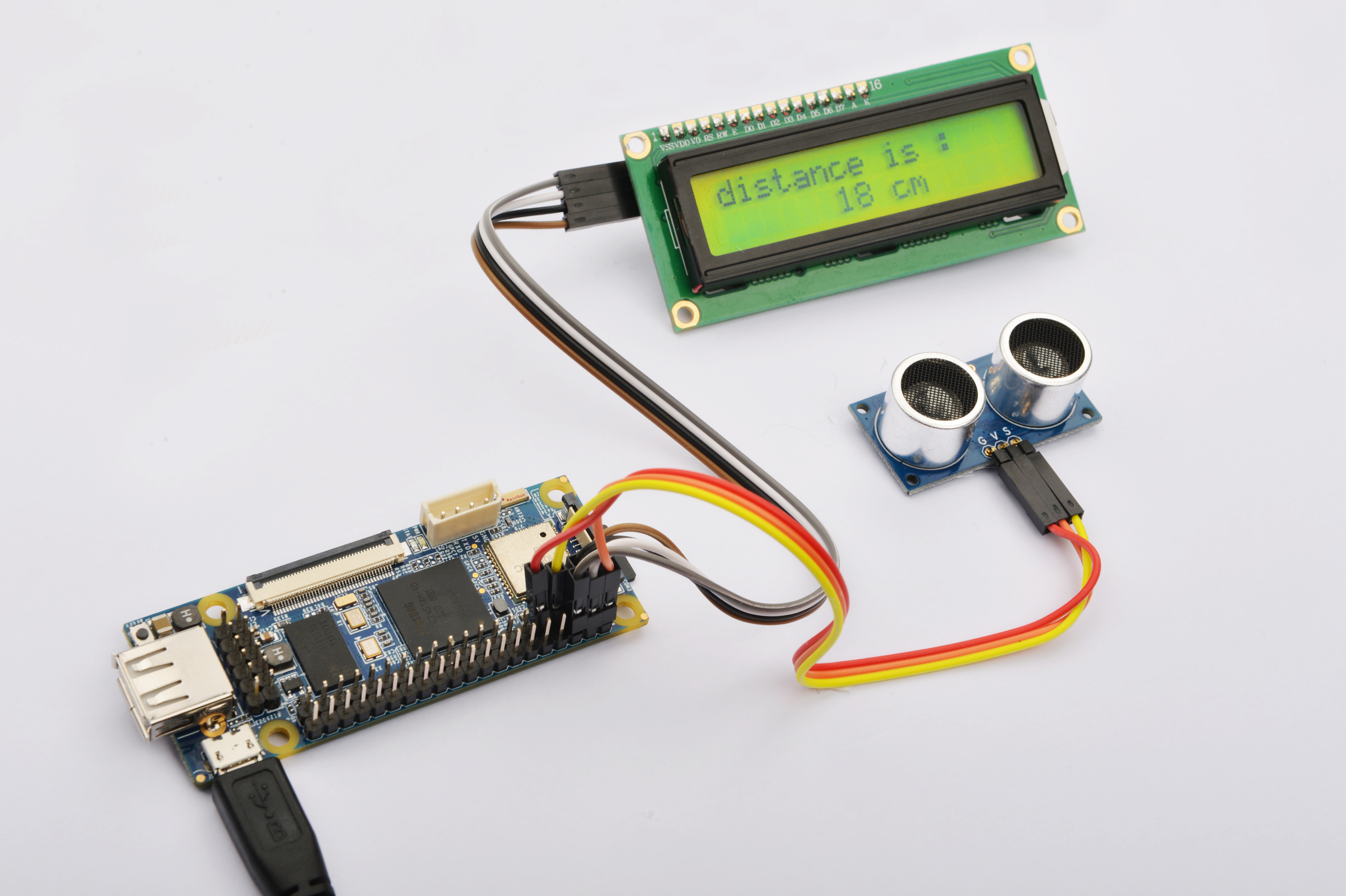
连接说明:
| Matrix-Sound_Sensor | NanoPi |
| S | Pin7 |
| V | Pin4 |
| G | Pin6 |
5.3 编译测试程序
进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到nanopi分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout nanopi
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为NanoPi-Debian配套的arm-linux-gcc-4.4.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger对应的测试程序为matrix-ultrasonic_ranger。
5.4 运行测试程序
拷贝库文件和测试程序到NanoPi的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* nanopi_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* nanopi_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动NanoPi,在Debian的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger的测试程序
注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件正常连接。
$ matrix-ultrasonic_ranger5.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int distance = -1; int pin = GPIO_PIN1; if (Hcsr04Init(pin) == -1) { printf("Fail to init hcsr04\n"); } if (Hcsr04Read(&distance) != -1) { printf("Get distance: %3d cm\n", distance); } else { printf("Faid to get distance\n"); } Hcsr04DeInit(); return 0; }
6 与Tiny4412连接使用
6.1 准备工作
参考Tiny4412光盘里的《友善之臂Ubuntu使用手册》,在Tiny4412上运行UbuntuCore系统,然后在主机PC上安装并使用相应的编译器。
注意:只能使用Tiny4412SDK-1506的底板。
6.2 硬件连接
参考下图连接模块Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger和Tiny4412
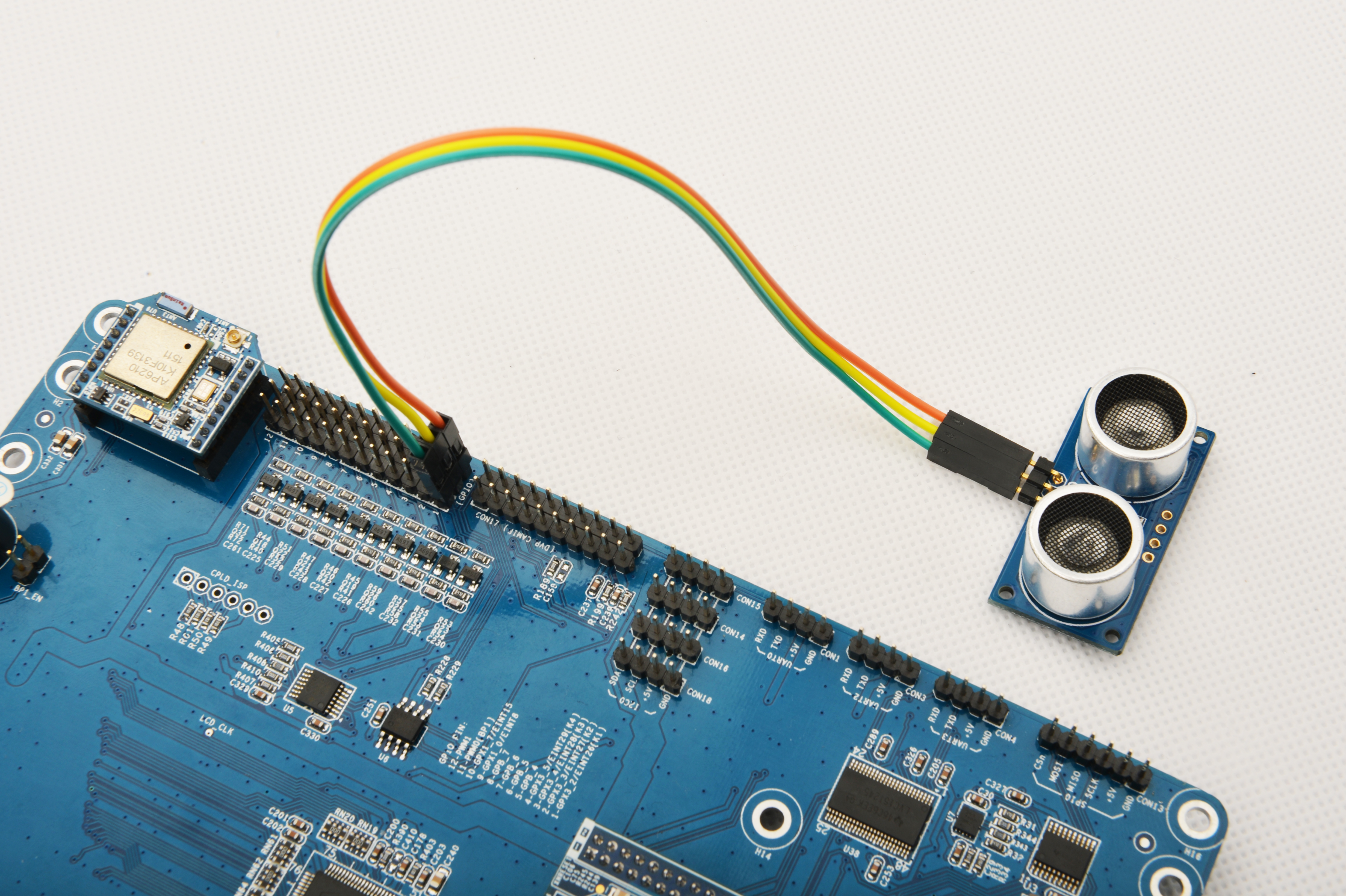
连接说明:
| Matrix- Ultrasonic Ranger | Tiny4412 |
| S | GPIO1 S |
| V | GPIO1 5V |
| G | GPIO1 GND |
6.3 编译测试程序
进入Matrix代码仓库,切换到tiny4412分支
$ cd matrix $ git checkout tiny4412
编译Matrix配件代码
$ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- $ make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- install
注意:请确保你的主机PC当前使用的交叉编译器为Tiny4412-UbuntuCore配套的arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-4.7.3。
编译出来的库文件位于install/lib目录下,而测试程序则位于install/usr/bin目录下,模块Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger对应的测试程序为matrix-ultrasonic_ranger。
6.4 运行测试程序
拷贝库文件和测试程序到Tiny4412的UbuntuCore的文件系统上
$ cp install/usr/bin/* tiny4412_rootfs/usr/bin/ $ cp install/lib/* tiny4412_rootfs/lib/ -d
然后启动Tiny4412,在UbuntuCore的shell终端中执行如下命令运行模块Matrix-Ultrasonic_Ranger的测试程序
注意:此模块并不支持热插拔,启动系统前需要确保硬件正常连接。
$ matrix-ultrasonic_ranger6.5 代码展示
int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int distance = -1; int pin = GPIO_PIN1; if (Hcsr04Init(pin) == -1) { printf("Fail to init hcsr04\n"); } if (Hcsr04Read(&distance) != -1) { printf("Get distance: %3d cm\n", distance); } else { printf("Faid to get distance\n"); } Hcsr04DeInit(); return 0; }